Abstract
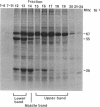
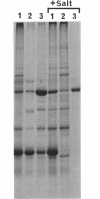
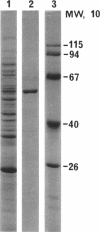
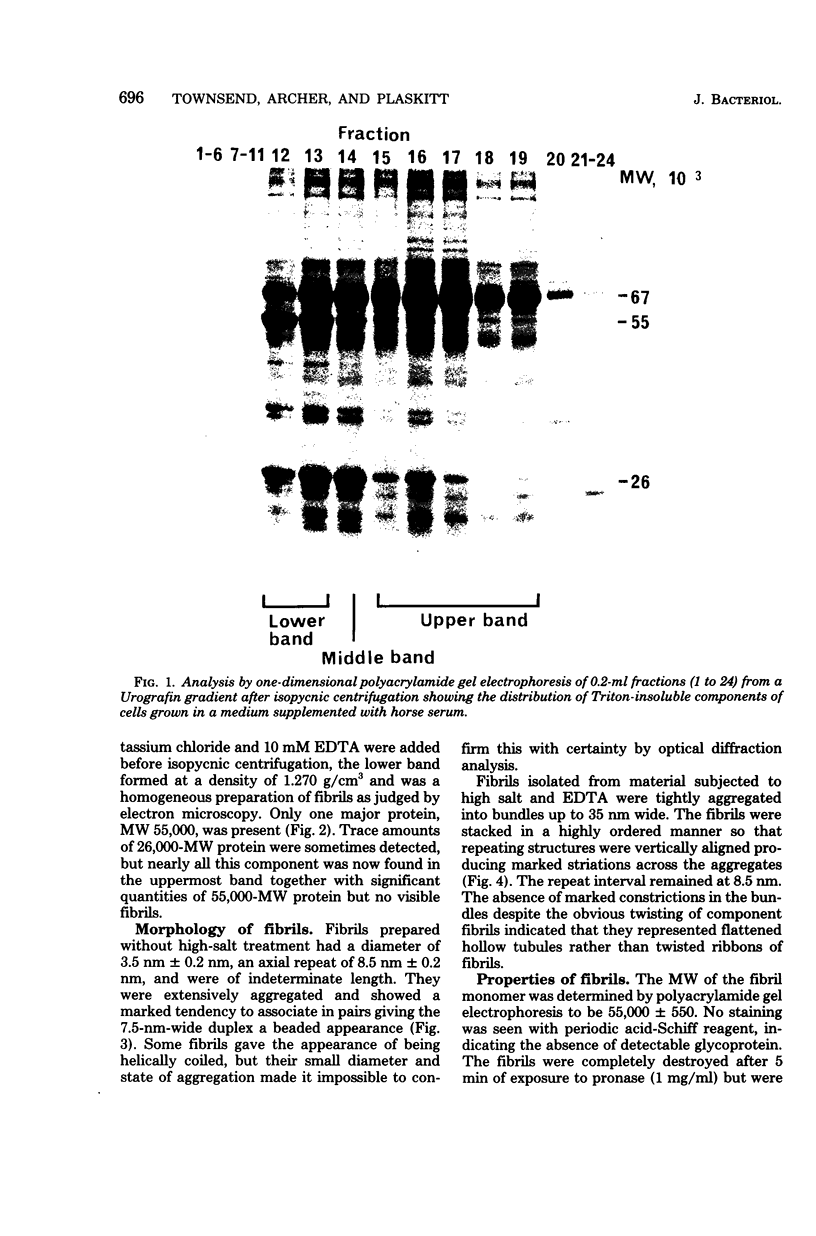
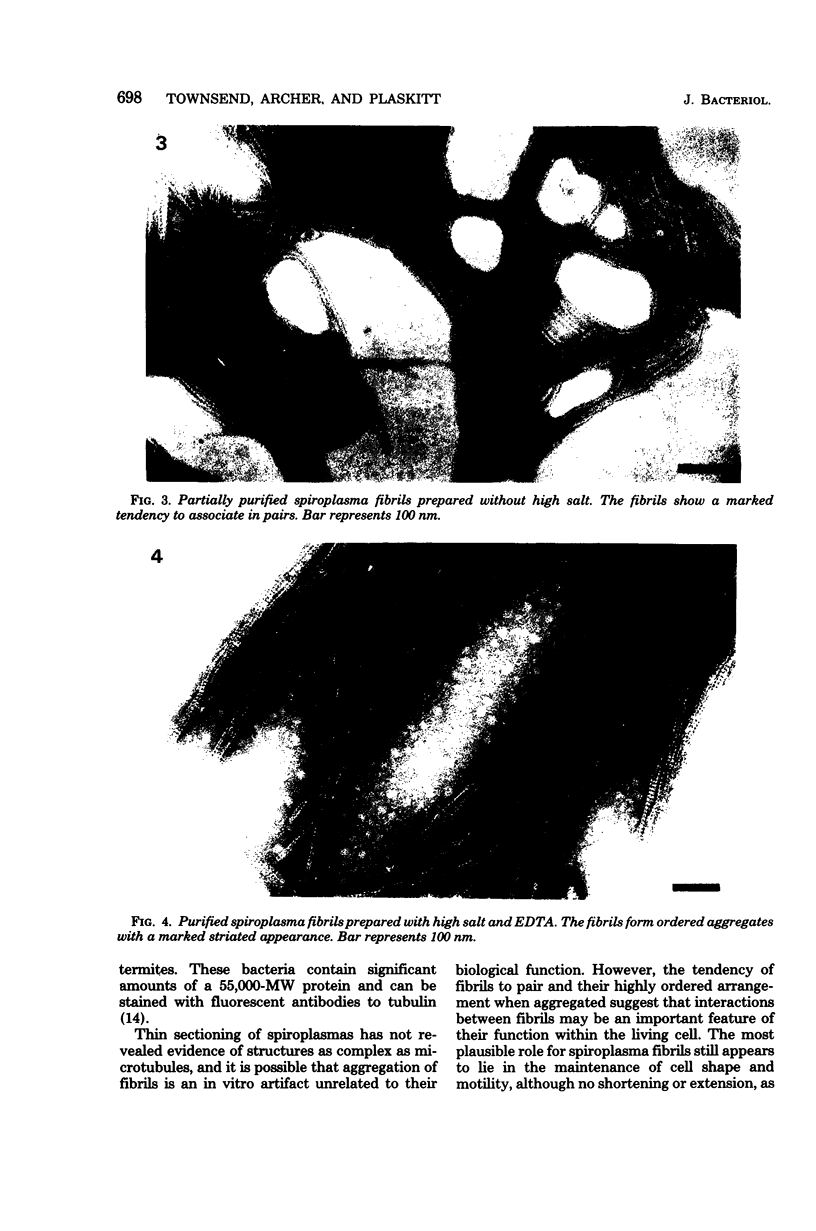
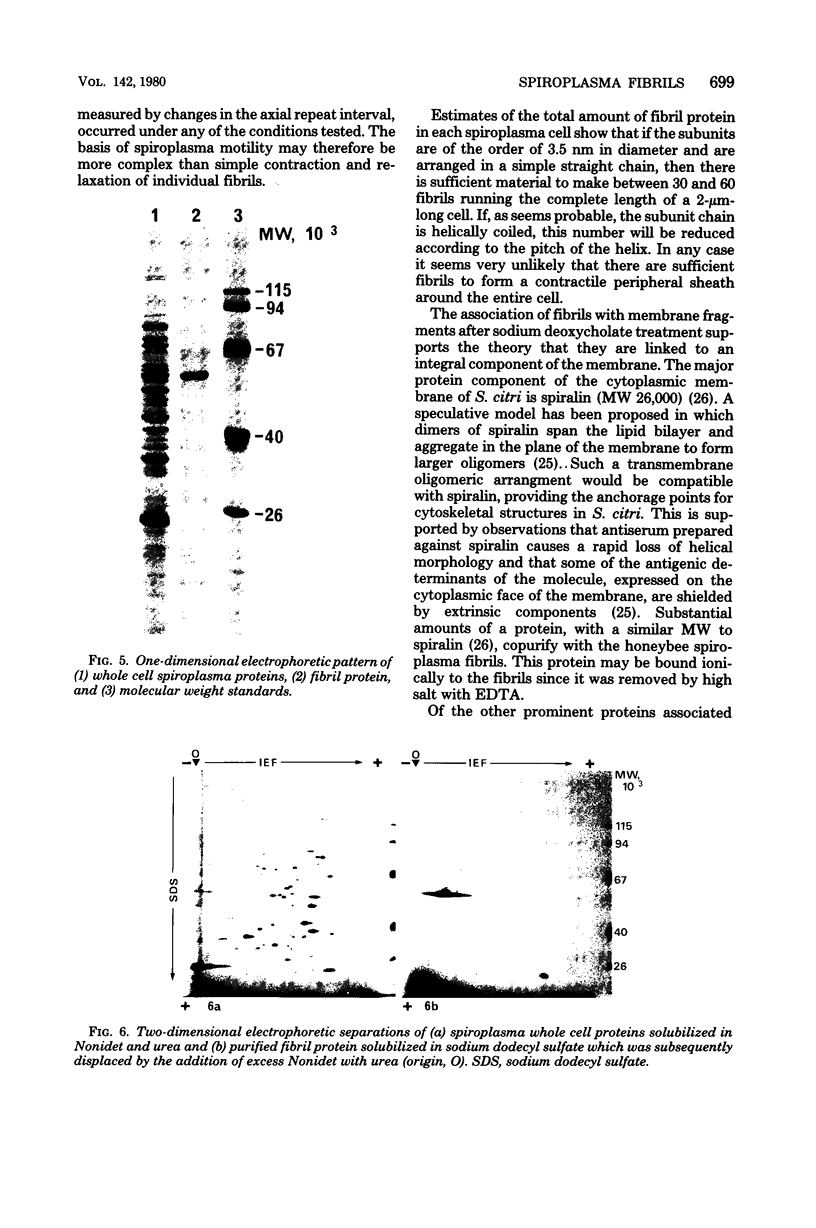
Fibrils 3.5 nm in diameter were released from the honeybee spiroplasma (BC3) by treatment with detergents and then purified by isopycnic centrifugation. Purified fibrils were flexuous, of indeterminate length, and had an axial repeat of 8.5 nm. The fibrils were associated in pairs, but in 1 M salt formed aggregates with a marked striated appearance. Pronase completely degraded the fibrils, but trypsin had little effect. The fibrils were composed of a single protein of molecular weight 55,000 which represented about 1% of the total cell protein. A protein of molecular weight 26,000 appeared to be associated with the fibrils. The significance of this in relation to membrane attachment and the possible role of fibrils in maintenance of cell shape and in motility are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Tully J. G., Popkin T. J., Bové J. M. Morphology, ultrastructure, and bacteriophage infection of the helical mycoplasma-like organism (Spiroplasma citri gen. nov., sp. nov.) cultured from "stubborn" disease of citrus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):367–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.367-386.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipert S. R., Black S. H. Characterization of the cytoplasmic fibrils of Treponema refringens (Nichols). Arch Microbiol. 1979 Mar 12;120(3):205–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00423067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. The structure and assembly of microtubules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:60–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Maniloff J., Gerling D. A. Inhibition of mycoplasma cell division by cytochalasin B. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of endoflagella and microtubules in Treponema reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulis L., To L., Chase D. Microtubules in prokaryotes. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1118–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.349692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. C. Extraction of an actin-like protein from the prokaryote Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4041–4045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Hasin M., Ne'eman Z., Rottem S. Isolation, chemical composition, and ultrastructural features of the cell membrane of the mycoplasma-like organism Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1421–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1421-1435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell A. W., Peterson J. E., Rodwell E. S. Striated fibers of the rho form of Mycoplasma: in vitro reassembly, composition, and structure. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1216–1229. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1216-1229.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. L. Unusual fibrils from the spirochete-like sex ratio organism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):904–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.904-906.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Johansson K. E., Hjérten S. Purification and characterization of spiralin, the main protein of the Spiroplasma citri membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]