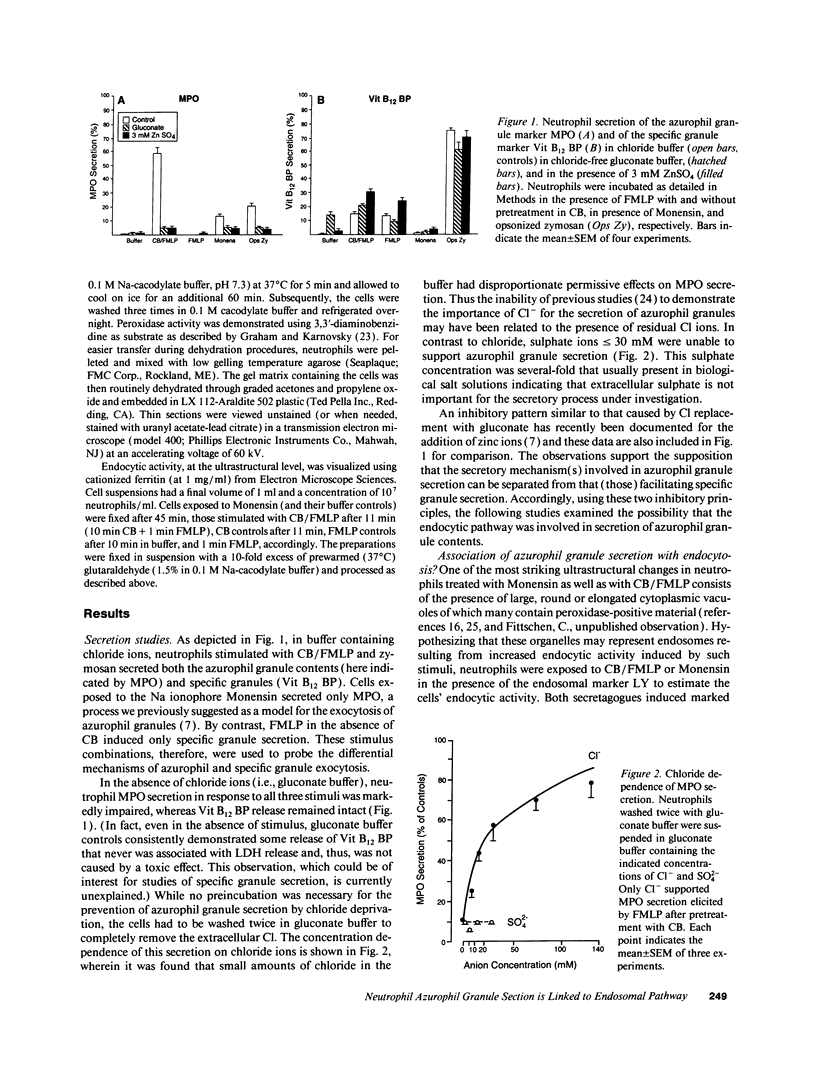
Abstract
Neutrophils contain at least two types of secretory granules. The present work links the secretion of the (lysosomal type) azurophil granules, but not that of specific granules, to endosomal transport mechanisms. (a) Selective stimulation of azurophil granule secretion by the Na-ionophore Monensin, or nonselective stimulation by FMLP after cytochalasin B pretreatment elicited marked pinocytic activity in parallel with azurophil granule release, whereas FMLP alone, selective for specific granules, elicited little fluid pinocytosis. (b) Pinosomes thus formed fused with azurophil granules, suggesting that exocytosis of azurophil granules might occur via endosomal organelles. This hypothesis was tested by determining the effect on the endosomal pathway(s) of two treatments that selectively prevent the release of azurophil granule contents without interfering with specific granule secretion, namely replacement of Cl- with gluconate- or the addition of zinc. Replacement of Cl- was found to impair the pinocytosis process itself, whereas ZnSO4 appeared to prevent the fusion between endosomes and azurophil granules. These data support the concept that the (lysosomal type) azurophil granules, but not the specific granules, are secreted through the endosomal pathway.
