Abstract
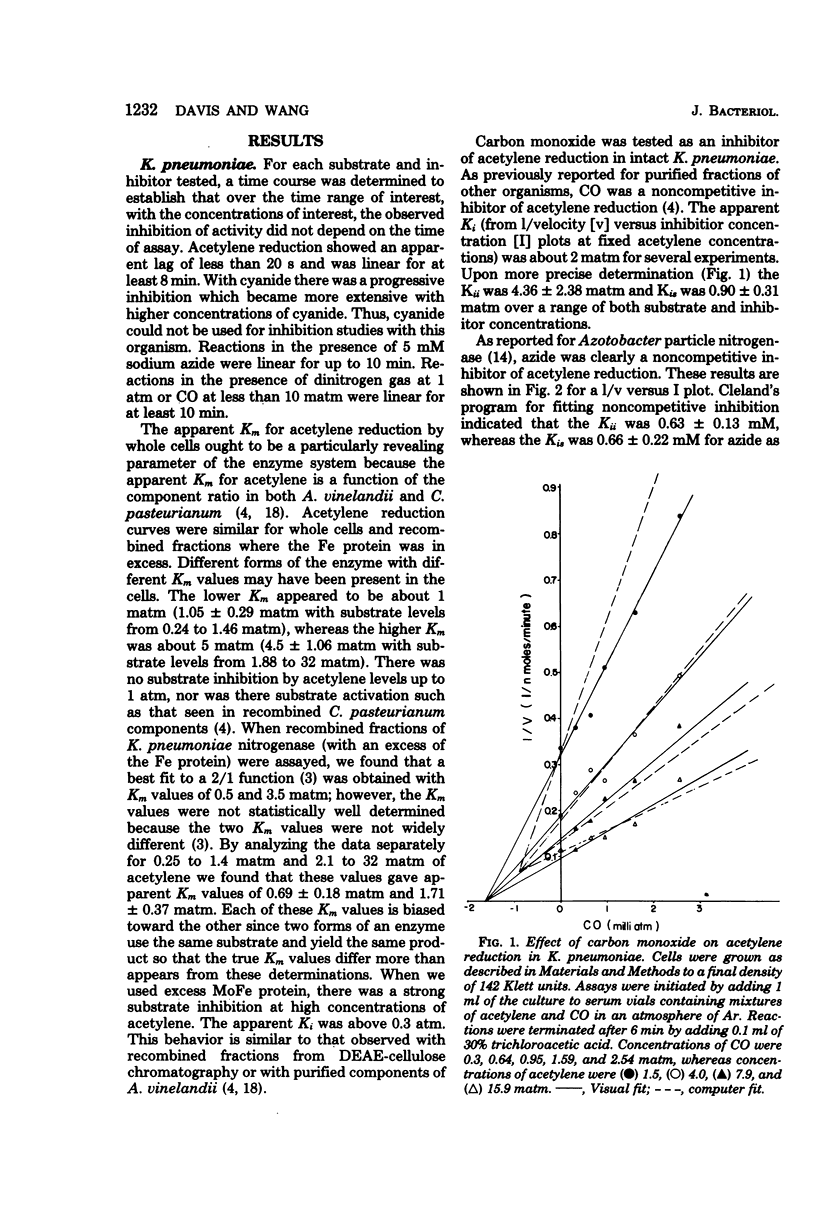
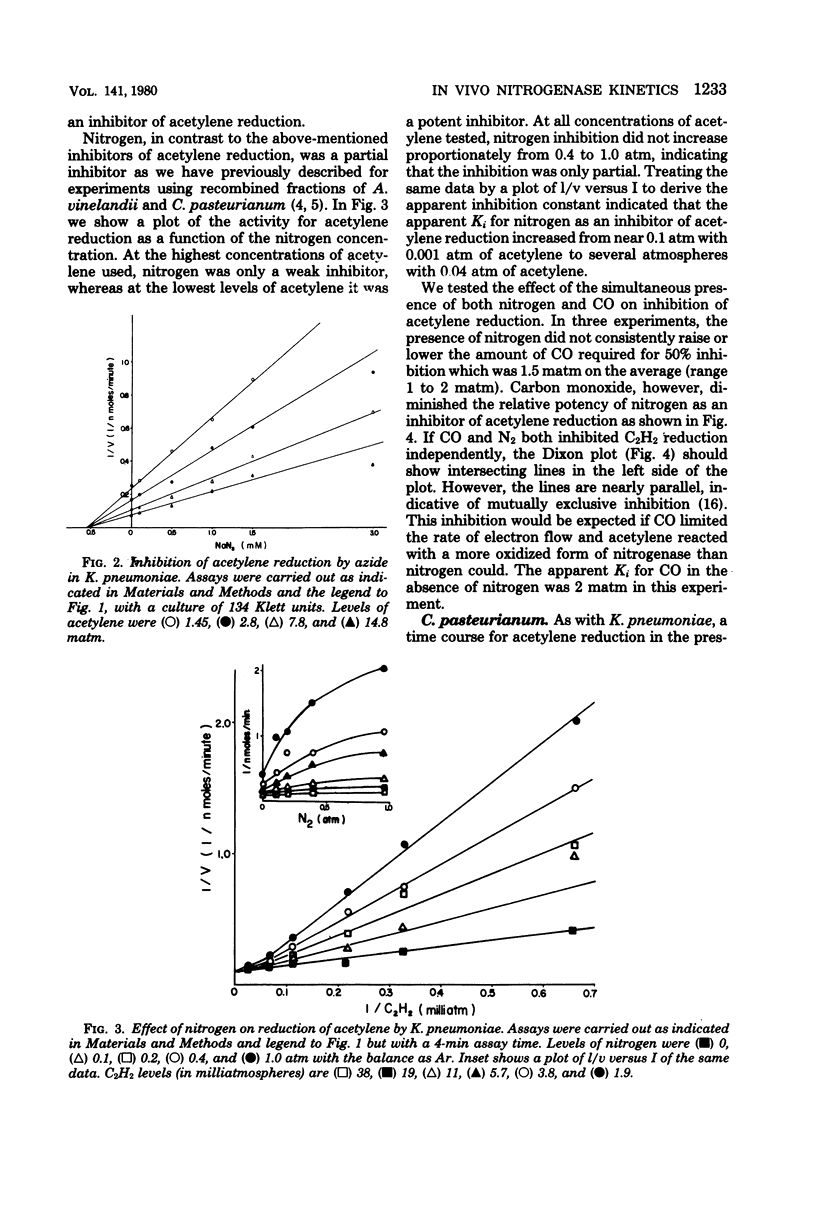
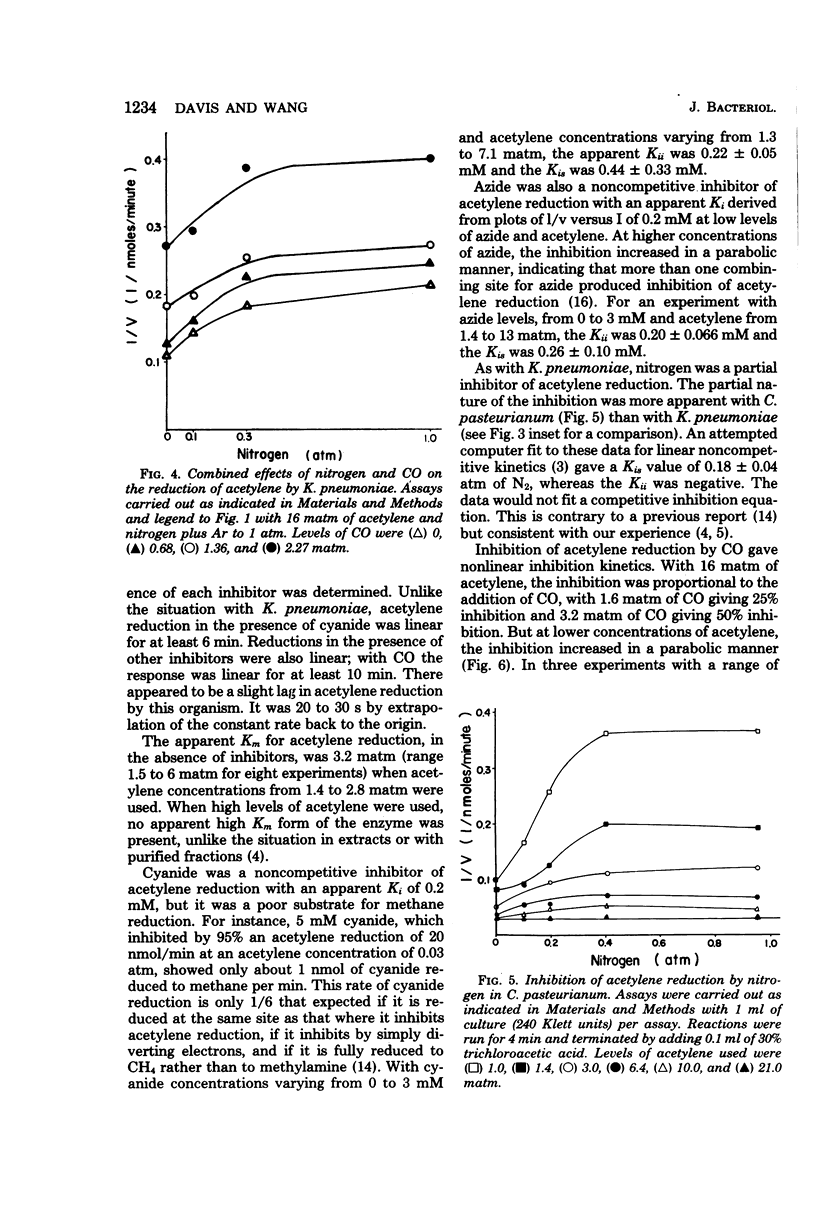
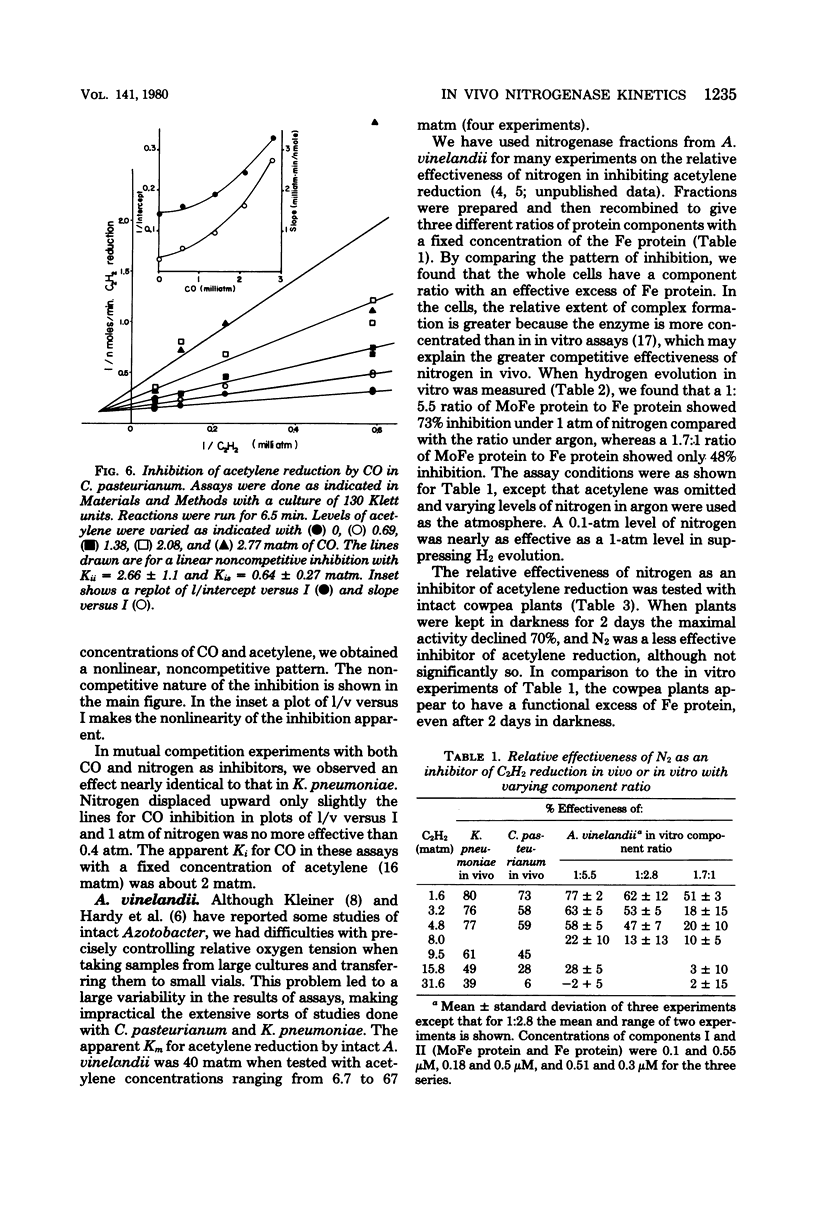
We measured some of the kinetic parameters of nitrogenase to intact systems of Clostridium pasteurianum and Klebsiella pneumoniae to compare them with the kinetics of the enzyme in vitro. We found that the enzyme showed multiple apparent Km values for acetylene reduction in vivo, as it does in vitro. Carbon monoxide was a noncompetitive inhibitor of acetylene reduction; azide was a noncompetitive inhibitor of acetylene reduction, and nitrogen was a partial inhibitor of acetylene reduction. Cyanide was a noncompetitive inhibitor of acetylene reduction in C. pasteurianum but it was a metabolic poison in K. pneumoniae, in addition to being an inhibitor of nitrogenase. The partial nature of nitrogen inhibition was apparent in assays where both nitrogen and CO were present. Nitrogen did not alter the apparent Ki for CO, nor did the presence of CO enhance the competitive effectiveness of nitrogen. By using recombined nitrogenase