Abstract
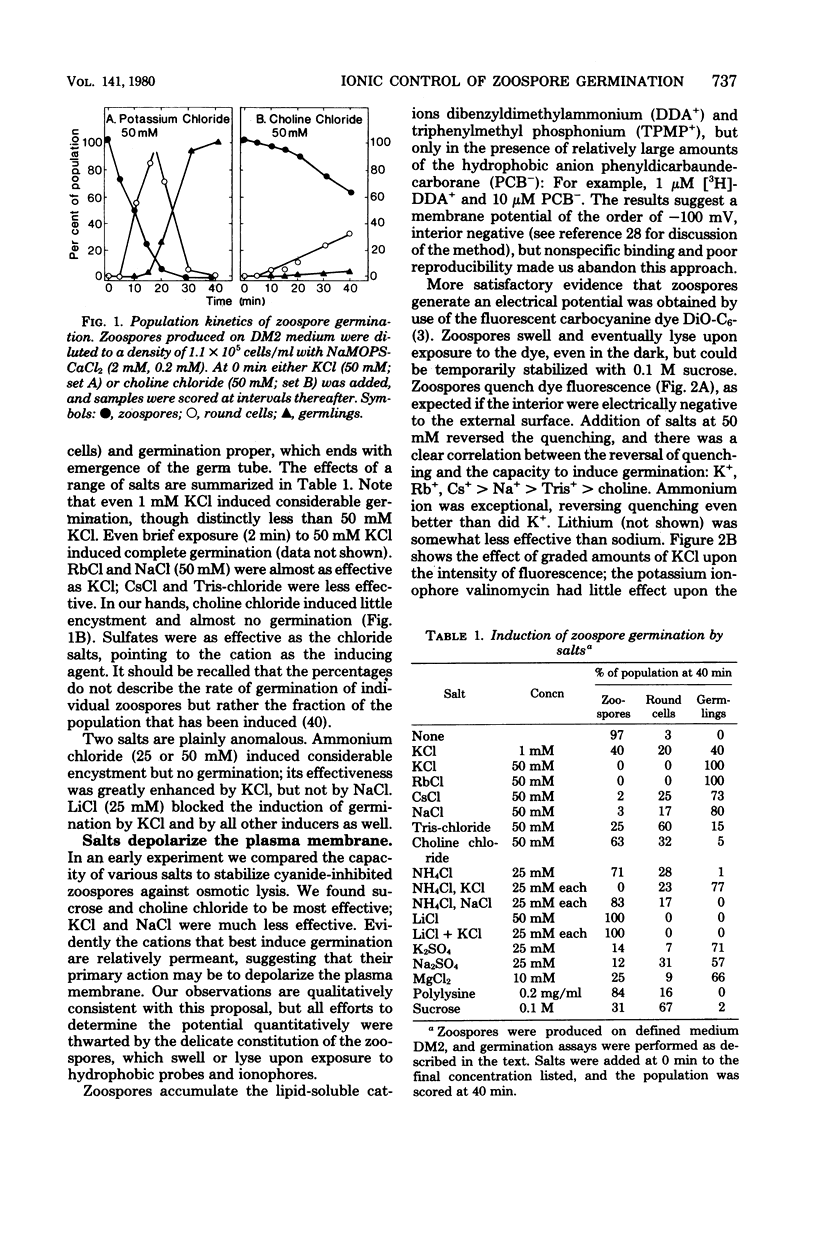
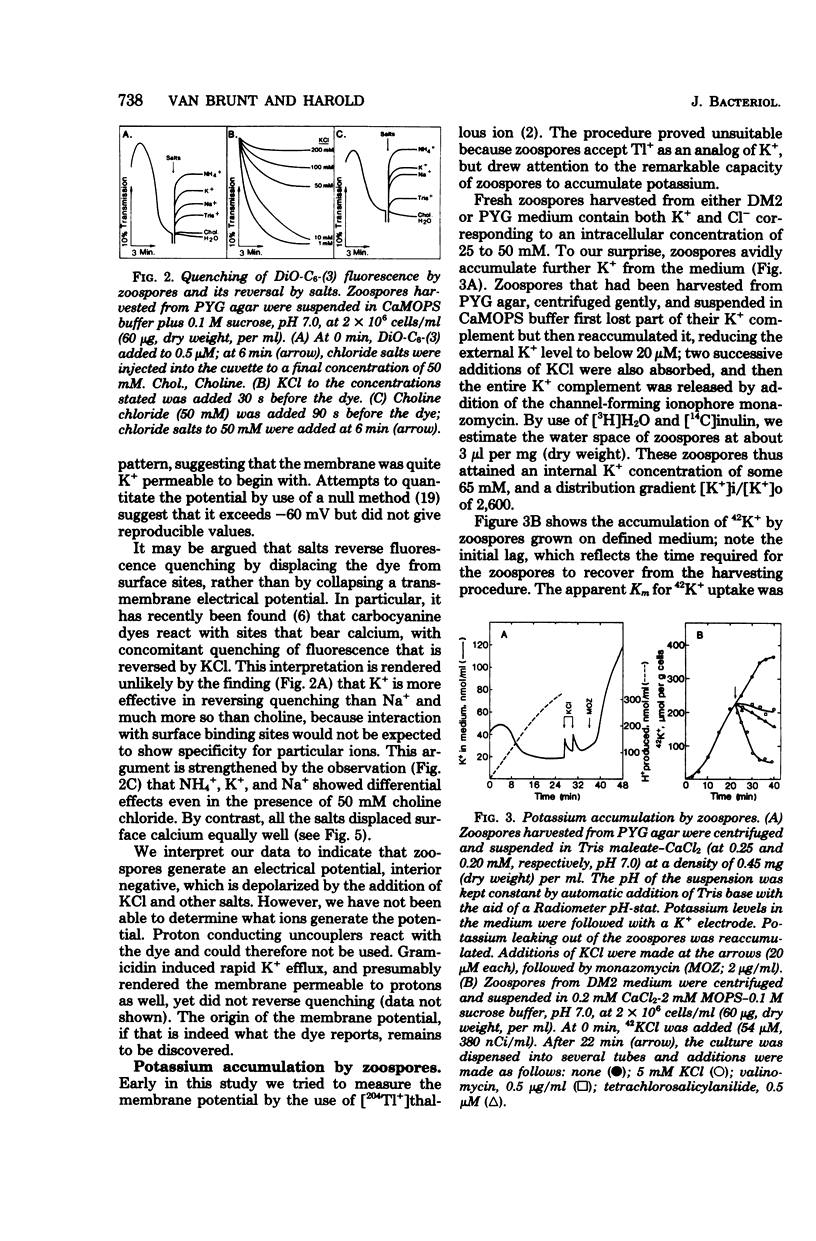
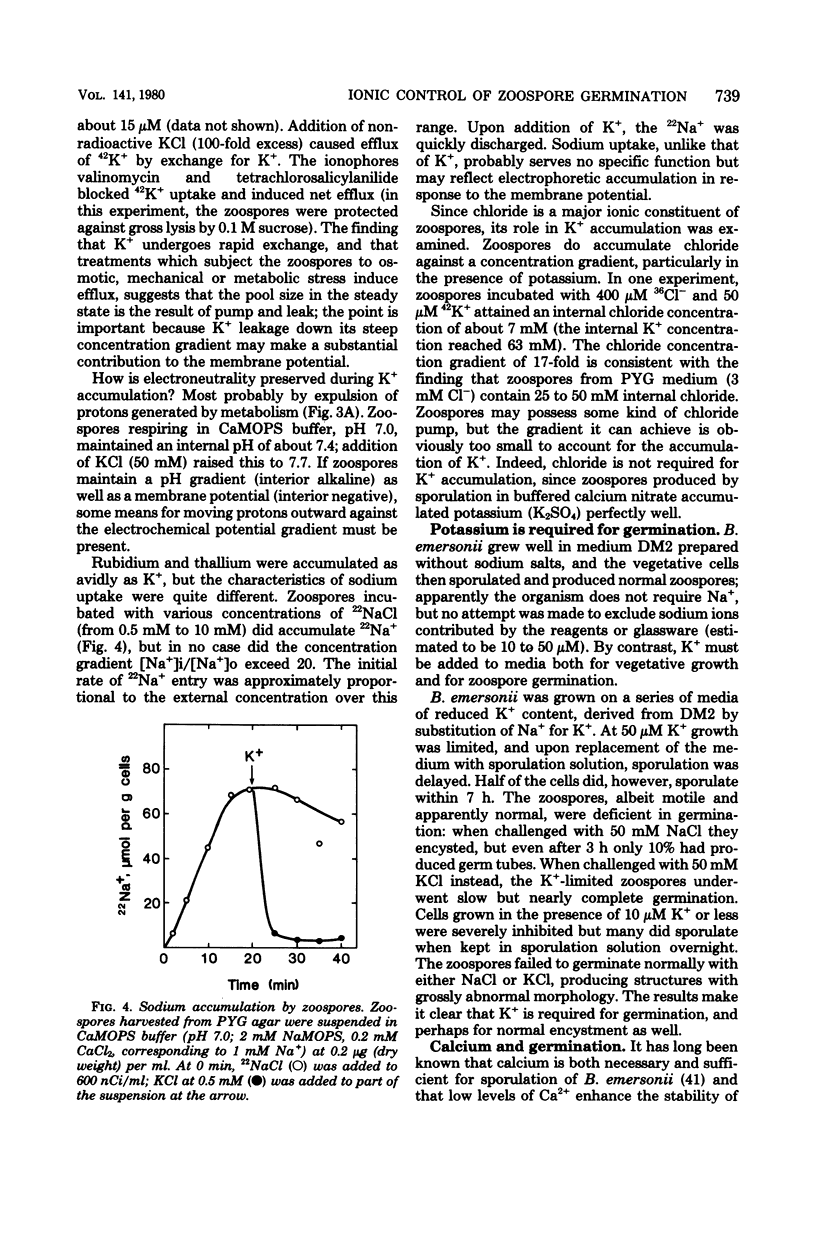
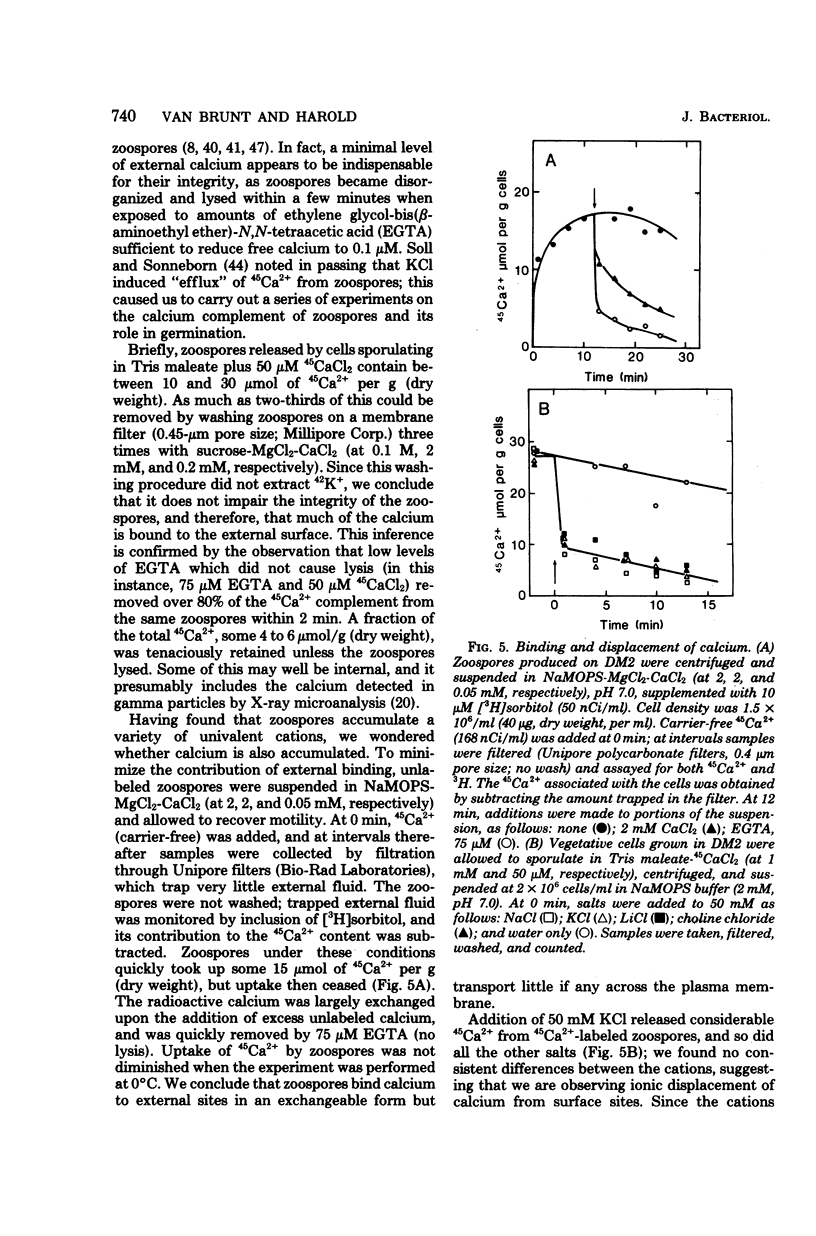
Encystment and germination of Blastocladiella emersonii zoospores involve a rapid and radical transformation of the motile but nongrowing spore into a sessile, growing germling. Certain inorganic ions, notably 50 mM KCl, are efficient inducers of germination. By use of the carbocyanine dye DiO-C6-(3), we found that KCl depolarizes the plasma membrane of zoospores and noted good correlation between depolarization and subsequent germination. Zoospores avidly accumulated K+ ions from the medium, attaining an internal concentration of over 50 mM and a concentration gradient of 2,500. Sodium ions, by contrast, were expelled. Internal K+ was required for normal germination but its function is not known. Zoospores also took up considerable amounts of calcium; most of this was associated with the external surface and appeared to be necessary for maintenance of zoospore integrity. KCl (50 mM) and other salts displaced surface calcium but this was not in itself sufficient to induce germination. The calcium ionophore A23187, in the presence of external calcium, was an effective inducer of germination, suggesting a possible role for cytosolic calcium in triggering the transformation. We propose that the first step in the induction of germination by salts is depolarization of the plasma membrane; subsequent events require the intervention of cytoplasmic signals.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P. Accumulation of thallous ions (Tl+) as a measure of the electrical potential difference across the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2899–2904. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstow W. E., Lovett J. S. Apical vesicles and microtubules in rhizoids of Blastocladiella emersonii: effects of actinomycin D and cycloheximide on development during germination. Protoplasma. 