Abstract
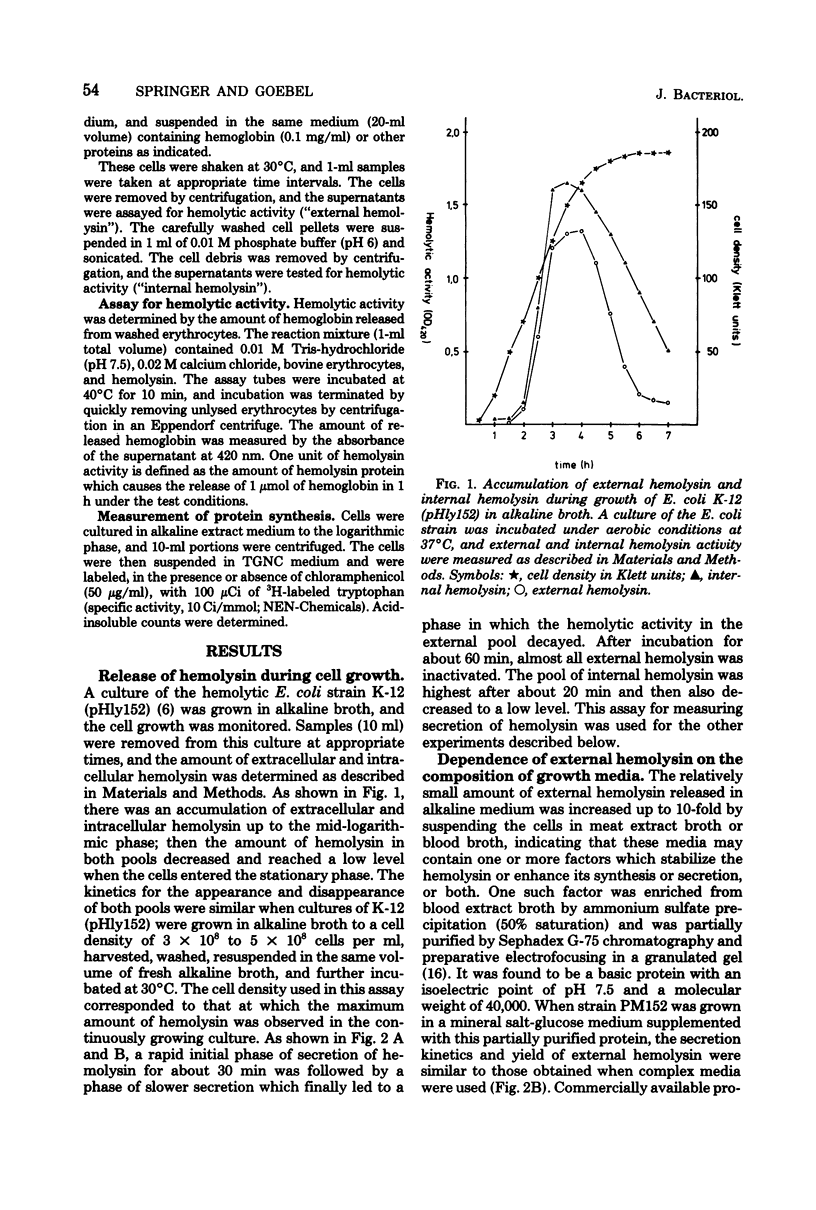
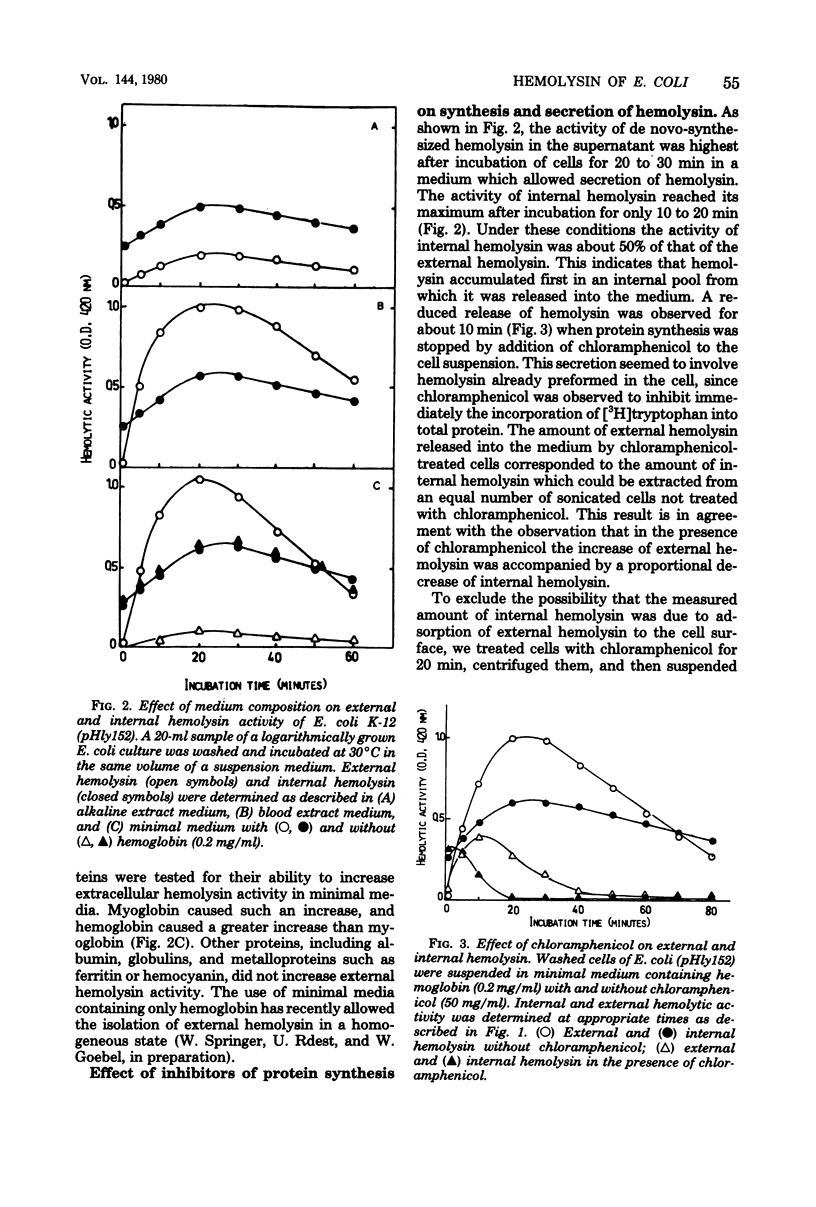
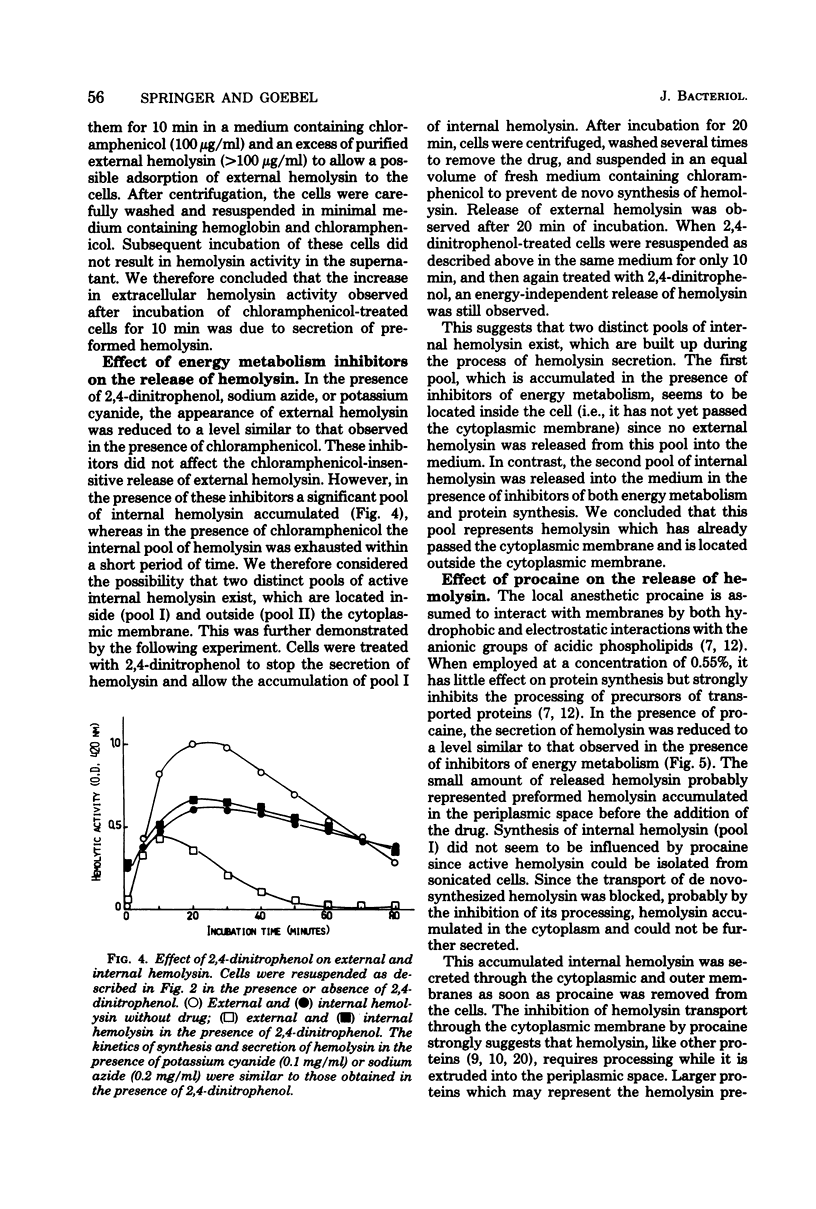
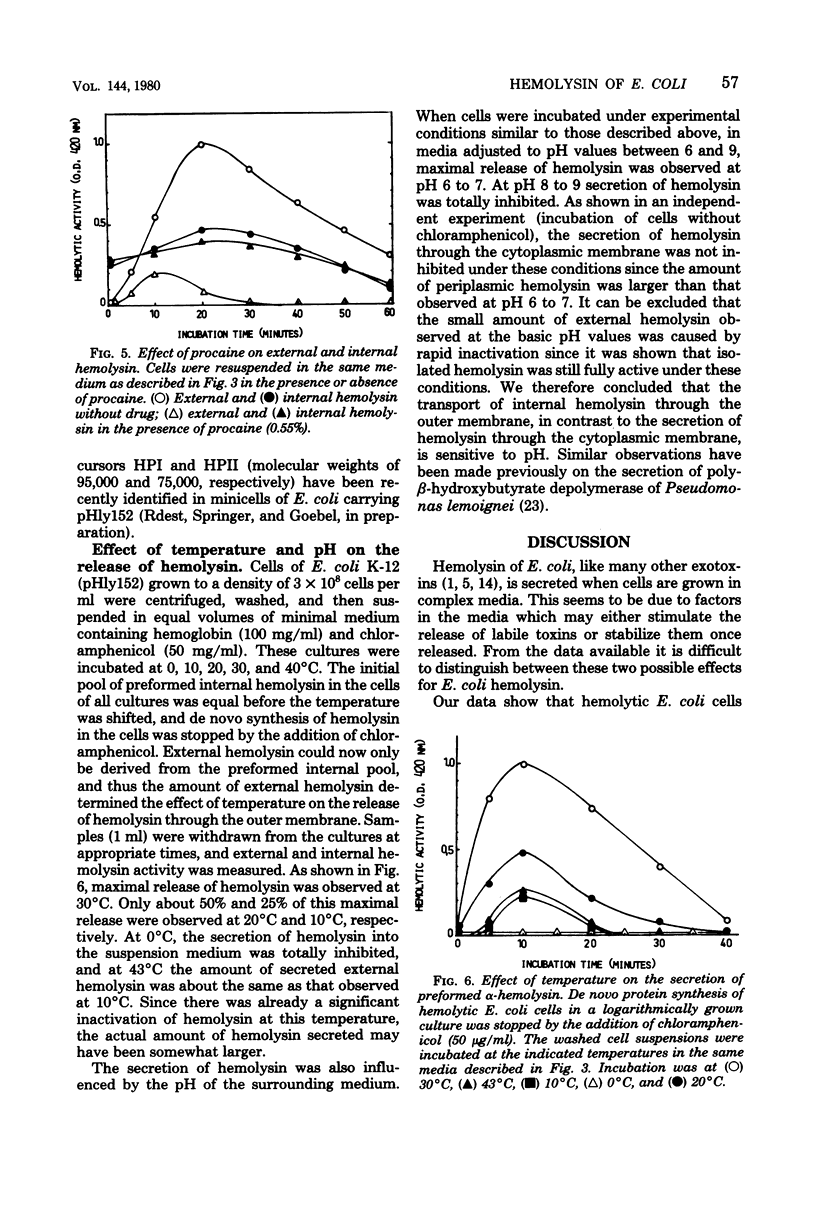
Hemolytic Escherichia coli cells were found to synthesize and secrete significant amounts of hemolysin into a mineral salt-glucose medium containing hemoglobin. The release of de novo-synthesized hemolysin was stopped in the presence of energy metabolism inhibitors such as 2,4-dinitrophenol, sodium azide, or potassium cyanide, resulting in an accumulation of intracellular hemolysin. A similar effect was observed in the presence of procaine, a neuroactive drug which inhibits the processing of exoproteins. Small amounts of hemolysin were secreted into the medium within approximately 10 min of inhibition of protein synthesis by chloramphenicol. This represented the final release of preformed periplasmic hemolysin en route to secretion through the outer membrane and was not caused by adsorption of external hemolysin to the cell surface. This secretion was not energy dependent but was inhibited above pH 8 and at low temperatures (10 to 20 degrees C). We concluded that two transport processes are involved in hemolysin secretion. De novo-synthesized hemolysin is extruded