Abstract
Background
International fish trade reached an import value of 62.8 billion Euro in 2006, of which 44.6% are covered by the European Union. Species identification is a key problem throughout the life cycle of fishes: from eggs and larvae to adults in fisheries research and control, as well as processed fish products in consumer protection.
Methodology/Principal Findings
This study aims to evaluate the applicability of the three mitochondrial genes 16S rRNA (16S), cytochrome b (cyt b), and cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) for the identification of 50 European marine fish species by combining techniques of “DNA barcoding” and microarrays. In a DNA barcoding approach, neighbour Joining (NJ) phylogenetic trees of 369 16S, 212 cyt b, and 447 COI sequences indicated that cyt b and COI are suitable for unambiguous identification, whereas 16S failed to discriminate closely related flatfish and gurnard species. In course of probe design for DNA microarray development, each of the markers yielded a high number of potentially species-specific probes in silico, although many of them were rejected based on microarray hybridisation experiments. None of the markers provided probes to discriminate the sibling flatfish and gurnard species. However, since 16S-probes were less negatively influenced by the “position of label” effect and showed the lowest rejection rate and the highest mean signal intensity, 16S is more suitable for DNA microarray probe design than cty b and COI. The large portion of rejected COI-probes after hybridisation experiments (>90%) renders the DNA barcoding marker as rather unsuitable for this high-throughput technology.
Conclusions/Significance
Based on these data, a DNA microarray containing 64 functional oligonucleotide probes for the identification of 30 out of the 50 fish species investigated was developed. It represents the next step towards an automated and easy-to-handle method to identify fish, ichthyoplankton, and fish products.
Introduction
World fishery production (capture fisheries and aquaculture) reached 143.6 million tons in 2006, 77% of which were used for human consumption. About 37% of the total production entered the international trade, with an import value of up to 62.8 billion Euro in 2006. Europe produces about 15.5 million tons of fish and fishery products per year, an amount that is insufficient to satisfy the demand. The import value of fish and fishery products for Europe reached about 28 billion Euro in 2006, comprising 44.6% of the global imports. Trading within the European Union (EU) is extremely important, because about 45% of imports and 84% of exports are being conducted between EU countries [1]. These figures underline the importance of the global trade in fish and fishery products, especially for the EU.
In order to protect the consumer, the EU has strict regulations for seafood labelling, which must include the species name (EU Council Regulation No 104/2000, EU Commission Regulation No 2065/2001). However, detection of commercial fraud by mislabelling is difficult, especially in processed products, where all morphological characters suitable for species identification have been eliminated. Furthermore, the large number of traded species from all over the world, e.g. 420 fish species in Germany, is making it impossible for the inspection authorities to control for correct labelling. The genetic identification of species can help to solve this problem [2]–[4]. For instance, a DNA sequencing study on food fish has revealed that three-quarters of fish sold in the United States of America as “red snapper” were mislabelled and belonged to other species [5]. Mislabelling can even threaten consumer health if toxic species enter the market, such as pufferfish that causes tetrodotoxin poisoning [6].
Accurate species identification is also essential in ichthyoplankton surveys for fisheries research, conducted to estimate stock of future year-classes and to fix fishing quota accordingly. For instance, eggs of cod, haddock, and whiting are difficult to differentiate by morphological characters. Genetic identification revealed that almost two thirds of “cod like” eggs from the Irish Sea have been misidentified, resulting in an overestimation of cod stocks [7].
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequences of cytochrome b (cyt b) and 16S rRNA (16S) genes are amongst the most widely used genetic markers for fish species identification [3], [4]. They have been widely applied in seafood control [5], [8]–[11], ichthyoplankton identification [12]–[15], fisheries control [16], [17], and species delineation [18]–[20]. Data bases have been established, containing complete cyt b and rhodopsin gene sequences of European marine fish species [21] (www.fishtrace.org), as well as partial 16S, cyt b, and COI sequences of anchovies [11] (http://anchovyid.jrc.ec.europa.eu) to enable a sequence-based identification of specimens.
However, in course of developing a unifying identification system for animal species an universal marker has been proposed to serve as a so-called “DNA barcode” [22], [23]. This DNA barcode is the sequence of the “Folmer fragment” [24], a polymorphic part of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene (COI), which can be used to identify closely related species as well as higher taxa in many animal phyla. The applicability of COI for species identification in fish [25] triggered actually the international initiative for barcoding all fishes (FISH-BOL; www.fishbol.org) [3], [26]. Additional studies have shown that genetic identification by “COI barcodes” can provide a useful tool to identify seafood for consumer protection [9], [27]–[30], to control fisheries [31]–[33], to detect possibly cryptic species [34]–[37], and even to describe new species [38].
DNA sequence-based identification utilises the refined Sanger sequencing method [39], [40], which is still the “gold standard” [41], but requires samples that contain DNA of only one specimen. However, this is not the case in ichthyoplankton or other mixed samples, where several target species need to be detected and discriminated amongst an even much higher number of other species. Most next generation sequencing methods are enabling the analysis of mixed samples, but need highly sophisticated and expensive equipment (for review see e.g. [3] and references therein).
In contrast, DNA microarrays, first created 20 years ago, are well established and able to differentiate hundreds of specimens simultaneously. They were primarily used for gene expression profiling, but recently several DNA microarrays have been developed for the identification of fishes [42]–[45] and other organisms (see references in [3]).
This study compares three genetic markers (16S, cyt b, and COI) used as identification tools to distinguish 50 fish species common in European seas in terms of (1) their power of resolution in sequence-based species identification (DNA barcoding) and (2) their applicability in oligonucleotide probe design for the development of a low density DNA microarray.
Materials and Methods
Sampling and DNA Extraction
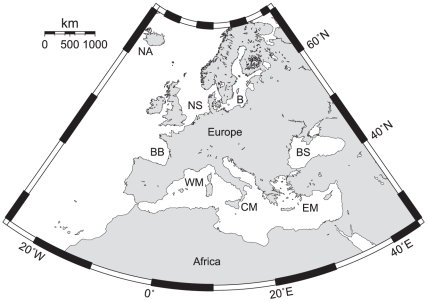
In order to account for intraspecific sequence variation and to avoid any misleading results due to restricted sampling in terms of specimens and geographic coverage [46], fishes were collected in eight different regions of the European seas: Northeastern Atlantic, North Sea, Baltic, Bay of Biscay, Western, Central, as well as Eastern Mediterranean, and Black Sea (Fig. 1, Table 1, Supporting Information Table S1). Taxonomic sampling focused on commercially important species such as anchovy, cod, flounder, hake, herring, plaice, sardine, and sole. However, considering that differentiation of closely related species constitutes a challenging task not only for morphological but genetic methods as well, the sampling scheme also included a number of sibling species and groups of closely related fishes that are commercially not important, in order to examine the resolution power of the markers in species delineation.
Figure 1. Map with sampling areas for fishes from European seas.
Northeastern Atlantic (NA), North Sea (NS), Baltic (B), Bay of Biscay (BB), Western Mediterranean (WM), Central Mediterranean (CM), Eastern Mediterranean (EM), and Black Sea (BS).
Table 1. Sequences utilised for the DNA barcoding approach.
