Abstract
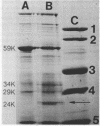
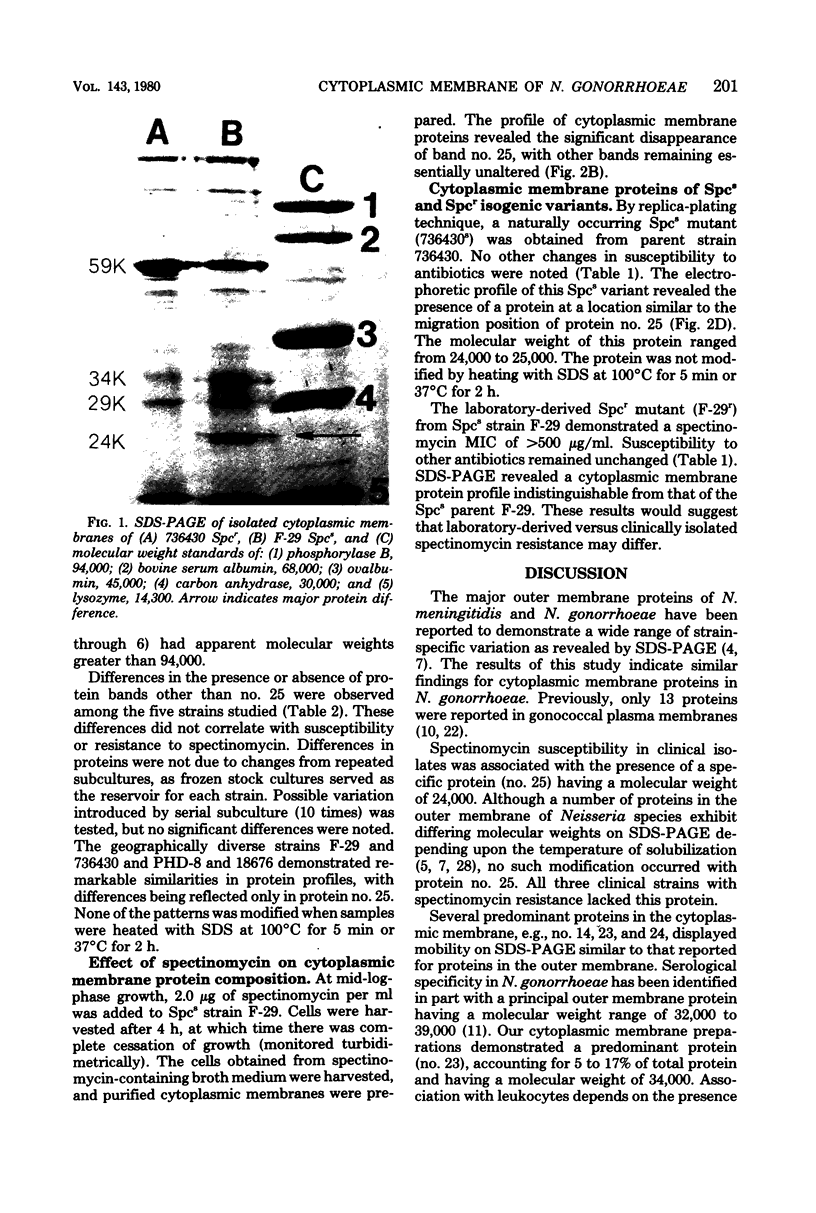
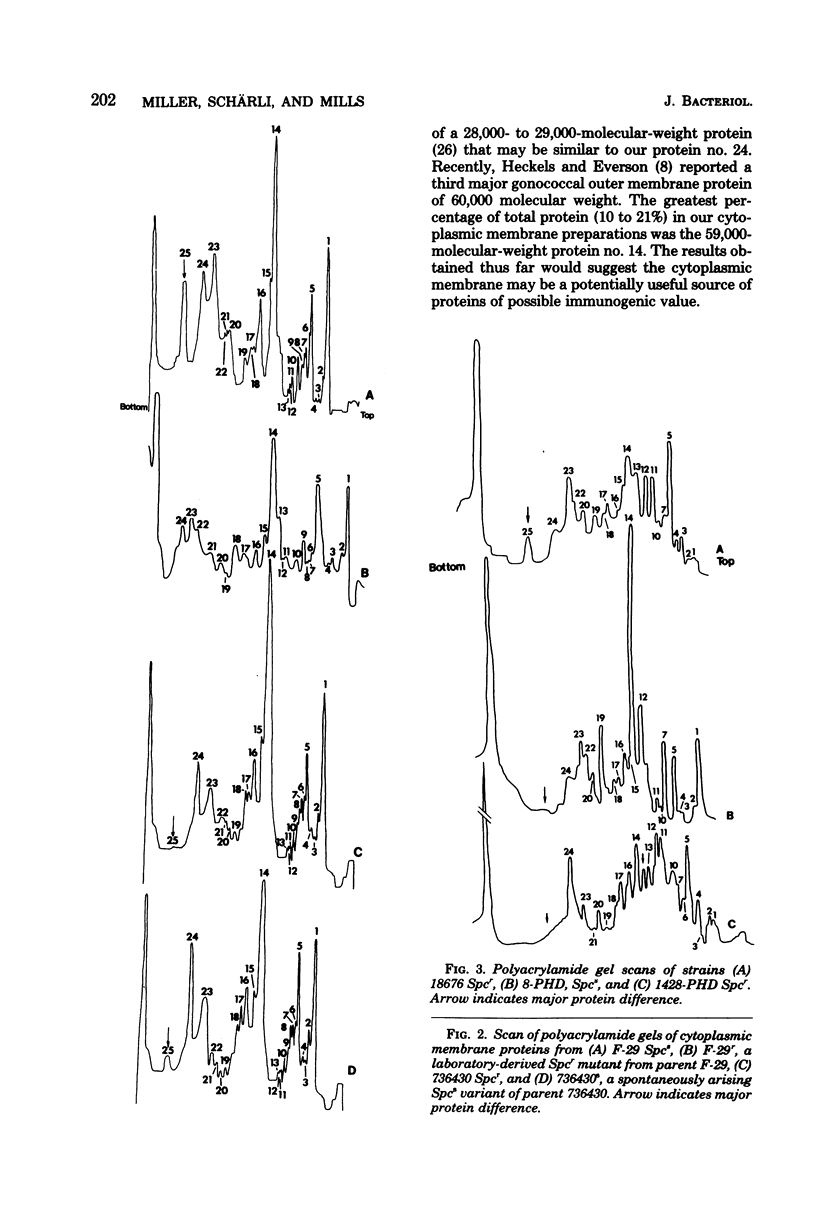
Cytoplasmic membranes were isolated and examined from two spectinomycin-susceptible and three spectinomycin-resistant clinical strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A laboratory-derived spectinomycin-resistant mutant, obtained by serial passage on gradually increasing concentrations of the antibiotic, and a susceptible revertant, spontaneously arising from one of the resistant clinical strains, were also studied. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis revealed that a major protein, comprising about 7% of total cytoplasmic membrane protein (molecular weight 24,000), was absent in the three clinically isolated spectinomycin-resistant strains. In a revertant, this protein reappeared. During treatment of one of the susceptible strains with spectinomycin, the protein disappeared. However, this correlation was not maintained in the laboratory-derived spectinomycin-resistant mutant. This mutant was of comparable resistant to the clinical isolates, but the 24,000-molecular-weight protein was present in normal quantities. In addition, spectinomycin resistant in clinical isolates was variable compared with stable resistance exhibited by the laboratory-derived mutant. These findings suggested that differences in laboratory-derived versus clinical spectinomycin resistance may be due to different types of resistance mutations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birge E. A., Kurland C. G. Reversion of a streptomycin-dependent strain of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(4):356–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00267704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. A spectinomycin dependent mutant of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 16;151(3):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00268789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F. Heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis and their organization within the membrane. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1127–1134. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1127-1134.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasenbank R., Guthrie C., Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G., Rosen L., Apirion D. Electrophoretic and immunological studies on ribosomal proteins of 100 Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 14;127(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00267778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Everson J. S. The isolation of a new outer membrane protein from the parent strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 May;106(1):179–182. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation of the major components of the outer membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. C., Peterson N. R., Weiss E. Characterization of spheroplast membranes of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):612–621. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.612-621.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.250-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Foster G. C., Sparling P. F. Ribosomal resistance to streptomycin and spectinomycin in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1293–1299. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1293-1299.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Kuemmerle N. B., Gentile G. Amoxycillin and ampicillin. A comparative study of in vitro sensitivity and induced morphological alterations in Serratia marcescens. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;19(3):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Yamagata H., Mizushima S. Interaction of cytoplasmic membrane and ribosomes in Escherichia coli: spectinomycin-induced disappearance of membrane protein I-19. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):326–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.326-332.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. The biology of the gonococcus. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;7(2):93–189. doi: 10.3109/10408417909083071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Schmidt H., Trier M., Bentzon M. W. Spectinomycin hydrochloride (Trobicin) in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Observation of resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Feb;49(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez W. J., Saz A. K. Differential binding of penicillin by membrane fractions from penicillin-susceptible and -resistant gonococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):589–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S. Release of soluble peptidoglycan from growing gonococci: hexaminidase and amidase activities. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):869–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.869-878.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Surface components affecting interactions between Neisserai gonorrhoeae and eucaryotic cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S138–S143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Jaffee H., Brown S. T., Edwards T., Biddle J. W., Thompson S. E. Spectinomycin-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. JAMA. 1977 May 30;237(22):2405–2406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered outer membrane protein in different colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1623-1627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E. The bactericidal action of spectinomycin on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3(4):323–329. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington JA I. I., Yu P. K. In vitro antibacterial activity of spectinomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):427–430. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]