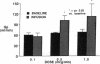Abstract
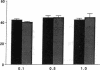
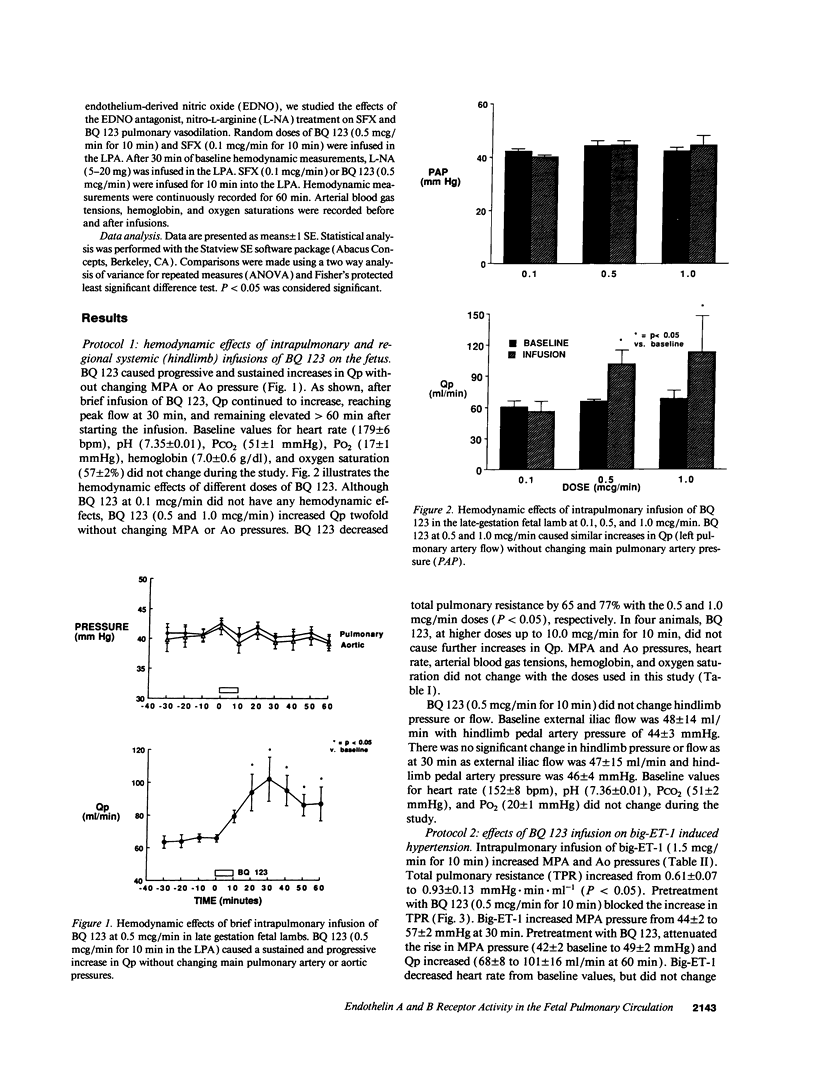
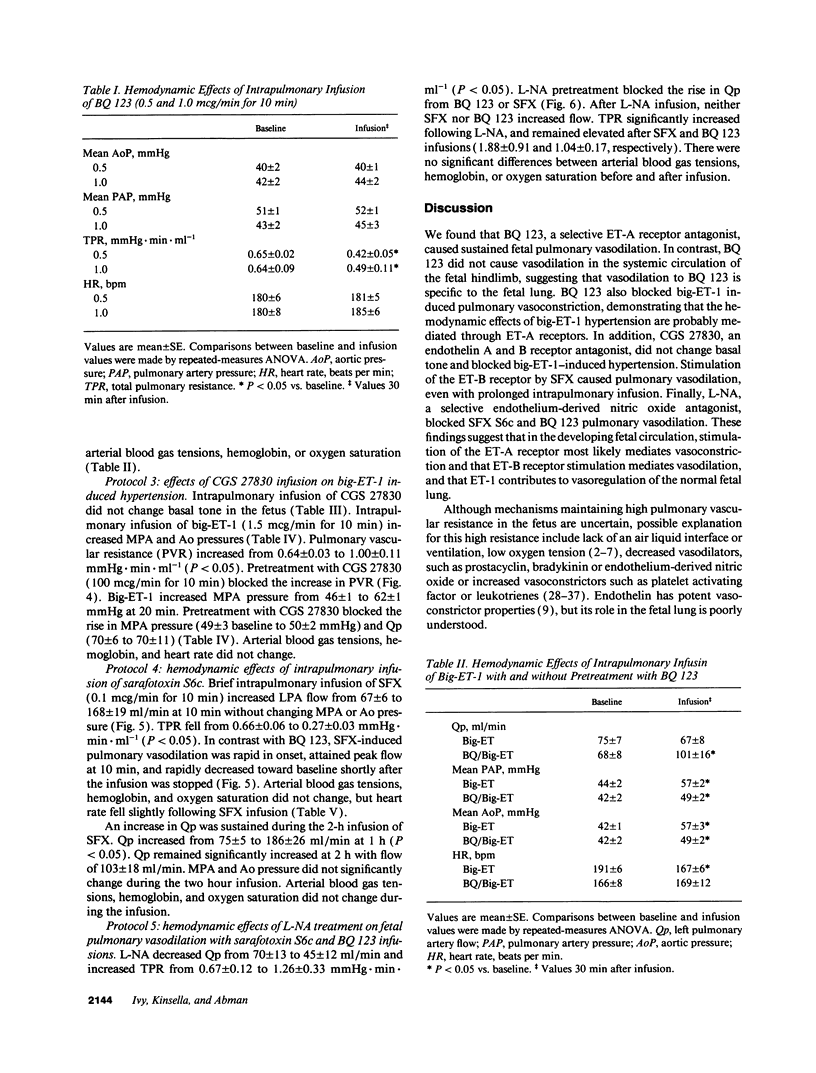
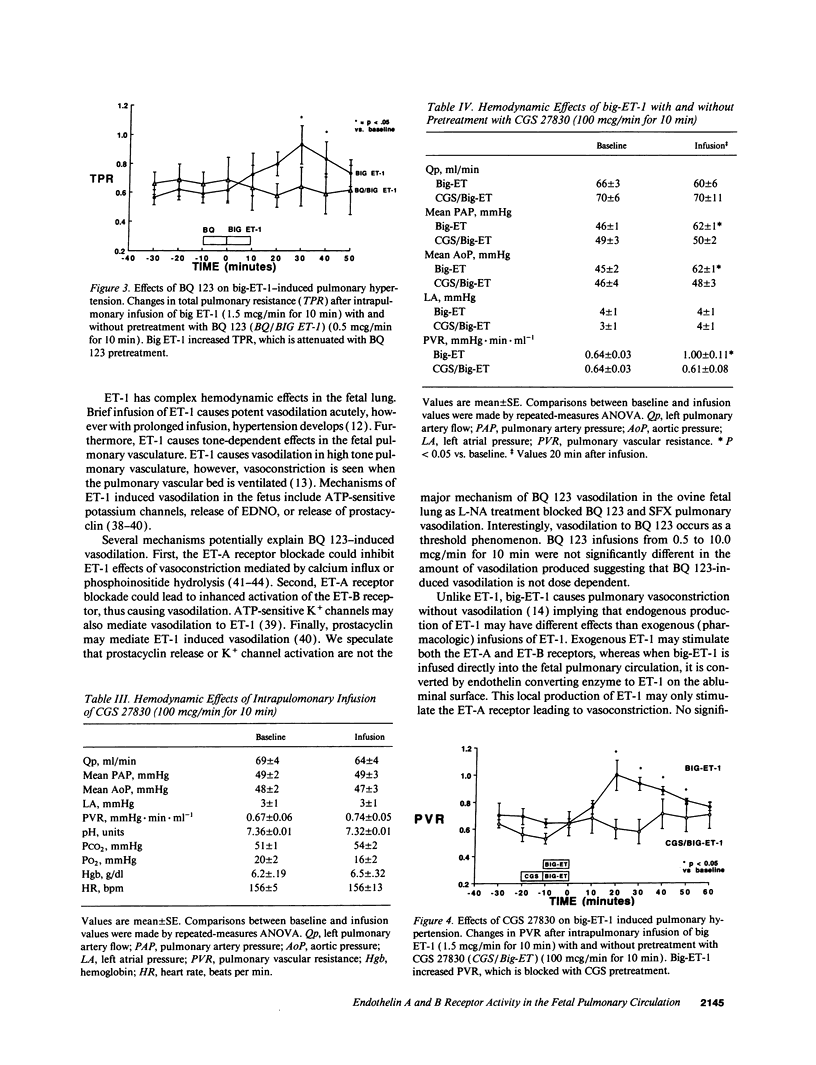
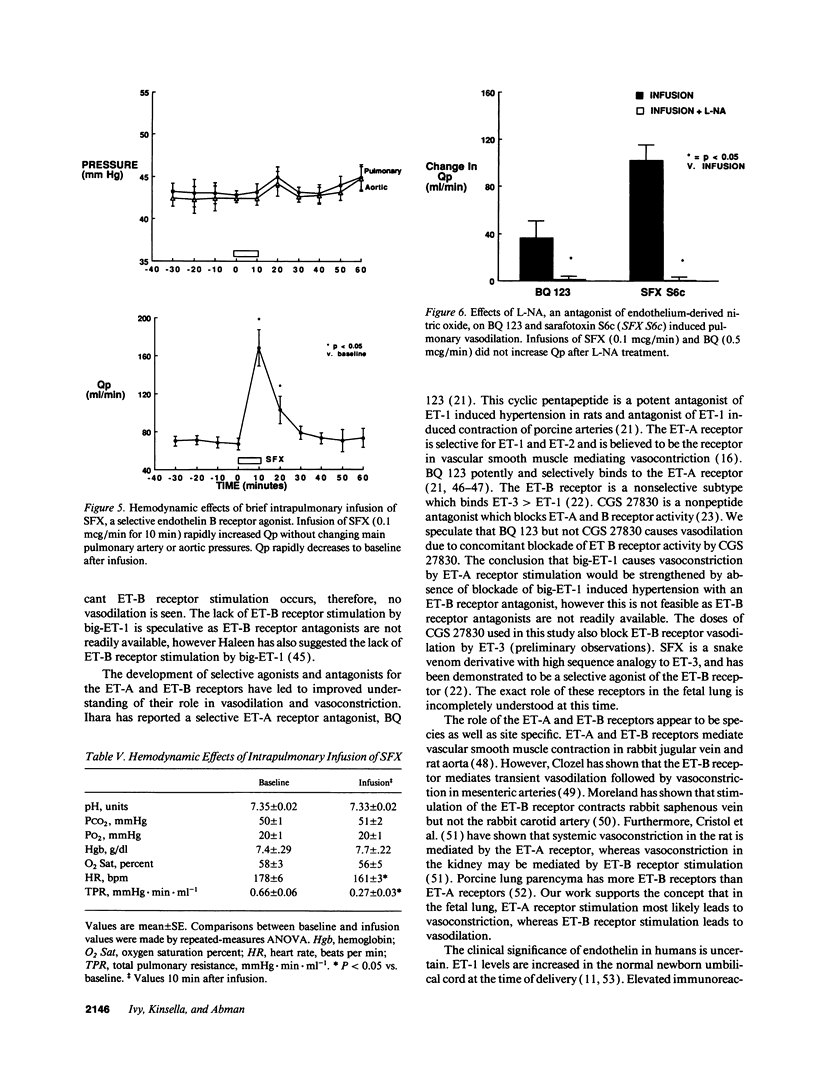
To determine the potential contribution of endothelin (ET) to modulation of high pulmonary vascular resistance in the normal fetus, we studied the effects of BQ 123, a selective ET-A receptor antagonist, and sarafoxotoxin S6c (SFX), a selective ET-B receptor agonist, in 31 chronically prepared late gestation fetal lambs. Brief intrapulmonary infusions of BQ 123 (0.1-1.0 mcg/min for 10 min) caused sustained increases in left pulmonary artery flow (Qp) without changing main pulmonary artery (MPA) and aortic (Ao) pressures. In contrast, BQ 123 did not change vascular resistance in a regional systemic circulation (the fetal hindlimb). To determine whether big-endothelin-1 (big-ET-1)-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction is mediated by ET-A receptor stimulation, we studied the effects of big-ET-1 with or without pretreatment with BQ 123. BQ 123 (0.5 mcg/min for 10 min) blocked the rise in total pulmonary resistance caused by big-ET-1. CGS 27830 (100 mcg/min for 10 min), an ET-A and -B receptor antagonist, did not change basal tone but blocked big-ET-1-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction. Brief and prolonged intrapulmonary infusion of SFX (0.1 mcg/min for 10 min) increased Qp twofold without changing MPA or Ao pressures. Nitro-L-arginine (L-NA), a selective endothelium-derived nitric oxide (EDNO) antagonist, blocked vasodilation caused by BQ 123 and SFX. We conclude that: (a) BQ 123 causes sustained fetal pulmonary vasodilation, but did not change vascular resistance in the fetal hindlimb; (b) Big-ET-1-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction may be mediated through ET-A receptor stimulation; and (c) ET-B receptor stimulation causes pulmonary vasodilation through EDNO release. These findings support the hypothesis that endothelin may play a role in modulation of high basal pulmonary vascular resistance in the normal fetus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abman S. H., Stenmark K. R. Changes in lung eicosanoid content during normal and abnormal transition in perinatal lambs. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):L214–L222. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.2.L214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abman S. H., Wilkening R. B., Ward R. M., Accurso F. J. Adaptation of fetal pulmonary blood flow to local infusion of tolazoline. Pediatr Res. 1986 Nov;20(11):1131–1135. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198611000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. W., Chatfield B. A., Koppenhafer S. A., Schaffer M. S., Wolfe R. R., Abman S. H. Circulating immunoreactive endothelin-1 in children with pulmonary hypertension. Association with acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Aug;148(2):519–522. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assali N. S., Johnson G. H., Brinkman C. R., 3rd, Huntsman D. J. Effects of bradykinin on the fetal circulation. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASSIN S., DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., ROSS B. B., STRANG L. B. THE VASCULAR RESISTANCE OF THE FOETAL AND NEWLY VENTILATED LUNG OF THE LAMB. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:61–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASSIN S., DAWES G. S., ROSS B. B. PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW AND VASCULAR RESISTANCE IN IMMATURE FOETAL LAMBS. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:80–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacoub P., Dorent R., Maistre G., Nataf P., Carayon A., Piette C., Godeau P., Cabrol C., Gandjbakhch I. Endothelin-1 in primary pulmonary hypertension and the Eisenmenger syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Feb 15;71(5):448–450. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90452-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. G., Dawes G. S., Fishman A. P., Hyman A. I., Perks A. M. The release of a bradykinin-like pulmonary vasodilator substance in foetal and new-born lambs. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):83–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassin S., Kristova V., Davis T., Kadowitz P., Gause G. Tone-dependent responses to endothelin in the isolated perfused fetal sheep pulmonary circulation in situ. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Mar;70(3):1228–1234. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.3.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield B. A., McMurtry I. F., Hall S. L., Abman S. H. Hemodynamic effects of endothelin-1 on ovine fetal pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):R182–R187. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.261.1.R182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi C. L., Neale R. F., Jr, Jackson R. H., Sills M. A. Characterization of rat lung endothelin receptor subtypes which are coupled to phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):611–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clozel M., Gray G. A., Breu V., Löffler B. M., Osterwalder R. The endothelin ETB receptor mediates both vasodilation and vasoconstriction in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90826-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristol J. P., Warner T. D., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Mediation via different receptors of the vasoconstrictor effects of endothelins and sarafotoxins in the systemic circulation and renal vasculature of the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):776–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., Télémaque S., Claing A., Ihara M., Yano M. Human big-endothelin-1 and endothelin-1 release prostacyclin via the activation of ET1 receptors in the rat perfused lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):773–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., WIDDICOMBE J. G., WYATT D. G. Changes in the lungs of the new-born lamb. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):141–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. Pulmonary hemodynamics at birth: effect of acute cyclooxygenase inhibition in lambs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Apr;64(4):1676–1682. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.4.1676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhörning G., Adams F. H., Norman A. Effect of lung expansion on the fetal lamb circulation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966 Sep;55(5):441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb15234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine does not inhibit the hindquarters vasodilator action of endothelin-1 in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 21;171(2-3):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haleen S. J., Davis L. S., LaDouceur D. M., Keiser J. A. Why big endothelin-1 lacks a vasodilator response. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S271–S273. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma K., Rodman D. M., O'Brien R. F., McMurtry I. F. Endothelin 1 causes pulmonary vasodilation in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):H48–H54. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.1.H48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M., Nies A. S., Melmon K. L. Bradykinin production associated with oxygenation of the fetal lamb. Circ Res. 1969 Nov;25(5):521–534. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.5.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Emori T., Eguchi S., Kanno K., Imai T., Ohta K., Marumo F. Endothelin receptor subtype B mediates synthesis of nitric oxide by cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1367–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI116338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Ishikawa K., Fukuroda T., Saeki T., Funabashi K., Fukami T., Suda H., Yano M. In vitro biological profile of a highly potent novel endothelin (ET) antagonist BQ-123 selective for the ETA receptor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20 (Suppl 12):S11–S14. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199204002-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Isozaki-Fukuda Y., Takedatsu M., Hirata Y., Kobayashi Y. Circulating levels of endothelin and atrial natriuretic factor during postnatal life. Acta Paediatr. 1992 Sep;81(9):676–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Hessler J. R., Green R. S. Mechanism of stimulation of pulmonary prostacyclin synthesis at birth. Prostaglandins. 1984 Dec;28(6):877–887. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Hessler J. R., Green R. S. The onset of breathing at birth stimulates pulmonary vascular prostacyclin synthesis. Pediatr Res. 1984 Oct;18(10):938–942. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198410000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Tyler T. L., Cassin S. Effect of indomethacin on pulmonary vascular response to ventilation of fetal goats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):H346–H351. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.4.H346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. B., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Gestational changes in pulmonary vascular responses in fetal lambs in utero. Circ Res. 1976 Oct;39(4):536–541. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.4.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock J. E., Hamilton F., Luide H., Coceani F., Olley P. M. Direct pulmonary vascular responses in the conscious newborn lamb. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Jan;48(1):188–196. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCumber M. W., Ross C. A., Glaser B. M., Snyder S. H. Endothelin: visualization of mRNAs by in situ hybridization provides evidence for local action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7285–7289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Kimura S., Yanagisawa M., Goto K. Molecular and cellular mechanism of endothelin regulation. Implications for vascular function. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1457–1468. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. C., Pelton J. T., Huggins J. P. Endothelins--from receptors to medicine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Feb;14(2):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90031-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkes R. K., MacMillan L. A., Bellan J. A., Kerstein M. D., McNamara D. B., Kadowitz P. J. Analysis of regional responses to endothelin in hindquarters vascular bed of cats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H598–H602. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland S., McMullen D. M., Delaney C. L., Lee V. G., Hunt J. T. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin F. C., 3rd, Egan E. A., Ferguson W., Lundgren C. E. Development of pulmonary vascular response to oxygen. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):H542–H546. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.3.H542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin F. C., 3rd, Egan E. A., Norfleet W. T. Indomethacin does not diminish the pulmonary vascular response of the fetus to increased oxygen tension. Pediatr Res. 1988 Dec;24(6):696–700. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198812000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamichi K., Ihara M., Kobayashi M., Saeki T., Ishikawa K., Yano M. Different distribution of endothelin receptor subtypes in pulmonary tissues revealed by the novel selective ligands BQ-123 and [Ala1,3,11,15]ET-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 15;182(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Kasai K., Konuma S., Emoto T., Banba N., Ishikawa M., Shimoda S. Immunoreactive endothelin concentrations in maternal and fetal blood. Life Sci. 1990;46(15):1045–1050. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90412-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. A., Kennaugh J., Koppenhafer S. L., Loomis M., Chatfield B. A., Abman S. H. Elevated immunoreactive endothelin-1 levels in newborn infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr. 1993 Jul;123(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shetty S. S., Okada T., Webb R. L., DelGrande D., Lappe R. W. Functionally distinct endothelin B receptors in vascular endothelium and smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):459–464. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soifer S. J., Loitz R. D., Roman C., Heymann M. A. Leukotriene end organ antagonists increase pulmonary blood flow in fetal lambs. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):H570–H576. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.3.H570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Inagami T., Hare G. M., Johns J. A. Endothelin action: Inhibition by a protein kinase C inhibitor and involvement of phosphoinositols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Cannon T. R., Mundin J. W., White D. G., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth muscle contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):858–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tod M. L., Cassin S. Endothelin-1-induced pulmonary arterial dilation is reduced by N omega-nitro-L-arginine in fetal lambs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 May;72(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.5.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tod M. L., Yoshimura K., Rubin L. J. Indomethacin prevents ventilation-induced decreases in pulmonary vascular resistance of the middle region in fetal lambs. Pediatr Res. 1991 May;29(5):449–454. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199105010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Renterghem C., Vigne P., Barhanin J., Schmid-Alliana A., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of action of the vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):977–985. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. M., Ritchie B. C., Adamson T. M., Maloney J. E. Effect of changing lung liquid volume on the pulmonary circulation of fetal lambs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jan;64(1):61–67. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkening R. B., Boyle D. W., Meschia G. Measurement of blood flow and oxygen consumption in the pelvic limb of fetal sheep. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1988 Apr;187(4):498–505. doi: 10.3181/00379727-187-42695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Jones K. L., Pettibone D. J., Lis E. V., Clineschmidt B. V. Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]