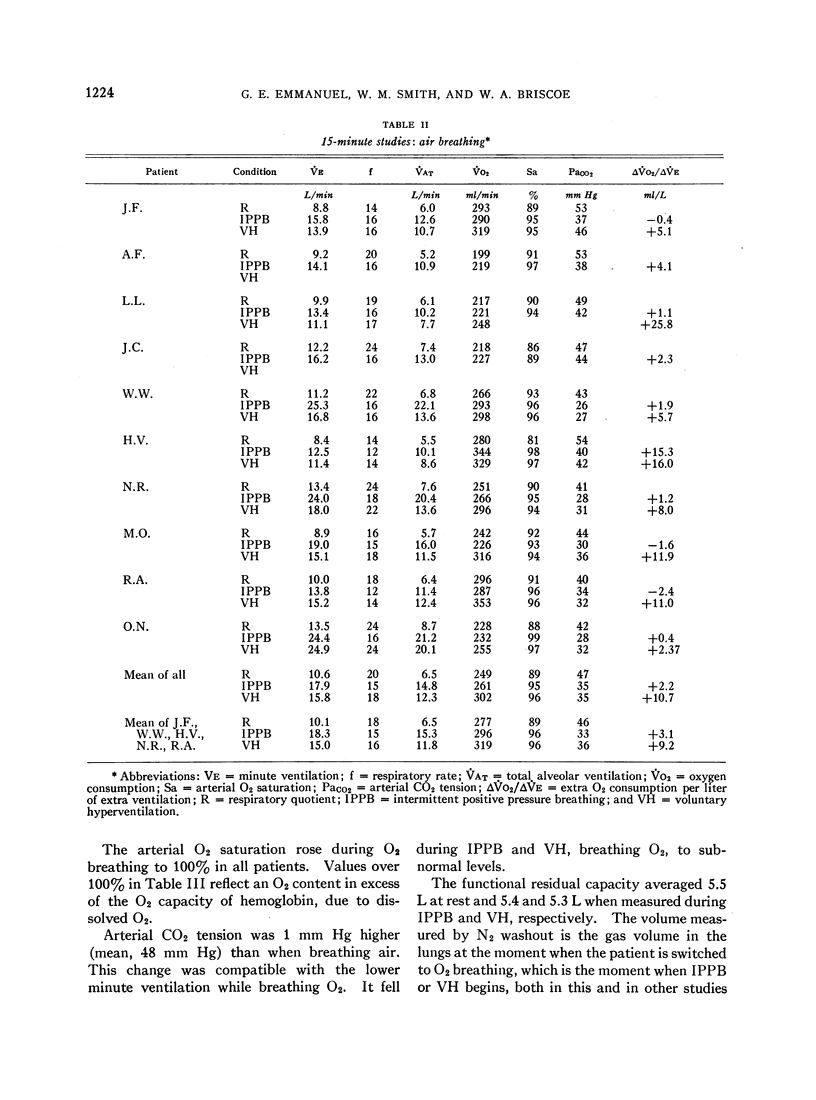
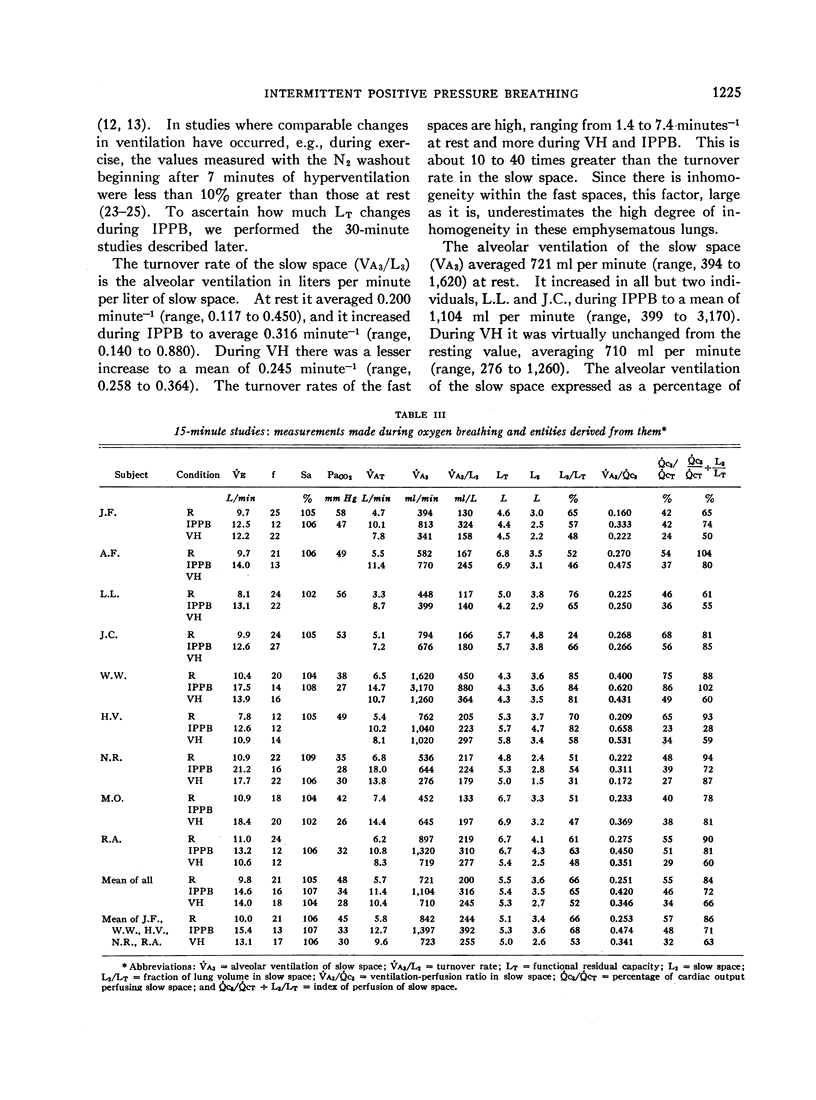
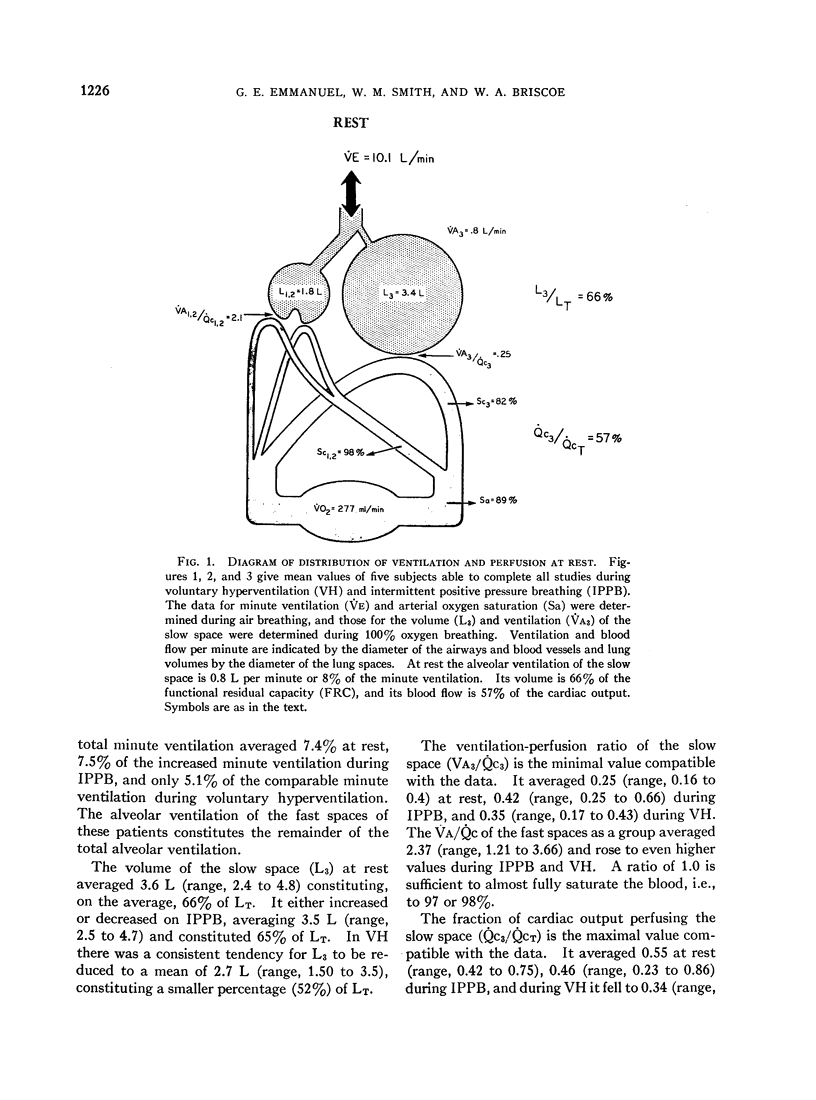
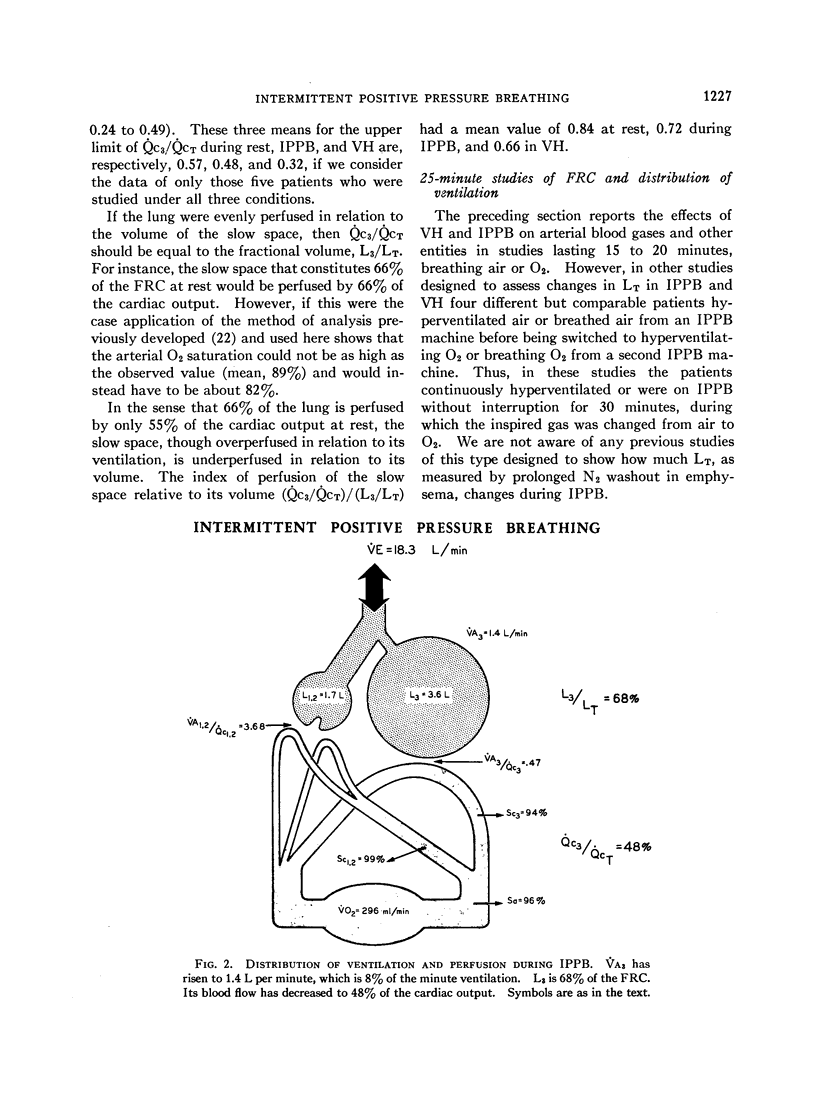
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYRES S. M., KOZAM R. L., LUKAS D. S. The effects of intermittent positive pressure breathing on intrathoracic pressure, pulmonary mechanics, and the work of breathing. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 Mar;87:370–379. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.87.3P1.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRISCOE W. A. A method for dealing with data concerning uneven ventilation of the lung and its effects on blood gas transfer. J Appl Physiol. 1959 May;14(3):291–298. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRISCOE W. A., COURNAND A. Uneven ventilation of normal and diseased lungs studied by an open-circuit method. J Appl Physiol. 1959 May;14(3):284–290. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRISCOE W. A. Further studies on the intrapulmonary mixing of helium in normal and emphysematous subjects. Clin Sci. 1952 Feb;11(1):45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. A., HEMINGWAY A., HEMINGWAY C. The effect of intermittent positive pressure breathing and of bronchodilator drugs on alveolar nitrogen clearance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Mar;83:340–353. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.83.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMANUEL G., BRISCOE W. A., COURNAND A. A method for the determination of the volume of air in the lungs: measurements in chronic pulmonary emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:329–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI104260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWLER W. S., CORNISH E. R., Jr, KETY S. S. Lung function studies. VIII. Analysis of alveolar ventilation by pulmonary N2 clearance curves. J Clin Invest. 