| Species | Family | Order | 16S | cyt b | COI | Total |
| Clupea harengus | Clupeidae | C | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Sardina pilchardus | Clupeidae | C | 11 | 7 | 18 | |
| Engraulis encrasicolus | Engraulidae | C | 11 | 8 | 12 | 31 |
| Gadus morhua | Gadidae | G | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Merlangius merlangus | Gadidae | G | 4 | 4 | 4 | 12 |
| Merluccius merluccius | Merlucciidae | G | 14 | 2 | 19 | 35 |
| Lophius budegassa | Lophiidae | L | 8 | 1 | 6 | 15 |
| Lophius piscatorius | Lophiidae | L | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Trachurus mediterraneus | Carangidae | P | 3 | 6 | 12 | 21 |
| Trachurus picturatus | Carangidae | P | 5 | 5 | 6 | 16 |
| Trachurus trachurus | Carangidae | P | 9 | 13 | 12 | 34 |
| Dicentrarchus labrax | Moronidae | P | 5 | 1 | 8 | 14 |
| Mullus barbatus | Mullidae | P | 10 | 12 | 12 | 34 |
| Mullus surmuletus | Mullidae | P | 14 | 13 | 3 | 30 |
| Scomber japonicus | Scombridae | P | 9 | 3 | 17 | 29 |
| Scomber scombrus | Scombridae | P | 4 | 2 | 11 | 17 |
| Epinephelus marginatus | Serranidae | P | 8 | 0 | 5 | 13 |
| Serranus cabrilla | Serranidae | P | 8 | 6 | 15 | 29 |
| Serranus hepatus | Serranidae | P | 8 | 6 | 5 | 19 |
| Serranus scriba | Serranidae | P | 6 | 1 | 5 | 12 |
| Boops boops | Sparidae | P | 9 | 7 | 23 | 39 |
| Diplodus sargus | Sparidae | P | 5 | 4 | 4 | 13 |
| Diplodus vulgaris | Sparidae | P | 8 | 7 | 22 | 37 |
| Pagellus acarne | Sparidae | P | 8 | 9 | 12 | 29 |
| Pagellus erythrinus | Sparidae | P | 10 | 7 | 15 | 32 |
| Sparus aurata | Sparidae | P | 7 | 6 | 11 | 24 |
| Arnoglossus laterna | Bothidae | Pl | 5 | 0 | 11 | 13 |
| Hippoglossoides platessoides | Pleuronectidae | Pl | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| Limanda limanda | Pleuronectidae | Pl | 11 | 3 | 6 | 20 |
| Microstomus kitt | Pleuronectidae | Pl | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| Platichthys flesus | Pleuronectidae | Pl | 11 | 2 | 4 | 17 |
| Pleuronectes platessa | Pleuronectidae | Pl | 9 | 0 | 2 | 11 |
| Lepidorhombus boscii | Scophthalmidae | Pl | 12 | 5 | 9 | 26 |
| Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis | Scophthalmidae | Pl | 5 | 3 | 8 | 16 |
| Phrynorhombus norvegicus | Scophthalmidae | Pl | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Psetta maxima | Scophthalmidae | Pl | 9 | 4 | 15 | 28 |
| Scophthalmus rhombus | Scophthalmidae | Pl | 9 | 8 | 13 | 30 |
| Buglossidium luteum | Soleidae | Pl | 5 | 0 | 13 | 18 |
| Microchirus variegatus | Soleidae | Pl | 4 | 2 | 9 | 15 |
| Pegusa impar | Soleidae | Pl | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Solea solea | Soleidae | Pl | 15 | 0 | 18 | 33 |
| Scorpaena notata | Scorpaenidae | S | 11 | 5 | 10 | 26 |
| Scorpaena porcus | Scorpaenidae | S | 8 | 4 | 0 | 12 |
| Helicolenus dactylopterus dactylopterus | Sebastidae | S | 9 | 10 | 20 | 39 |
| Chelidonichthys lucernus | Triglidae | S | 10 | 11 | 16 | 37 |
| Eutrigla gurnardus | Triglidae | S | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Trigla lyra | Triglidae | S | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| Trigloporus lastoviza | Triglidae | S | 7 | 0 | 5 | 12 |
| Macrorhamphosus scolopax | Centriscidae | Sy | 7 | 8 | 6 | 21 |
| Zeus faber | Zeidae | Z | 8 | 0 | 15 | 23 |
| Total | 369 | 212 | 447 | 1023 |
Abbreviations: 16S: 16S rRNA gene (accession numbers: FN687913–FN688280), cyt b: cytochrome b gene (accession numbers: FN688281–FN688492), COI: cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene (accession numbers: FN688905–FN689348), C: Clupeiformes, G: Gadiformes, L: Lophiiformes, P: Perciformes, Pl: Pleuronectiformes, S: Scorpaeniformes, Sy: Syngnathiformes, Z: Zeiformes. For details see Supporting Information Table S1.
Voucher specimens and tissue samples were preserved in absolute ethanol and were frozen at −20°C or stored at 4°C. DNA was extracted from muscle tissue with the DNeasy tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) or gill filaments with the Agowa mag midi DNA isolation kit (AGOWA, Berlin, Germany) according to the instructions of the manufacturers.
Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequencing
Three mitochondrial genes were screened as potential markers for species identification in this study: (1) 16S, (2) cyt b, and (3) COI. A fragment of 16S was amplified and sequenced as described in Kochzius et al. (2008) [42].
The cyt b fragment was amplified with the newly designed primers CytbF (5′-GGC TGA TTC GGA ATA TGC AYG CNA AYG G-3′) and CytbR (5′-GGG AAT GGA TCG TAG AAT TGC RTA NGC RAA-3′). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with a total volume of 15 µl contained 1.5 µl 10× reaction buffer, 1.5 µl dNTPs (10 mM), 0.05 µl of each primer (100 pmol/µl), 5 µl DNA-extract, 0.3 µl Teg polymerase (3 U/µl; comparable with Taq polymerase; Prokaria, Reykjavik, Iceland), and 6.6 µl deionised ultra-pure water. Thermal profile began at 94°C for 4 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94°C (30 s), 52°C (30 s), and 72°C (90 s), with a final step of 7 min at 72°C.
In order to amplify a fragment of COI, degenerated primers were designed on the basis of the universal COI primers for fish published by Ward et al. (2005) [25]: COI-Fish-F (5′-TTC TCA ACT AAC CAY AAA GAY ATY GG-3′) and COI-Fish-R (5′-TAG ACT TCT GGG TGG CCR AAR AAY CA-3′. The volume of the PCRs was 15 µl and contained 1.5 µl 10× reaction buffer, 1.5 µl dNTPs (10 mM), 0.05 µl of each primer (100 pmol/µl), 3 µl DNA-extract, 0.2 µl Teg polymerase (3 U/µl; Prokaria, Reykjavik, Iceland), and 9.7 µl deionised water. Thermal profile started with 94°C for 4 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94°C (50 s), 59°C (50 s), and 72°C (90 s), finalised at 72°C for 7 min.
PCR products were purified by using the ExoSAP-IT for PCR clean-up (GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden). The newly designed sequencing primer cytbFseq (5′- GGC TGA TTC GGA ATA TGC A-3′) was used to sequence the cyt b PCR products. The COI product were sequenced with the PCR primers shown above. The BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit (ver. 3.1, PE Biosystems, Foster City, USA) and an ABI Prism 3730 automated DNA Analyser (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) were used according to the manufacturer's instructions.
DNA Barcoding
Sequences of 50 marine fish species were obtained to compare the applicability of the 16S, cyt b, and COI genes as markers for DNA barcoding. Multiple alignments of these orthologous sequences were performed with the programme Clustal W [47] as implemented in BioEdit (version 7.0.4.1) [48] to ensure that all sequences of each marker gene provide a homologous fragment. Cytochrome b and COI sequences were translated into amino acids with the program Squint (www.cebl.auckland.ac.nz) in order to exclude sequencing errors and to avoid the inclusion of pseudogene sequences in the datasets. For each marker, unrooted Neighbour Joining (NJ) trees were constructed and genetic p-distance was calculated within species, genera, families, and orders with the programme MEGA (version 3.1) [49]. Evaluation of statistical confidence in nodes was based on 1000 non-parametric bootstrap replicates [50]. Since the aim of this task was to identify species using barcodes, phylogenetic trees were constructed without selecting a priori an evolutionary model appropriate for the dataset.
In Silico Oligonucleotide Probe Design
The design of oligonucleotide probes was based on sequence alignments used for DNA barcoding that also included additional sequences obtained from international sequence data bases: 35 for 16S, 69 for cyt b, and 23 for COI. Gaps in the 16S sequence alignment were removed before probe design. Species-specific oligonucleotide probes that cover all sequences of one species and do not match any other species were designed with a computer programme developed by the bioinformatics groups of the Centre for Applied Gene Sensor Technology (CAG) and the Zentrum für Technomathematik (ZeTeM), both at University of Bremen [51]. Probe design was performed in order to meet the following criteria: (1) optimal length of 23 to 27 bp, (2) melting temperature (Tm) of 81 to 85°C based on the unified model [52], (3) GC content of 52% to 54%, (4) appropriate secondary structure of the oligonucleotides and the target sequence, (5) possible dimer formation, and (6) a suitable probe-target binding energy. The programme RNAfold [53] was employed to compute minimal free energy structures. Probes showing strong secondary structures or binding to a region of the target with such a strong secondary structure were not used. The selected oligonucleotide probes were tested in silico against >900 16S (365 species), >2700 cyt b (324 species), and >270 COI (93 species) sequences of fishes occurring in European seas. These sequences were obtained from EMBL sequence data base (92%) and were sequenced in course of this study (8%).
