Abstract
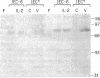
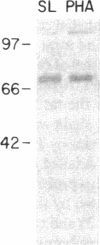
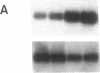
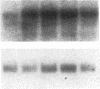
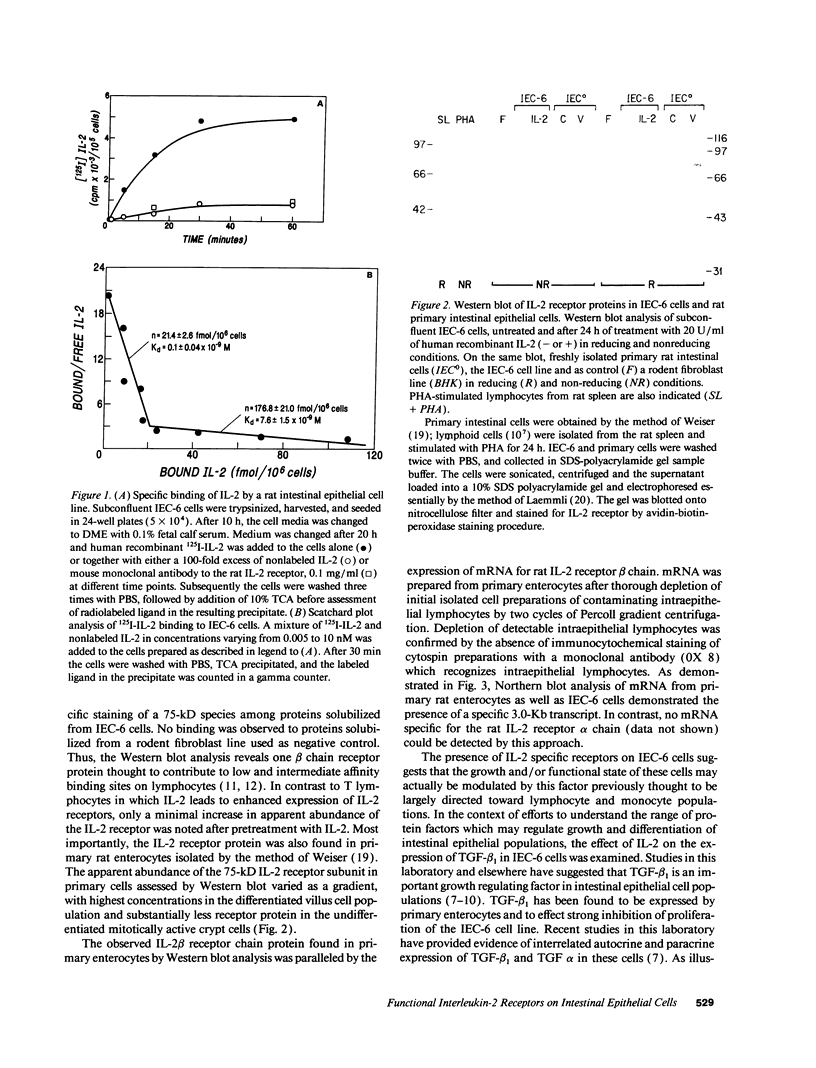
The presence of receptors for the cytokine IL-2 was assessed in the IEC-6 cell line established from normal rat crypt epithelium and primary intestinal epithelial cells. 125I-IL-2 was found to specifically bind to subconfluent IEC-6 cells. Maximal binding was observed within 30 min after addition of the ligand; binding could be inhibited by excess unlabeled IL-2 or addition of antibody to the IL-2 receptor. Both intermediate and low affinity receptors with approximate Kd of 10 and 100 pM, respectively were present. Kinetic analysis were consistent with the results of Western blot analysis using an antisera to the 75-kD IL-2 receptor beta chain. IL-2 receptors appeared to be functional; addition of IL-2 led to modulation of proliferation with initial stimulation at 24 h followed by inhibition at 48 h. This effect could be blocked by addition of antibody to the IL-2 receptor beta chain. IL-2 treatment could be shown to enhance expression (range = 4- to 50-fold stimulation) of TGF-beta, as well as the lectin protein mac-2, in IEC-6 cells. The relevance of observations in the IEC-6 cell line to intestinal mucosa in vivo was supported by the demonstration of a gradient of expression of the IL-2 receptor in primary rat intestinal epithelial cells by Western blot analysis. In addition, mRNA for the IL-2 receptor-beta chain was demonstrated by Northern blot analysis using mRNA from primary rat intestinal epithelial cells depleted of detectable contaminating intraepithelial lymphocytes by two cycles of fractionation on Percoll gradients. Collectively, these observations suggest that the range of cellular targets of the putative lymphokine IL-2 is broader than appreciated, and IL-2 may serve to integrate epithelial and lymphocyte responses in the intestinal mucosa.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnard J. A., Beauchamp R. D., Coffey R. J., Moses H. L. Regulation of intestinal epithelial cell growth by transforming growth factor type beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Musch M. W., Mayer L. Interleukins 1 and 3 stimulate anion secretion in chicken intestine. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jun;98(6):1518–1524. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91084-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherayil B. J., Weiner S. J., Pillai S. The Mac-2 antigen is a galactose-specific lectin that binds IgE. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1959–1972. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen P. K., Letourneau P. C. Interleukin-2 enhances chick and rat sympathetic, but not sensory, neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Apr;25(4):443–452. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks R. L., Malek T. R., Yue B. Y. Expression of a p55 interleukin-2 receptor-like molecule on corneal epithelial cells. Reg Immunol. 1990 Jan-Feb;3(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama S. Y., Podolsky D. K. Differential expression of transforming growth factors alpha and beta in rat intestinal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1768–1773. doi: 10.1172/JCI114080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokowa M., Lynch K., Podolsky D. K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: transforming growth factor beta inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Sharon M., Gnarra J. R. Structure and function of interleukin-2 receptors. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;352:179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Sporn M. Cytokines in context. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):981–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page T. H., Dallman M. J. Molecular cloning of cDNAs for the rat interleukin 2 receptor alpha and beta chain genes: differentially regulated gene activity in response to mitogenic stimulation. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2133–2138. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Wands J., Trelstad R. L., Isselbacher K. J. Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine. Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):248–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringheim G. E., Freimark B. D., Robb R. J. Quantitative characterization of the intrinsic ligand-binding affinity of the interleukin 2 receptor beta chain and its modulation by the alpha chain and a second affinity-modulating element. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991 Jun;10(3):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg I., Cherayil B. J., Isselbacher K. J., Pillai S. Mac-2-binding glycoproteins. Putative ligands for a cytosolic beta-galactoside lectin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18731–18736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Tada H., Sabe H., Honjo T. Biochemical evidence for a third chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22186–22191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirota K., LeDuy L., Yuan S. Y., Jothy S. Interleukin-6 and its receptor are expressed in human intestinal epithelial cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58(4):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02890085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemori S., Ciacci C., Podolsky D. K. Regulation of transforming growth factor expression in rat intestinal epithelial cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2216–2221. doi: 10.1172/JCI115256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takács L., Kovacs E. J., Smith M. R., Young H. A., Durum S. K. Detection of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta gene expression by in situ hybridization. Tissue localization of IL-1 mRNA in the normal C57BL/6 mouse. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3081–3095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber P. G., Gumucio D. L., Wang W. Isolation of intestinal epithelial cells for the study of differential gene expression along the crypt-villus axis. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):G895–G903. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.6.G895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The interleukin-2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2681–2684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. G., Miyamoto T. Radioprotection of the intestinal crypts of mice by recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha. Radiat Res. 1990 Jul;123(1):112–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]