Abstract
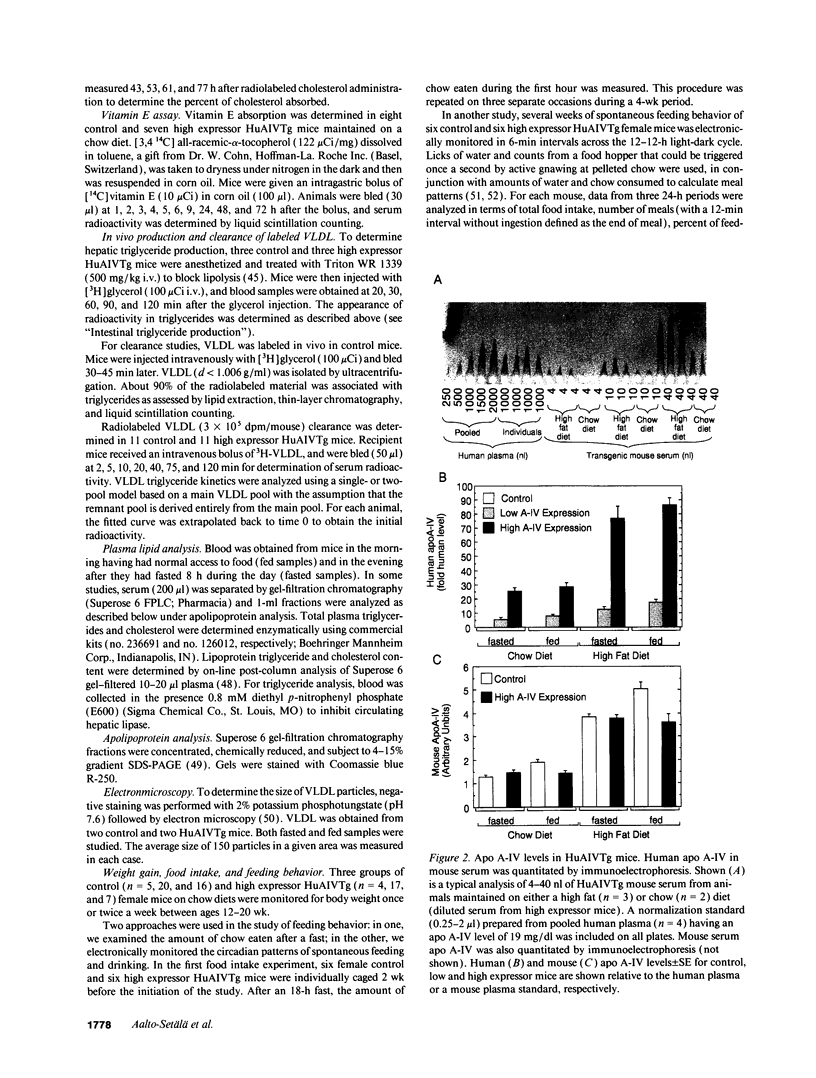
Two transgenic mouse lines, expressing low or high amounts of human apo A-IV were created. In low and high expressor HuAIVTg mice on a chow diet, serum human apo A-IV levels were 6 and 25 times the normal human level and on a high fat diet, they were 12 and 77 times higher. Human apo A-IV was equally distributed between lipoprotein (mainly HDL) and lipid-free fractions. Intestinal absorption of radiolabeled cholesterol and triglycerides was unaffected in HuAIVTg mice. Vitamin A, carried exclusively in chylomicrons and their remnants, was catabolized normally. When an intragastric vitamin E bolus is given to the HuAIVTg mice, the initial absorption and appearance in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins was similar to that observed in normal mice. However, elevated amounts of vitamin E were subsequently observed in the VLDL of the HuAIVTg mice. Furthermore, in the fed state, serum VLDL triglycerides were markedly elevated in HuAIVTg mice. This effect was greater in high expressor mice. Serum total cholesterol was not elevated, but the distribution was altered in the HuAIVTg mice; VLDL-C was increased at the expense of VLDL-C. Kinetic studies suggested a delayed clearance of VLDL in HuAIVTg mice. Apo A-IV has been suggested to be a satiety factor, but no effect on feeding behavior or weight gain was observed in these HuAIVTg mice. In summary, our studies with HuAIVTg mice show that additional apo A-IV does not effect intestinal absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins, and at least chronic elevation of plasma apo A-IV does not effect feeding behavior in this model system.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto-Setälä K., Fisher E. A., Chen X., Chajek-Shaul T., Hayek T., Zechner R., Walsh A., Ramakrishnan R., Ginsberg H. N., Breslow J. L. Mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia in human apolipoprotein (apo) CIII transgenic mice. Diminished very low density lipoprotein fractional catabolic rate associated with increased apo CIII and reduced apo E on the particles. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1889–1900. doi: 10.1172/JCI116066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agellon L. B., Walsh A., Hayek T., Moulin P., Jiang X. C., Shelanski S. A., Breslow J. L., Tall A. R. Reduced high density lipoprotein cholesterol in human cholesteryl ester transfer protein transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10796–10801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apfelbaum T. F., Davidson N. O., Glickman R. M. Apolipoprotein A-IV synthesis in rat intestine: regulation by dietary triglyceride. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):G662–G666. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.5.G662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Sachdev O. P., Lee E. S., Williams K. J., Blum C. B., Glickman R. M. Effect of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV among lipoproteins of human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Sachdev O. P., Megna L., Glickman R. M. Distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):11–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Siebenkas M. V., Williams K. J. Effects of apolipoproteins A-IV and A-I on the uptake of phospholipid liposomes by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):862–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Green M. H., Berg T., Norum K. R. Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):399–404. doi: 10.1126/science.2218545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammerman M., Sandkuijl L. A., Halaas J. L., Chung W., Breslow J. L. An apolipoprotein CIII haplotype protective against hypertriglyceridemia is specified by promoter and 3' untranslated region polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4562–4566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLamatre J. G., Hoffmeier C. A., Lacko A. G., Roheim P. S. Distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV between the lipoprotein and the lipoprotein-free fractions of rat plasma: possible role of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res. 1983 Dec;24(12):1578–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delamatre J. G., Roheim P. S. The response of apolipoprotein A-IV to cholesterol feeding in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 13;751(2):210–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dole V. P., Ho A., Gentry R. T. An improved technique for monitoring the drinking behavior of mice. Physiol Behav. 1983 Jun;30(6):971–974. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(83)90264-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Gorder N. L., Benson D. M., Gotto A. M., Jr Apolipoprotein A-IV. A determinant for binding and uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15714–15718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Mantulin W. W., Rohde M. F., Gotto A. M., Jr, Pownall H. J., Sherrill B. C. Conformational properties of human and rat apolipoprotein A-IV. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Boguski M. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. The nucleotide and derived amino acid sequence of human apolipoprotein A-IV mRNA and the close linkage of its gene to the genes of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):1998–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Paik Y. K., Boguski M. S., Freeman M., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Structure and expression of the human apolipoprotein A-IV gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7973–7981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Nordhausen R. W. Electron microscopy of negatively stained lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:442–457. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto K., Cardelli J. A., Tso P. Increased apolipoprotein A-IV in rat mesenteric lymph after lipid meal acts as a physiological signal for satiation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):G1002–G1006. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.6.G1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto K., Fukagawa K., Sakata T., Tso P. Suppression of food intake by apolipoprotein A-IV is mediated through the central nervous system in rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1830–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI116395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Krishnan S., Beigel Y., Gotto A. M., Jr Plasma metabolism of apolipoprotein A-IV in humans. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):813–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Scheraldi C. A., Yacoub L. K., Saxena U., Bisgaier C. L. Lipoprotein ApoC-II activation of lipoprotein lipase. Modulation by apolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4266–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W., Quinet E. Human apolipoprotein A-IV. Intestinal origin and distribution in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI109745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Lefkowitch J. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W., Quinet E., Blum C. B. Apolipoprotein localization and quantitation in the human intestine. Gastroenterology. 1982 Dec;83(6):1223–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Nutting D. F., Fujimoto K., Cardelli J. A., Black D., Tso P. Transport of lipid and apolipoproteins A-I and A-IV in intestinal lymph of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1613–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A., Chin A. Circadian feeding and drinking patterns of genetically obese mice fed solid chow diet. Physiol Behav. 1988;43(5):651–656. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(88)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingold K. U., Burton G. W., Foster D. O., Hughes L., Lindsay D. A., Webb A. Biokinetics of and discrimination between dietary RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols in the male rat. Lipids. 1987 Mar;22(3):163–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02537297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K. Apolipoprotein multigene family: tandem organization of human apolipoprotein AI, CIII, and AIV genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Ferris E., Haddad I. A. DNA inversion within the apolipoproteins AI/CIII/AIV-encoding gene cluster of certain patients with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7198–7202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Norum R. A., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. An inherited polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein A-I gene locus related to the development of atherosclerosis. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):718–720. doi: 10.1038/301718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Oettgen P., Haddad I. A., Antonarakis S. E. Structure, evolution, and polymorphisms of the human apolipoprotein A4 gene (APOA4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Yunis I., Zannis V. I. Structure, evolution, and tissue-specific synthesis of human apolipoprotein AIV. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3962–3970. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. A DNA insertion in the apolipoprotein A-I gene of patients with premature atherosclerosis. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):823–825. doi: 10.1038/305823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayden H. J., Traber M. G. Absorption, lipoprotein transport, and regulation of plasma concentrations of vitamin E in humans. J Lipid Res. 1993 Mar;34(3):343–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieft K. A., Bocan T. M., Krause B. R. Rapid on-line determination of cholesterol distribution among plasma lipoproteins after high-performance gel filtration chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1991 May;32(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrost L., Gambert P., Meunier S., Morgado P., Desgres J., d'Athis P., Lallemant C. Correlation between apolipoprotein A-IV and triglyceride concentrations in human sera. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre M., Roheim P. S. Metabolism of apolipoprotein A-IV. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1603–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Castle C. K., Murray R. W., Rehberg E. F., Polites H. G., Melchior G. W. The role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in primate apolipoprotein A-I metabolism. Insights from studies with transgenic mice. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Jun;12(6):736–744. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum R. A., Lakier J. B., Goldstein S., Angel A., Goldberg R. B., Block W. D., Noffze D. K., Dolphin P. J., Edelglass J., Bogorad D. D. Familial deficiency of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III and precocious coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 24;306(25):1513–1519. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206243062503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas J. M., Cassidy D. K., Civeira F., Bisgaier C. L., Schaefer E. J. Familial apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, and A-IV deficiency and premature atherosclerosis due to deletion of a gene complex on chromosome 11. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16339–16342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Hagiwara K., Arai H., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of the alpha-tocopherol transfer protein from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80999-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seishima M., Bisgaier C. L., Davies S. L., Glickman R. M. Regulation of hepatic apolipoprotein synthesis in the 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol-treated rat. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jun;32(6):941–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seishima M., Noma A., Torizawa H., Muto Y. Changes of serum apolipoprotein levels after oral administration of fat in human subjects. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Sep;73(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. R., Weinberg R. B. Serum apolipoprotein A-IV and lipoprotein cholesterol in patients undergoing total parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1988 Aug;95(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Katsuki M., Shimada M., Gotoda T., Harada K., Murase T., Fukazawa C., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Overexpression of apolipoprotein E in transgenic mice: marked reduction in plasma lipoproteins except high density lipoprotein and resistance against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1750–1754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Katsuki M., Yamamoto K., Gotoda T., Harada K., Shimada M., Yazaki Y. Plasma lipoprotein metabolism in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein E. Accelerated clearance of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2084–2091. doi: 10.1172/JCI116091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y., Lefevre M., Roheim P. S. The role of apolipoprotein A-IV in reverse cholesterol transport studied with cultured cells and liposomes derived from an ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 14;878(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Utermann G. Activation of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase by human apolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2258–2264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Burton G. W., Hughes L., Ingold K. U., Hidaka H., Malloy M., Kane J., Hyams J., Kayden H. J. Discrimination between forms of vitamin E by humans with and without genetic abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1171–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Burton G. W., Ingold K. U., Kayden H. J. RRR- and SRR-alpha-tocopherols are secreted without discrimination in human chylomicrons, but RRR-alpha-tocopherol is preferentially secreted in very low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Rudel L. L., Burton G. W., Hughes L., Ingold K. U., Kayden H. J. Nascent VLDL from liver perfusions of cynomolgus monkeys are preferentially enriched in RRR- compared with SRR-alpha-tocopherol: studies using deuterated tocopherols. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):687–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Sokol R. J., Kohlschütter A., Yokota T., Muller D. P., Dufour R., Kayden H. J. Impaired discrimination between stereoisomers of alpha-tocopherol in patients with familial isolated vitamin E deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1993 Feb;34(2):201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Beisiegel U. Apolipoprotein A-IV: a protein occurring in human mesenteric lymph chylomicrons and free in plasma. Isolation and quantification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh A., Azrolan N., Wang K., Marcigliano A., O'Connell A., Breslow J. L. Intestinal expression of the human apoA-I gene in transgenic mice is controlled by a DNA region 3' to the gene in the promoter of the adjacent convergently transcribed apoC-III gene. J Lipid Res. 1993 Apr;34(4):617–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh A., Ito Y., Breslow J. L. High levels of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice result in increased plasma levels of small high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles comparable to human HDL3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6488–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Dantzker C., Patton C. S. Sensitivity of serum apolipoprotein A-IV levels to changes in dietary fat content. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jan;98(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91285-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Scanu A. M. Isolation and characterization of human apolipoprotein A-IV from lipoprotein-depleted serum. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):52–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Spector M. S. The self-association of human apolipoprotein A-IV. Evidence for an in vivo circulating dimeric form. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14279–14286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub M. S., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L. Different patterns of postprandial lipoprotein metabolism in normal, type IIa, type III, and type IV hyperlipoproteinemic individuals. Effects of treatment with cholestyramine and gemfibrozil. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1110–1119. doi: 10.1172/JCI112926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Bruckheimer S. M., Lusis A. J., LeBoeuf R. C., Kinniburgh A. J. Mouse apolipoprotein A-IV gene: nucleotide sequence and induction by a high-lipid diet. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3807–3814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Yusin M., Ren I., Kuhlenkamp J., Hirano T., Stolz A., Kaplowitz N. Identification, purification, and immunochemical characterization of a tocopherol-binding protein in rat liver cytosol. J Lipid Res. 1992 Mar;33(3):343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. A single blood sample dual isotope method for the measurement of cholesterol absorption in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):862–865. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]