Preparation of DNA Microarrays and Hybridisation Experiments
Glass slides coated with aminosilane (3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane) and a PDITC-linker (1,4-phenylendiisothiocyanate) (Asper Biotech, Tartu, Estonia) were used for microarray production. A spotting robot based on a modified version of the contactless TopSpot® technology [54] was used to spot oligonucleotide probes (Thermo Hybaid, Ulm, Germany) with a 5′-amino-C6-modification in 150 mM Na3PO4 buffer (pH 8.5) at a concentration of 20 µM onto the glass slides. The spotted volume of this oligonucleotide solution was 200 pl, producing a spot diameter of approximately 220 µm. Afterwards, the microarrays were incubated for 16 h in a wet chamber to ensure efficient covalent binding of the oligonucleotides to the surface. Finally, the microarrays were shrink-wrapped under a nitrogen atmosphere and were stored at 4°C for up to 6 months. Each probe was spotted in three replicates.
DNA of the 50 target fish species (Table 1) was separately amplified and labelled with 5′-Cy5-modified primers for single target hybridisation experiments. A fragment of 16S was amplified and labelled as described in Kochzius et al. (2008) [42].
Labelled cyt b fragments of 626 bp length were PCR amplified with the 5′-Cy5-modified primers CytbF and CytbR. Reactions were conducted in a volume of 100 µl containing 10 µl 10× reaction buffer, 8 µl MgCl2 (50 mM), 4 µl dNTPs (5 mM), 4 µl of each primer (10 µM), 4 µl DNA-extract, 0.4 µl Taq polymerase (5 U/µl), 2 µl BSA (20 mg/ml), and 63.6 µl deionised water. The thermo-profile started at 94°C (2 min), followed by 40 cycles at 94°C (60 s), 45°C (90 s), and 72°C (60 s), finalised for 5 min at 72°C.
Amplification of labelled COI fragments of 710 bp length was performed with the 5′-Cy5-modified primer pair COI-Fish-F and COI-Fish-R. The PCR solution contained 10 µl 10× reaction buffer, 8 µl MgCl2 (50 mM), 4 µl dNTPs (5 mM), 4 µl of each primer (10 µM), 5 µl DNA-extract, 0.4 µl Taq polymerase (5 U/µl), 4 µl BSA (20 mg/ml), and 60.6 µl deionised water in a volume of 100 µl. Thermo-cycling did start at 94°C, with 35 subsequent cycles at 94°C (50 s), 45°C (50 s), and 72°C (90 s). The final step was 3 min at 72°C.
The Cy5-labelled PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). Hybridisation experiments were performed with 50 target fish species (Table 1). The purified Cy5-labelled PCR product and a 5′-Cy3-labelled positive control (5′-CGT GTG AGT CGA TGG ATC ATA-3′) at concentrations of 10 and 1 nM, respectively, were hybridised to the microarray in a volume of 130 µl using GeneFrames® (ABgene House, Epsom, UK). Hybridisation was conducted at 50°C for 2 h in a hybridisation oven. Afterwards, GeneFrames® were removed and the microarrays were washed 5 minutes each with 2×SSC (sodium chloride trisodium citrate) buffer containing 0.05% SDS (sodium dodecyl sulphate), 1×SSC containing 0.05% SDS, and 1×SSC. Finally, the microarrays were dried in a centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 3 minutes. Each hybridisation experiment was conducted in three replicates.
Measurement of Fluorescence Signals and Data Analysis
Hybridisation signals were measured using an Axon 4000B fluorescence microarray scanner at 635 nm (Cy5) and 528 nm (Cy3). The fluorescence signal analysis was conducted with the software GenePix 4.1 (Axon, Union City, USA). Spots that showed artefacts caused during the spotting process (e.g., inhomogeneous spots documented by a monitoring camera during spotting) or the experiment (e.g. air bubbles) were removed from the analysis. The fluorescence signal of each probe was measured as arbitrary units and the arithmetic mean was calculated. Only signals with a minimum value of 1000 arbitrary units were considered in data analysis.
Results
DNA Barcoding
A data set of 369 16S (418–452 bp; accession numbers FN687913–FN688280 ), 212 cyt b (404 bp; accession numbers FN688281–FN688492), and 447 COI (455 bp; accession numbers FN688905–FN689348) sequences of 50 fish species from European seas was obtained and these sequences are available at the EMBL sequence data base (Table 1, Supporting Information Table S1). No stop codons, insertions, and deletions were observed in the cyt b and COI sequences, indicating that they represent fragments of functional mitochondrial genes and not nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes (Numts) [55].
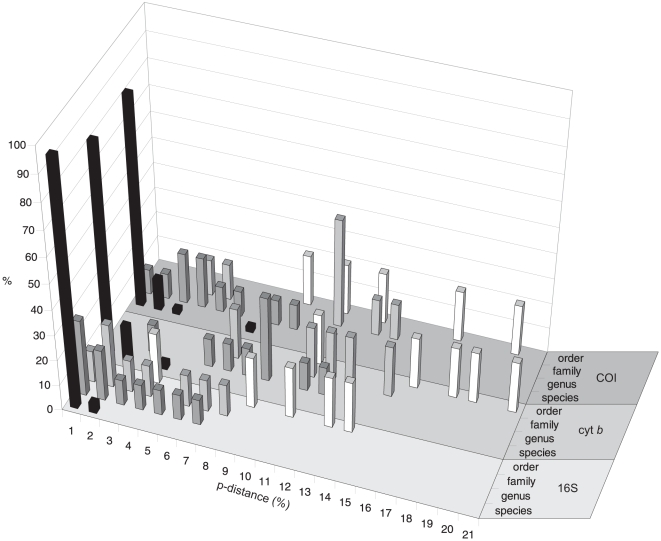
The 16S sequences showed the lowest mean genetic p-distances at all taxonomic levels, from species to orders, while the highest values were observed for cyt b, except at the species level (Table 2). The p-distance frequency distribution of the three markers did not showed any evidence for a barcoding gap (Fig. 2), which is an ideal case where the genetic divergence among nucleotide sequences at within- and between-species levels do not overlap [46]. However, in cyt b, the overlap of p-distance variation at within- and between-species levels was strongly reduced.
Table 2. Summary of genetic p-distances (%) within different taxonomic levels.
| 16S | cyt b | COI | ||||
| comparison within | Mean p-distance | SE | Mean p-distance | SE | Mean p-distance | SE |
| species | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.22 | 0.59 | 0.17 |
| genera | 2.66 | 0.46 | 7.72 | 0.86 | 3.96 | 0.52 |
| families | 4.35 | 0.53 | 10.94 | 0.91 | 9.42 | 0.86 |
| orders | 10.78 | 0.90 | 16.38 | 1.04 | 13.52 | 1.02 |
Values are calculated from partial sequences of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA (16S; n = 369), cytochrome b (cyt b; n = 212), and cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI; n = 447) genes of 50 fish species from European seas.
Figure 2. Frequency distribution of genetic p-distances.
Data for different taxonomic levels for partial sequences from mitochondrial 16S rRNA (16S), cytochrome b (cyt b), and cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) genes of fishes from European seas.
