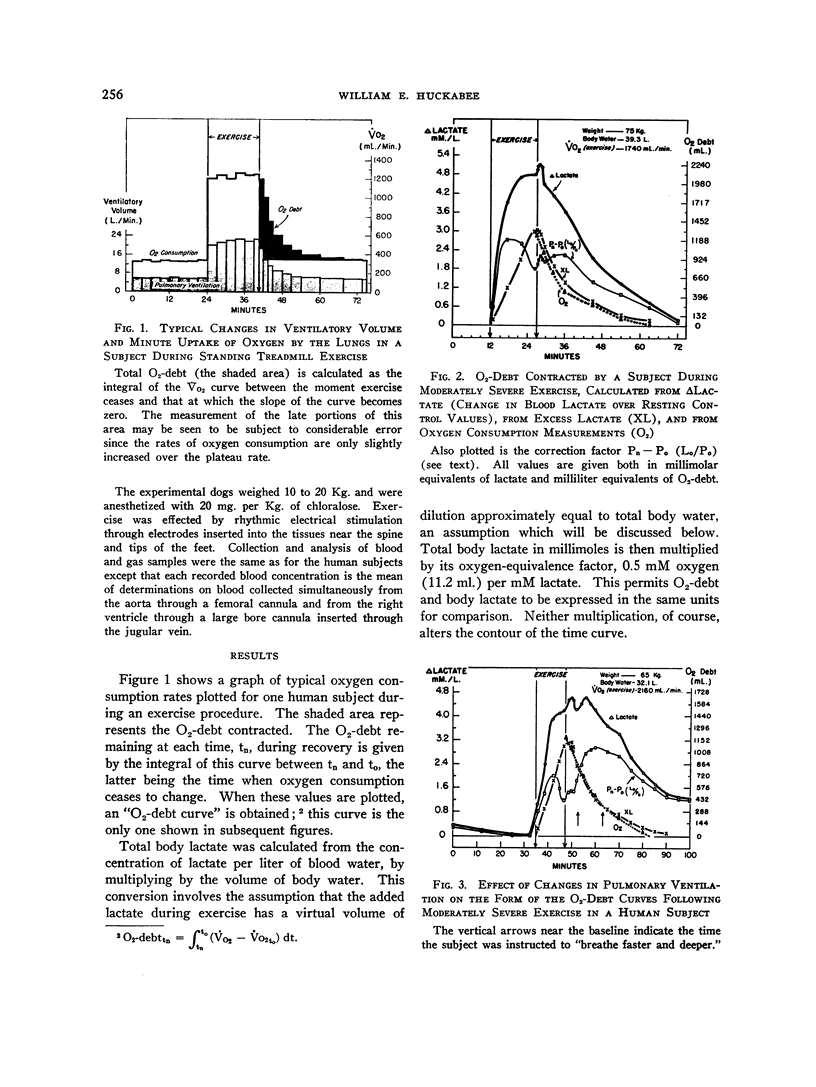
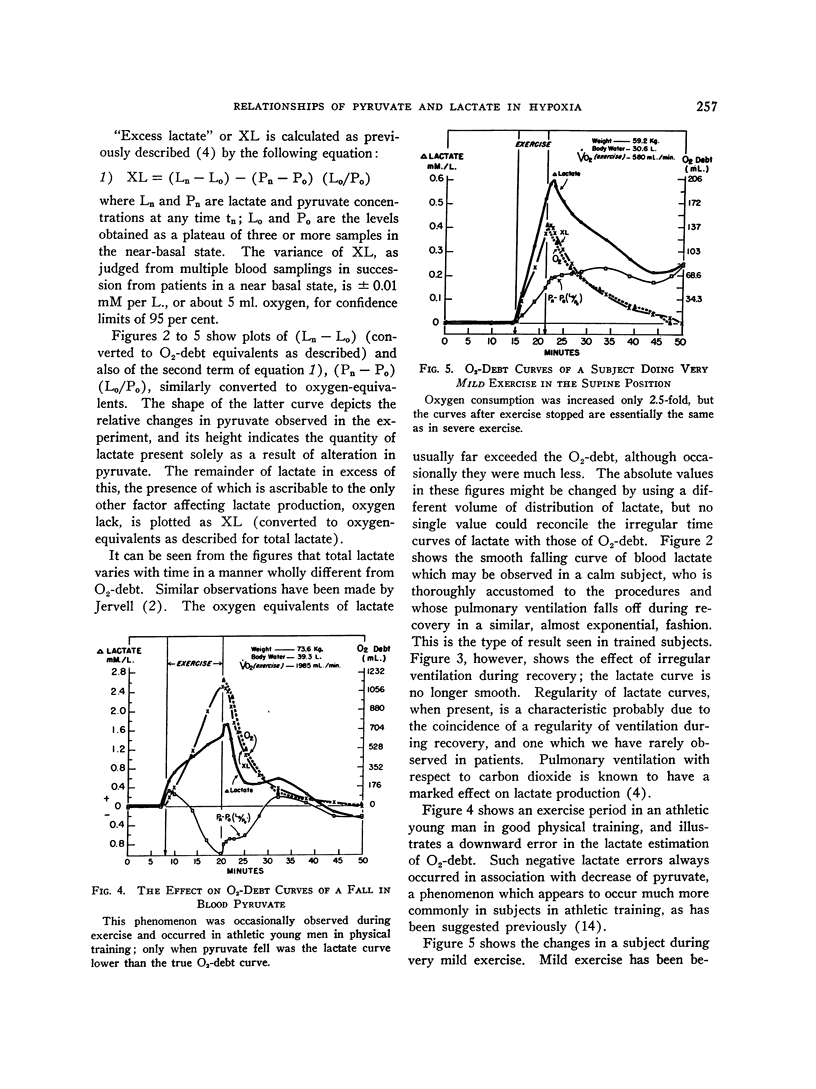
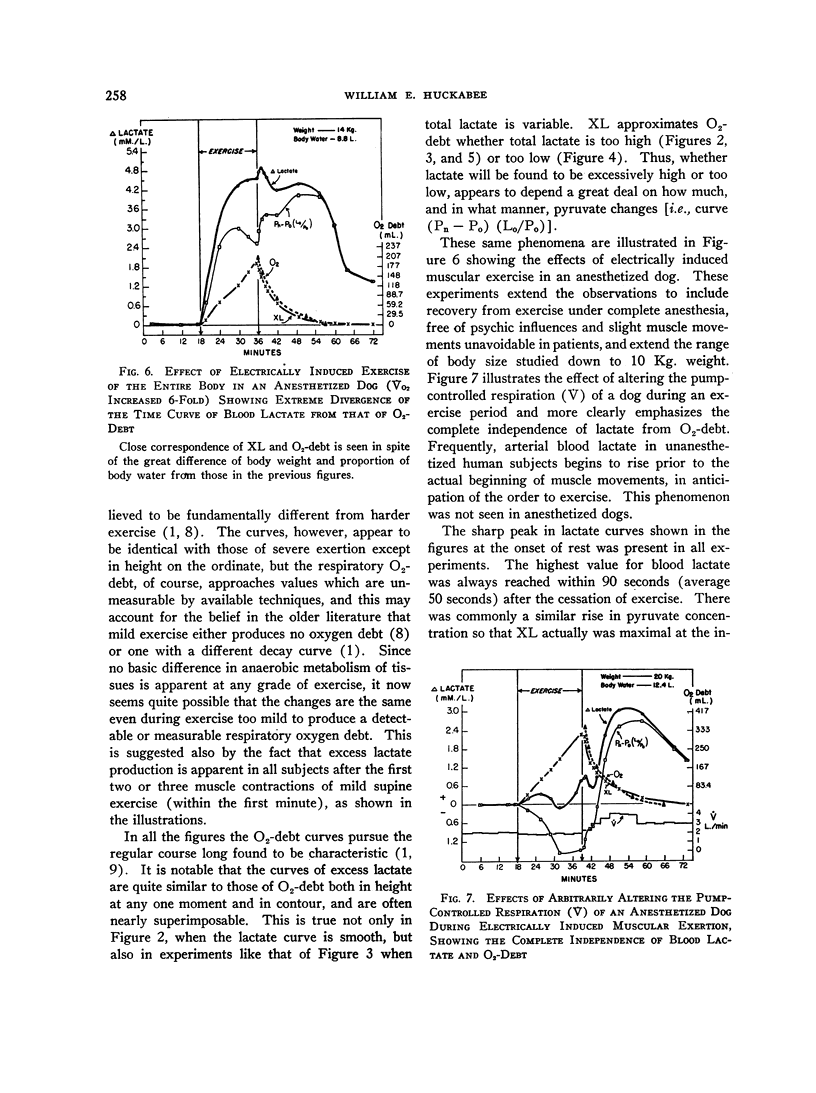
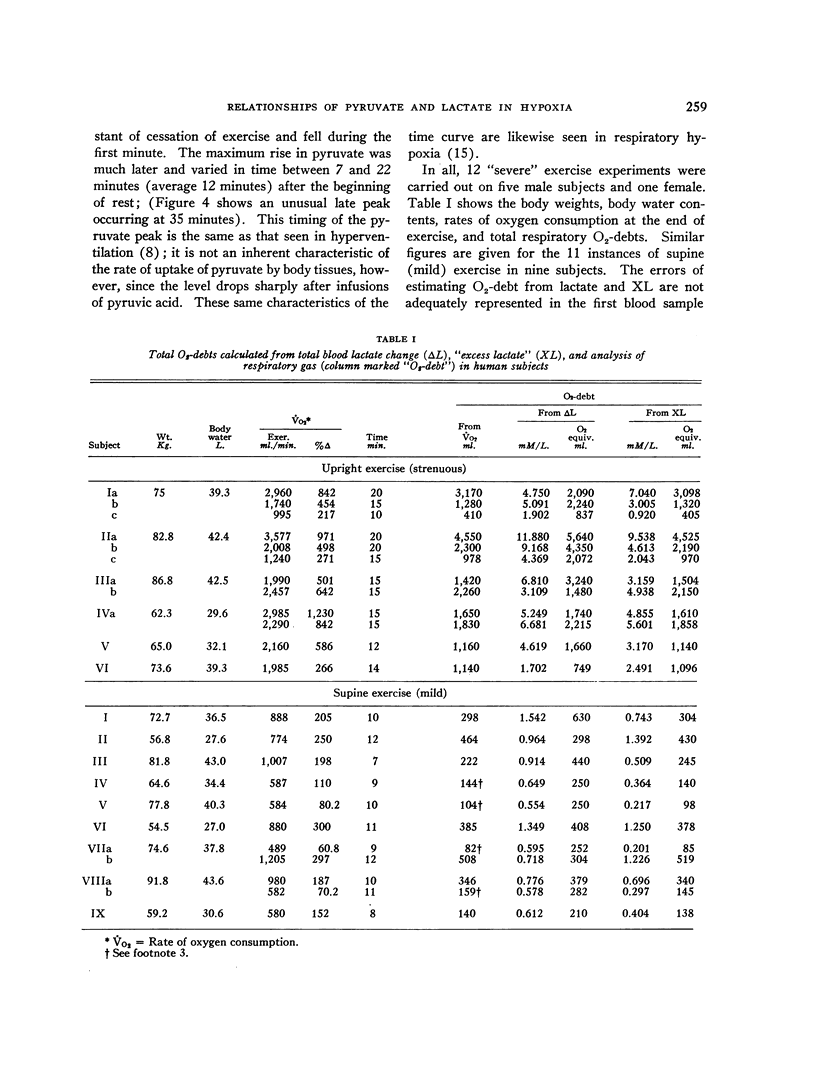
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPERT N. R., ROOT W. S. Relationship between excess respiratory metabolism and utilization of intravenously infused sodium racemic lactate and sodium L(-) lactate. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jun;177(3):455–462. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock A. V., Dill D. B., Edwards H. T. LACTIC ACID IN THE BLOOD OF RESTING MAN. J Clin Invest. 1932 Jul;11(4):775–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI100450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook L. C., Hurst R. H. Blood lactic acid in man during rest. J Physiol. 1933 Oct 25;79(4):443–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devadatta S. C. The diffusion of lactate into and from muscle. J Physiol. 1933 Sep 4;79(2):194–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Control of concentration gradients of pyruvate and lactate across cell membranes in blood. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):163–170. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Relationships of pyruvate and lactate during anaerobic metabolism. I. Effects of infusion of pyruvate or glucose and of hyperventilation. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI103603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Relationships of pyruvate and lactate during anaerobic metabolism. III. Effect of breathing low-oxygen gases. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):264–271. doi: 10.1172/JCI103605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Use of 4-aminoantipyrine for determining volume of body water available for solute dilution. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakins J., Long C. N. OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, OXYGEN DEBT AND LACTIC ACID IN CIRCULATORY FAILURE. J Clin Invest. 1927 Jun;4(2):273–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI100123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owles W. H. Alterations in the lactic acid content of the blood as a result of light exercise, and associated changes in the co(2)-combining power of the blood and in the alveolar co(2) pressure. J Physiol. 1930 Apr 14;69(2):214–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]