Abstract
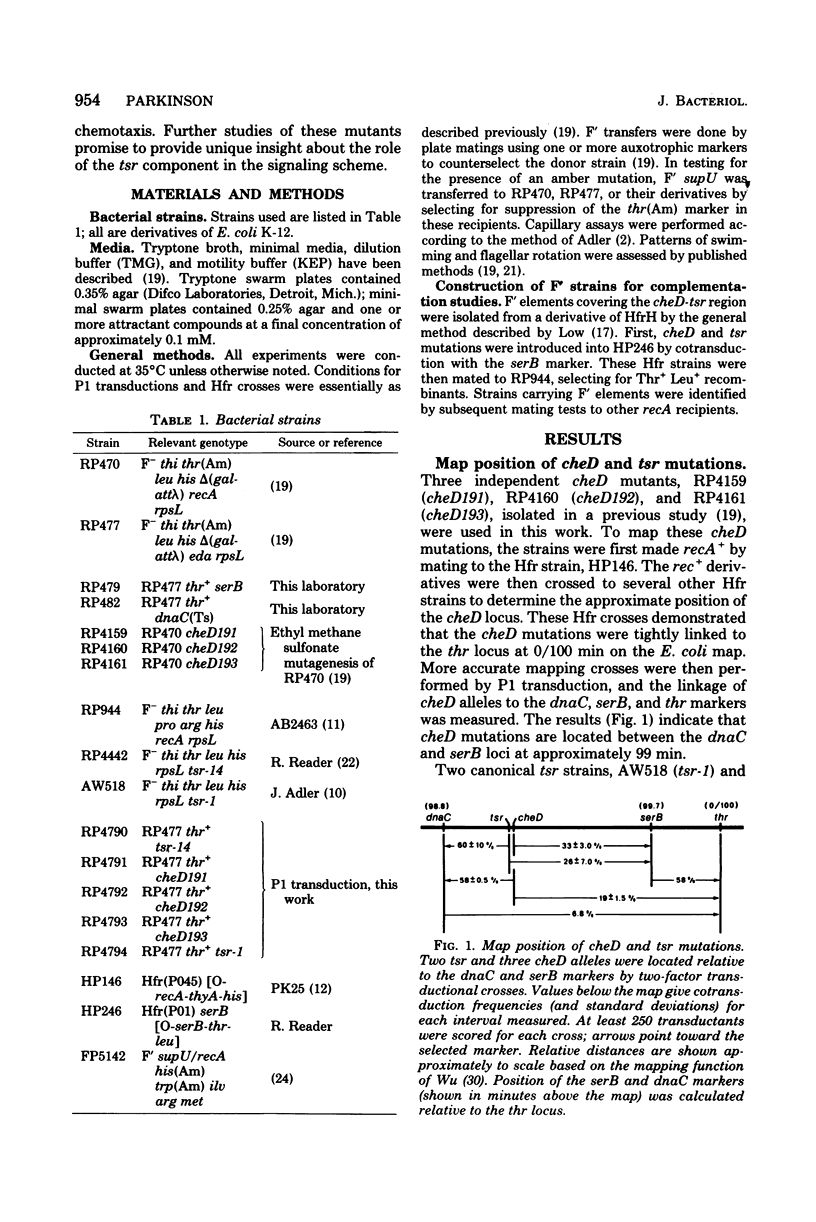
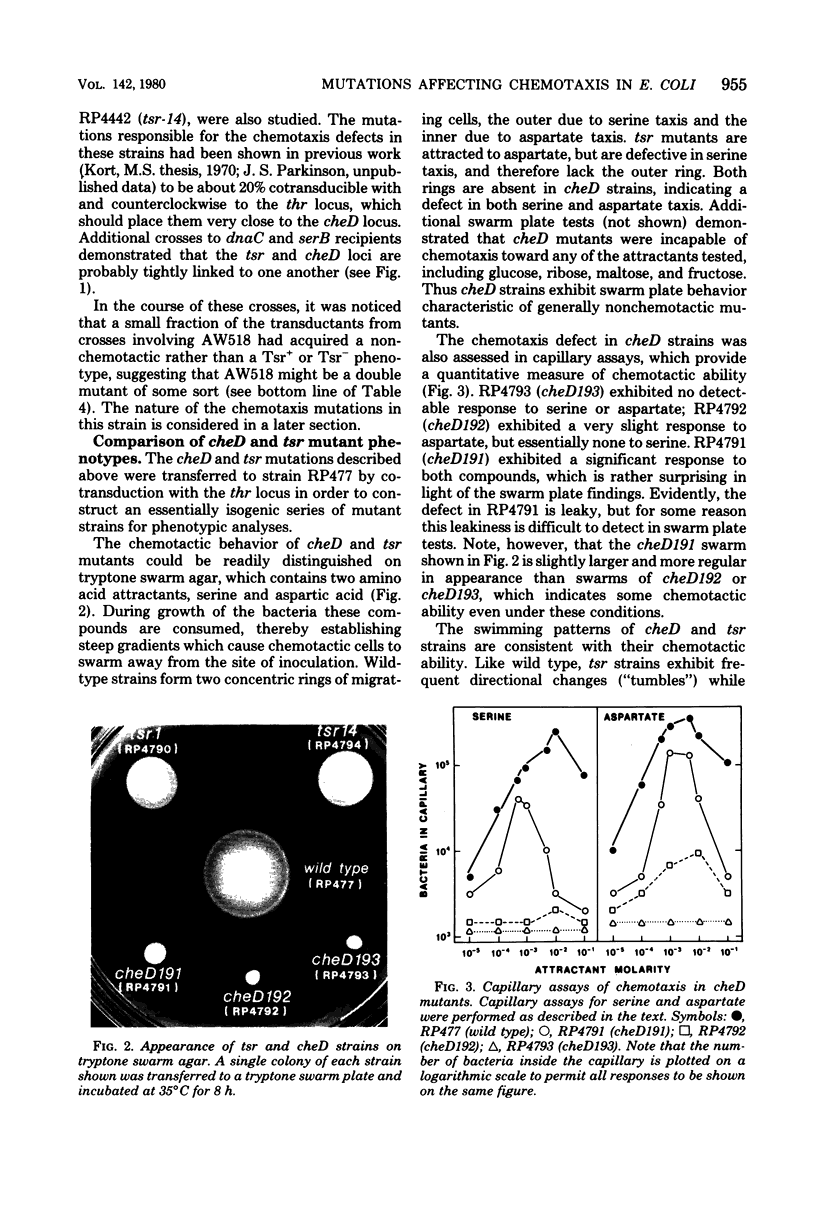
The genetic relationship between tsr and cheD mutations, which affect chemotactic ability and map at approximately 99 min on the Escherichia coli chromosome, was investigated. Mutants defective in tsr function typically exhibited wild-type swimming patterns, but were unable to carry out chemotactic responses to a number of attractant and repellent chemicals. In contrast, cheD mutants swam smoothly, with few spontaneous directional changes, and were generally nonchemotactic. In complementation tests, cheD mutations, unlike tsr, proved to be dominant to wild type, suggesting that the cheD defect might be due to an active inhibitor of chemotaxis. Mutations that inactivated the putative inhibitor were obtained by selecting for restoration of chemotactic ability or for loss of cheD dominance. The resultant double mutants were shown to carry the original cheD mutation and a second tightly linked mutation, some of which exhibited nonsense or temperature-sensitive phenotypes, implying that they had occurred in a structural gene for a protein. All such double mutants behaved like typical tsr mutants in all other respects, including complementation pattern, swimming behavior, and chemotactic ability. These findings implied that either overproduction of tsr product or synthesis of an aberrant tsr product was responsible for the chemotaxis defect of cheD strains. Such mutants should be useful in analyzing the role of the tsr product in chemotactic responses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Parkinson J. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Functional homology of chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.107-114.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Failure of sensory adaptation in bacterial mutants that are defective in a protein methylation reaction. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: role of a protein methylation reaction in sensory adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P. Parallel pathways for transduction of chemotactic signals in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):98–100. doi: 10.1038/283098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Mutants in transmission of chemotactic signals from two independent receptors of E. coli. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P. L. Isolation of high-frequency recombining strains from Escherichia coli containing the V colicinogenic factor. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):205–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.205-214.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koiwai O., Hayashi H. Studies on bacterial chemotaxis. IV. Interaction of maltose receptor with a membrane-bound chemosensing component. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort E. N., Goy M. F., Larsen S. H., Adler J. Methylation of a membrane protein involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Behavioral genetics in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:397–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Tso W. W., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Pleiotropic aspartate taxis and serine taxis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Apr;111(2):363–374. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubik B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Potentiation, desensitization, and inversion of response in bacterial sensing of chemical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: methylation of che gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll L., Berg P. Recessive lethals: a new class of nonsense suppressors in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):392–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Chemotactic mechanism of Salmonella typhimurium: preliminary mapping and characterization of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):223–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.223-231.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]