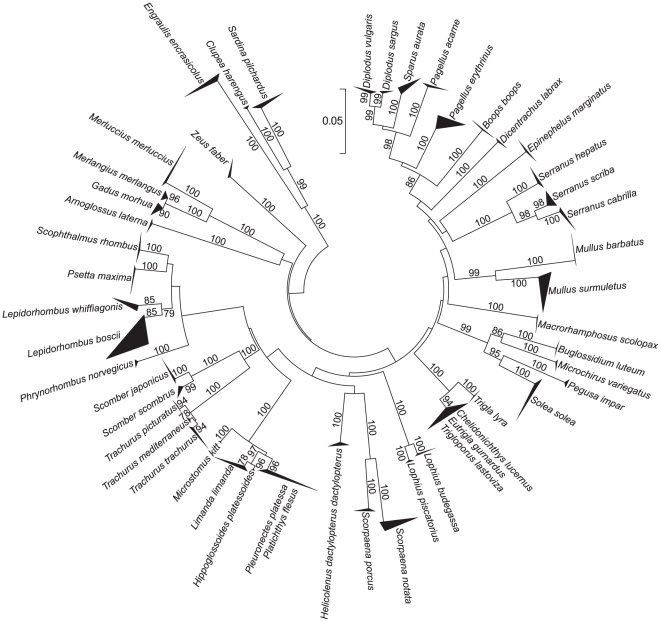
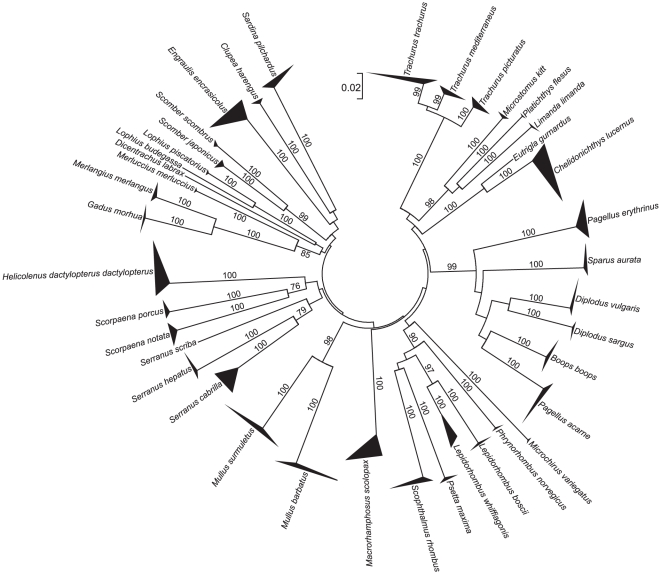
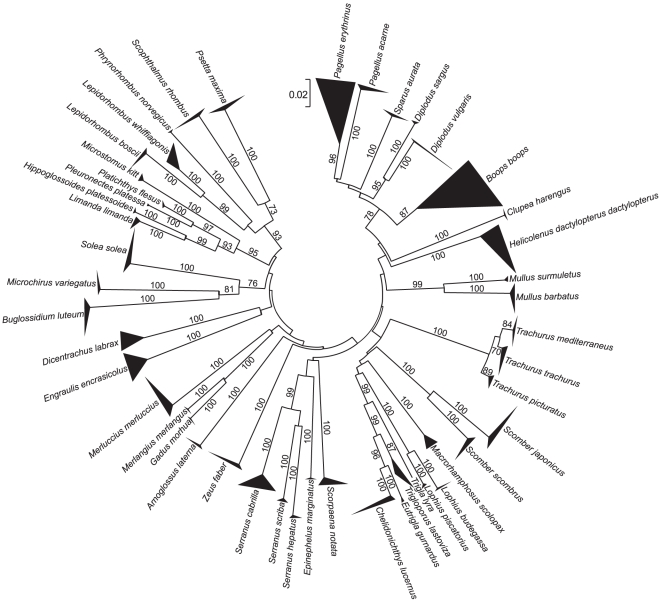
All NJ trees resolved species-specific clades that were supported by high bootstrap values (Fig. 3, Fig. 4, and Fig. 5), except for the 16S tree that was unable to separate the nucleotide sequences of the closely related flatfish species Pleuronectes platessa and Platichthys flesus and of the gurnards Chelidonichthys lucernus, Eutrigla gurnardus, and Trigloporus lastoviza (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis (16S).
Neighbour Joining tree for partial sequences of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene of fishes from European seas. The number of sequences and their geographic origin for each species are given in Table 1 and Supporting Information Table S1. Bootstrap values based on 1000 replicates are indicated at branches.
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis (cyt b).
Neighbour Joining tree for partial sequences of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene of fishes from European seas. The number of sequences and their geographic origin for each species are given in Table 1 and Supporting Information Table S1. Bootstrap values based on 1000 replicates are indicated at branches.
Figure 5. Phylogenetic analysis (COI).
Neighbour Joining tree for partial sequences of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene of fishes from European seas. The number of sequences and their geographic origin for each species are given in Table 1 and Supporting Information Table S1. Bootstrap values based on 1000 replicates are indicated at branches.
DNA microarray
A total of 319 oligonucleotide probes (16S: 46; cyt b: 123; COI: 150) were designed for the 50 target species (Table 1, Supporting Information Table S1) and tested within 255 hybridisation experiments with 3 replicates each (data not shown). Several probes were not functional due to low signal intensities as well as false-positive or false-negative signals. A total of 64 probes unambiguously identified 30 target fish species (Table 3, Supporting Information Table S2, and Fig. 6). However, the portion of the in silico selected probes that gave successful hybridisation signals with target species was greatly variable among gene markers: 20 16S-probes for 15 species (43.5%), 31 cyt b-probes for 16 species (25.2%), and 13 COI-probes for 10 species (8.7%).
Table 3. Oligonucleotide probes for the identification of fish species from European seas.
| No. | Species | Probe ID | Probe sequence (5′>3′) |
| 1 | Sardina pilchardus | Cytb_Sarpil_l25_p203 | CACAGTTCTTCACCTGCTCTTCCTC |
| 2 | Sardina pilchardus | Cytb_Sarpil_l26_p170 | CCACTTCTTGTTCCCATTCGTGATCG |
| 3 | Engraulis encrasicolus | COI_Engenc_l27_p182 | CCTTCTCCTCTTAGCATCATCTGGTGT |
| 4 | Engraulis encrasicolus | Cytb_Engenc_l23_p194 | TGCAGGTGTTACTATCCTTCACC |
| 5 | Gadus morhua | Cytb_Gadmor_l26_p362 | CGCACCTAATTTACTCGGAGATCCAG |
| 6 | Gadus morhua | Cytb_Gadmor_l27_p351 | CTCGCCCTCTTCGCACCTAATTTACTC |
| 7 | Merlangius merlangus | Cytb_Mermer_l23_p334 | TTCTAGGCTTAACTGCTCTGGCC |
| 8 | Merluccius merluccius | Cytb_Mercmerc_l23_p325 | CTCTGCTCCTTATCGCCCTAACA |
| 9 | Merluccius merluccius | Cytb_Mercmerc_l24_p252 | GTAGGGCTCAACTCTGATGCAGAC |
| 10 | Merluccius merluccius | COI_Mercmerc_l23_p398 | ACCCCTCTTTGTTTGATCCGTCC |
| 11 | Lophius budegassa | Cytb_Lopbud_l25_p194 | CCTGGCAATAACCGTTATCCACCTC |
| 12 | Lophius budegassa | Cytb_Lopbud_l26_p325 | CAGTCGTCTTAATTACGCTCACAGCC |
| 13 | Dicentrarchus labrax | 16S_Diclab_l25_p202 | GGGAGACTACCTTAATTACCCCTGG |
| 14 | Dicentrarchus labrax | 16S_Diclab_l23_p236 | AAAAGCTAAAGGTACCCCTCCCC |
| 15 | Dicentrarchus labrax | COI_Diclab_l25_p378 | GCCATTTCCCAGTACCAAACTCCTT |
| 16 | Dicentrarchus labrax | Cytb_Diclab_l23_p199 | GTGCCACAATACTACACCTCCTT |
| 17 | Dicentrarchus labrax | Cytb_Diclab_l27_p216 | CTCCTTTTTCTTCATCAAACGGGCTCC |
| 18 | Dicentrarchus labrax | Cytb_Diclab_l27_p247 | ACCCCTTAGGCCTTAACTCAGATGTAG |
| 19 | Mullus barbatus | 16S_Mulbar_l25_p357 | CTTCTGACCTACAAGATCCGGCCAA |
| 20 | Scomber japonicus | 16S_Scojap_l23_p223 | CCCCTAACAAGGGGCCAAACTTA |
| 21 | Scomber scombrus | Cytb_Scosco_l25_p324 | GCCGTTCTCCTTATAGGCCTTACCT |
| 22 | Scomber scombrus | Cytb_Scosco_l25_p335 | TATAGGCCTTACCTCCCTAGCACTC |
| 23 | Epinephelus marginatus | 16S_Epimar_l24_p216 | TAATACCCTCAACAACAGGACACG |
| 24 | Serranus hepatus | COI_Serhep_l26_p232 | GAACTGTTTATCCGCCTTTAGCTGGT |
| 25 | Serranus hepatus | COI_Serhep_l27_p243 | CCGCCTTTAGCTGGTAACTTAGCTCAC |
| 26 | Serranus scriba | COI_Serscr_l23_p233 | AACGGTTTACCCACCACTTGCTG |
| 27 | Serranus scriba | COI_Serscr_l27_p428 | TGCAGTTCTCCTACTTCTATCCCTTCC |
| 28 | Boops boops | 16S_Booboo_l23_p314 | AGCACCACACTCCTAAACCCAAG |
| 29 | Boops boops | 16S_Booboo_l24_p241 | CCTAGTGAATCCTGCTCTAATGTC |