fractions, we found that the ability of nitrogen to inhibit hydrogen evolution or acetylene reduction varied with the ratio of protein components. The in vivo inhibition of acetylene reduction by dinitrogen was comparable to that obtained with an excess of the Fe protein in vitro. We conclude that there is an effective excess of the Fe protein available under active growth conditions in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brill W. J., Steiner A. L., Shah V. K. Effect of molybdenum starvation and tungsten on the synthesis of nitrogenase components in Klebsiella pneumonia. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):986–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.986-989.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulen W. A., LeComte J. R. Nitrogenase complex and its components. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:456–470. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C., Henzl M. T., Burris R. H., Orme-Johnson W. H. Iron-sulfur clusters in the molybdenum-iron protein component of nitrogenase. Electron paramagnetic resonance of the carbon monoxide inhibited state. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4860–4869. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. VII. Effect of component ratio, ATP and H2 on the distribution of electrons to alternative substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 22;403(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. C., Chen C. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed reductions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):256–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Quantitative relations for the repression of nitrogenase synthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii by ammonia. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00455935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin A., Burris R. H. Inhibitors of nitrogen fixation in extracts from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 15;111(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENGRA R. M., WILSON P. W. Physiology of nitrogen fixation by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jan;75(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.1.21-25.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parejko R. A., Wilson P. W. Kinetic studies on Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2016–2018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Ortiz J. M., Burris R. H. Interactions among substrates and inhibitors of nitrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):537–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.537-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. I. Repression and derepression of the iron-molybdenum and iron proteins of nitrogenase in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):498–511. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. VI. Acetylene reduction assay: Dependence of nitrogen fixation estimates on component ratio and acetylene concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTLAKE D. W., WILSON P. W. Molecular hydrogen and nitrogen fixation by Clostridium pasteurianum. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Dec;5:617–620. doi: 10.1139/m59-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


