Abstract
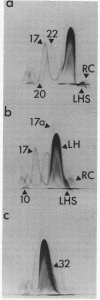
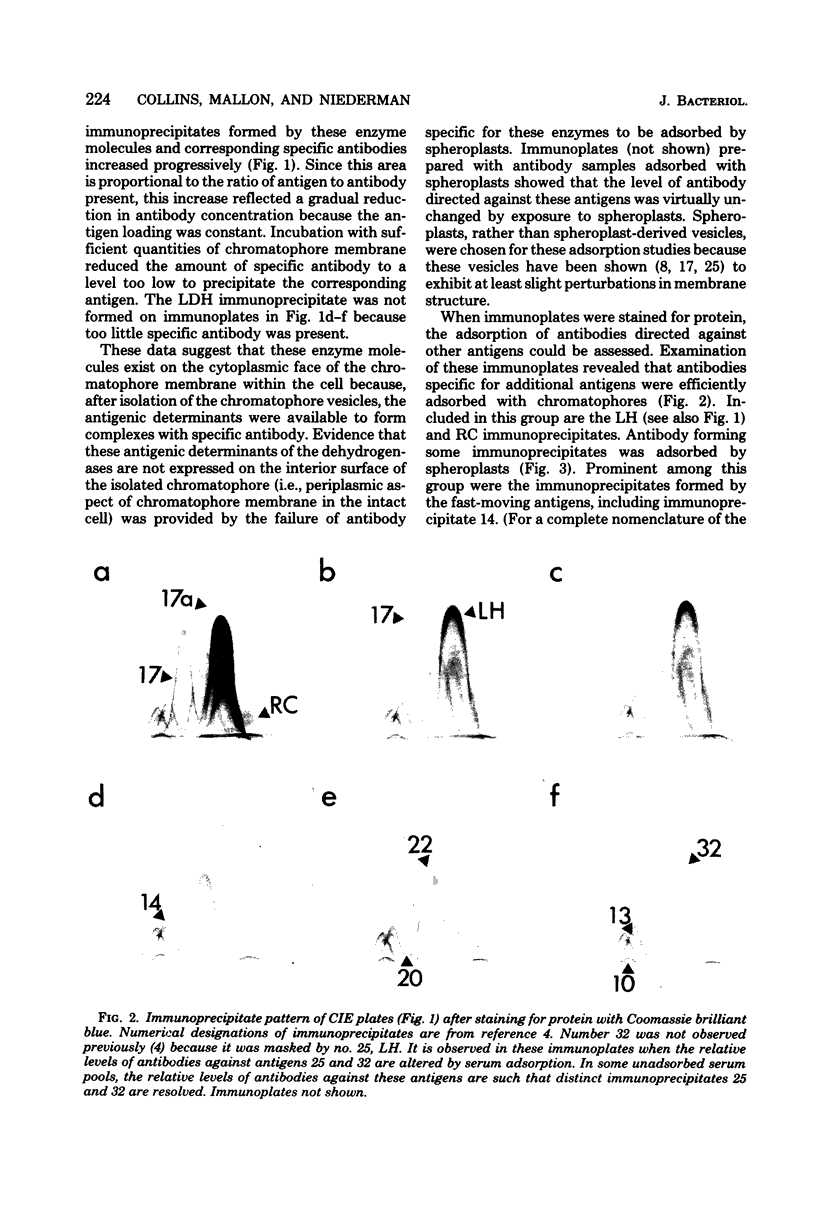
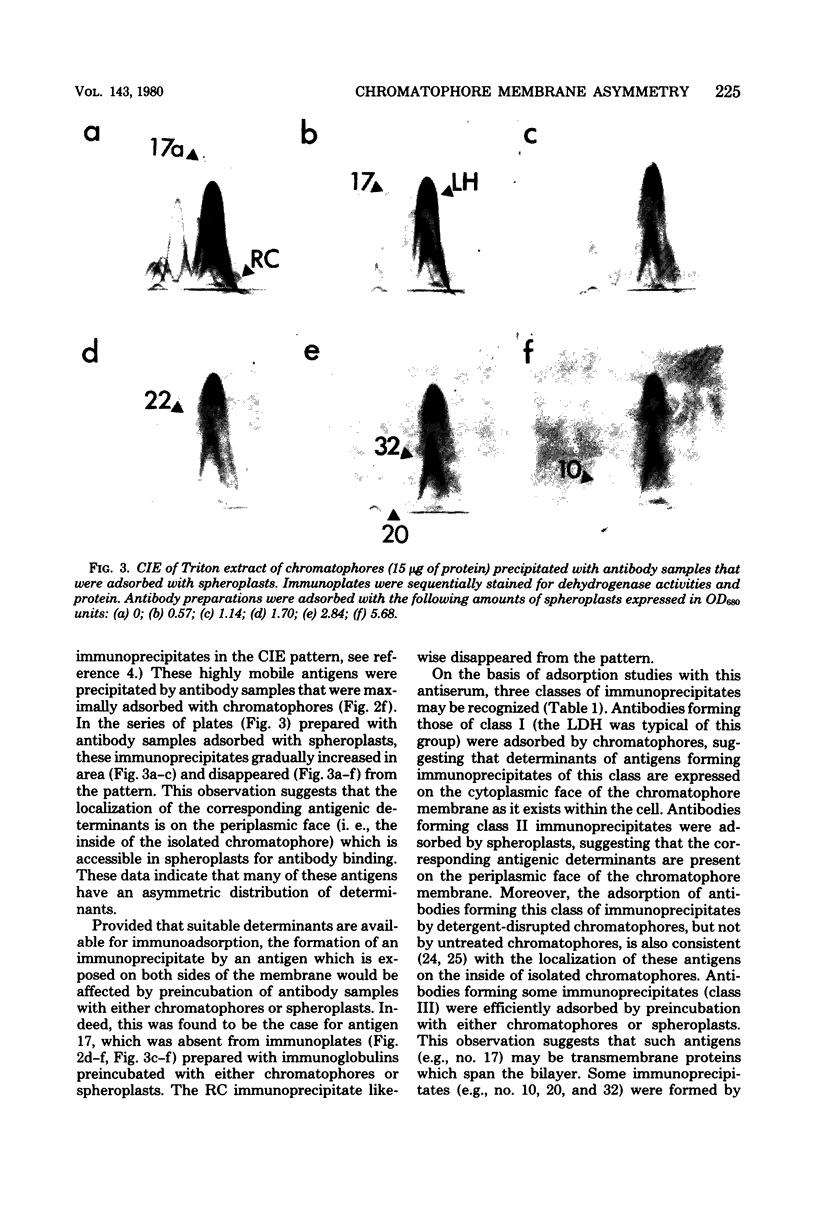
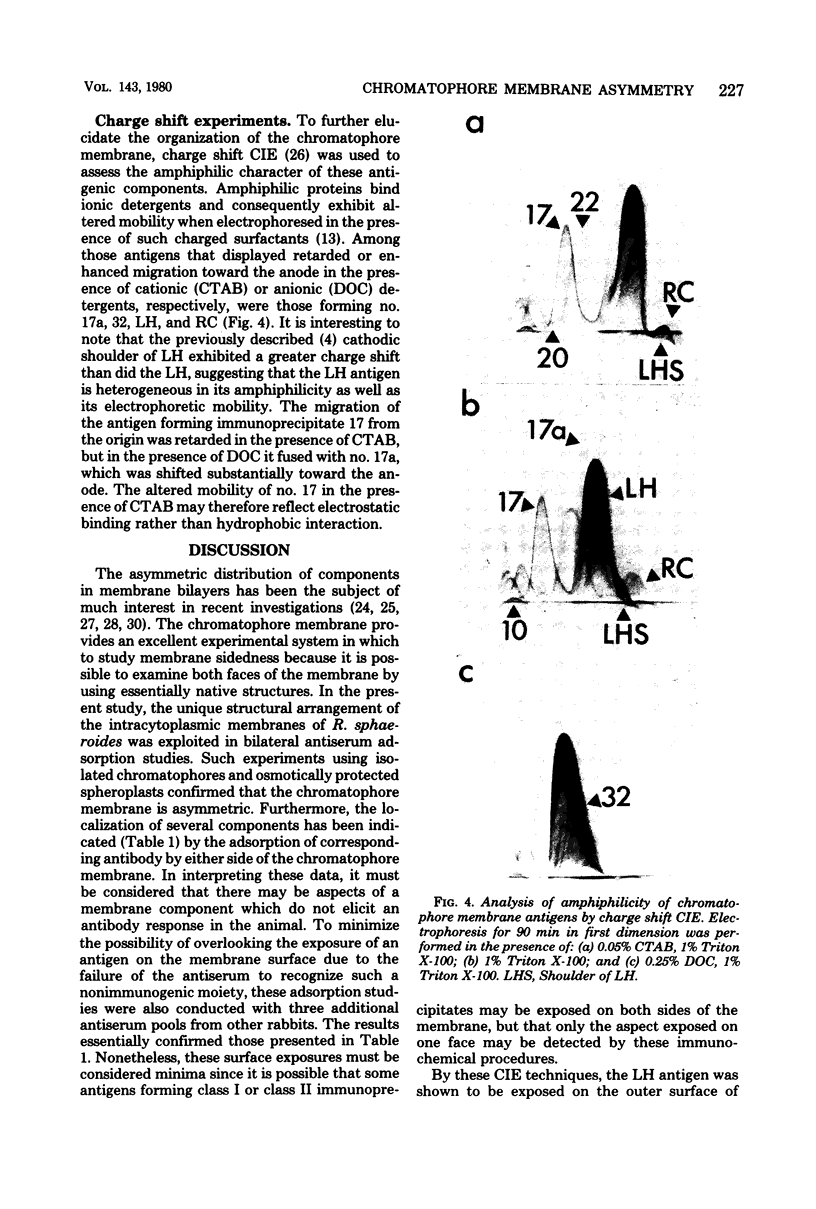
The asymmetric structure of the Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides chromatophore membrane was examined in detail by crossed immunoelectrophoresis techniques. Because these methods are quantitative and allow increased resolution and sensitivity, it was possible to analyze simultaneously the relative transmembrane distribution of a number of previously identified antigenic components. This was demonstrated by analysis of immunoglobulin samples that were adsorbed by preincubation with either isolated chromatophores or osmotically protected spheroplasts. The photochemical reaction center, the light-harvesting bacteriochlorophyll a-protein complex, the L-lactate dehydrogenase, and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase (EC 1.6.99.3) were found to be exposed on the chromatophore surface (cytoplasmic aspect of the membrane within the cell). Other antigenic components were found to be exposed on the surface of spheroplasts (periplasmic aspect of the in vivo chromatophore membrane). Antigens with determinants expressed on both sides of the chromatophore membrane were also identified. Charge shift crossed immunoelectrophoresis confirmed the suggested amphiphilic character of the pigment-protein complexes and identified several additional amphiphilic membrane components.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., KUNISAWA R. The fine structure of Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:401–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Mallon D. E., Niederman R. A. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of chromatophore membranes from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1089–1092. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1089-1092.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodospirillum rubrum: physicochemical properties of chromatophore fractions isolated from osmotically and mechanically disrupted cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1326–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1326-1338.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Salton M. R. Solubility characteristics of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membrane components in detergents and chaotropic salts analyzed by immunoelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 3;553(1):40–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Seÿen H. G., Konings W. N. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles and chromatophoresis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Kaplan S. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriochlorophyll-containing protein from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2732–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. C., MARR A. G. LOCATION OF CHLOROPHYLL IN RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1402–1412. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1402-1412.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Charge shift electrophoresis: simple method for distinguishing between amphiphilic and hydrophilic proteins in detergent solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):529–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Dorpema J. W., Konings W. N. Transport of amino acids in membrane vesicles of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides energized by respiratory and cyclic electron flow. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):397–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. N., Holmes N. G., Jones O. T., Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. VII. Photochemical properties of a fraction enriched in newly synthesized bacteriochlorophyll a-protein complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 8;548(2):253–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lommen M. A., Takemoto J. Comparison, by freeze-fracture electron microscopy, of chromatophores, spheroplast-derived membrane vesicles, and whole cells of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):730–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.730-741.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K., Nishimura M. Sidedness of membrane structures in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Electrochemical titration of the spectrum changes of carotenoid in spheroplasts, spheroplast membrane vesicles and chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 11;459(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman R. A., Mallon D. E., Langan J. J. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. IV. Assembly of chromatophores in low-aeration cell suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 13;440(2):429–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J. Proteins exposed at the surface of chromatophores of Rhodospirillum rubrum: the orientation of isolated chromatophores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 2;509(3):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Antigenic architecture of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1422–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Molecular structure of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3148–3152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Antigenic and enzymatic architecture of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Membrane asymmetry and expression of cell surface antigens of Micrococcus lysodeikticus established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):974–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.974-985.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Baccarini-Melandri A., Hauska G. A., Melandri B. A., Crofts A. R. Asymmetry of an energy transducing membrane the location of cytochrome c2 in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 15;387(2):212–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer K., Austin L. A. Bacteriochlorophyll-protein complexes from the light-harvesting antenna of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):2011–2019. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P., Moyle J. The polarity of proton translocation in some photosynthetic microorganisms. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Apr;8(3):450–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Salton M. R. Antigenic analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1273–1288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1273-1288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A., Okamura M. Y., Lopes A. D., Moskowitz E., Feher G. Characterization of reaction centers from photosynthetic bacteria. II. Amino acid composition of the reaction center protein and its subunits in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides R-26. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 26;13(7):1403–1410. doi: 10.1021/bi00704a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto J., Bachmann R. C. Orientation of chromatophores and spheroplast-derived membrane vesicles of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: analysis by localization of enzyme activities. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jul;195(2):526–534. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90379-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]