1974;82(1):103–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01276874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E., Godeau F., Schorderet M., Schorderet-Slatkine S. Steroid-induced meiotic division in Xenopus laevis oocytes: surface and calcium. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):593–598. doi: 10.1038/275593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler T., Russell J. T., Martonosi A. Optical probe responses on sarcoplasmic reticulum: oxacarbocyanines as probes of membrane potential. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):579–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. The inhibition of cell functions after viral infection. A proposed general mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Williams J. A. Intracellular divalent cation release in pancreatic acinar cells during stimulus-secretion coupling. I. Use of chlorotetracycline as fluorescent probe. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):371–385. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epel D. The program of fertilization. Sci Am. 1977 Nov;237(5):128–138. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1177-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes S. L., Mennucci L., da Costa Maia J. C. Adenylate cyclase activity and cyclic AMP metabolism during cytodifferentiation of Blastocladiella emersonii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 15;541(2):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Ion currents and physiological functions in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:181–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Laris P. C. Determination of membrane potentials in human and Amphiuma red blood cells by means of fluorescent probe. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):519–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson T. E., Cantino M. E. Calcium is a prominent constituent of the gamma particle in the zoospore of Blastocladiella emersonii as revealed by x-ray microanalysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90309-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F., Nuccitelli R. Electrical controls of development. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:445–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F., Robinson K. R., Nuccitelli R. Local cation entry and self-electrophoresis as an intracellular localization mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;238:372–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb26805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. G. Membrane cation transport and the control of proliferation of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:19–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger H., Trösch W., Müller G. Changes in nuclear electrolytes of Chironomus thummi salivary gland cells during development. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Aug;80(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Hermann T. E. Characterization of ionomycin as a calcium ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5892–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett J. S. Growth and differentiation of the water mold Blastocladiella emersonii: cytodifferentiation and the role of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):345–404. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.345-404.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R., Jaffe L. F. The ionic components of the current pulses generated by developing fucoid eggs. Dev Biol. 1976 Apr;49(2):518–531. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Cyclic AMP and the plasma membrane potential in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7146–7150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway E. B., Gilkey J. C., Jaffe L. F. Free calcium increases explosively in activating medaka eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):623–627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K. R. Electrical currents through full-grown and maturing Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K. R., Jaffe L. F. Polarizing fucoid eggs drive a calcium current through themselves. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1167318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Pettican P. Vasopressin stimulation of mouse 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selitrennikoff C. P., Sonneborn D. R. Alkaline phosphatase of Blastocladiella emersonii: partial purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):249–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.249-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara T., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of protein synthesis, intracellular electrolytes and cataract formation in vitro. Nature. 1977 Dec 1;270(5636):406–411. doi: 10.1038/270406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman P. M., Epstein P. M. Cyclic nucleotide metabolism coupled to cytodifferentiation of Blastocladiella emersonii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman P. M., Huh M. M., Sun L. Protein synthesis during zoospore germination in the aquatic phycomycete Blastocladiella emersonii. Dev Biol. 1974 Sep;40(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Bromberg R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in the water mold. Blastocladiella emersonii. I. Measurement of germination and sequence of subcellular morphological changes. Dev Biol. 1969 Sep;20(3):183–217. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in Blastocladiella emersonii. 3. Structural changes in relation to protein and RNA synthesis. J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):679–699. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in Blastocladiella emersonii. IV. Ion control over cell differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1972 Mar;10(2):315–333. doi: 10.1242/jcs.10.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in Blastocladiella emersonii: cell differentiation without protein synthesis? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in the water mold. Blastocladiella emersonii. II. Influence of cellular and environmental variables on germination. Dev Biol. 1969 Sep;20(3):218–235. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Pall M. L. Control of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels by depolarizing agents in fungi. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):397–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.397-403.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell L. C., Cantino E. C. The induction and early events of germination in the zoospore of Blastocladiella emersonii. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1971;6(6):1–44. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. Optical probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1976 Jun 30;27(4):317–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01869143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenseel M. H., Nuccitelli R., Jaffe L. F. Large electrical currents traverse growing pollen tubes. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):556–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuhrmann P., Ineichen H., Riesen-Willi U., Lezzi M. Change in nuclear potassium electrochemical activity and puffing of potassium-sensitive salivary chromosome regions during Chironomus development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):806–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