| 30 | Diplodus sargus | Cytb_Dipsar_l23_p197 | CGCCATAACCATGCTTCACCTCT |
| 31 | Pagellus acarne | 16S_Pagaca_l23_p316 | GTACTACACTCCCACATCCGAGA |
| 32 | Sparus aurata | 16S_Spaaur_l23_p201 | AGAACAGCTCACGTCAAACACCC |
| 33 | Sparus aurata | Cytb_Spaaur_l26_p187 | TCGTCATTGCAGCCATAACCATACTG |
| 34 | Sparus aurata | Cytb_Spaaur_l27_p205 | CCATACTGCATCTTCTGTTCCTCCATG |
| 35 | Arnoglossus laterna | COI_Arnlat_l17_p387 | ATGTACCAAGCACCCCT |
| 36 | Hippoglossoides platessoides | COI_Hippla_l26_p236 | CGTGTATCCTCCCCTTGCTGGAAATC |
| 37 | Platichthys flesus | Cytb_Plafle_l23_p250 | CCACAGGGCTAAACTCAGACTCT |
| 38 | Platichthys flesus | Cytb_Plafle_l23_p328 | TTCTCCTTACTGCACTGGCTTCG |
| 39 | Platichthys flesus | Cytb_Plafle_l25_p197 | GGCCGCAACAGTAATTCACCTACTC |
| 40 | Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis | 16S_Lepwhi_l24_p323 | CCCCACCAACTCCTCCAAACTAGA |
| 41 | Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis | COI_Lepwhi_l19_p370 | AACCCGCTACTGTCACCAT |
| 42 | Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis | COI_Lepwhi_l26_p362 | CAACATAAAACCCGCTACTGTCACCA |
| 43 | Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis | Cytb_Lepwhi_l23_p312 | CTCCTTGGCTTCGCAGTTCTCTT |
| 44 | Phrynorhombus norvegicus | 16S_Phrnor_l23_p326 | AGCACCCATCCCAATTACTCCTC |
| 45 | Phrynorhombus norvegicus | Cytb_Phrnor_l23_p328 | TACTTCTGACGGCACTCACATCC |
| 46 | Phrynorhombus norvegicus | Cytb_Phrnor_l25_p311 | CCTTCTTGGCTTCGCAGTACTTCTG |
| 47 | Psetta maxima | 16S_Psemax_l25_p321 | CCCCTTAACTCCTCCAAATGAGAGC |
| 48 | Psetta maxima | Cytb_Psemax_l23_p321 | TTCGTCGTCCTCTTGACAGCACT |
| 49 | Psetta maxima | Cytb_Psemax_l23_p337 | CAGCACTCGCAACCCTAGCTTTA |
| 50 | Psetta maxima | Cytb_Psemax_l25_p195 | GCAGCAGTAACGGTTATTCACCTCC |
| 51 | Microchirus variegatus | Cytb_Micvar_l23_p343 | TGGCAGCCCTAGCAATATTCTCC |
| 52 | Microchirus variegatus | Cytb_Micvar_l25_p312 | CTCCTCGGATTCTCGATCCTACTCA |
| 53 | Microchirus variegatus | Cytb_Micvar_l27_p325 | CGATCCTACTCATTTTATTGGCAGCCC |
| 54 | Pegusa impar | 16S_Pegimp_l23_p206 | GCCCGTCCCCAAACCTGAAATAA |
| 55 | Pegusa impar | 16S_Pegimp_l26_p313 | GCACTTTACCCCATTACTCTTTGCTC |
| 56 | Solea solea | 16S_Solsol_l23_p202 | TTCAGCCCGTCCCCAAATTCTAA |
| 57 | Solea solea | 16S_Solsol_l25_p321 | CCCTTCACTCCCTGCTCTTAGAAAC |
| 58 | Solea solea | COI_Solsol_l25_p191 | TCTCACCTCATCCGTTGTTGAAGCC |
| 59 | Scorpaena notata | 16S_Sconot_l25_p241 | CTGGTGGACCTCTTCCCTAATGTCT |
| 60 | Scorpaena porcus | 16S_Scopor_l26_p209 | CCATGTCACTAACCCTTTGATACAGG |
| 61 | Scorpaena porcus | 16S_Scopor_l24_p312 | GGCACACCCGTTCCTTCAATTAAG |
| 62 | Scorpaena porcus | Cytb_Scopor_l25_p332 | CCTTCTTGGCCTTACAATACTCGCG |
| 63 | Helicolenus dactylopterus dactylopterus | COI_Heldac_l19_p374 | CCCAGCGATCTCTCAATAC |
| 64 | Zeus faber | 16S_Zeufab_l26_p187 | GAGCTTTAGACCTAATGCAGTCCACG |
Probe ID: 16S, Cytb, and COI indicate the mitochondrial 16S rRNA, cytochrome b, and cytochrome oxidase subunit I marker genes, respectively; the number following “l” is the length of the oligonucleotide probe and the number after “p” the position in the target sequence alignment. For details see Supporting Information Table S2.
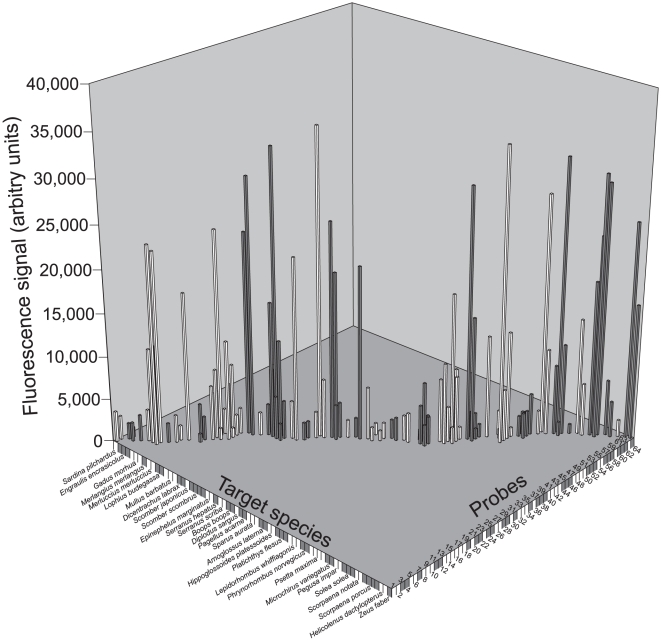
Figure 6. DNA microarray hybridisation experiments.
Mean signal intensities of single target hybridisations to 64 oligonucleotide probes on a DNA microarray for the identification of 30 fish species from European seas. For numbers given to oligonucleotide probes refer to Table 3 and Supporting Information Table S2.
Overall, the signal intensity was highly variable among individuals used in the hybridisation experiments and among probes of the three gene markers, ranging from 1,004 to 35,273 a.u.. (1) Some probes showed a large variation in signal intensity when PCR products of different individuals of the target species were hybridised on the microarray. For instance, in cod (Gadus morhua) the values for different specimens showed a 5–6 fold difference. (2) Among gene markers, the median value of the hybridisation signals obtained with the 16S-probes was much higher (11,915 a.u.) than those of the COI (3,027 a.u.) and cyt b probes (3,014 a.u.). However, this general pattern was not observed in all species. For example, the COI-probes of the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) showed higher values than the cyt b and 16S probes (Table 3, Supporting Information Table S2, and Fig. 6). (3) Finally, additional variation among probes also resulted from the lack of positive hybridisation signals of some probes in some specimens of ten target species (i.e. Engraulis encrasicolus, Merluccius merluccius, Dicentrarchus labrax, Serranus scriba, Sparus aurata, Platichthys flesus, Lepidorhombus whiffiagonis, Psetta maxima, Pegusa impar, and Solea solea). However, for these species, at least one designed probe showed a clear positive signal (Fig. 6).
