Abstract
(a) The thyroxine-binding proteins were investigated in 23 cases of untreated thyrotoxicosis and 16 cases of untreated hypothyroidism, employing reverse flow paper electrophoresis with the glycine acetate system at pH 8.6 in the Durrum type cell.
(b) In active thyrotoxicosis, all sera exhibited diminished thyroxine-binding prealbumin (TBPA) capacities. however, 17 of the 23 sera also had diminished thryroxine-binding alpha globulin (TBG) capacities, as well as markedly elevated free thyroxine fractions. In contrast, six thyrotoxic sera had normal TBG capacities and normal or slightly elevated free thyroxine fractions.
(c) In hypothyroidism, the TBPA capacities showed no consistent deviation from the normal range. 11 of the 16 sera had elevated TBG capacities as well as markedly diminished free thyroxine fractions. In contrast, five hypothyroid sera had normal TBG capacities and normal or nearly normal free thyroxine fractions.
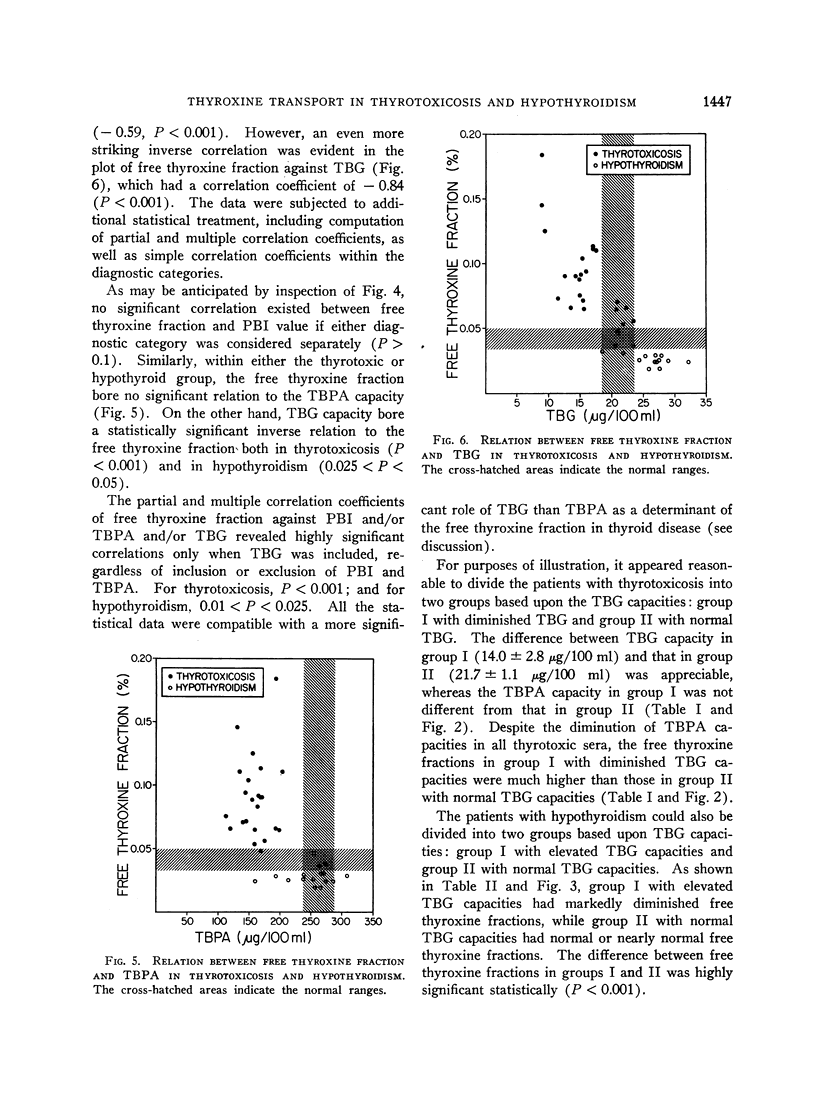
(d) In thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism, the inverse correlation between free thyroxine fraction and TBG was much closer than that with TBPA. When diagnostic categories were considered separately, only TBG bore a significant inverse relation to the free thyroxine fraction. It is therefore suggested that in thyroid diseases TBG may sometimes play a more important role than TBPA in determining the free thyroxine fraction.
(e) The demonstrated variations in the binding proteins were considered sufficient to explain the abnormalities of the free thyroxine fractions in thyroid disease.
