Abstract
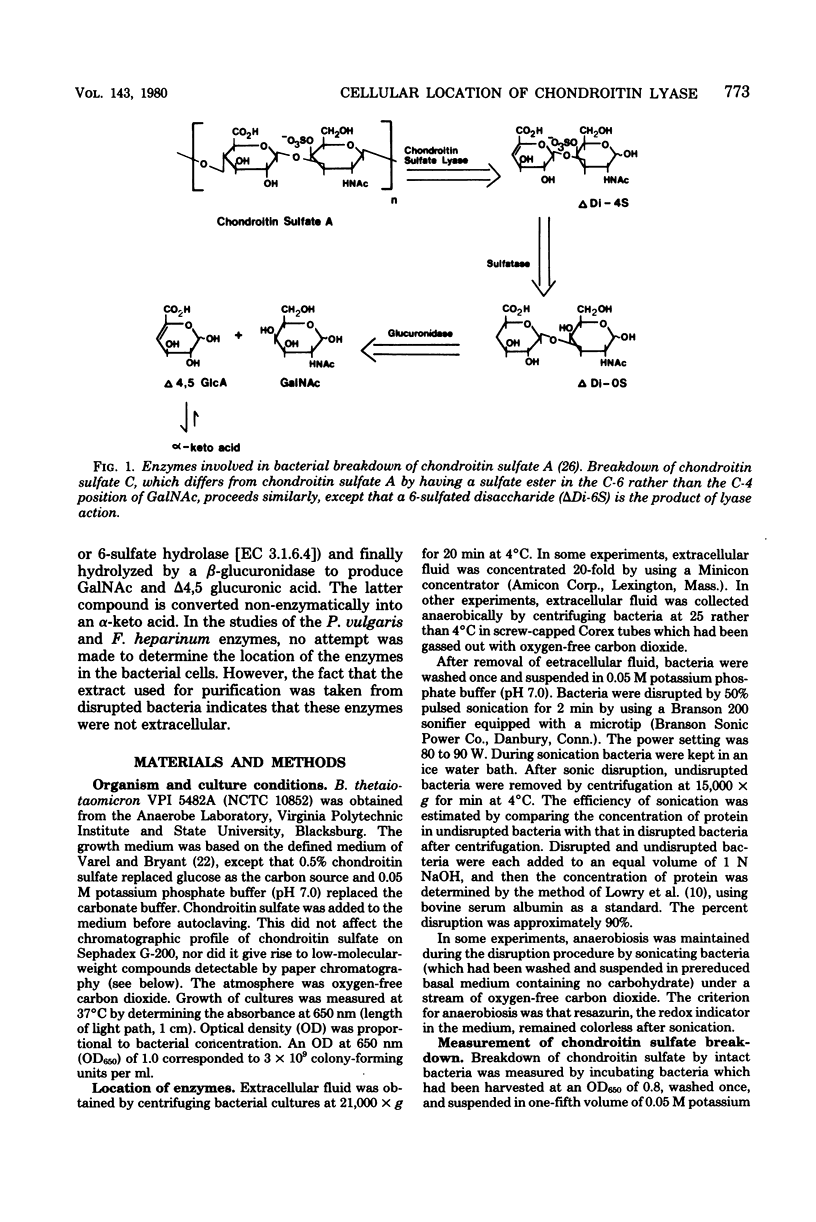
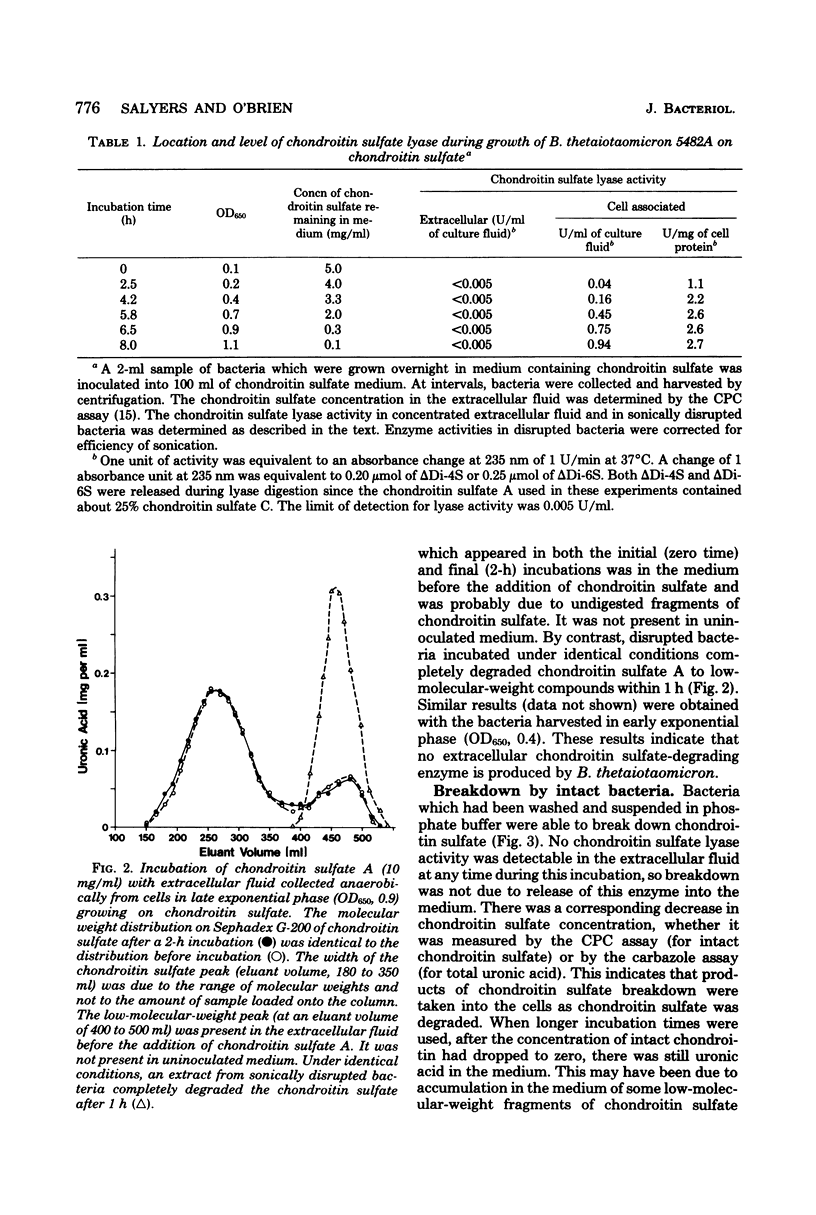
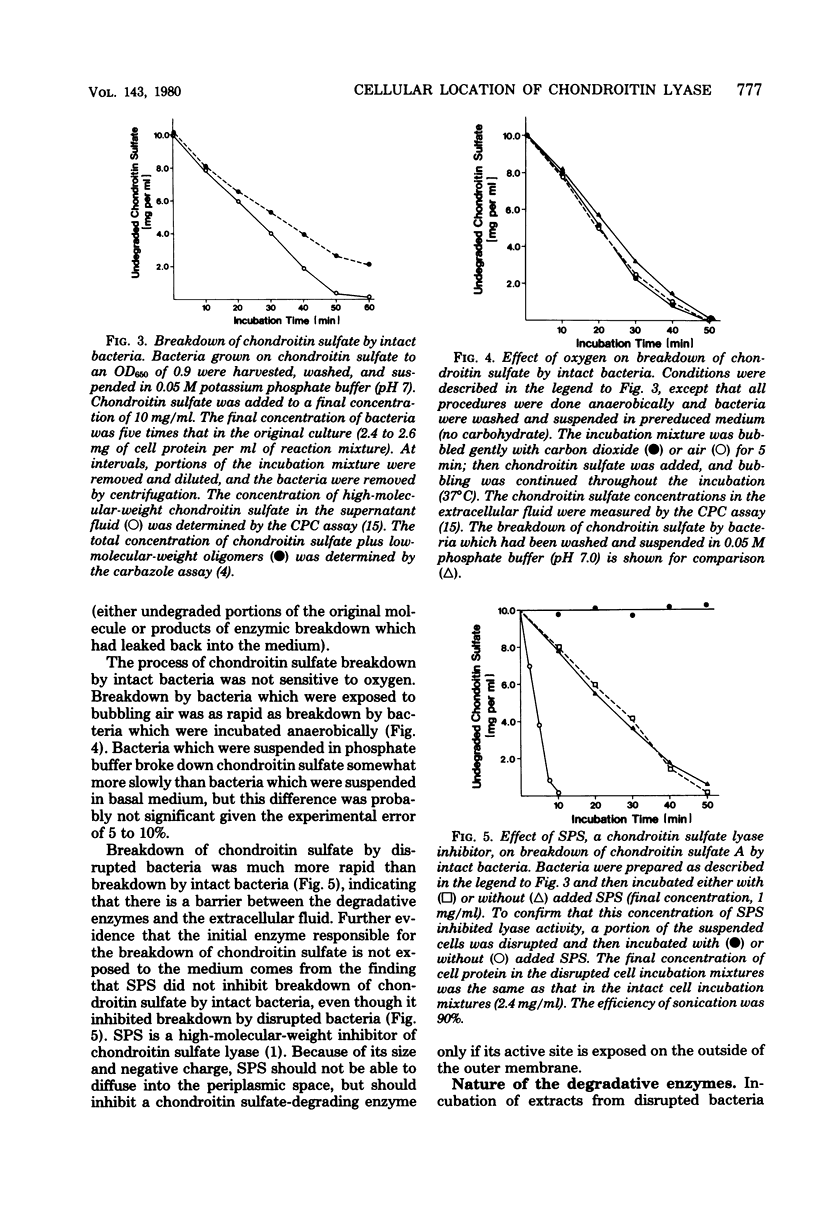
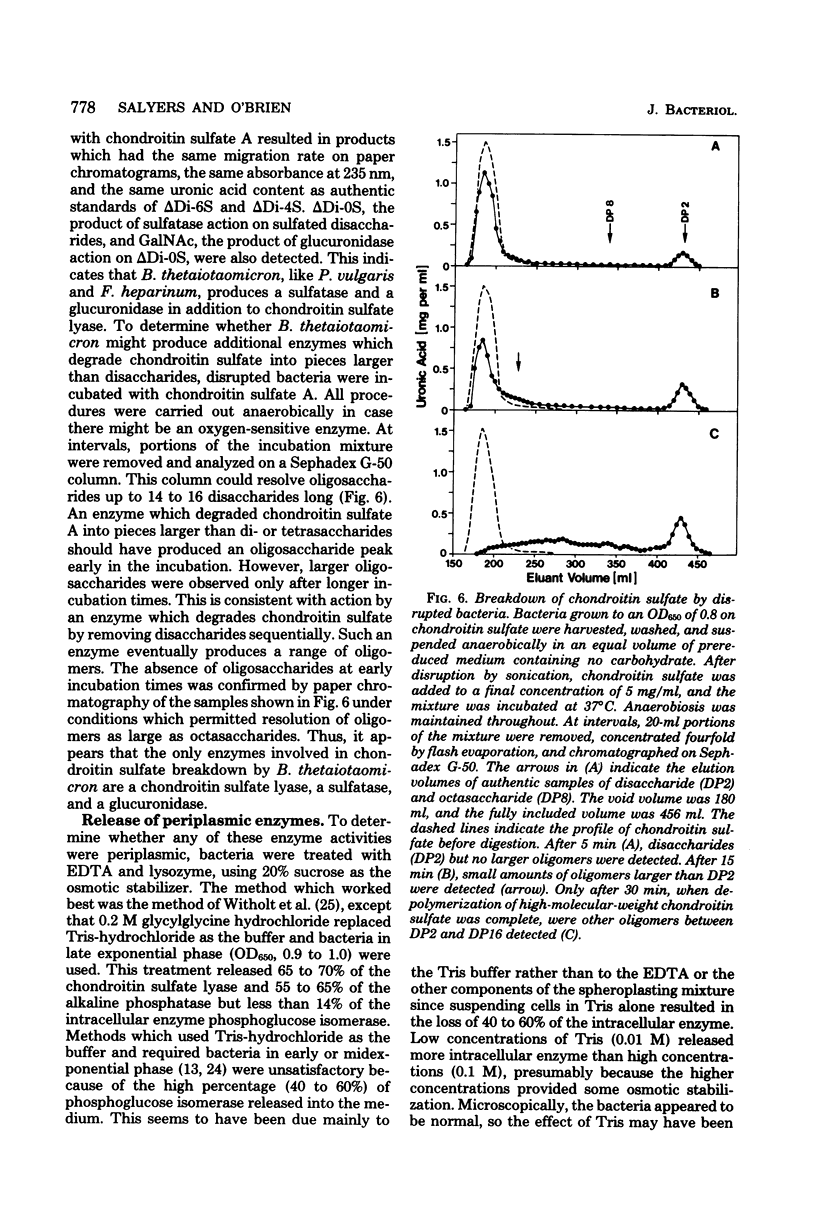
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, a gram-negative anaerobe found in human colons, could utilize chondroitin sulfate, a tissue mucopolysaccharide, as its sole source of carbohydrate. The enzymes responsible for the breakdown of chondroitin sulfate by B. thetaiotaomicron were similar to those produced by Proteus vulgaris and Flavobacterium heparinum and included a lyase (EC 4.2.2.4), which degraded chondroitin sulfate into sulfated disaccharides, sulfatases (EC 3.1.6.4), which removed the sulfate residues, and a glucuronidase, which broke the unsulfated disaccharides into monosaccharide components. Chondroitin sulfate lyase, the first enzyme in the breakdown sequence, was not extracellular. It