Abstract
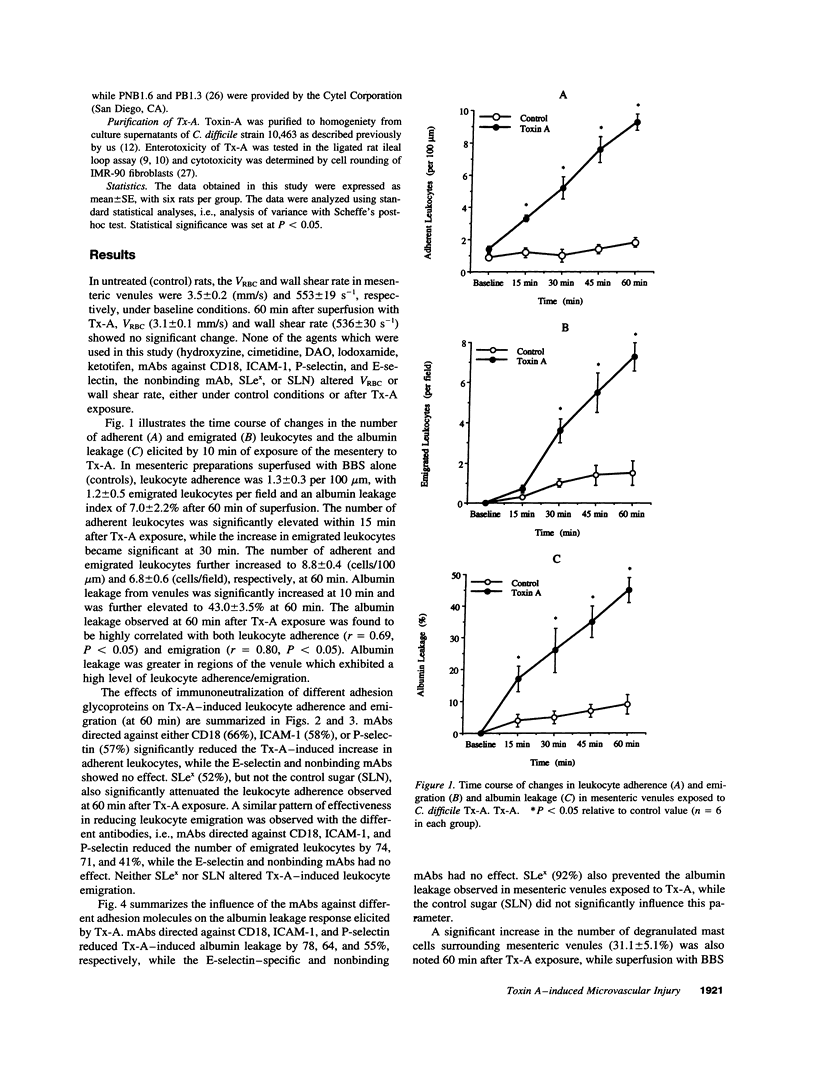
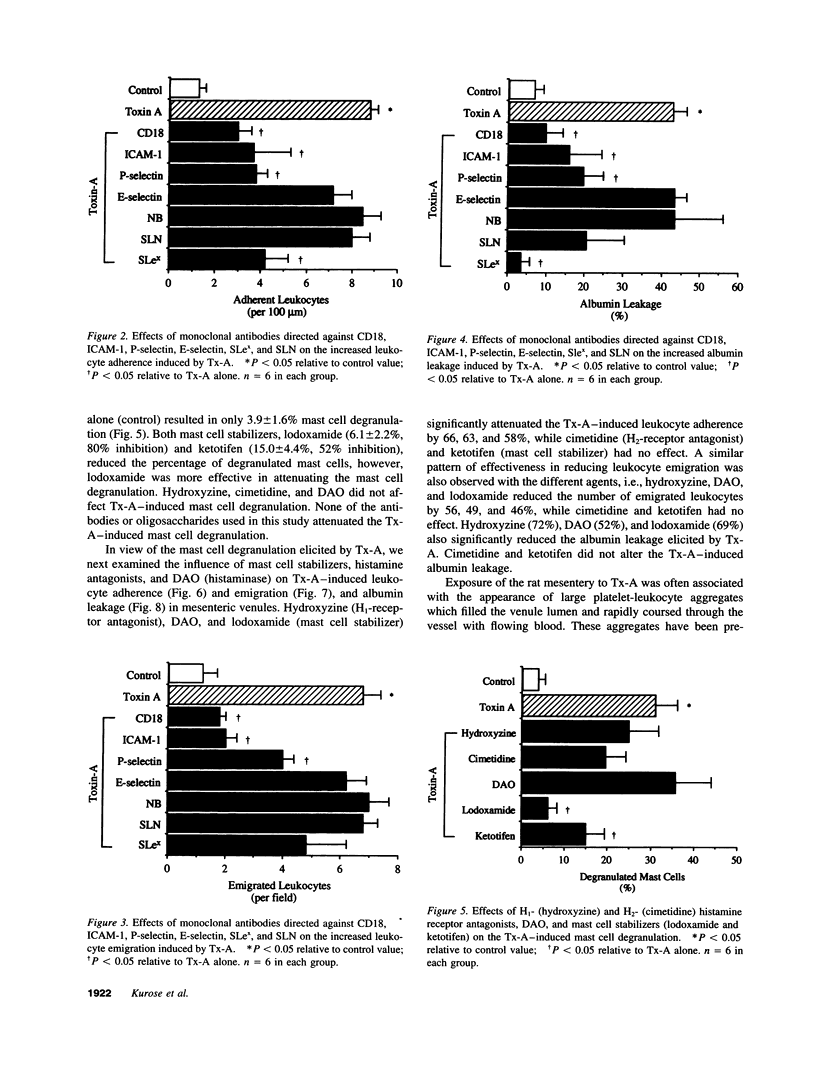
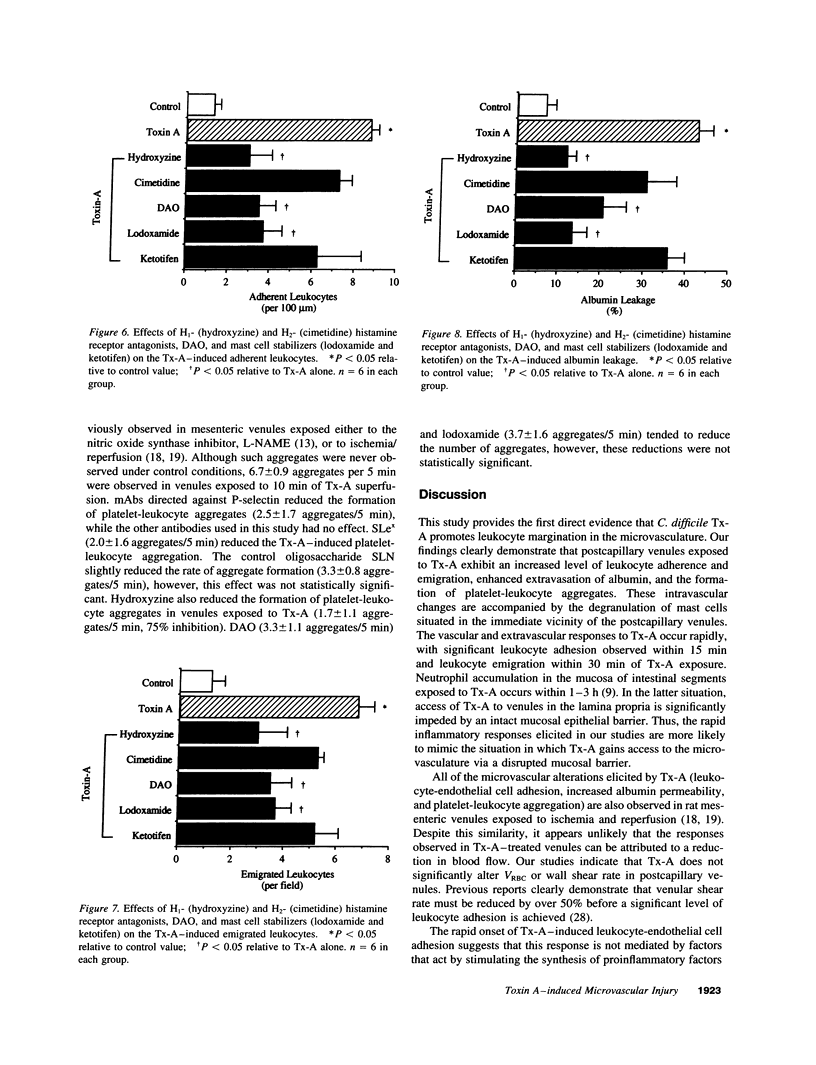
Clostridium difficile toxin A (Tx-A) mediates secretion and inflammation in experimental enterocolitis. Intravital video microscopy was used to define the mechanisms that underlie the inflammatory reactions elicited by direct exposure of the microvasculature to Tx-A. Leukocyte adherence and emigration, leukocyte-platelet aggregation, and extravasation of FITC-albumin were monitored in rat mesenteric venules exposed to Tx-A. Significant increases in leukocyte adherence and emigration (LAE) and albumin leakage were noted within 15-30 min of Tx-A exposure. These responses were accompanied by mast cell degranulation and the formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregates. The Tx-A-induced increases in LAE and albumin leakage were significantly attenuated by pretreatment with either monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the leukocyte adhesion glycoproteins, CD11/CD18, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and P-selectin (but not E-selectin) or with sialyl Lewis x, a counter-receptor for P-selectin. The mast cell stabilizer, lodoxamide, an H1- (but not an H2-) receptor antagonist, and diamine oxidase (histaminase) were also effective in reducing the LAE and albumin leakage elicited by Tx-A. The platelet-leukocyte aggregation response was blunted by an mAb against P-selectin, sialyl Lewis x, and the H1-receptor antagonist. These observations indicate that Tx-A induces a leukocyte-dependent leakage of albumin from postcapillary venules. Mast cell-derived histamine appears to mediate at least part of the leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and platelet-leukocyte aggregation by engaging H1-receptors on endothelial cells and platelets to increase the expression of P-selectin. The adhesion glycoproteins CD11/CD18 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 also contribute to the inflammatory responses elicited by toxin A.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asako H., Kurose I., Wolf R., DeFrees S., Zheng Z. L., Phillips M. L., Paulson J. C., Granger D. N. Role of H1 receptors and P-selectin in histamine-induced leukocyte rolling and adhesion in postcapillary venules. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1508–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI117129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asako H., Wolf R. E., Granger D. N., Korthuis R. J. Phalloidin prevents leukocyte emigration induced by proinflammatory stimuli in rat mesentery. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 2):H1637–H1642. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.6.H1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Onderdonk A. B., Cisneros R. L., Kasper D. L. Clindamycin-associated colitis due to a toxin-producing species of Clostridium in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):701–705. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienvenu K., Russell J., Granger D. N. Leukotriene B4 mediates shear rate-dependent leukocyte adhesion in mesenteric venules. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):906–911. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk J., Hedqvist P., Arfors K. E. Increase in vascular permeability induced by leukotriene B4 and the role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Inflammation. 