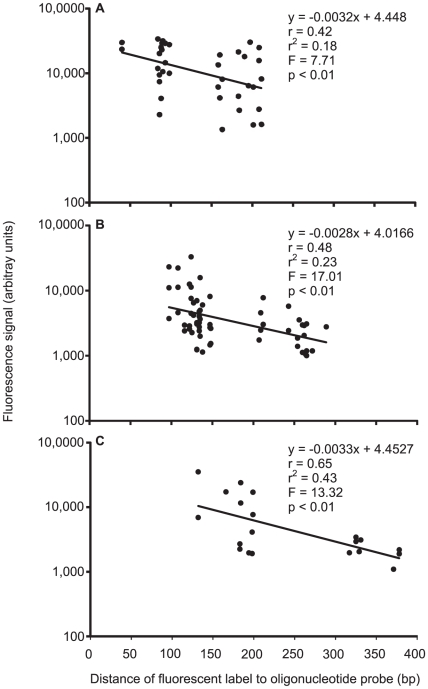
The hybridisation signal intensity decreased as the distance between the binding site and the fluorescent label in the oligonucleotide probe increased (Fig. 7). This “position of label” (POL) effect [56], [57] was significant for all markers (p<0.01) and higher in the COI probes (r = 0.65) than in the cyt b (r = 0.48) and 16S probes (r = 0.42).
Figure 7. Position of label effect.
Relationship of signal intensity and distance of fluorescent label to oligonucleotide probes based on partial sequences of mitochondrial (A) 16S rRNA, (B) cytochrome b, and (C) cytochrome oxidase subunit I genes of fishes from European seas.
Discussion
DNA Barcoding
All three mitochondrial sequence markers were useful for the identification of the 50 target species (Fig. 3, Fig. 4, and Fig. 5). However, all of them had some limitations. Even though mean genetic p-distances were different at the multiple taxonomic levels suggesting the existence of a “barcoding gap” (Table 2), the frequency distribution of p-distances did not support the presence of such a gap (Fig. 2). This consistently supports the issue that mean values of genetic distances exaggerate the size of the “barcoding gap” [58]. In our data, the extent of overlap between genetic variation observed at within- and between-species levels was different among markers, with the largest overlap shown by 16S. The lack of a “barcoding gap” in COI was also observed in a comprehensive study on publicly available sequences of marine and freshwater fishes [59], available from the Barcoding of Life Database (BOLD) [60]. A limitation of the 16S marker was the lack of resolution in the species separation of related flatfish (P. platessa and P. flesus) and gurnard species (C. lucernus, E. gurnardus, and T. lastoviza). Even though the two flatfish species and other gurnards are known to hybridise [61], [62], the failing of 16S in discriminating them is not likely caused by introgression, because the same species and specimens were clearly separated by COI. Therefore, it is more reasonable to explain such lack of resolution with the rather low mutation rate in 16S. So far only six fish species were potentially affected by introgression in DNA barcoding studies [25], [63] and it is rather a minor problem in applying mtDNA in fish species identification [26].
The results clearly show that Numts, which may interfere in mtDNA-based species identification, are of no concern in this study. Numts are copies of mitochondrial genes or fragments of them that have been transferred to the nuclear genome. Since most Numts are smaller than 400 bp [64], it is very unlikely that they can amplify with the primer sets used in this study. Moreover, Numts are not expressed and consequently they can have a much higher mutation rate that is likely to lead to stop codons, gaps, or radical changes in the amino acid sequence in protein coding genes, which can be easily detected with bioinformatic analysis. Overall, Numts are also rather of little concern in applying mtDNA for species identification [26] and were not considered in this study as potential artefact.
DNA Microarray
In silico probe design yielded a high number of potentially functional probes, but hybridisation experiments showed that most of them did not perform as expected from bioinformatic computations. Such a discrepancy between the performance exhibited by probes in silico and experimental hybridisations has already been reported by other studies for DNA [65] and RNA [66], suggesting that dynamics and processes of the hybridisation are still not understood. The unpredictable performance of probes in the microarray experiments lead to high variation of hybridisation signals. The median value of 16S hybridisation signals was four times higher than those obtained with cyt b and COI probes. However, most functional oligonucleotide probes were based on cyt b sequences and they also detected the highest number of target species (Table 3, Supporting Information Table S2). Even though most potentially functional probes could be designed based on COI, more than 90% had to be rejected due to cross-hybridisations and lack of signal in hybridisation experiments. In comparison, the rejection rates of 16S (56%) and cyt b (74%) probes were lower. Comparatively, in Penicillium approximately 60% of COI-based probes developed for species detection were rejected [65]. Overall, these results indicate that all oligonucleotide probes have to be tested intensively by hybridisation experiments to evaluate their functionality in species identification, preferably with several individuals of the target species together with a high number of non-target species. The in silico study on the effectiveness of mammalian COI and cyt b sequences for probe design suggested that both genes yield a high number of probes [67]. However, since the behaviour of oligonucleotide probes in hybridisation experiments cannot be predicted, in silico results should be handled with caution. The present study rather suggests that COI and cyt b are not well suited for probe design in fish species and similar findings were reported for the COI in fungi [65]. Sequences of ribosomal genes (e.g. 16S) seem to be more suitable for the design of functional probes in the studied fish species. This should be related to the secondary structure of the rDNA, showing single stranded linear DNA, single stranded loops, and double stranded stems. The loop region is characterised by a high insertion/deletion polymorphism (indel), which is a valuable feature making these sequences suitable for the design of highly specific oligonucleotide probes [42]. On the contrary, the disadvantage of 16S rDNA sequences is the lack of discrimination power among closely related species. However, this problem can be overcome by analysing in parallel other gene markers.
Absolute signal intensities were very heterogeneous in this study, the maximum value being 35-fold higher than the minimum value (Fig. 6). Great variation in signal intensities commonly affects DNA microarray hybridisation experiments (e.g., [68]–[72]). On the one hand, variation in signal intensity given by a certain oligonucleotide probe can occur among different experimental replicates and this might be related to differences in the quality of slides or solutions used for the hybridisation and washing steps. It is also reported that increased atmospheric ozone concentrations cause the oxidation of Cy5, hence decreasing fluorescence signal intensities [73], [74]. On the other hand, large differences in signal intensities among oligonucleotide probes might be related to the number and position of mismatches. Additionally, there are also sequence specific differences [75]. This study has also shown differences of the mean signal intensity among the three markers. While oligonucleotide probes based on cyt b and COI showed almost identical mean values of signal intensity, the mean value for 16S-probes was about four times higher. This might be explained by the secondary structure of the target DNA. In 16S, all oligonucleotide probes bind to the variable regions j and l [42], which represent large single-stranded loops. Therefore, the binding sites in the 16S target DNA are freely accessible for the oligonucleotide probes. In contrast, secondary structures of the protein coding cyt b and COI DNA fragments might hamper access of the probes to the binding sites in the target DNA.
The position of label relative to the target DNA-probe duplex might cause variation of the signal intensities among different oligonucleotide probes. Highest signal intensities are given by probes with a low distance between the fluorescent label and the binding site. Signal intensity decreases with increasing distance [56], [57]. The highest correlation was found in COI, followed by cyt b and 16S (Fig. 5). This was due to the fact that the maximum distance of the binding site to the fluorescence label is only about 200 bp in 16S, while it is almost 300 bp in cyt b and almost 400 bp in COI. Our results support that the 16S fragment is the most suited marker for microarray probe design, compared to cyt b and COI fragments.
Conclusions
The present study showed that the investigated mitochondrial sequence markers perform differently in DNA barcoding and microarray analyses for the identification of fish species. While cyt b and COI are equally well suited for the sequence based species identification of fishes, 16S has drawbacks in discriminating closely related species. In contrast, 16S-probes performed appreciably better than probes based on cyt b and COI in DNA microarray hybridisation experiments. Oligonucleotide probes based on 16S showed a lower rejection rate after hybridisation experiments, higher mean signal intensity, and weaker position of lable (POL) effect. Therefore, 16S sequences can be recommended for designing oligonucleotide probes for fish species identification based on DNA microarrays. In order to allow the discrimination of closely related species, additional markers, such as cyt b or a nuclear gene would be helpful. Unfortunately, COI was not suitable for the design of oligonucleotide probes for the target species, discouraging the utilisation of the huge number of COI barcode sequences in the Barcoding of Life Database (BOLD) [60] as a data source for the development of DNA microarrays for the identification of fish species.
This study has shown that mitochondrial sequence markers can be useful tools for the identification of European marine fishes. Species assignment is very important in the context of fisheries research, fisheries control, and consumer protection. The development of the described DNA microarray for the identification of 30 fish species represents the next step towards an automated and easy-to-handle assay that can be applied in ichthyoplankton surveys, by companies involved in fish trade as well as authorities concerned with fisheries control and consumer protection.