appeared to be located in the periplasmic space since lyase activity was released by treatment with ethylenediaminetetraacetate and lysozyme. Moreover, sodium polyanethole sulfonate, a high-molecular-weight inhibitor of chondroitin lyase, did not inhibit breakdown of chondroitin sulfate by intact bacteria. The sulfatase and glucuronidase appeared to be intracellular. None of these enzymes was strongly bound to membranes, and none of the steps in the breakdown of chondroitin sulfate was sensitive to oxygen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Silbert J. E. Copolymers of chondroitin 4-sulfate and chondroitin 6-sulfate in chick embryo epiphyses and other cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7646–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Hök M. Glycosaminoglycans and their binding to biological macromolecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:385–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEIGER A. [Separation of simple sugars on cellulose lavers]. J Chromatogr. 1962 Nov;9:374–376. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Yamagata T., Suzuki S. Enzymatic methods for the determination of small quantities of isomeric chondroitin sulfates. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A. Energy sources of major intestinal fermentative anaerobes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):158–163. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Kotarski S. F. Induction of chondroitin sulfate lyase activity in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):781–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.781-788.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Palmer J. K., Wilkins T. D. Laminarinase (beta-glucanase) activity in Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1118-1124.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P. Nutritional features of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.251-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. A method for the determination of the molecular weight and molecular-weight distribution of chondroitin sulphate. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Protoplast formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):668–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.668-670.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witholt B., Boekhout M., Brock M., Kingma J., Heerikhuizen H. V., Leij L. D. An efficient and reproducible procedure for the formation of spheroplasts from variously grown Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jul;74(1):160–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


