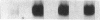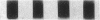Abstract
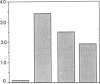
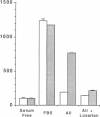
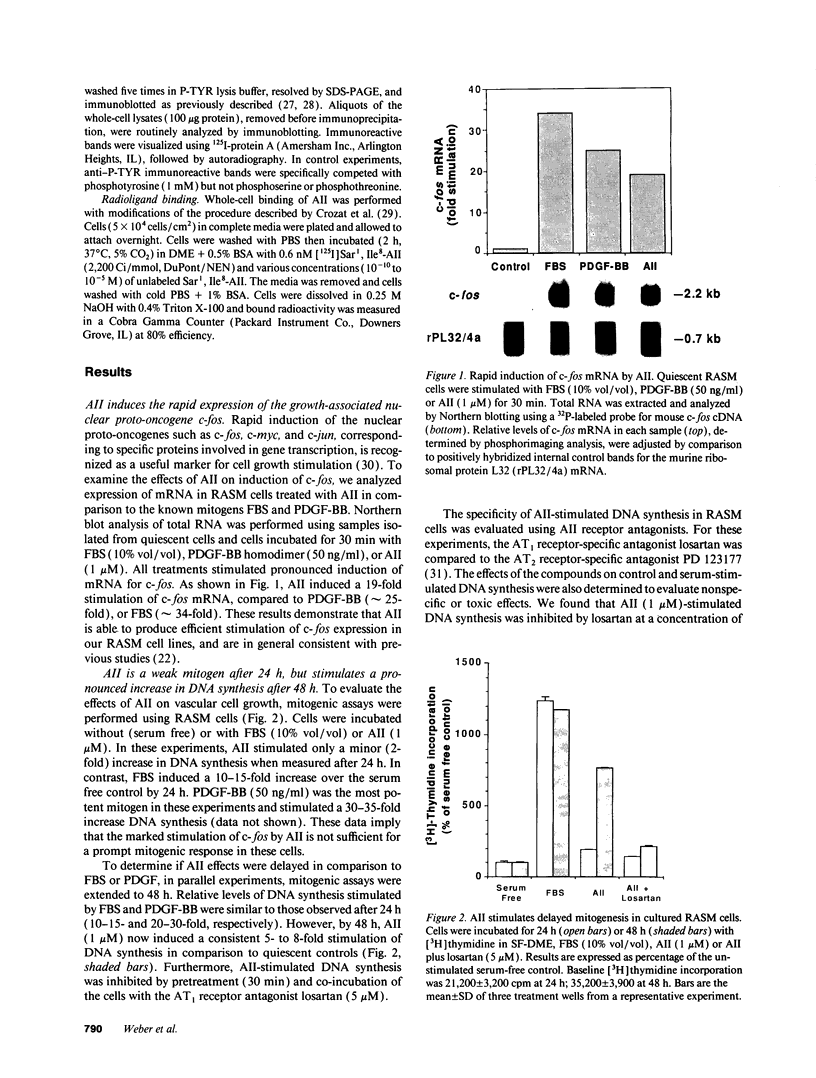
By means of a rat aortic smooth muscle (RASM) cell culture model, the effects of angiotensin II (AII) on early proto-oncogene gene expression, DNA synthesis, and cell proliferation were measured and compared to known mitogens. In 24-h [3H]-thymidine incorporation assays, AII was found to be a weak mitogen when compared to potent mitogens such as fetal bovine serum and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). In contrast, when assays were carried out for 48 h, AII induced a significant dose-dependent stimulation of DNA synthesis, which more than doubled at 3 nM AII, and was maximal (five- to eightfold above control) at 100 nM AII. Treatment of cells with the AII type 1 receptor antagonist losartan inhibited the mitogenic effects of AII. AII also stimulated smooth muscle cell proliferation, as indicated by an absolute increase in cell number after AII stimulation of RASM cells for 5 d. AII stimulation of RASM cell growth correlated with the increased expression of specific endogenous growth factors, including transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and PDGF A-chain. However, addition of either PDGF- or TGF-beta 1-neutralizing antibodies failed to significantly reduce the delayed mitogenic effects induced by AII. In contrast, we found that AII-stimulated mitogenesis could be inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by the growth factor inhibitor drug suramin. Taken together, our results indicate that enhanced endogenous growth factor expression may represent the direct mechanism by which AII promotes smooth muscle cell growth in some vascular hyperproliferative diseases.
