Abstract
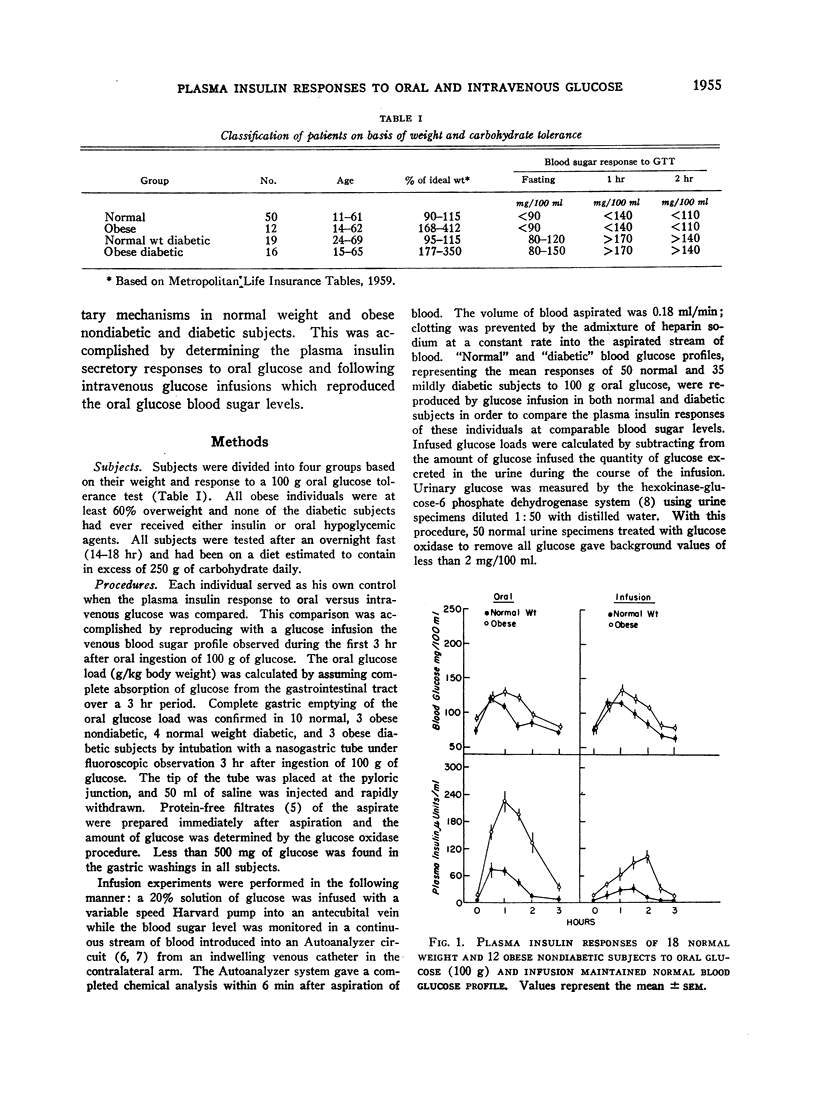
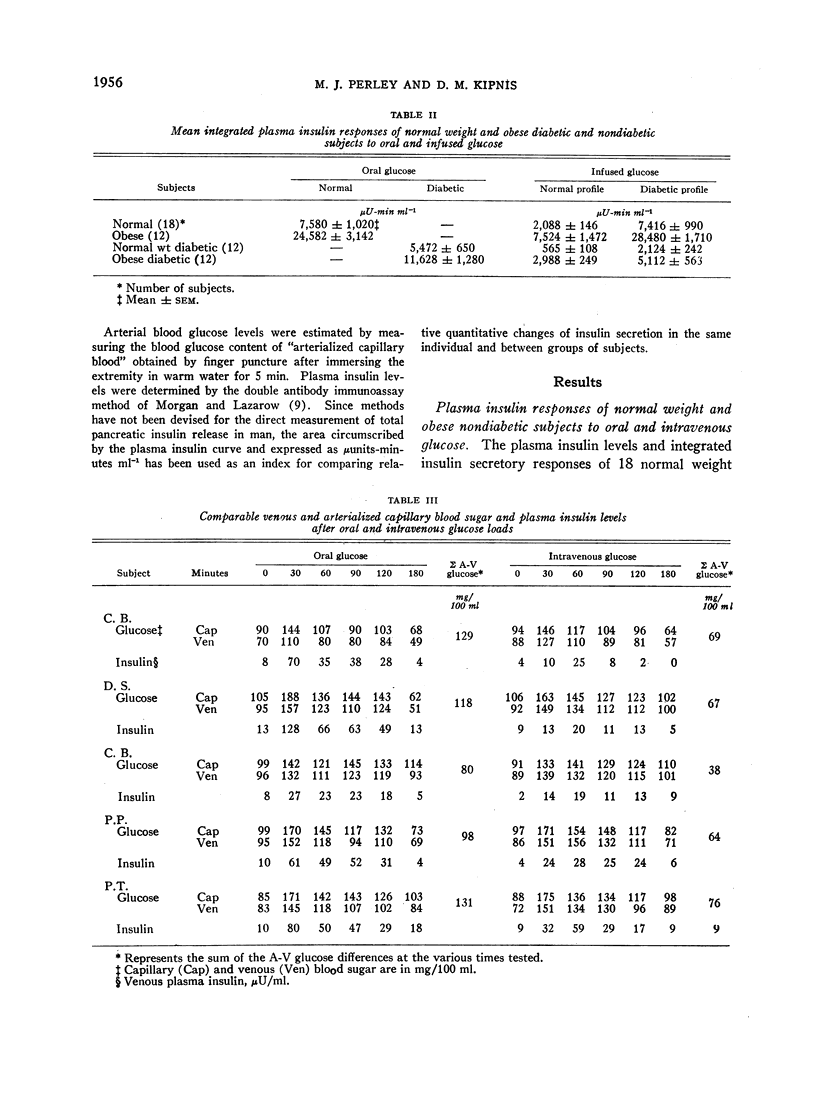
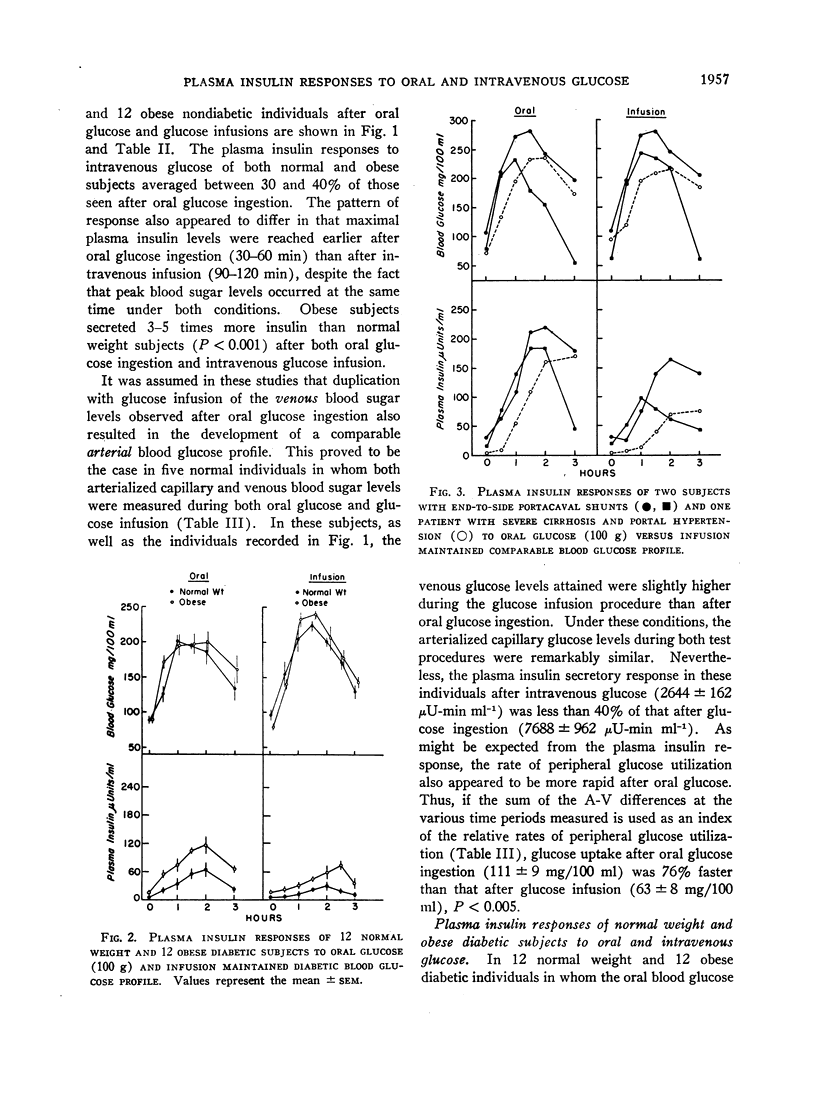
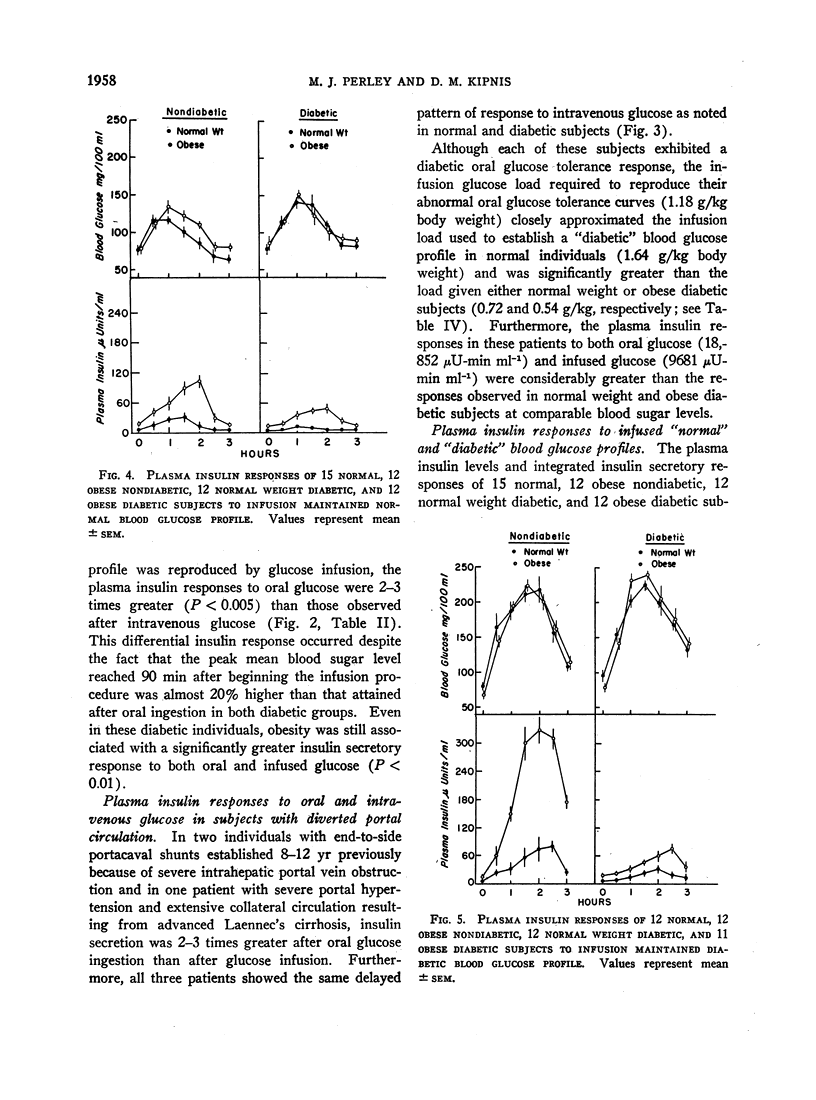
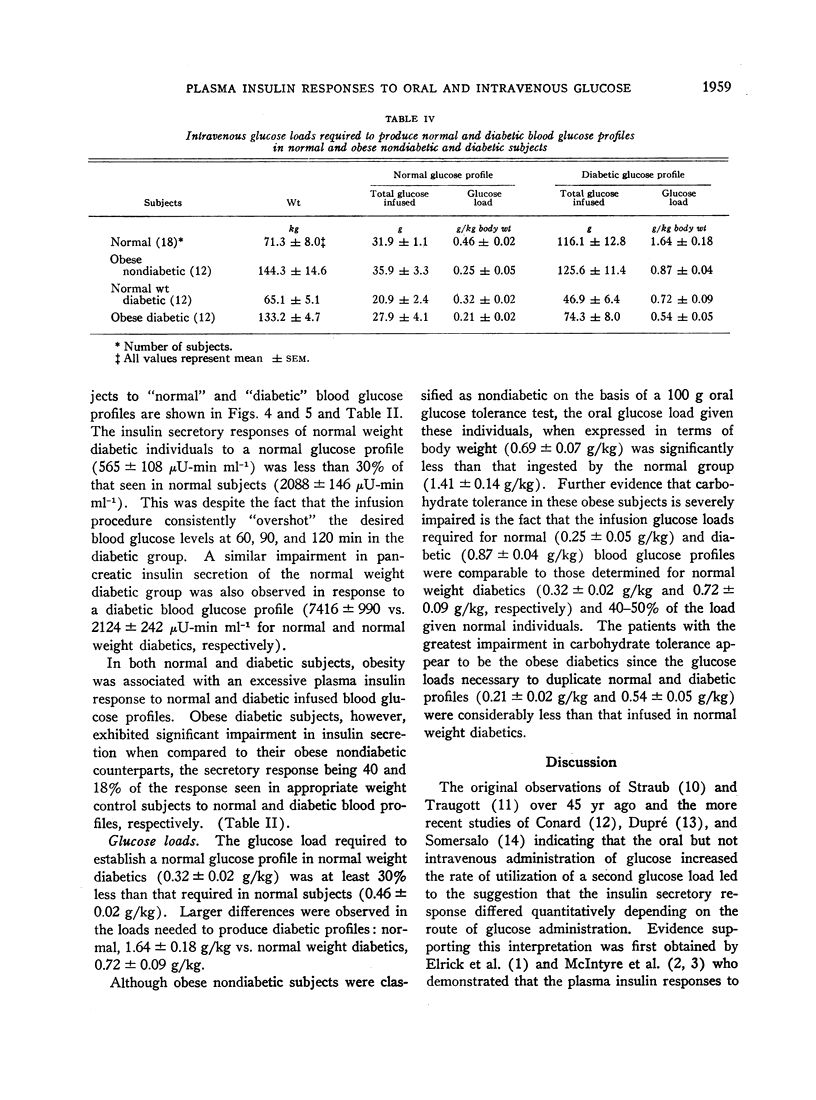
The plasma insulin responses of normal weight and obese, diabetic, and nondiabetic subjects to intravenous glucose was only 30-40% of that seen after oral glucose, indicating that alimentary mechanism(s) in addition to the arterial blood sugar concentration regulate insulin secretion. Observations made in subjects with diverted portal circulation indicate that the alimentary insulinogenic mechanism is located in the intestinal tract. The insulinogenic potency of the alimentary and glycemic stimuli expressed in terms of insulin secretion per gram of glucose were remarkably similar within each group of individuals. Between these groups, however, there were considerable differences. Obesity, with or without associated diabetes, was associated with a true hypersecretory responsiveness, whereas diabetes was characterized, with or without obesity, by a marked impairment in insulin secretion. The experimental design used in these studies permitted quantitation of the magnitude of the glycemic component of an oral glucose load. As a consequence of impaired insulin secretion, a greater than normal proportion of the oral glucose load escapes initial hepatic extraction in the maturity-onset diabetic and enters