Abstract
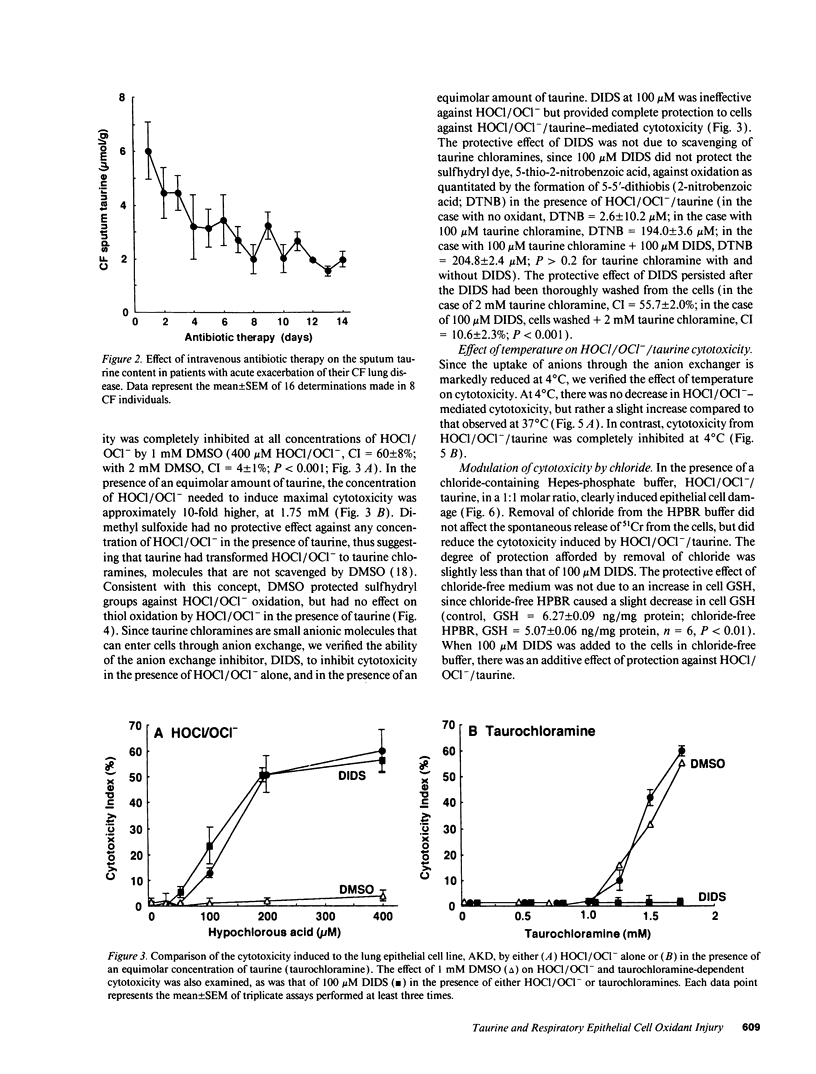
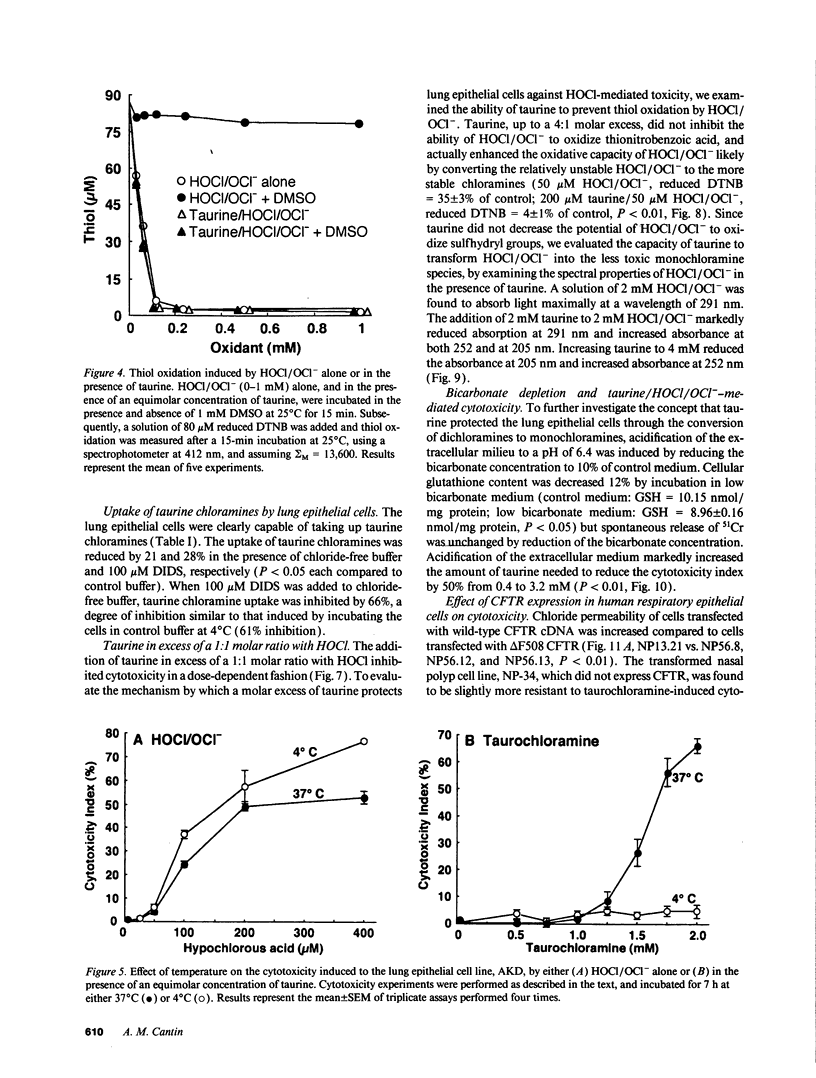
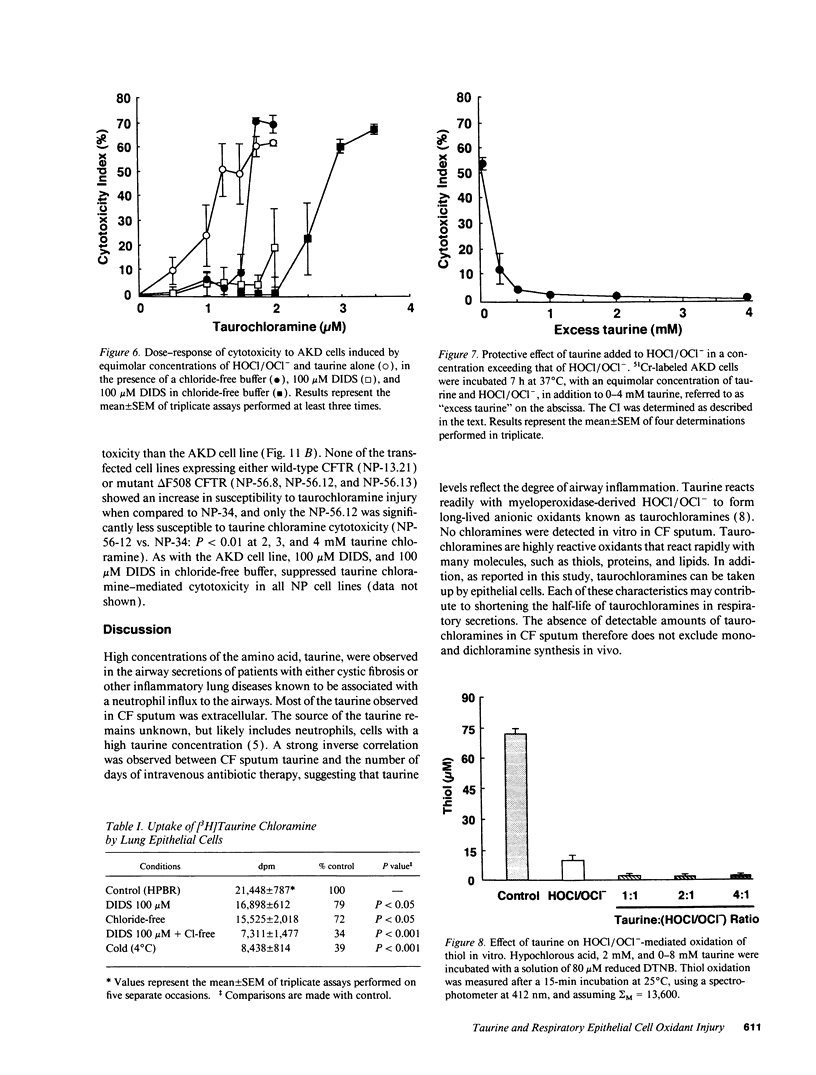
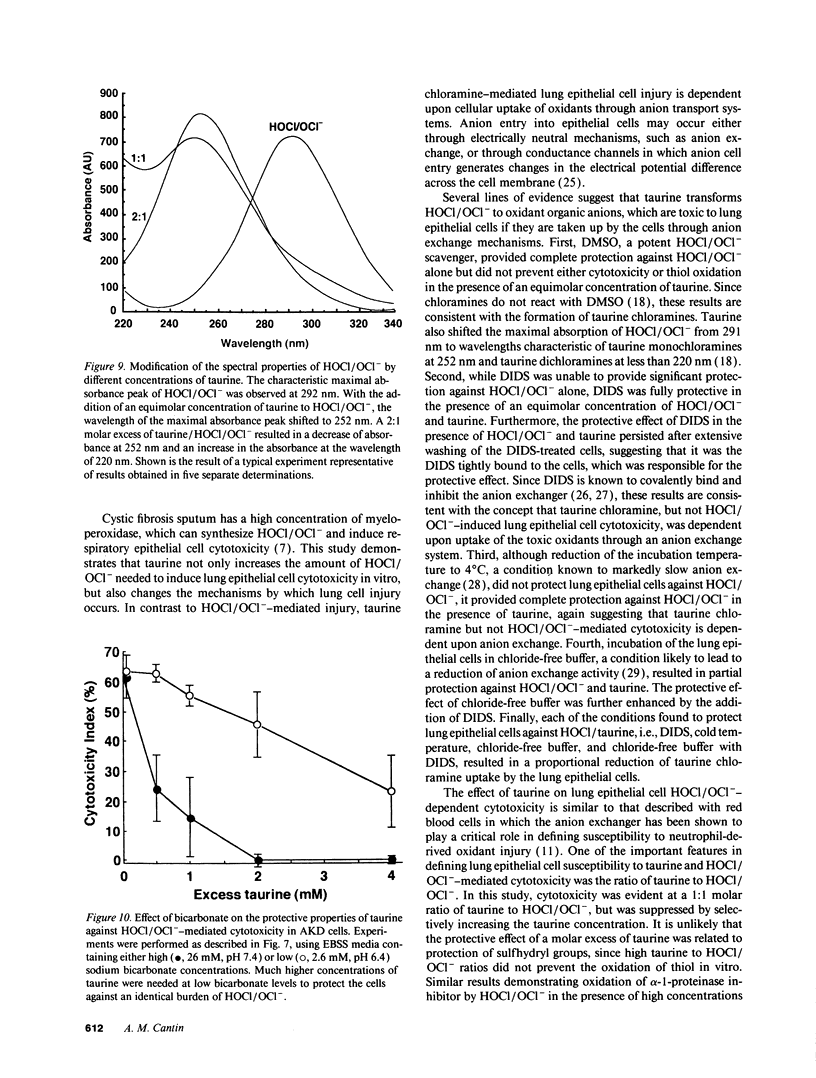
Airway secretions of cystic fibrosis patients were found to contain high concentrations of taurine, which decreased with antibiotic therapy during acute respiratory exacerbations. Taurine, in a 1:1 molar ratio with HOCl/OCl-, caused a 10-fold increase in the amount of HOCl/OCl- needed to induce cytotoxicity to the cat lung epithelial cell line, AKD. Although DMSO protected cells against HOCl/OCl(-)-mediated injury, the presence of an equimolar concentration of taurine with HOCl/OCl- prevented DMSO from protecting cells and sulfhydryl groups against oxidation, suggesting the formation of taurine chloramines. Spectral properties confirmed the formation of monochloramines and dichloramines. Chloride-free buffer, DIDS, and low temperature (4 degrees C) each protected the cells against taurine/HOCl/OCl-, indicating that taurine chloramine uptake through anion transport pathways was required to induce cytotoxicity. A molar excess of taurine inhibited cytotoxicity, to induce cytotoxicity. A molar excess of taurine inhibited cytotoxicity, by decreasing taurine dichloramines and increasing the formation of less toxic taurine monochloramines. We conclude that taurine can protect lung epithelial cells by converting HOCl/OCl- to anionic monochloramines, but that taurine dichloramines can be toxic to respiratory epithelial cells through mechanisms that depend upon epithelial cell anion transport.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruoma O. I., Halliwell B., Hoey B. M., Butler J. The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):251–255. doi: 10.1042/bj2560251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks M. A., Martin W. G., Pailes W. H., Castranova V. Taurine uptake by isolated alveolar macrophages and type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1079–1086. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D., Hans H., Passow H. Identification by site-directed mutagenesis of Lys-558 as the covalent attachment site of H2DIDS in the mouse erythroid band 3 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 3;985(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E., Li C. H., Kartner N., Bridges R. J., Jensen T. J., Ramjeesingh M., Riordan J. R. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. A., Bai C., Jones D. P. Glutathione protection in alveolar type II cells from fetal and neonatal rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L305–L312. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., North S. L., Fells G. A., Hubbard R. C., Crystal R. G. Oxidant-mediated epithelial cell injury in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1665–1673. doi: 10.1172/JCI113005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., North S. L., Hubbard R. C., Crystal R. G. Normal alveolar epithelial lining fluid contains high levels of glutathione. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jul;63(1):152–157. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A., Bégin R., Rola-Pleszczynski M., Boileau R. Heterogeneity of bronchoalveolar lavage cellularity in stage III pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 1983 Mar;83(3):485–486. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A., Woods D. E. Protection by antibiotics against myeloperoxidase-dependent cytotoxicity to lung epithelial cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):38–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI116196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney R. W. Taurine: its biological role and clinical implications. Adv Pediatr. 1985;32:1–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning G. M., Anderson M. P., Amara J. F., Marshall J., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Processing of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is temperature-sensitive. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):761–764. doi: 10.1038/358761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniazeff A. J., Stoner G. D., Terry L., Wagner R. M., Hoppenstand R. D. Characteristics of epithelial cella cultured from feline lung. Lab Invest. 1976 May;34(5):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learn D. B., Fried V. A., Thomas E. L. Taurine and hypotaurine content of human leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Aug;48(2):174–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLusky I. B., Gold R., Corey M., Levison H. Long-term effects of inhaled tobramycin in patients with cystic fibrosis colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;7(1):42–48. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed J. R., Mohammed B. S., Pawluk L. J., Bucci D. M., Baker N. R., Davis W. B. Purification and cytotoxic potential of myeloperoxidase in cystic fibrosis sputum. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Dec;112(6):711–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra N. K., Cheng P. W., Parker J. C., Paradiso A. M., Yankaskas J. R., Boucher R. C., Boat T. F. Sulfate concentrations and transport in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1231–C1237. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Brown S. E., Crandall E. D. Cl-/HCO3- exchange modulates intracellular pH in rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5599–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. W., Banks M. A., Castranova V., Martin W. G. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography technique for taurine quantitation. J Chromatogr. 1988 Nov 11;454:311–316. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)88624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. C., Weber A. M., Morin C. L., Combes J. C., Nusslé D., Mégevand A., Lasalle R. Abnormal biliary lipid composition in cystic fibrosis. Effect of pancreatic enzymes. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 15;297(24):1301–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712152972401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. J., Welsh M. J. cAMP stimulates bicarbonate secretion across normal, but not cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1148–1153. doi: 10.1172/JCI115696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorscher E. J., Fuller C. M., Bridges R. J., Tousson A., Marchase R. B., Brinkley B. R., Frizzell R. A., Benos D. J. Identification of a membrane protein from T84 cells using antibodies made against a DIDS-binding peptide. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):C136–C147. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.1.C136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Beutler E. Oxidized glutathione levels in erythrocytes of glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase-deficient subjects. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):23–24. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92892-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp G., Tümmler B., Gappa M., Albus A., Potel J., Döring G., von der Hardt H. Long-term tobramycin aerosol therapy in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;6(2):91–98. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950060207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Test S. T., Lampert M. B., Ossanna P. J., Thoene J. G., Weiss S. J. Generation of nitrogen-chlorine oxidants by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1172/JCI111544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Jefferson M. M. Preparation and characterization of chloramines. Methods Enzymol. 1986;132:569–585. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)32042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Melton D. F., Jefferson M. M. Evidence for a role of taurine in the in vitro oxidative toxicity of neutrophils toward erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3321–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Jefferson M. M., Grisham M. B. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed incorporation of amines into proteins: role of hypochlorous acid and dichloramines. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6299–6308. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. N. Excessive fecal taurine loss predisposes to taurine deficiency in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Mar-Apr;7(2):214–219. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198803000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Mechanisms of airway epithelial ion transport. Clin Chest Med. 1986 Jun;7(2):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Tallan H. H., Lin Y. Y., Gaull G. E. Taurine: biological update. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:427–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