Supporting Information
Sequences utilised for the DNA barcoding approach. Abbreviations: 16S: 16S rRNA gene, cyt b: cytochrome b gene, COI: cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene, O: order, C: Clupeiformes, G: Gadiformes, L: Lophiiformes, P: Perciformes, Pl: Pleuronectiformes, S: Scorpaeniformes, Sy: Syngnathiformes, Z: Zeiformes, NA: Northeastern Atlantic, NS: North Sea, B: Baltic, BB: Bay of Biscay, WM: Western Mediterranean, CM: Central Mediterranean, EM: Eastern Mediterranean, and BS: Black Sea. No number in cell = 0.
(0.22 MB DOC)
Oligonucleotide probes for the identification of fish species from European seas. Probe ID: 16S, Cytb, and COI indicate the mitochondrial 16S rRNA, cytochrome b, and cytochrome oxidase subunit I marker genes, respectively; the number following “l” is the length of the oligonucleotide probe and the number after “p” the position in the target sequence alignment. Oligo mfe: minimal free energy of the secondary structure of the oligonucleotide; Dimer mfe: minimal free energy of the dimer of two identical oligonucleotide molecules. Values for mfe are given in kcal/mol. Mean fluorescence signal intensity as shown in Fig. 6 and its standard deviation (SD) is given in arbitrary units. Please note that some probes have been hybridised with several specimens of the target species.
(0.23 MB DOC)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank S. Roll and F. Meyerjürgens for producing the microarrays.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: The research project “Fish & Chips (Towards DNA chip technology as a standard analytical tool for the identification of marine organisms in biodiversity and ecosystem research)” (www.fish-and-chips.uni-bremen.de) was funded by the European Commission in the Framework of the 6th Framework Programme (http://ec.europa.eu/research/fp6/index_en.cfm) under the contract no. 505491. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.FAO. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. 2009. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome.
- 2.Ogden R. Fisheries forensics: the use of DNA tools for improving compliance, traceability and enforcement in the fishing industry. Fish Fish. 2008;9:462–472. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kochzius M. Trends in fishery genetics. In: Beamish RJ, Rothschild BJ, editors. The future of fisheries science in North America. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Fish & Fisheries Series 31, Springer; 2009. pp. 453–493. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Teletchea F. Molecular identification methods of fish species: reassessment and possible applications. Rev Fish Biol Fish. 2009;19:265–293. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marko PB, Lee SC, Rice AM, Gramling JM, Fitzhenry TM, et al. Misslabelling of a depleted reef fish. Nature. 2004;430:309–310. doi: 10.1038/430309b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cohen NJ, Deeds JR, Wong ES, Hanner RJ, Yancy HF, et al. Public health response to puffer fish (Tetrodotoxin) poisoning from mislabelled product. J Food Prot. 2009;72:810–817. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-72.4.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fox CJ, Taylor MI, Pereyra R, Villasana MI, Rico C. TaqMan DNA technology confirms likely overestimation of cod (Gadus morhua L.) egg abundance in the Irish Sea: implications for the assessment of the cod stock and mapping of spawning areas using egg-based methods. Mol Ecol. 2005;14:879–884. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Quinteiro J, Sotelo CG, Rehbein H, Pryde SE, Medina I, et al. Use of mtDNA direct polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sequencing and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism methodologies in species identification of canned tuna. J Agric Food Chem. 1998;46:1662–1669. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sotelo CG, Calo-Mata P, Chapela MJ, Pérez-Martín RI, Rehbein H, et al. Identification of flatfish (Pleuronectiforme) species using DNA-based techniques. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:4562–4569. doi: 10.1021/jf010452a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Santaclara FJ, Cabado AG, Vieites JM. Development of a method for genetic identification of four species of anchovies: E. encrasicolus, E. anchoita, E. ringens and E. japonicus. Eur Food Res Technol. 2006;223:609–614. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jérôme M, Martinsohn JT, Ortega D, Carreau P, Verrez-Bagnis V, et al. Towards fish and seafood traceability: anchovy species determination in fish products by molecular markers and support through a public domain database. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:3460–3469. doi: 10.1021/jf703704m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Aoyama J, Mochioka N, Otake T, Ishikawa S, Kawakami Y, et al. Distribution and dispersal of anguillid leptocephali in the western Pacific revealed by molecular analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1999;188:193–200. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rocha-Olivares A, Moser GH, Stannard J. Molecular identification and description of pelagic young of the rockfishes Sebastes constellatus and Sebastes ensifer. Fish Bull. 2000;98:353–363. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Akimoto S, Kinoshita S, Sezaki K, Mitani I, Watabe S. Identification of alfonsino and related fish species belonging to the genus Beryx with mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene and its application on their pelagic eggs. Fishe Sci. 2002;68:1242–1249. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Richardson DE, Vanwye JD, Exum AM, Cowen RK, Crawford DL. High-throughput species identification: from DNA isolation to bioinformatics. Mol Ecol Notes. 2006;7:199–207. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Greig TW, Moore MK, Woodley CM, Quattro JM. Mitochondrial gene sequences useful for species identification of western North Atlantic Ocean sharks. Fish Bull. 2005;103:516–523. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hoelzel AR. Shark fishing in fin soup. Conserv Genet. 2001;2:69–72. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kochzius M, Söller R, Khalaf MA, Blohm D. Molecular phylogeny of the lionfish genera Dendrochirus and Pterois (Scorpaenidae, Pteroinae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phyl Evol. 2003;28:396–403. doi: 10.1016/s1055-7903(02)00444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lemer S, Aurelle D, Vigliola L, Durand J-D, Borsa P. Cytochrome b barcoding, molecular systematic and geographic differentiation in rabbitfishes (Siganidae). Comptes Rendus Biologies. 2007;330:86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2006.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Timm J, Figiel M, Kochzius M. Contrasting patterns in species boundaries and evolution of anemonefishes (Amphiprioninae, Pomacentridae) in the centre of marine biodiversity. Mol Phyl Evol. 2008;49:268–276. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.04.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sevilla RG, Diez A, Norén M, Mouchel O, Jérôme M, et al. Primers and polymerase chain reaction conditions for DNA barcoding teleost fish based on the mitochondrial cytochrome b and nuclear rhodopsin genes. Mol Ecol Notes. 2007;7:730–734. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc R Soc Biol Sci Ser B. 2003;270:313–321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR. Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc R Soc Biol Sci Ser B. 2003;270(Suppl 1):S96–99. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1994;3:294–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert PDN. DNA barcoding Australia's fish species. Philos Trans Royal Soc B. 2005;360:1847–1857. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ward RD, Hanner R, Hebert PDN. The campain to DNA barcode all fishes, FISH-BOL. J Fish Biol. 2009;74:329–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.02080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Espiñeira M, Gonzáles-Lavín N, Vieites JM, Santaclara F. Development of a method for the genetic identification of flatfish species on the basis of mitochondrial DNA sequences. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:8954–8961. doi: 10.1021/jf800570r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith PJ, McVeagh SM, Steinke D. DNA barcoding for the identification of smoked fish products. J Fish Biol. 2008;72:464–471. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wong EH-K, Hanner RH. DNA barcoding detects market substitution in North American seafood. Food Res Int. 2008;41:828–837. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yancy HF, Zemlak TS, Mason JA, Washington JD, Tenge BJ, et al. Potential use of DNA barcodes in regulatory science: applications of the Regulatory Fish Encyclopedia. J Food Prot. 2008;71:210–217. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-71.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ward RD, Holmes BH, White WT, Last PR. DNA barcoding Australasian chondrichthyans: results and potential uses in conservation. Mar Freshw Res. 2008;59:57–71. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moura T, Silva MC, Figueiredo I, Neves A, Muñoz PD, et al. Molecular barcoding of north-east Atlantic deep-water sharks: species identification and application to fisheries management and conservation. Mar Freshw Res. 2008;59:214–223. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Holmes BH, Steinke D, Ward RD. Identification of shark and ray fins using DNA barcoding. Fish Res. 2009;95:280–288. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Smith PJ, Steinke D, McVeagh SM, Stewards AL, Struthers CD, et al. Molecular analysis of Shuthern Ocean skates (Bathyraja) reveals a new species of Antarctic skate. J Fish Biol. 2008b;73:1170–1182. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ward RD, Holmes BH, Yearsley GK. DNA barcoding reveals a likely second species of Asian sea bass (barramundi) (Lates calcarifer). J Fish Biol. 2008a;72:458–463. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Steinke D, Zemlak TS, Hebert PDN. Barcoding Nemo: DNA-based identification for the marine ornamental fish trade. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zemlak TS, Ward RD, Connell AD, Holmes BH, Hebert PDN. DNA barcoding reveals overlooked marine fishes. Mol Ecol Resources. 2009;9:237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Astarloa de JMD, Mabragaña E, Hanner R, Figueroa DE. Morphological and molecular evidence for a new species of longnose skate (Rajiformes: Rajidae: Dipturus) from Argentinean waters based on DNA barcoding. Zootaxa. 2008;1921:35–46. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Smith LM, Sanders JZ, Kaiser RJ, Hughes P, Dodd C, et al. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986;321:674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Prober JM, Trainor GL, Dam RJ, Hobbs FW, Robertson CW, et al. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987;238:336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hutchison CA., III DNA sequencing: bench to bedside and beyond. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:6227–6237. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kochzius M, Nölte N, Weber H, Silkenbeumer N, Hjörleifsdottir S, et al. DNA microarrays for identifying fishes. Mar Biotechnol. 2008;10:207–217. doi: 10.1007/s10126-007-9068-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Teletchea F, Bernillon J, Duffraisse M, Laudet V, Hänni C. Molecular identification of vertebrate species by oligonucleotide microarray in food and forensic samples. J Appl Ecol. 2008;45:967–975. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yoon HK, Kim G-E, Jeong D, Jung JW, Chung IH, et al. Development of salmon identification DNA chip based on mitochondrial COIII-ND3-ND4L variations. Biochip Journal. 2008;2:287–295. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yoon HK, Jeong D, Chung IH, Jung JW, Oh MJ, et al. Rapid species identification of elasmobranch fish (skates and rays) using oligonucleotide microarray. Biochip Journal. 2009;3:87–96. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Meyer CP, Paulay G. DNA barcoding: error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biology. 2005;3:e422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Thompson JG, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignments through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary analysis and sequence alignment. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 2004;5:150–163. doi: 10.1093/bib/5.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985;39:783–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nölte M. Optimization of oligonucleotide sets for DNA microarrays. 2002. Ph.D. thesis, University of Bremen, Germany.
