Abstract
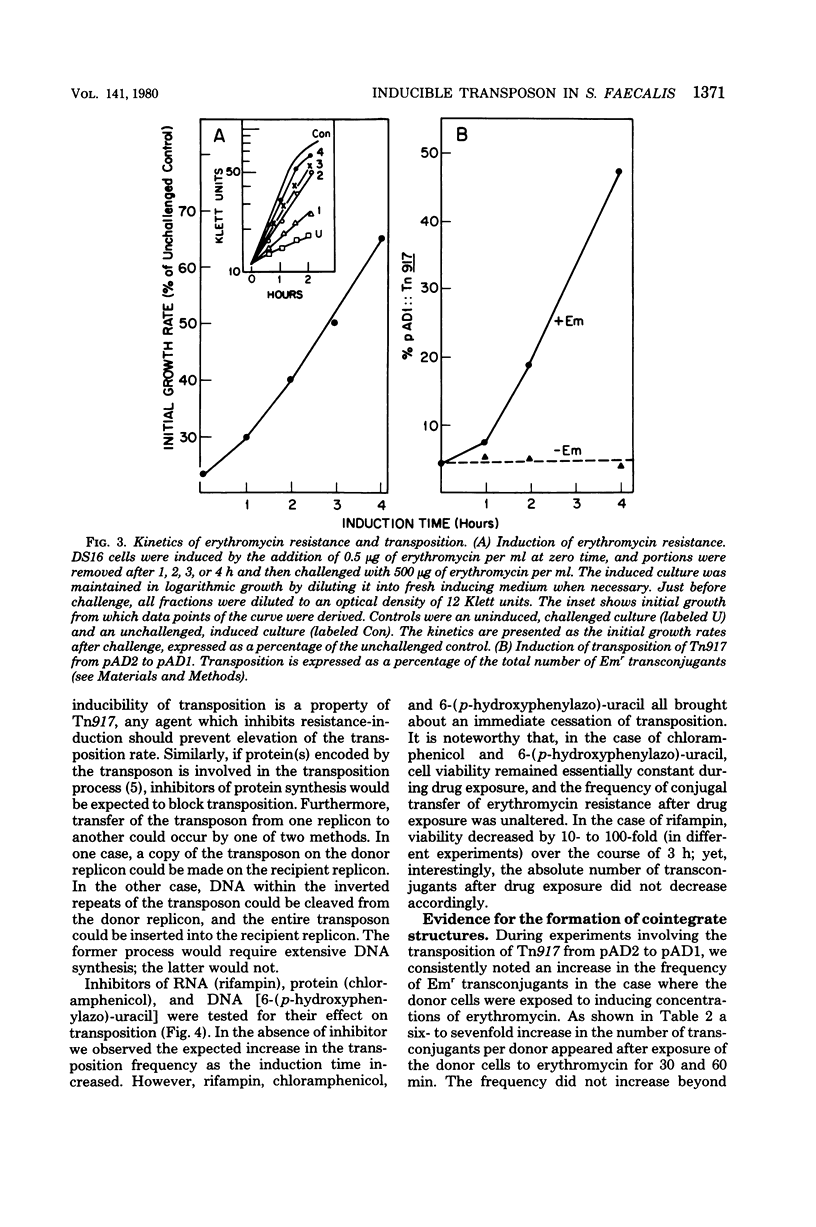
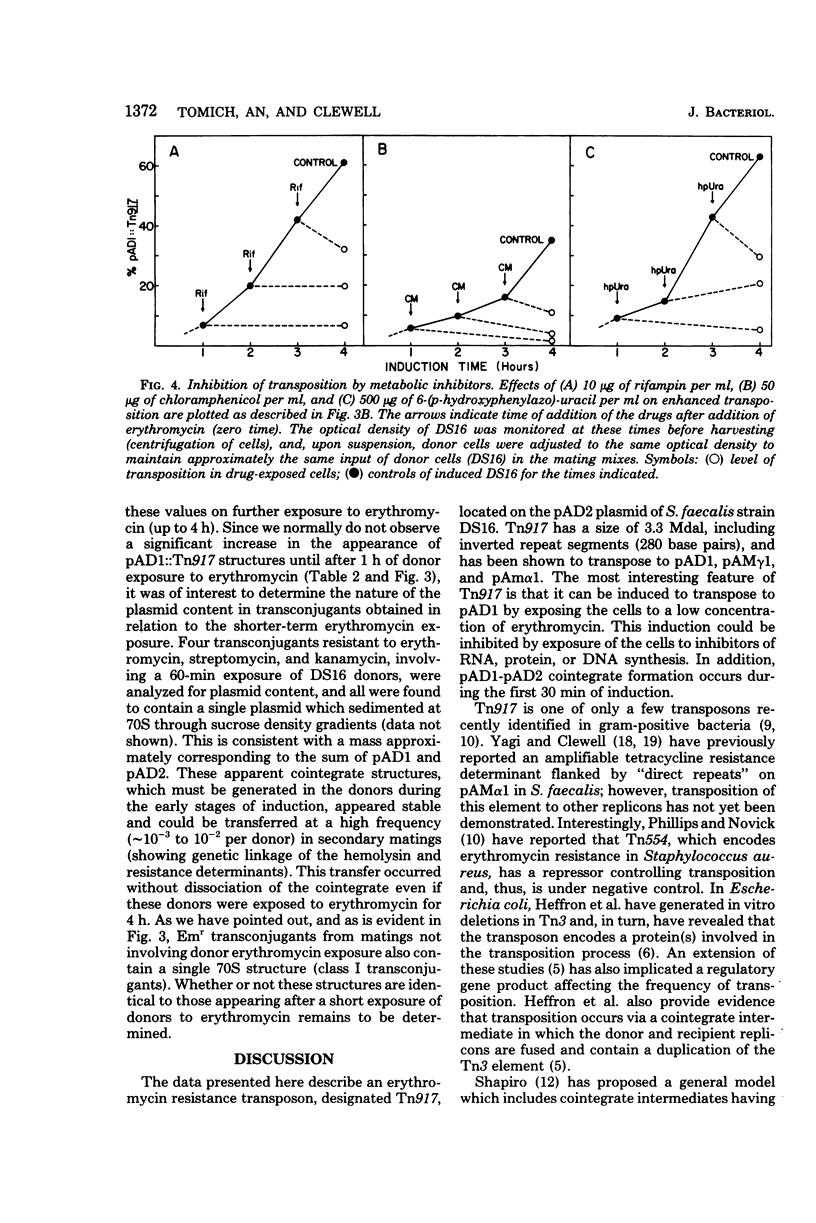
Streptococcus faecalis strain DS16 harbors two plasmids, a conjugative plasmid, pAD1, which encodes hemolysin and bacteriocin activities, and a nonconjugative plasmid, pAD2, encoding resistance to streptomycin, kanamycin, and erythromycin, the latter of which is inducible. The erythromycin resistance determinant is located on a 3.3-megadalton transposable element designated Tn917, which could be transposed to pAD1 as well as to two other plasmids, pAm gamma 1 and pAM alpha 1. When strain DS16 was exposed to low (inducing) concentrations of erythromycin for a few hours, the frequency of Tn917 transposition from pAD2 to pAD1 increased by an order of magnitude. This induction paralleled induction of erythromycin resistance and was prevented by exposing the cells to inhibitors of deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid or protein synthesis. The exposure of strain DS16 to inducing concentrations of erythromycin also enhanced the frequency of erythromycin-resistant transconjugants appearing during mating. Initially, cointegrate molecules, whose molecular weights were approximately the sum of pAD1 and pAD2, accounted for these transconjugants; however, as the induction time increased, pAD1::Tn917 became increasingly prominent.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Clewell D. B. Transmissible toxin (hemolysin) plasmid in Streptococcus faecalis and its mobilization of a noninfectious drug resistance plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.784-790.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Bedinger P., Champoux J. J., Falkow S. Deletions affecting the transposition of an antibiotic resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Hobbs S. J. Conjugal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):360–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.360-372.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Translocatable elements in procaryotes. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Edelman I., Schwesinger M. D., Gruss A. D., Swanson E. C., Pattee P. A. Genetic translocation in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S., Novick R. P. Tn554--a site-specific repressor-controlled transposon in Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):476–478. doi: 10.1038/278476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwesinger M. D. Additive recombination in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):872–902. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.872-902.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Hsu M. T., Otsubo E., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. I. Structure of F-prime factors. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):471–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P. DNA rearrangements in procaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. A transposon (Tn917) in Streptococcus faecalis that exhibits enhanced transposition during induction of drug resistance. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1217–1221. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Damle S. P., Clewell D. B. Plasmid-related transmissibility and multiple drug resistance in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes strain DS16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):828–830. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Clewell D. B. Identification and characterization of a small sequence located at two sites on the amplifiable tetracycline resistance plasmid pAMalpha1 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):400–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.400-406.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Clewell D. B. Plasmid-determined tetracycline resistance in Streptococcus faecalis: tandemly repeated resistance determinants in amplified forms of pAMalpha1 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):583–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]