by an energy-dependent process through the cytoplasmic membrane and probably requires processing. In the periplasmic space a small internal pool of preformed hemolysin is accumulated temporarily before being transported through the outer membrane. Release of hemolysin through the outer membrane does not require energy or de novo protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CITRI N., GARBER N., SELA M. The effect of urea and guanidine hydrochloride on activity and optical rotation of penicillinase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3454–3459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Bayer M. E. Membrane-bound enterotoxin of Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):381–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayda R. C., Henderson G. W., Markovitz A. Neuroactive drugs inhibit trypsin and outer membrane protein processing in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Royer-Pokora B., Lindenmaier W., Bujard H. Plasmids controlling synthesis of hemolysin in Escherichia coli: molecular properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.964-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Beckwith J. Synthesis and processing of an Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase precursor in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1440–1444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen S. E., Short E. C., Jr, kurtz H. J., Mussen H. K., Wu G. K. Studies on the origin of the alpha-haemolysin produced by Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):173–189. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G., Wickner W. Translational and post-translational cleavage of M13 procoat protein: extracts of both the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli contain leader peptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):236–240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Rdest U., Springer W., Goebel W. Plasmid cistrons controlling synthesis and excretion of the exotoxin alpha-haemolysin of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00397234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radola B. J. Isoelectric focusing in layers of granulated gels. I. Thin-layer isoelectric focusing of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 21;295(2):412–428. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Synthesis of exported proteins by membrane-bound polysomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Synthesis of exported proteins by membrane-bound polysomes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Arbuthnott J. P. Partial characterisation of Escherichia coli haemolysin. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. The haemolysins of Escherichia coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:197–211. doi: 10.1002/path.1700850119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Lampen J. O. A mechanism for penicillinasesecretion in Bacillus licheniformis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):962–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa J., Inouye S., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Precursors of major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1126–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short E. C., Kurtz H. J. Properties of the Hemolytic Activities of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):678–687. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.678-687.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Merrick J. M. Extracellular enzyme secretion by Pseudomonas lemoignei. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.152-161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