Full text
PDF
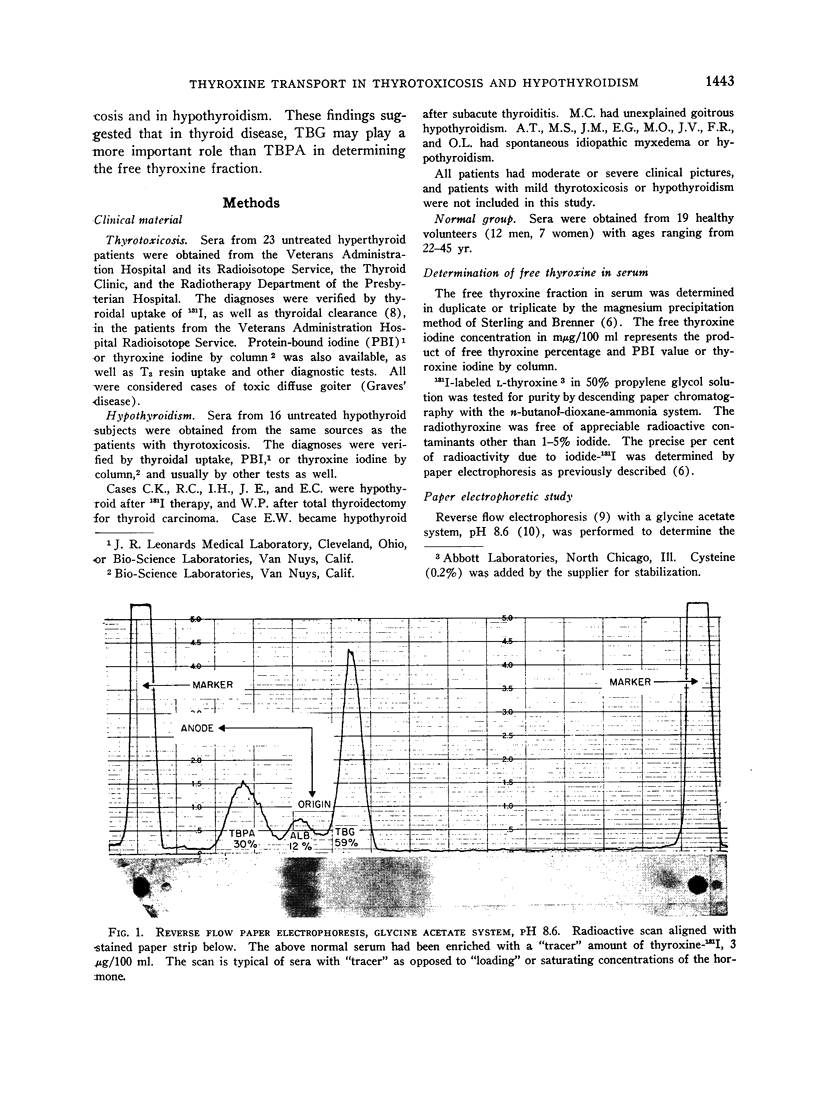






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., SORRENTINO J., ROSWIT B. The determination of thyroidal and renal plasma I131 clearance rates as a routine diagnostic test of thyroid dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1952 Feb;31(2):141–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI102585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Oppenheimer J. H. Factors influencing the concentration of free and total thyroxine in patients with nonthyroidal disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Feb;26(2):195–201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuarón A. Relationship between the in vitro uptake of 131-I-triiodothyronine by erythrocytes and its binding by serum proteins in thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Jan;26(1):53–64. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELZINGA K. E., CARR E. A., Jr, BEIERWALTES W. H. Adaptation of the standard Durrum-type cell for reverse-flow paper electrophoresis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Aug;36:125–131. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Pre-albumin: a thyroxinebinding protein of human plasma. Endocrinology. 1958 Aug;63(2):256–259. doi: 10.1210/endo-63-2-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E., Dawber N. A., Lee G. Y. A new method for measuring the free thyroid hormone in human serum and an analysis of the factors that influence its concentration. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1679–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H. CLINICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN A PATIENT WITH AN IDIOPATHIC DECREASE IN THE THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN OF PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40(11):2053–2063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWALLEN C. G., RALL J. E., BERMAN M. Studies of iodoalbumin metabolism. II. The effects of thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):88–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI103798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPEHNEIMER J. H., SURKS M. I., BERNSTEIN G., SMITY J. C. METABOLISM OF IODINE-131--LABELED THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN IN MAN. Science. 1965 Aug 13;149(3685):748–750. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3685.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SURKS M. I., SMITH J. C., SQUEF R. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HUMAN THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Martinez M., Bernstein G. Determination of the maximal binding capacity and protein concentration of thyroxine-binding prealbumin in human serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Mar;67(3):500–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. Proteins associated with the thyroid hormones. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:415–489. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. The interaction of thyroid hormones and protein in biological fluids. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1957;13:161–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. Reverse-flow zone electrophoresis; a method for determining the thyroxine-binding capacity of serum protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSCHILD M. A., BAUMAN A., YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. The effect of large doses of desiccated thyroid on the distribution and metabolism of albumin-I 131 in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):422–428. doi: 10.1172/JCI103438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN J. N., SCHWARTZ H. L., FELDMAN E. B., KYDO D. M., CARTER A. C. Correlation of the red blood cell uptake of I-131-L-triiodothyronine and thyroxine-binding globulin capacity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Oct;22:1002–1006. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-10-1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socolow E. L., Woeber K. A., Purdy R. H., Holloway M. T., Ingbar S. H. Preparation of I-131-labeled human serum prealbumin and its metabolism in normal and sick patients. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1600–1609. doi: 10.1172/JCI105266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA S., STARR P. Clinical observations on serum globulin thyroxine-binding capacity, using a simplified technique. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Jan;19(1):84–91. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-1-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