1952 Jan;31(1):40–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI102575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAIMOW W., CATHCART R. T., GOODMAN E. The use of intermittent positive pressure breathing in the prevention of the carbon dioxide narcosis associated with oxygen therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Jun;81:815–822. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.81.6.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITTS H. W., Jr, FILLER J., FISHMAN A. P., COURNAND A. The efficiency of ventilation during voluntary hyperpnea: studies in normal subjects and in dyspneic patients with either chronic pulmonary emphysema or obesity. J Clin Invest. 1959 Aug;38(8):1339–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI103909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMEZ D. M., BRISCOE W. A., CUMMING G. CONTINUOUS DISTRIBUTION OF SPECIFIC TIDAL VOLUME THROUGHOUT THE LUNG. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:683–692. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON B., MOTLEY H. L., THEODOS P. A., LANG L. P., TOMASHEFSKI J. Considerations of the clinical and physiologic factors in the treatment of chronic pulmonary conditions. Dis Chest. 1951 Mar;19(3):271–287. doi: 10.1378/chest.19.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. M., FERRER M. I. A clinical consideration of cor pulmonale. Circulation. 1960 Feb;21:236–255. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.21.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKAM J. B., BLAIR E., FRAYSER R. An open-circuit helium method for measuring functional residual capacity and defective intrapulmonary gas mixing. J Clin Invest. 1954 Sep;33(9):1277–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI103003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMESON A. G., FERRER M. I., HARVEY R. M. Some effects of mechanical respirators upon respiratory gas exchange and ventilation in chronic pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Oct;80:510–521. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.4P1.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTLEY H. L., TOMASHEFSKI J. F. Effect of high and low oxygen levels and intermittent positive pressure breathing on oxygen transport in the lungs in pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Oct;3(4):189–196. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.4.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. S., SIRI W. E., JONES H. B. Lung ventilation patterns determined by analysis of nitrogen elimination rates; use of mass spectrometer as a continuous gas analyzer. J Clin Invest. 1950 May;29(5):577–590. doi: 10.1172/JCI102295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL M. S., SALOMON A., DULFANO M. J., HERSCHFUS J. A. Intermittent positive pressure breathing; its use in the inspiratory phase of respiration. N Engl J Med. 1954 Feb 11;250(6):225–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195402112500601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON G. P. Pressure breathing in chronic obstructive lung disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1963 May;42:197–227. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196305000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMART R. H., DAVENPORT C. K., PEARSON G. W. Intermittent positive pressure breathing in emphysema of chronic lung diseases. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Dec 6;150(14):1385–1390. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.03680140023005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumalchantra Y., Park S. S., Williams M. H., Jr The effect of intermittent positive pressure breathing (IPPB) in acute ventilatory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Dec;92(6):885–893. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.6P1.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIERNEY D. F., NADEL J. A. Concurrent measurements of functional residual capacity by three methods. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Nov;17:871–873. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.6.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRES G., LYONS H. A., EMERSON P. The effects of intermittent positive pressure breathing on the intrapulmonary distribution of inspired air. Am J Med. 1960 Dec;29:946–954. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU N., MILLER W. F., CADE R., RICHBURG P. Intermittent positive pressure breathing in patients with chronic bronchopulmonary disease; a comparative evaluation of the effects of intermittent positive pressure breathing alone, oxygen-nebulized bronchodilator alone, and the two procedures together. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 May;71(5):693–703. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.71.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]