Full text
PDF


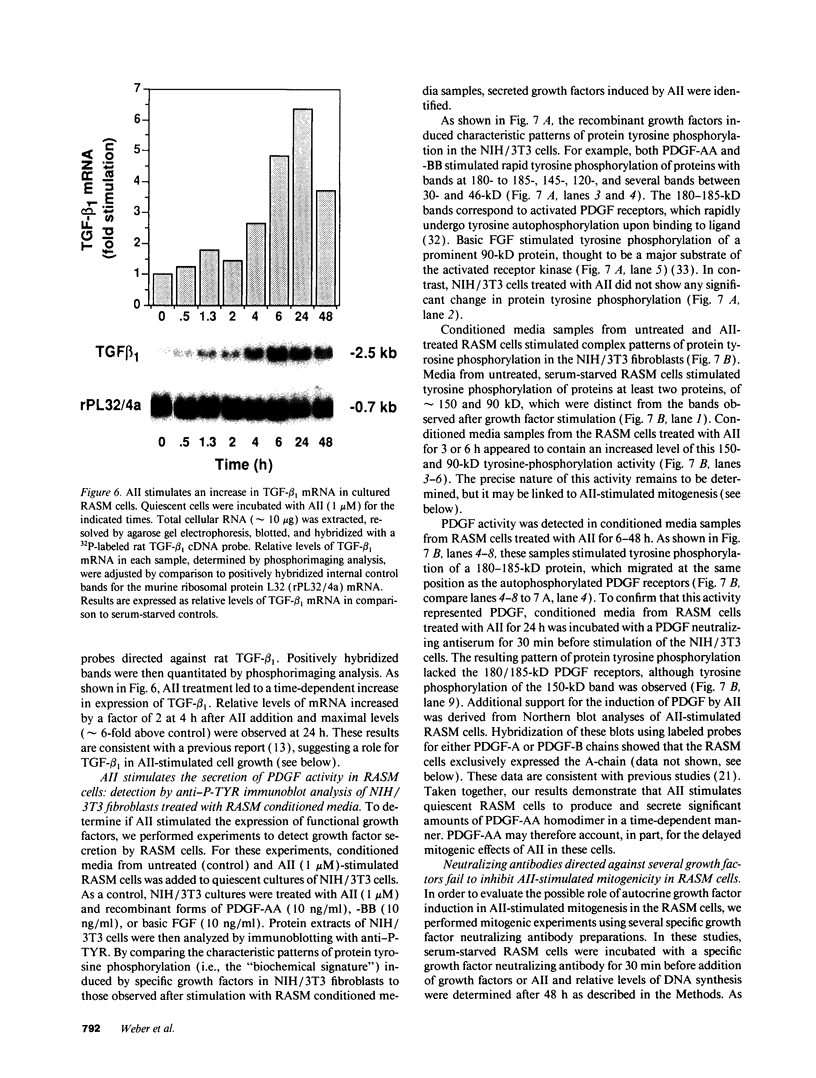
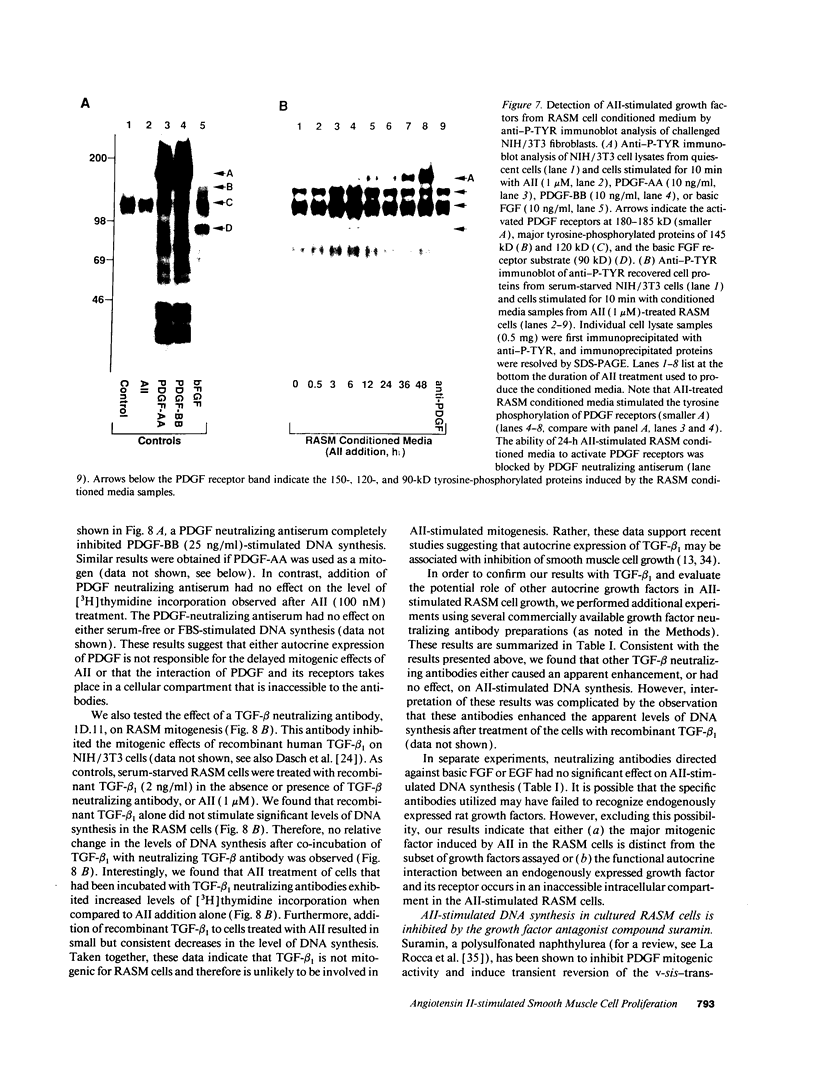
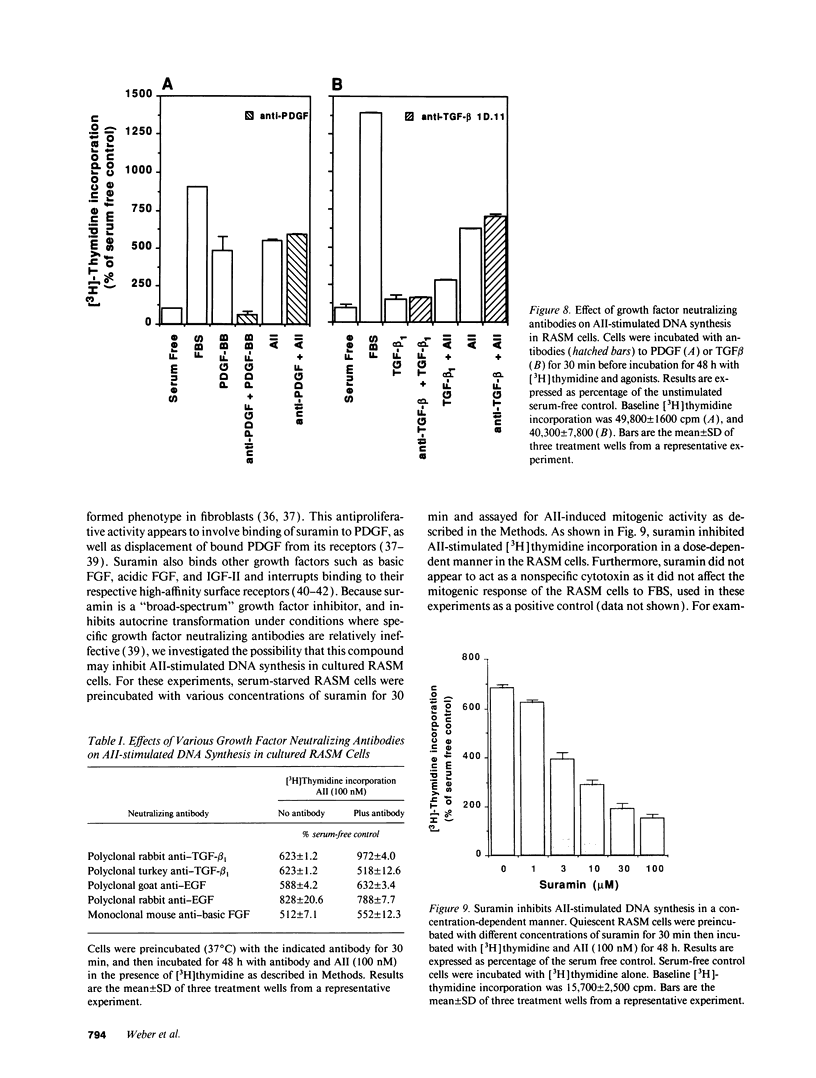
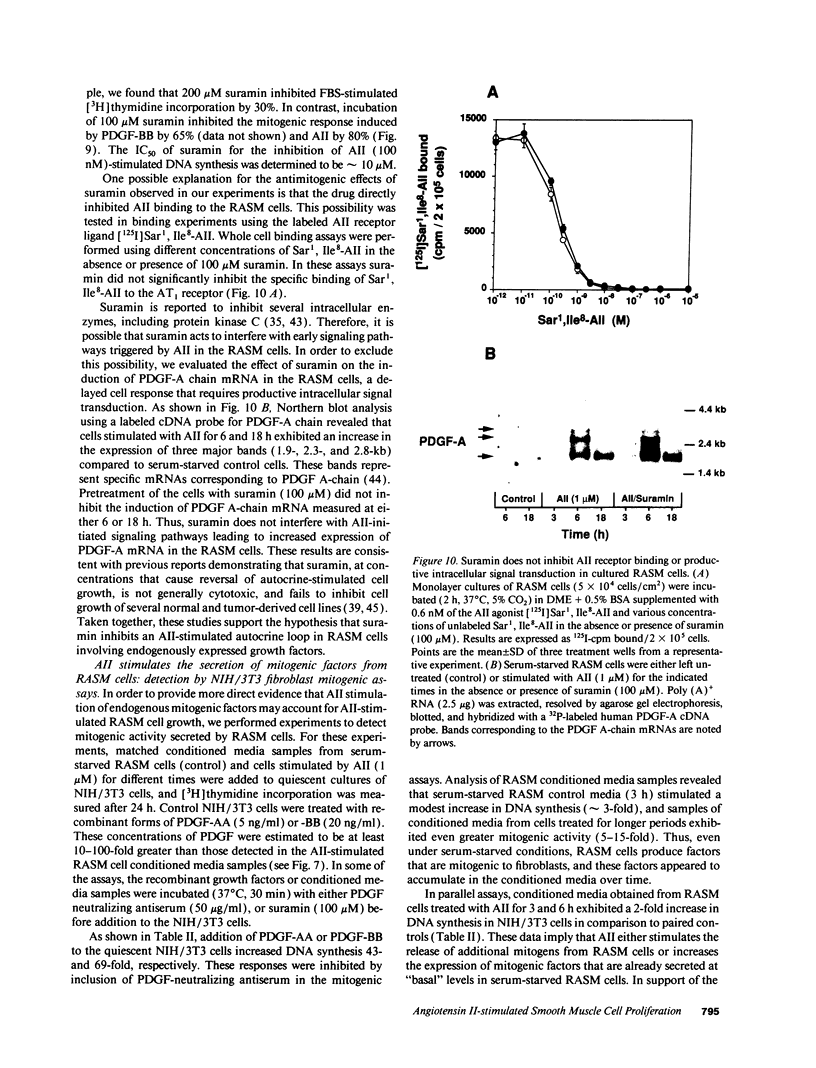


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberg G., Ferrer P. Effects of captopril on atherosclerosis in cynomolgus monkeys. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 5):S65–S72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejcek B. E., Li D. Y., Deuel T. F. Transformation by v-sis occurs by an internal autoactivation mechanism. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1496–1499. doi: 10.1126/science.2551043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Efficient reversion of simian sarcoma virus-transformation and inhibition of growth factor-induced mitogenesis by suramin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6440–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Lind P., Urdea M. S., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Philpott K., Mellor A. L. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):695–699. doi: 10.1038/320695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Boswell M., Robertson A. L., Jr Effects of angiotensin II and vasopressin on human smooth muscle cells in vitro. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Oct;35(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Lotti V. J. Two distinct angiotensin II receptor binding sites in rat adrenal revealed by new selective nonpeptide ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Barr P. J., Cousens L. S., Fretto L. J., Williams L. T. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors stimulate tyrosine kinase activity in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):988–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crozat A., Penhoat A., Saez J. M. Processing of angiotensin II (A-II) and (Sar1,Ala8)A-II by cultured bovine adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Jun;118(6):2312–2318. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-6-2312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemen M. J., Lombardi D. M., Bosman F. T., Schwartz S. M. Angiotensin II induces smooth muscle cell proliferation in the normal and injured rat arterial wall. Circ Res. 1991 Feb;68(2):450–456. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.2.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch J. R., Pace D. R., Waegell W., Inenaga D., Ellingsworth L. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing transforming growth factor-beta. Bioactivity neutralization and transforming growth factor beta 2 affinity purification. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1536–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco E., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Kraus M. H., Molloy C. J., Aaronson S. A., Di Fiore P. P. Autocrine interaction between TGF alpha and the EGF-receptor: quantitative requirements for induction of the malignant phenotype. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):831–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diliberto P. A., Gordon G., Herman B. Regional and mechanistic differences in platelet-derived growth factor-isoform-induced alterations in cytosolic free calcium in porcine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12612–12617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar C. E., Browder T. M., Abrams J. S., Nienhuis A. W. COOH-terminal-modified interleukin-3 is retained intracellularly and stimulates autocrine growth. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1493–1496. doi: 10.1126/science.2789432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns G. A., Raines E. W., Sprugel K. H., Motani A. S., Reidy M. A., Ross R. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1653454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming T. P., Matsui T., Heidaran M. A., Molloy C. J., Artrip J., Aaronson S. A. Demonstration of an activated platelet-derived growth factor autocrine pathway and its role in human tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1355–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming T. P., Matsui T., Molloy C. J., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Autocrine mechanism for v-sis transformation requires cell surface localization of internally activated growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8063–8067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer A. A., Peach M. J., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):749–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachelli C., Bae N., Lombardi D., Majesky M., Schwartz S. Molecular cloning and characterization of 2B7, a rat mRNA which distinguishes smooth muscle cell phenotypes in vitro and is identical to osteopontin (secreted phosphoprotein I, 2aR). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 14;177(2):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91870-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. H., Dzau V. J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and vascular hypertrophy in hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 1990 Feb;4(1):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01857638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. H., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy vs. hyperplasia. Autocrine transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression determines growth response to angiotensin II. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):456–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI115881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosang M. Suramin binds to platelet-derived growth factor and inhibits its biological activity. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(3):265–273. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Rapid turnover of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in sis-transformed cells and reversal by suramin. Implications for the mechanism of autocrine transformation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12608–12618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckle W. R., Prokop C. A., Dy R. C., Herman B., Earp S. Angiotensin II stimulates protein-tyrosine phosphorylation in a calcium-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6290–6298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman R. F., Bean J. S., Zimmerman K. M., Brown R. F., Steinberg M. I. Losartan, a nonpeptide angiotensin II (Ang II) receptor antagonist, inhibits neointima formation following balloon injury to rat carotid arteries. Life Sci. 1991;49(25):PL223–PL228. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90298-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. T., Williams L. T. Autocrine stimulation of intracellular PDGF receptors in v-sis-transformed cells. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):914–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2829358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rocca R. V., Stein C. A., Myers C. E. Suramin: prototype of a new generation of antitumor compounds. Cancer Cells. 1990 Apr;2(4):106–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyall F., Morton J. J., Lever A. F., Cragoe E. J. Angiotensin II activates Na+-H+ exchange and stimulates growth in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens Suppl. 1988 Dec;6(4):S438–S441. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198812040-00138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney C. W., Azzi A., Huang K. P. Effects of suramin, an anti-human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase agent, on protein kinase C. Differential activation and inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5424–5428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majesky M. W., Giachelli C. M., Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Rat carotid neointimal smooth muscle cells reexpress a developmentally regulated mRNA phenotype during repair of arterial injury. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):759–768. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middaugh C. R., Mach H., Burke C. J., Volkin D. B., Dabora J. M., Tsai P. K., Bruner M. W., Ryan J. A., Marfia K. E. Nature of the interaction of growth factors with suramin. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):9016–9024. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minniti C. P., Maggi M., Helman L. J. Suramin inhibits the growth of human rhabdomyosarcoma by interrupting the insulin-like growth factor II autocrine growth loop. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1830–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Taylor D. S., Weber H. Angiotensin II stimulation of rapid protein tyrosine phosphorylation and protein kinase activation in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7338–7345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Quarto N. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells with basic fibroblast growth factor or the hst/K-fgf oncogene causes downregulation of the fibroblast growth factor receptor: reversal of morphological transformation and restoration of receptor number by suramin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2519–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Alexander R. W., Griendling K. K., Runge M. S., Bernstein K. E. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):233–236. doi: 10.1038/351233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Gilliland G. K., Eldridge C. S., Kraft A. S. Induction of the proto-oncogene c-jun by angiotensin II. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5536–5540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Induction of platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and c-myc gene expressions by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1419–1424. doi: 10.1172/JCI114032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., Pledger W. J. Cellular mechanisms regulating proliferation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1988;22:139–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K. Control of hypertrophic versus hyperplastic growth of vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):H1755–H1765. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.6.H1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K., Geisterfer A. A., Yang Y. W., Komoriya A. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced growth inhibition and cellular hypertrophy in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):771–780. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K. Influence of blood pressure on development of aortic medial smooth muscle hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1987 Feb;9(2):178–187. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J., Dostal D. E. The angiotensin II receptor and the actions of angiotensin II. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;16 (Suppl 4):S25–S30. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199016004-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachinidis A., Ko Y., Nettekoven W., Wieczorek A. J., Düsing R., Vetter H. The effect of angiotensin II on DNA synthesis varies considerably in vascular smooth muscle cells from different Wistar-Kyoto rats. J Hypertens. 1992 Oct;10(10):1159–1164. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199210000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Ji H., Clark A. J., Shapira H., Catt K. J. Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9455–9458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Yamano Y., Bardhan S., Iwai N., Murray J. J., Hasegawa M., Matsuda Y., Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):230–233. doi: 10.1038/351230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Foy L., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Derivation and properties of platelet-derived growth factor-independent rat smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1417–1428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Heimark R. L., Majesky M. W. Developmental mechanisms underlying pathology of arteries. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1177–1209. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Burden T., Hahn A. W., Resink T. J., Bühler F. R. Modulation of extracellular matrix by angiotensin II: stimulated glycoconjugate synthesis and growth in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;16 (Suppl 4):S36–S41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouffer G. A., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II-induced mitogenesis of spontaneously hypertensive rat-derived cultured smooth muscle cells is dependent on autocrine production of transforming growth factor-beta. Circ Res. 1992 Apr;70(4):820–828. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.4.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Berk B. C., Izumo S., Tsuda T., Alexander R. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Angiotensin II induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle. Role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. N., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Reidy M. A. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules by cultured arterial smooth muscle cells accompanies proliferation after arterial injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]