- 52.SantaLucia J. A unified view of polymer, dumbbell, and oligonucleotide DNA nearest-neighbor thermodynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:1460–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hofacker IL, Fontana W, Stadler PF, Bonhoeffer LS, Tacker M, et al. Fast folding and comparison of RNA secondary structures (The Vienna RNA package). Monatshefte für Chemie (Chemical Monthly) 1994;125:167–188. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ducrée J, Gruhler H, Hey N, Müller M, Békési S, et al. TOPSPOT - a new method for the fabrication of microarrays. 2000. pp. 317–322. Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS 2000), 23–27 January 2000;
- 55.Bensasson D, Zhang D-X, Hartl DL, Hewitt GM. Mitochondrial pseudogenes: evolution's misplaced witness. Trends Ecol Evol. 2001;16:314–321. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(01)02151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Peytavi R, Tang L-Y, Raymond FR, Boissinot K, Bissonnette L, et al. Correlation between microarray DNA hybridization efficiency and the position of short capture probe on the target nucleic acid. Biotechniques. 2005;39:89–96. doi: 10.2144/05391RR01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang L, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B. Position of the fluorescent label is a crucial factor determining signal intensity in microarray hybridisations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e166. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Meier R, Zhang G, Ali F. The use of mean instead of smallest interspecific distances exaggerates the size of the “barcoding gap” and leads to misidentification. Syst Biol. 2008;57:809–813. doi: 10.1080/10635150802406343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ward RD. DNA barcode divergence among species and genera of birds and fishes. Mol Ecol Resources. 2009;9:1077–1085. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN. BOLD: the barcode of life data system ( www.barcodinglife.org). Mol Ecol Notes. 2007;7:355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.McClure MR, McEachran JD. Hybridization between Prionotus alatus and P. paralatus in the Northern Gulf of Mexico (Pisces: Triglidae). Copeia. 1992;1992:1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kijewska A, Burzyński A, Wenne R. Molecular identification of European flounder (Platichthys flesus) and its hybrids with European plaice (Pleuronectes platessa). ICES J Mar Sci. 2009;66:902–906. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hubert N, Hanner R, Holm E, Mandrak NE, Taylor E, et al. Identifying Canadian freshwater fishes through DNA barcodes. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Richly E, Leister D. NUMTs in sequenced eukaryotic genomes. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;21:1081–1084. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Chen W, Seifert KA, Lévesque CA. A high density COX1 barcode oligonucleotide array for identification and detection of species of Penicillium subgenus Penicillium. Mole Ecol Resources. 2009;9:114–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pozhitkov A, Noble PA, Domazet-Lošo T, Nolte AW, Sonnenberg R, et al. Test of rRNA hybridization to microarrays suggest that hybridization characteristics of oligonucleotide probes for species discrimination cannot be predicted. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:e66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hajibabaei M, Singer GAC, Clare EL, Hebert PDN. Design and application of DNA arrays and DNA barcodes in biodiversity monitoring. BMC Biol. 2007;5:24. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-5-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Peplies J, Glöckner FO, Amann R. Optimization strategies for DNA microarray-based detection of bacteria with 16S rRNA targeting oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:1397–1407. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.3.1397-1407.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Warsen AE, Krug MK, LaFrentz S, Stanek DR, Loge F, et al. Simultaneous discrimination between 15 fish pathogens by using 16S ribosomal DNA PCR and DNA microarrays. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:4216–4221. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.7.4216-4221.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Korimbocus J, Scaramozzino N, Lacroix B, Crance JM, Garin D, et al. DNA probe array for the simultaneous identification of herpesviruses, enteroviruses, and flaviviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:3779–3787. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.3779-3787.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rønning SB, Rudi K, Berdal KG, Holst-Jensen A. Differentiation of important and closely related cereal plant species (Poaceae) in food by hybridisation to an oligonucleotide array. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53:8874–8880. doi: 10.1021/jf0514569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Tobler NE, Pfunder M, Herzog K, Frey JE, Altwegg M. Rapid detection and species identification of Mycobacterium spp. using real-time PCR and DNA-microarray. J Microbiol Methods. 2006;66:116–124. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fare TL, Coffey EM, Dai H, He YD, Kessler DA, et al. Effects of atmospheric ozone on microarray data quality. Anal Chem. 2003;75:4672–4675. doi: 10.1021/ac034241b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Branham WS, Melvin CD, Han T, Desai VG, Moland CL, et al. Elimination of laboratory ozone leads to a dramatic improvement in the reproducibility of microarray gene expression measurements. BMC Biotechnol. 2007;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Todt S. Untersuchungen zur Hybridisierungseffizienz von Oligonukleotiden in DNA-Mikroarray-Experimenten. 2005. 148 PhD thesis, University of Bremen.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Sequences utilised for the DNA barcoding approach. Abbreviations: 16S: 16S rRNA gene, cyt b: cytochrome b gene, COI: cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene, O: order, C: Clupeiformes, G: Gadiformes, L: Lophiiformes, P: Perciformes, Pl: Pleuronectiformes, S: Scorpaeniformes, Sy: Syngnathiformes, Z: Zeiformes, NA: Northeastern Atlantic, NS: North Sea, B: Baltic, BB: Bay of Biscay, WM: Western Mediterranean, CM: Central Mediterranean, EM: Eastern Mediterranean, and BS: Black Sea. No number in cell = 0.
(0.22 MB DOC)
Oligonucleotide probes for the identification of fish species from European seas. Probe ID: 16S, Cytb, and COI indicate the mitochondrial 16S rRNA, cytochrome b, and cytochrome oxidase subunit I marker genes, respectively; the number following “l” is the length of the oligonucleotide probe and the number after “p” the position in the target sequence alignment. Oligo mfe: minimal free energy of the secondary structure of the oligonucleotide; Dimer mfe: minimal free energy of the dimer of two identical oligonucleotide molecules. Values for mfe are given in kcal/mol. Mean fluorescence signal intensity as shown in Fig. 6 and its standard deviation (SD) is given in arbitrary units. Please note that some probes have been hybridised with several specimens of the target species.
(0.23 MB DOC)