Abstract
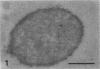
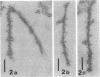
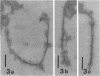
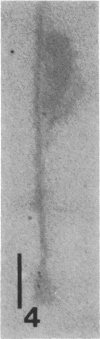
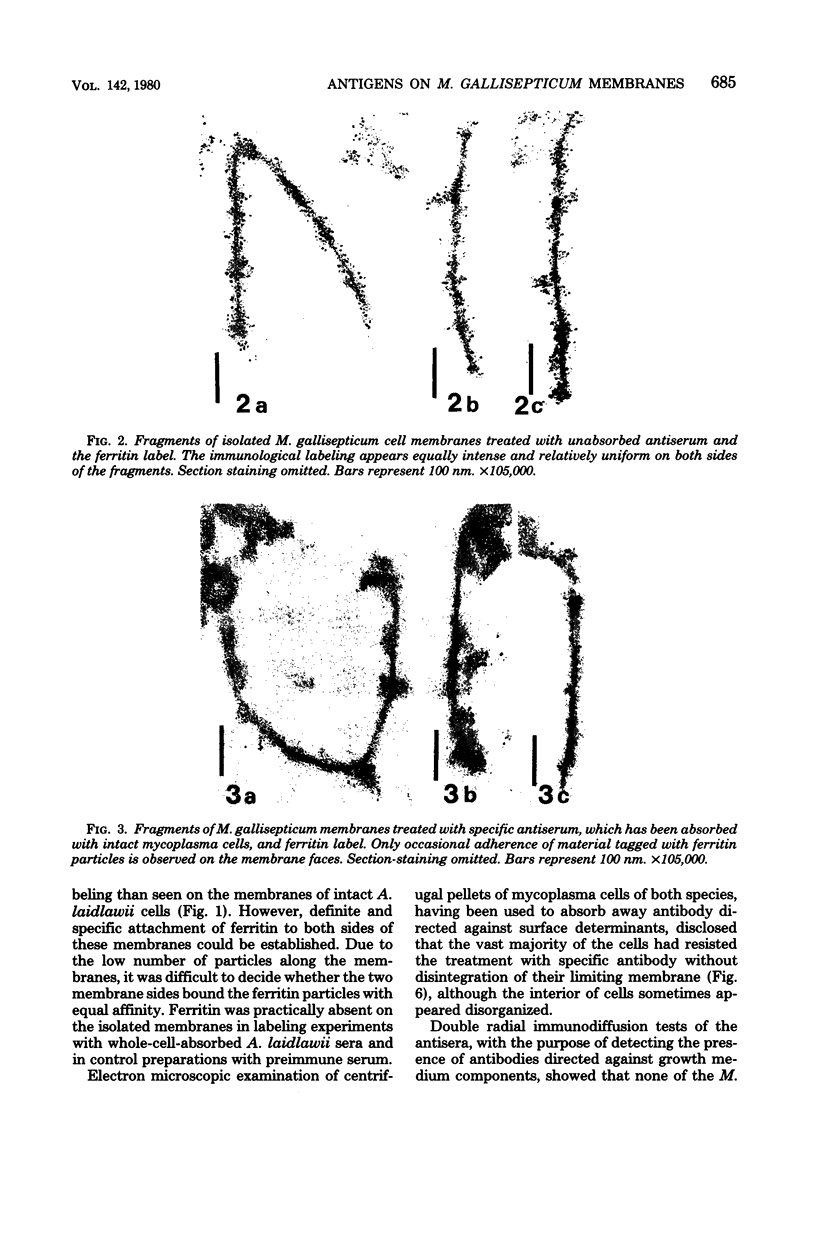
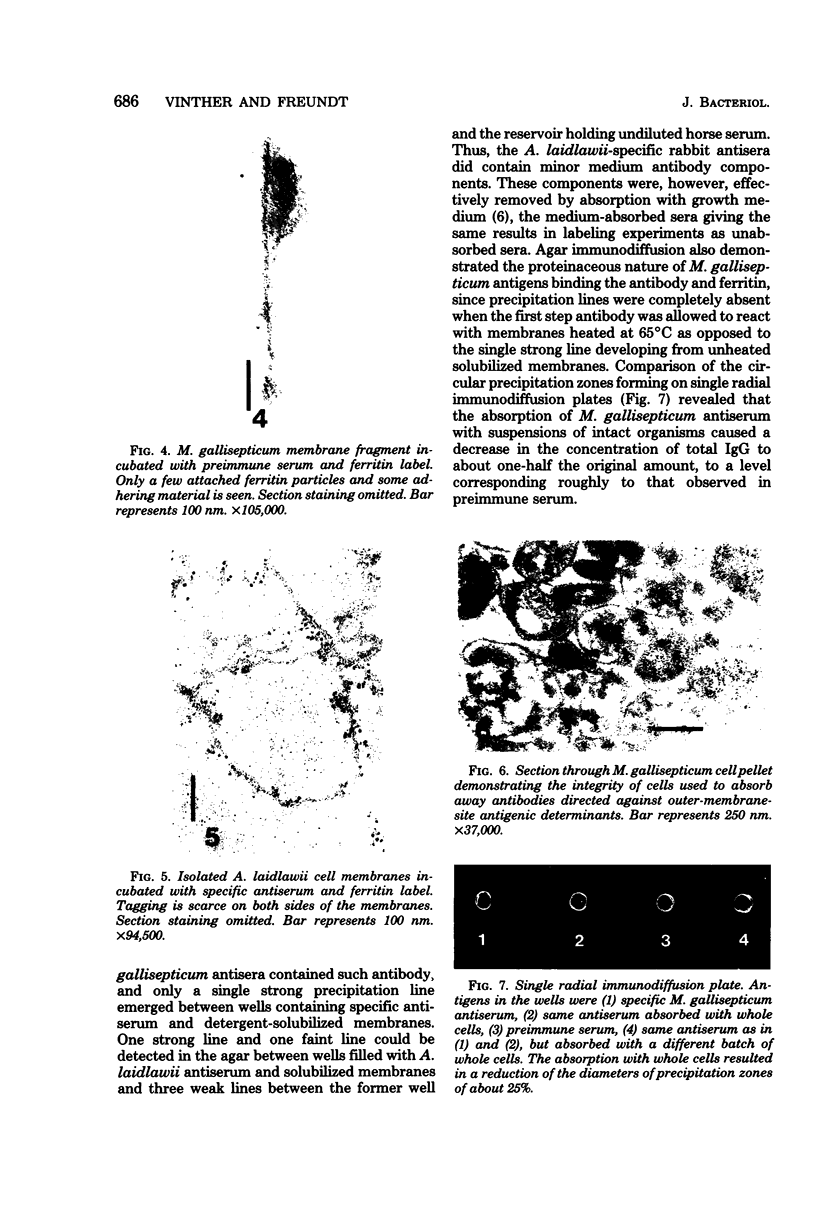
The transverse disposition of exposed protein antigens on the two faces of isolated Mycoplasma gallisepticum membranes have been investigated by using indirect immunoferritin labeling to accomplish visualization of the antigens at the ultrastructural level. Comparison between the labeling patterns obtained with unabsorbed specific mycoplasma antiserum and antiserum from which antibodies directed against outer side determinants had been removed revealed that the majority of protein antigens were the same on the opposed membrance faces or at least displayed extensive interside cross-reactivity. The relatively scarce tagging of isolated Acholeplasma laidlawii membranes, contrary to membranes on intact organisms observed in this investigation, precluded conclusions regarding the disposition of membrane antigens of this species. The advantages and limitations of the employed method in disposition studies and the factors influencing the transverse distribution of membrane proteins in mycoplasmas are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar A., Rottem S., Kahane I., Razin S. Characterization of the mycoplasma membrane proteins. VI. Composition and disposition of proteins in membranes from aging Mycoplasma hominis cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):258–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar A., Rottem S., Razin S. Characterization of the mycoplasma membrane proteins. IV. Disposition of proteins in the membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):228–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar A., Rottem S., Razin S. Is the vertical disposition of Mycoplasma membrane proteins affected by membrane fluidity? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 19;552(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T., Krogsgaard-Jensen A. Application of indirect immunofluorescence, indirect haemagglutination and polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis to human T-mycoplasmas. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):345–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T. Modifications of the growth inhibition test and its application to human T-mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):528–533. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.528-533.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury J. M., Jordan F. T. The absorption of -globulins to Mycoplasma gallisepticum and the possible role in non-specific serological reactions. Vet Rec. 1971 Sep 11;89(11):318–318. doi: 10.1136/vr.89.11.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erno H., Stipkovits L. Bovine mycoplasmas: cultural and biochemical studies. I. Acta Vet Scand. 1973;14(3):436–449. doi: 10.1186/BF03547431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Immunological analysis of Mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.187-194.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Serological cross-reaction between lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma neurolyticum. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):149–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.149-153.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn S., Razin S. Isolation, ultrastructure and antigenicity of Mycoplasma gallisepticum membranes. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):725–737. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D., Chanock R. M. Color test for the measurement of antibody to T-strain mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.6-12.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Binding of proteins to mycoplasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):876–886. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Stein O., Razin S. Reassembly of Mycoplasma membranes disaggregated by detergents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinther O., Freundt E. A. Electron microscopical study of antibody binding to Mycoplasma gallisepticum: indirect immunoferritin labelling. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Feb;87B(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]