Abstract
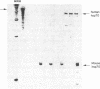
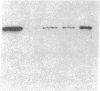
Expression of heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) is stimulated during ischemia, but its proposed cytoprotective function during metabolic stress has remained conjectural. We introduced a human hsp70 gene into mouse 10T1/2 cells and assessed the susceptibility of these cells to injury in response to conditions that mimic ischemia. Transiently transfected cells, in the absence of stress, expressed human hsp70 to levels equal to or greater than those induced by heat shock, as assessed by RNAse protection, immunoblot, and immunohistochemical analyses. By comparison to cells transfected with a control plasmid, cells expressing the human hsp70 transgene were resistant to injury induced by glucose deprivation and inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. These results provide direct evidence for a cytoprotective function of hsp70 during metabolic stress.
Full text
PDF


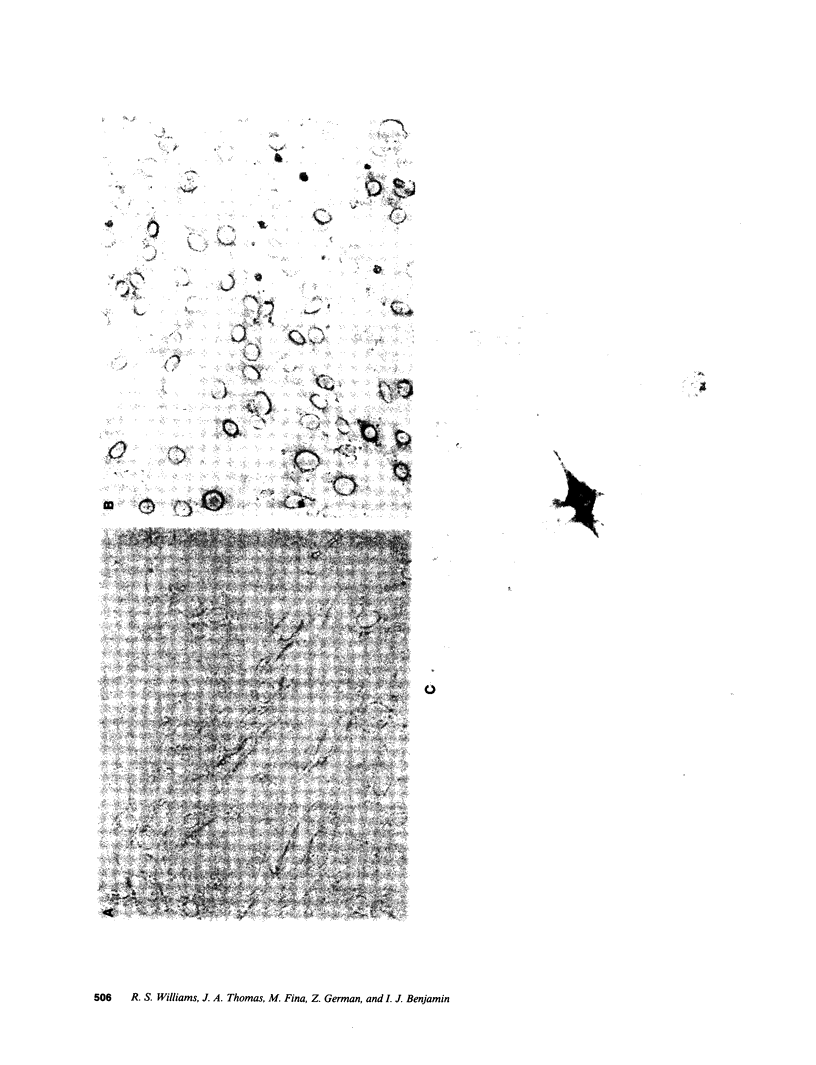

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthan J., Goldberg A. L., Voellmy R. Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3083508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baler R., Welch W. J., Voellmy R. Heat shock gene regulation by nascent polypeptides and denatured proteins: hsp70 as a potential autoregulatory factor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1151–1159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin I. J., Horie S., Greenberg M. L., Alpern R. J., Williams R. S. Induction of stress proteins in cultured myogenic cells. Molecular signals for the activation of heat shock transcription factor during ischemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1685–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI115768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin I. J., Kröger B., Williams R. S. Activation of the heat shock transcription factor by hypoxia in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6263–6267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang H. L., Terlecky S. R., Plant C. P., Dice J. F. A role for a 70-kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2799391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie R. W., Karmazyn M., Kloc M., Mailer K. Heat-shock response is associated with enhanced postischemic ventricular recovery. Circ Res. 1988 Sep;63(3):543–549. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillmann W. H., Mehta H. B., Barrieux A., Guth B. D., Neeley W. E., Ross J., Jr Ischemia of the dog heart induces the appearance of a cardiac mRNA coding for a protein with migration characteristics similar to heat-shock/stress protein 71. Circ Res. 1986 Jul;59(1):110–114. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly T. J., Sievers R. E., Vissern F. L., Welch W. J., Wolfe C. L. Heat shock protein induction in rat hearts. A role for improved myocardial salvage after ischemia and reperfusion? Circulation. 1992 Feb;85(2):769–778. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.2.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J. H., Rossi J. M., Solomon J., Solomon N., Lindquist S. The consequences of expressing hsp70 in Drosophila cells at normal temperatures. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1402–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang P. J., Ostermann J., Shilling J., Neupert W., Craig E. A., Pfanner N. Requirement for hsp70 in the mitochondrial matrix for translocation and folding of precursor proteins. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):137–143. doi: 10.1038/348137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton A. A., Brecher P., Apstein C. S. Rapid expression of heat shock protein in the rabbit after brief cardiac ischemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):139–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI114963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt J., Gunning P., Porreca P., Ng S. Y., Lin C. S., Kedes L. Molecular cloning and characterization of mutant and wild-type human beta-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1961–1969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Li L. G., Liu Y. K., Mak J. Y., Chen L. L., Lee W. M. Thermal response of rat fibroblasts stably transfected with the human 70-kDa heat shock protein-encoding gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Li L., Liu R. Y., Rehman M., Lee W. M. Heat shock protein hsp70 protects cells from thermal stress even after deletion of its ATP-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2036–2040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sotelo J., Wiederrecht G., Okuda A., Parker C. S. The yeast heat shock transcription factor contains a transcriptional activation domain whose activity is repressed under nonshock conditions. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleros D. R., Welch W. J., Fink A. L. Interaction of hsp70 with unfolded proteins: effects of temperature and nucleotides on the kinetics of binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5719–5723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Jennings R. B., Tatum A. H. Pathobiology of acute myocardial ischemia: metabolic, functional and ultrastructural studies. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Jul 20;52(2):72A–81A. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Heat shock is lethal to fibroblasts microinjected with antibodies against hsp70. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):433–436. doi: 10.1126/science.3175665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. D., Liu G. S., Olsson R. A., Downey J. M. Intravenous pretreatment with A1-selective adenosine analogues protects the heart against infarction. Circulation. 1992 Feb;85(2):659–665. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.2.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa-Miwa A., Uchida Y., Nakamura F., Tomaru T., Kido H., Kamijo T., Sugimoto T., Kaji K., Utsuyama M., Kurashima C. Salvage of infarcted myocardium by angiogenic action of basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.1382313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]