the peripheral circulation. Therefore, in the noninsulin-requiring maturity-onset diabetic, the glycemic insulinogenic stimulus for a given oral glucose load is significantly greater than in normal subjects and accounts for the excessive plasma insulin responses observed late in the course of an oral glucose tolerance test.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALSANO F., PITUCCO G., MUSCA A., DINOTO V. NEW INTERPRETATION OF ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE. Lancet. 1964 Oct 17;2(7364):865–865. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90724-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS T. W., BREGANT R., VANPEENAN H. J., HOOD T. E. OBSERVATIONS ON BLOOD GLUCOSE CONCENTRATION OF HUMAN SUBJECTS DURING CONTINUOUS SAMPLING. Diabetes. 1965 Apr;14:186–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.4.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The plasma insulin response to glucose infusion in healthy subjects and in diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):278–304. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUPRE J. AN INTESTINAL HORMONE AFFECTING GLUCOSE DISPOSAL IN MAN. Lancet. 1964 Sep 26;2(7361):672–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., STIMMLER L., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. PLASMA INSULIN RESPONSE TO ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE ADMINISTRATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAM J. H., GRODSKY G. M., PAVLATOS F. C., FORSHAM P. H. CRITICAL FACTORS IN EXCESSIVE SERUM-INSULIN RESPONSE TO GLUCOSE. OBESITY IN MATURITY-ONSET DIABETES AND GROWTH HORMONE IN ACROMEGALY. Lancet. 1965 Feb 6;1(7380):286–289. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., HELMREICH E., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. IV. The distribution of glucose between plasma and muscle. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer H., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Effect upon insulin secretion of physiologic doses of glucagon administered via the portal vein. Diabetes. 1967 May;16(5):283–288. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.5.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., UNGER R. H. The physiologic significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. I. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-free insulin adminstered via the portal vein and via a peripheral vein on the magnitude of hypoglycemia and peripheral glucose utilization. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):631–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI103646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE N., HOLDSWORTH C. D., TURNER D. S. NEW INTERPRETATION OF ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE. Lancet. 1964 Jul 4;2(7349):20–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade R. C., Kneubuhler H. A., Schulte W. J., Barboriak J. J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by pancreozymin. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):141–144. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):867–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMOLS E., MARRI G., MARKS V. PROMOTION OF INSULIN SECRETION BY GLUCAGON. Lancet. 1965 Aug 28;2(7409):415–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOW R. O., CORNFIELD J. Quantitative relations between the oral and intravenous glucose tolerance curves. Am J Physiol. 1954 Dec;179(3):435–438. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER C., LINDER M., MACAULAY A., FERRARI A., KESSLER G. Continuous in vivo determination of blood glucose in human subjects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jul 22;87:658–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb23229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Plasma insulin concentrations in nondiabetic and early diabetic subjects. Determinations by a new sensitive immuno-assay technic. Diabetes. 1960 Jul-Aug;9:254–260. doi: 10.2337/diab.9.4.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Glick S. M., Roth J., Berson S. A. Plasma insulin and growth hormone levels in obesity and diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):357–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