1982 Jun;6(2):189–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00916243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Membrane proteins involved in phagocyte adherence to endothelium. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Letourneau R., Kelly C., O'Keane J. C., Jaffer A., Theoharides T. C., Pothoulakis C. Neuronal involvement in the intestinal effects of Clostridium difficile toxin A and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1994 Sep;107(3):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E. Modulation of venular microvessel permeability by calcium influx into endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2456–2466. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.7.1563597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. J. Determination of volumetric flow in capillary tubes using an optical Doppler velocimeter. Microvasc Res. 1987 Sep;34(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove C. H., Wang S. Z., Price S. B., Phelps C. J., Lyerly D. M., Wilkins T. D., Johnson J. L. Molecular characterization of the Clostridium difficile toxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):480–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.480-488.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Müller F., Däubener W., Fischer H. G., Hadding U., Northoff H. Cytokine response by human monocytes to Clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3659–3666. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3659-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng J. G., Bevilacqua M. P., Moore K. L., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M., Kim J. M., Bliss G. A., Zimmerman G. A., McEver R. P. Rapid neutrophil adhesion to activated endothelium mediated by GMP-140. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):757–760. doi: 10.1038/343757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Benoit J. N., Suzuki M., Grisham M. B. Leukocyte adherence to venular endothelium during ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G683–G688. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House S. D., Lipowsky H. H. Leukocyte-endothelium adhesion: microhemodynamics in mesentery of the cat. Microvasc Res. 1987 Nov;34(3):363–379. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. P., Becker S., Linevsky J. K., Joshi M. A., O'Keane J. C., Dickey B. F., LaMont J. T., Pothoulakis C. Neutrophil recruitment in Clostridium difficile toxin A enteritis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1172/JCI117080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubes P., Suzuki M., Granger D. N. Modulation of PAF-induced leukocyte adherence and increased microvascular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):G859–G864. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.5.G859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose I., Anderson D. C., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Paulson J. C., Todd R. F., Rusche J. R., Granger D. N. Molecular determinants of reperfusion-induced leukocyte adhesion and vascular protein leakage. Circ Res. 1994 Feb;74(2):336–343. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.2.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose I., Kubes P., Wolf R., Anderson D. C., Paulson J., Miyasaka M., Granger D. N. Inhibition of nitric oxide production. Mechanisms of vascular albumin leakage. Circ Res. 1993 Jul;73(1):164–171. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose I., Wolf R., Grisham M. B., Granger D. N. Modulation of ischemia/reperfusion-induced microvascular dysfunction by nitric oxide. Circ Res. 1994 Mar;74(3):376–382. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.3.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose I., Yamada T., Wolf R., Granger D. N. P-selectin-dependent leukocyte recruitment and intestinal mucosal injury induced by lactoferrin. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Jun;55(6):771–777. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.6.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen E., Celi A., Gilbert G. E., Furie B. C., Erban J. K., Bonfanti R., Wagner D. D., Furie B. PADGEM protein: a receptor that mediates the interaction of activated platelets with neutrophils and monocytes. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Parry J. V., Price A. B., Davies D. R., Dolby J., Tyrrell D. A. Undescribed toxin in pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1977 May 14;1(6071):1246–1248. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6071.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence M. B., McIntire L. V., Eskin S. G. Effect of flow on polymorphonuclear leukocyte/endothelial cell adhesion. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1284–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Saum K. E., MacDonald D. K., Wilkins T. D. Effects of Clostridium difficile toxins given intragastrically to animals. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):349–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.349-352.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayadas T. N., Johnson R. C., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O., Wagner D. D. Leukocyte rolling and extravasation are severely compromised in P selectin-deficient mice. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):541–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80055-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Beckstead J. H., Moore K. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Bainton D. F. GMP-140, a platelet alpha-granule membrane protein, is also synthesized by vascular endothelial cells and is localized in Weibel-Palade bodies. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):92–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI114175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P. Selectins: novel receptors that mediate leukocyte adhesion during inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Mar 4;65(3):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. D., Pothoulakis C., Baeker T. R., LaMont J. T., Rothstein T. L. Macrophage-dependent stimulation of T cell-depleted spleen cells by Clostridium difficile toxin A and calcium ionophore. Cell Immunol. 1990 Mar;126(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90308-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. J., Ketley J. M., Haslam S. C., Stephen J., Burdon D. W., Candy D. C., Daniel R. Effect of toxin A and B of Clostridium difficile on rabbit ileum and colon. Gut. 1986 Jan;27(1):78–85. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Polley M. J., Bayer R. J., Nunn M. F., Paulson J. C., Ward P. A. Neutrophil-dependent acute lung injury. Requirement for P-selectin (GMP-140). J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1600–1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI116029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Varani J., Dame M. K., Lane C. L., Smith C. W., Anderson D. C., Ward P. A. Role of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) in neutrophil-mediated lung injury in rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1396–1406. doi: 10.1172/JCI115446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Varani J., Warren J. S., Till G. O., Smith C. W., Anderson D. C., Todd R. F., 3rd, Ward P. A. Roles of beta 2 integrins of rat neutrophils in complement- and oxygen radical-mediated acute inflammatory injury. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1847–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., Karmeli F., Kelly C. P., Eliakim R., Joshi M. A., O'Keane C. J., Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Rachmilewitz D. Ketotifen inhibits Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced enteritis in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1993 Sep;105(3):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90886-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Eglow R., Gao N., Rubins J. B., Theoharides T. C., Dickey B. F. Characterization of rabbit ileal receptors for Clostridium difficile toxin A. Evidence for a receptor-coupled G protein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):119–125. doi: 10.1172/JCI115267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., Sullivan R., Melnick D. A., Triadafilopoulos G., Gadenne A. S., Meshulam T., LaMont J. T. Clostridium difficile toxin A stimulates intracellular calcium release and chemotactic response in human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1741–1745. doi: 10.1172/JCI113514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raud J., Lindbom L. Leukocyte rolling and firm adhesion in the microcirculation. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90866-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Lasky L. A. Cell adhesion. Sticky sugars for selectins. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):196–197. doi: 10.1038/349196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Pellett S., Wilkins T. D. Purification and characterization of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1032-1040.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamatani T., Kotani M., Miyasaka M. Characterization of the rat leukocyte integrin, CD11/CD18, by the use of LFA-1 subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):627–633. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G., Pothoulakis C., O'Brien M. J., LaMont J. T. Differential effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B on rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G., Pothoulakis C., Weiss R., Giampaolo C., Lamont J. T. Comparative study of Clostridium difficile toxin A and cholera toxin in rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1186–1192. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Modulation by prostanoids of the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells: involvement in mucosal protection? Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):314–317. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90867-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. J., Holt J. W., Paulson J. C., Anderson D. C., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Todd R. F., 3rd, Rusche J. R., Granger D. N. Molecular determinants of lipid mediator-induced leukocyte adherence and emigration in rat mesenteric venules. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):H847–H853. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.3.H847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