Full text
PDF

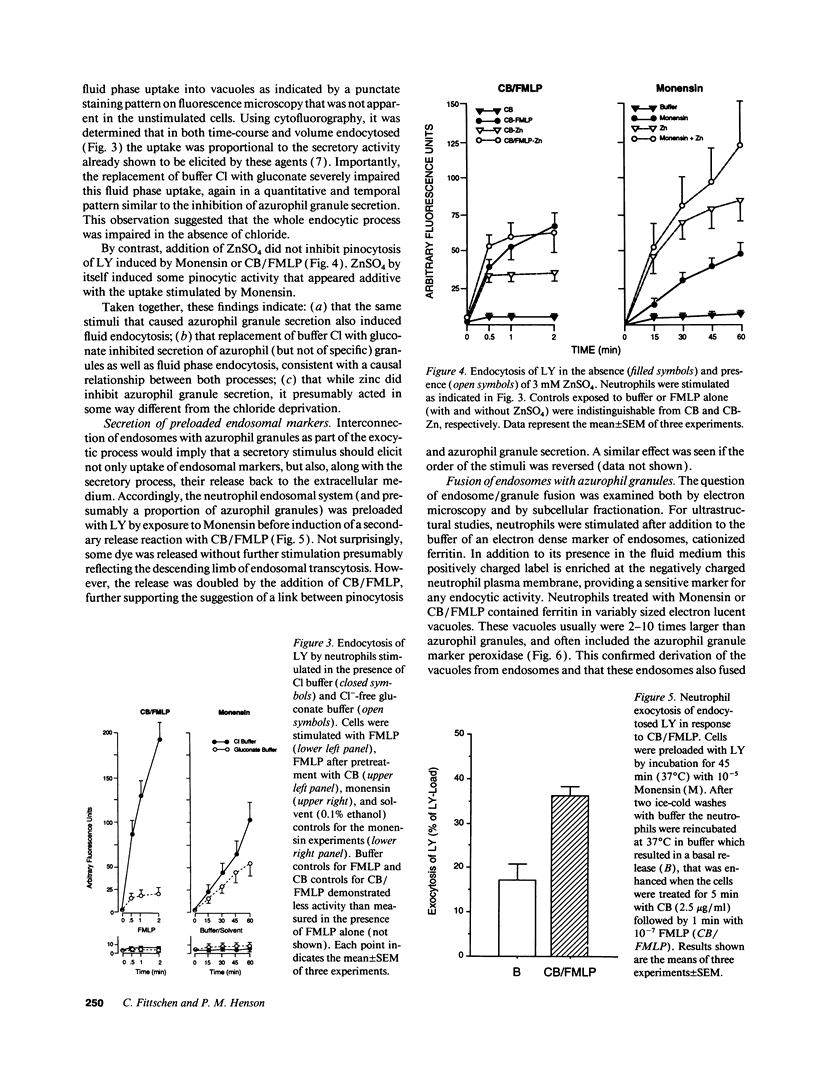
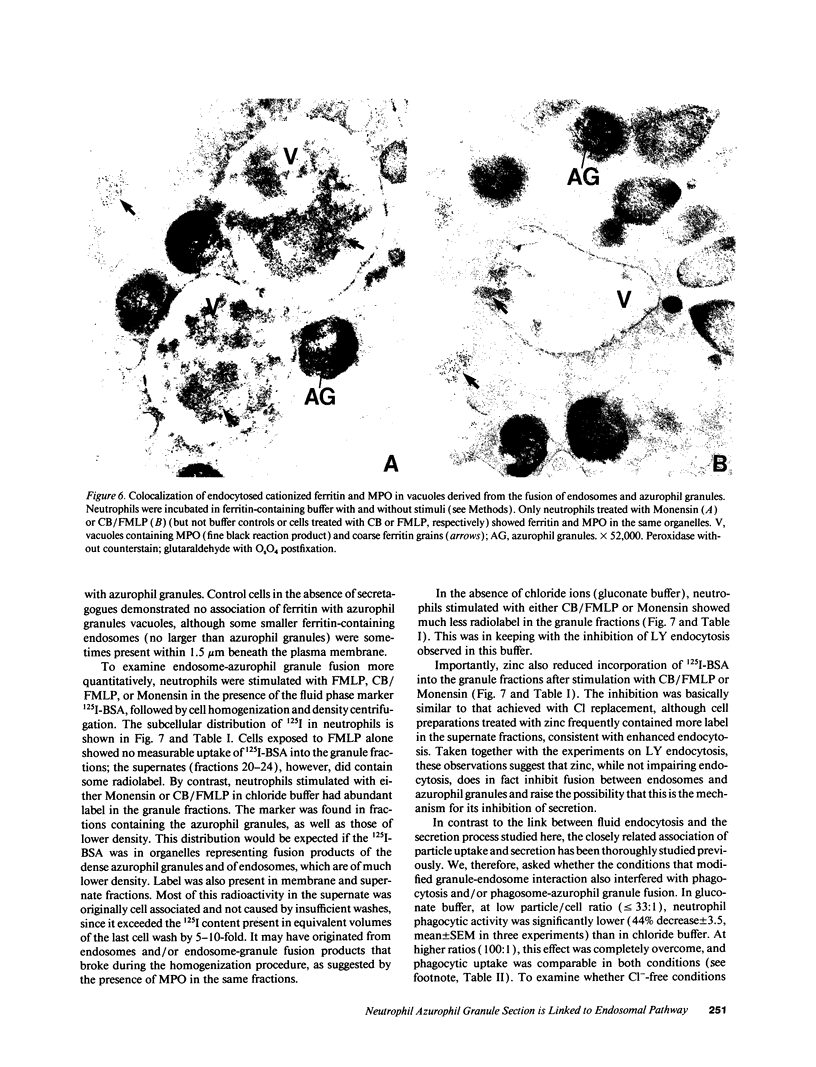
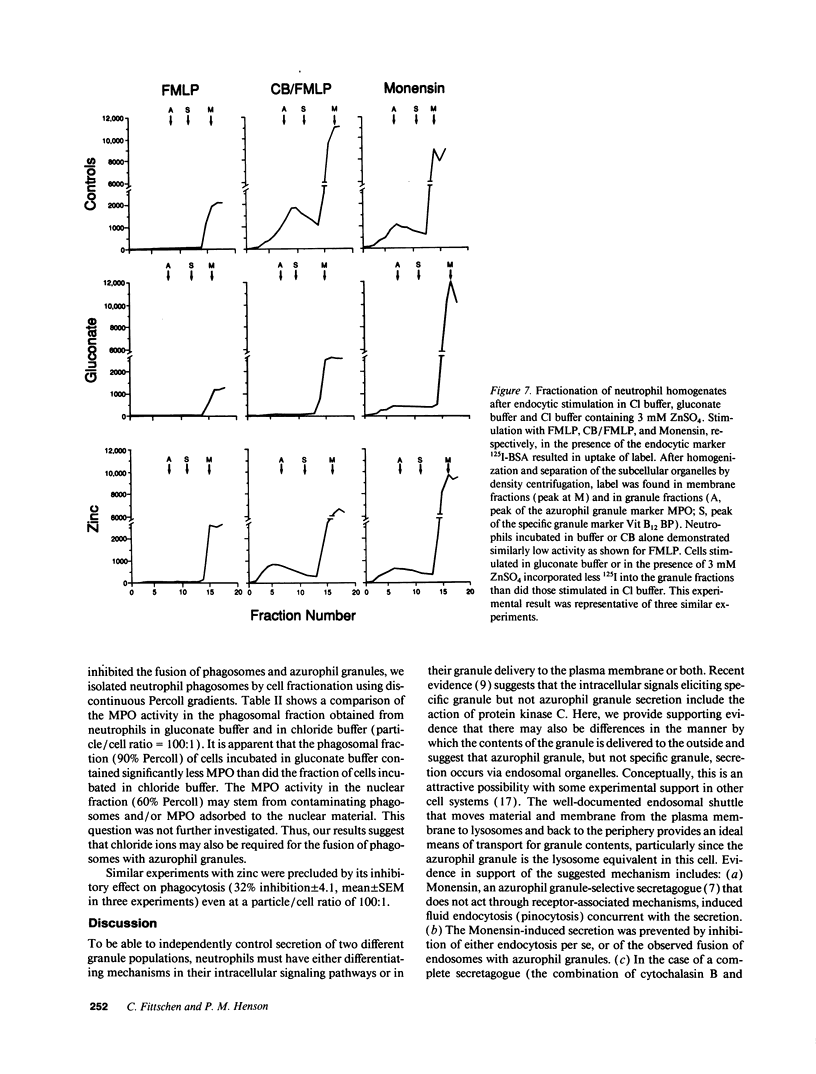
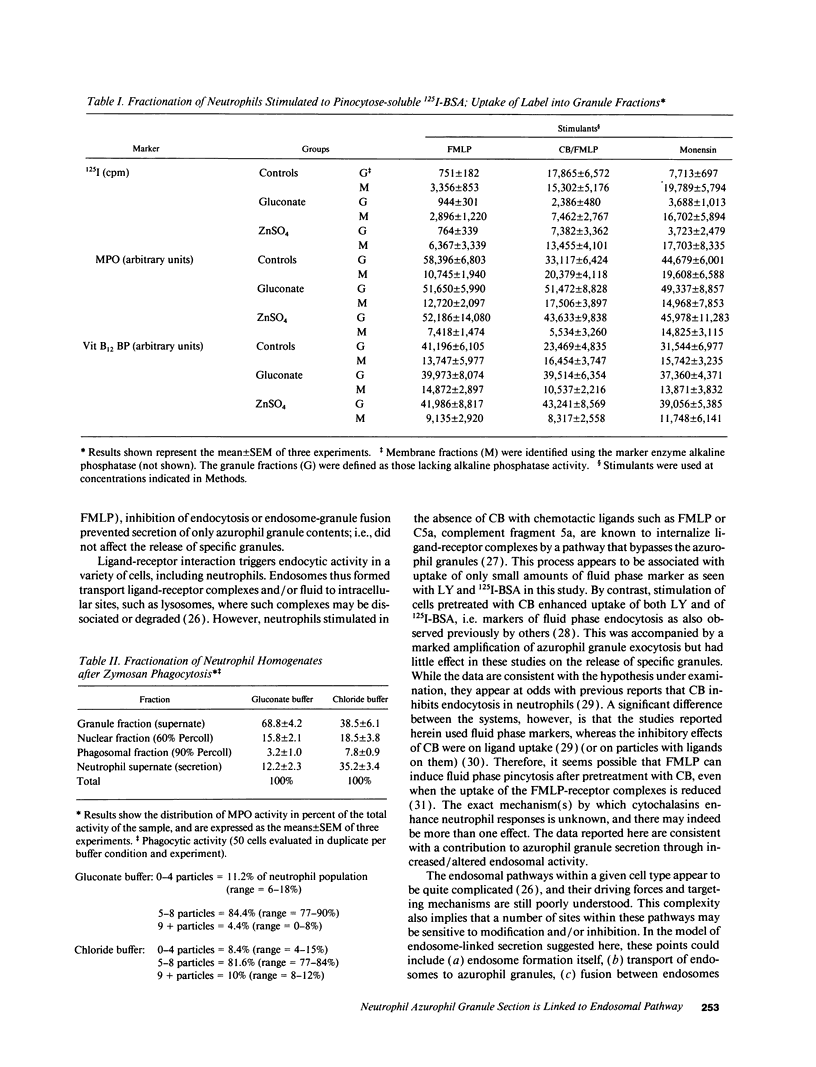
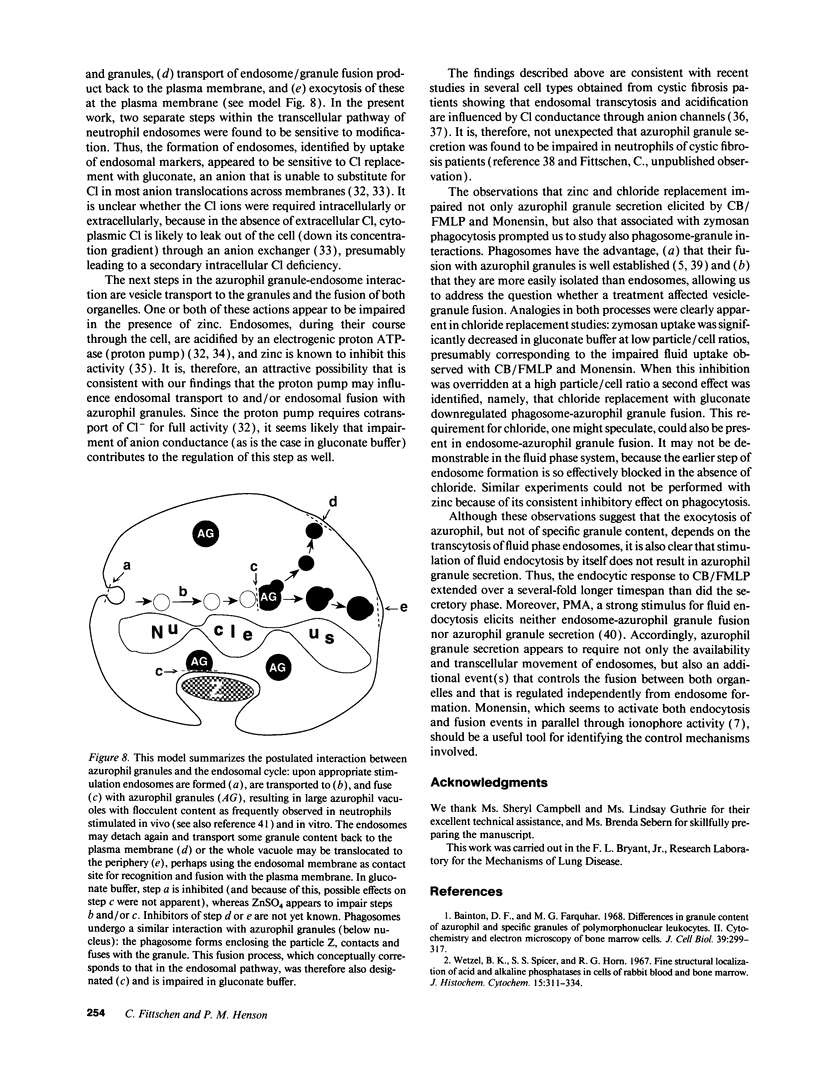

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. II. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy of bone marrow cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):299–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F. Sequential degranulation of the two types of polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules during phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):249–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barasch J., Kiss B., Prince A., Saiman L., Gruenert D., al-Awqati Q. Defective acidification of intracellular organelles in cystic fibrosis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):70–73. doi: 10.1038/352070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentwood B. J., Henson P. M. The sequential release of granule constitutents from human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Low R. B. Endocytosis: a review of mechanisms and plasma membrane dynamics. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2100001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury N. A., Jilling T., Berta G., Sorscher E. J., Bridges R. J., Kirk K. L. Regulation of plasma membrane recycling by CFTR. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):530–532. doi: 10.1126/science.1373908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratton D. L., Dreyer E., Kailey J. M., Fadok V. A., Clay K. L., Henson P. M. The mechanism of internalization of platelet-activating factor in activated human neutrophils. Enhanced transbilayer movement across the plasma membrane. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):514–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C. Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis. Front Biol. 1978;46:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. H., McCabe E., Langweiler M. Characterization of f-Met-Leu-Phe-stimulated fluid pinocytosis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1986 May;7(3):251–262. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fittschen C., Henson P. M. Selective secretion of azurophil granule contents induced by monovalent cation ionophores in human neutrophils: evidence for direct ionophore effects on the granule membrane. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Nov;50(5):517–528. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Schmid S., Mellman I. A possible role for Na+,K+-ATPase in regulating ATP-dependent endosome acidification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEBLAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. RAPID CHARCOAL ASSAY FOR INTRINSIC FACTOR (IF), GASTRIC JUICE UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY, ANTIBODY TO IF, AND SERUM UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Kopaniak M. M., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Modulation of multiple neutrophil functions by preparative methods or trace concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):101–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Mechanisms of exocytosis in phagocytic inflammatory cells. Parke-Davis Award Lecture. Am J Pathol. 1980 Dec;101(3):494–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Enhancement of immunologically induced granule exocytosis from neutrophils by cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):290–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. I. The role of antibody and complement on nonphagocytosable surfaces or phagocytosable particles. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1535–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. II. Mechanisms of release during phagocytosis, and adherence to nonphagocytosable surfaces. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1547–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Zanolari B., Schwartzman N. A., Hong S. R. Intracellular control of human neutrophil secretion. I. C5a-induced stimulus-specific desensitization and the effects of cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman T. C., Bowers B. Hydrolase secretion is a consequence of membrane recycling. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):246–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Painter R. G., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. Membrane-cytoskeleton interactions and the regulation of chemotactic peptide-induced activation of human granulocytes: the effects of dihydrocytochalasin B. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(3):241–253. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis R. K., Dahinden C. A., Chang C. M., Jesaitis A. J. Investigations on the role of Golgi-mediated, ligand-receptor processing in the activation of granulocytes by chemoattractants: differential effects of monensin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 11;927(3):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp T., Schram-Doumont A., van Geffel R., Kram R., Szpirer C. Alteration of the N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced response in cystic fibrosis neutrophils. Pediatr Res. 1986 Jun;20(6):520–526. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198606000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Eisenstat B. A., Hoffstein S. T., Dunham P. B., Weissmann G. Anion channel blockers inhibit lysosomal enzyme secretion from human neutrophils without affecting generation of superoxide anion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2721–2725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Rutherford L. E., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. I. Kinetic analysis of changes in calcium permeability. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4070–4075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Moriyama Y., Takano T. Identification and characterization of a proton pump on lysosomes by fluorescein-isothiocyanate-dextran fluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2758–2762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley R. T., Kinkade J. M., Jr, Akin D. T., Gilbert C. S., Guzman G. S. Monensin disruption of neutrophil granule genesis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):537–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philips M. R., Abramson S. B., Kolasinski S. L., Haines K. A., Weissmann G., Rosenfeld M. G. Low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins in human neutrophil granule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1289–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches D. W., Young S. K., Seccombe J. F., Henson J. E., Clay K. L., Henson P. M. The subcellular distribution of platelet-activating factor in stimulated human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3062–3070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Ratzlaff R., De Weer P. Anion/anion exchange in human neutrophils. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Aug;88(2):195–217. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J. Micromolar concentrations of free calcium provoke secretion of lysozyme from human neutrophils permeabilized with saponin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1859–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C., Rosenthal A. S., Gelb N. A., Kimball H. R. Separation and characterization of human neutrophil granules. Am J Pathol. 1974 Oct;77(1):41–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B. K., Spicer S. S., Horn R. G. Fine structural localization of acid and alkaline phosphatases in cells of rabbit blood and bone marrow. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Jun;15(6):311–334. doi: 10.1177/15.6.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E., Rice W. G., Kinkade J. M., Jr, Merrill A. H., Jr, Arnold R. R., Lambeth J. D. Protein kinase C inhibition by sphingoid long-chain bases: effects on secretion in human neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 15;259(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Bralove D. A., Gallin J. I. The differential mobilization of human neutrophil granules. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate and ionophore A23187. Am J Pathol. 1977 May;87(2):273–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]