Abstract
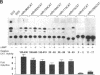
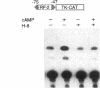
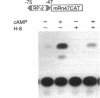
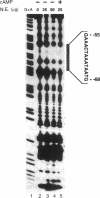
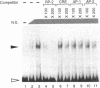
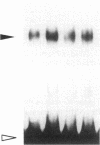
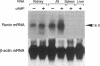
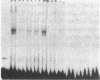
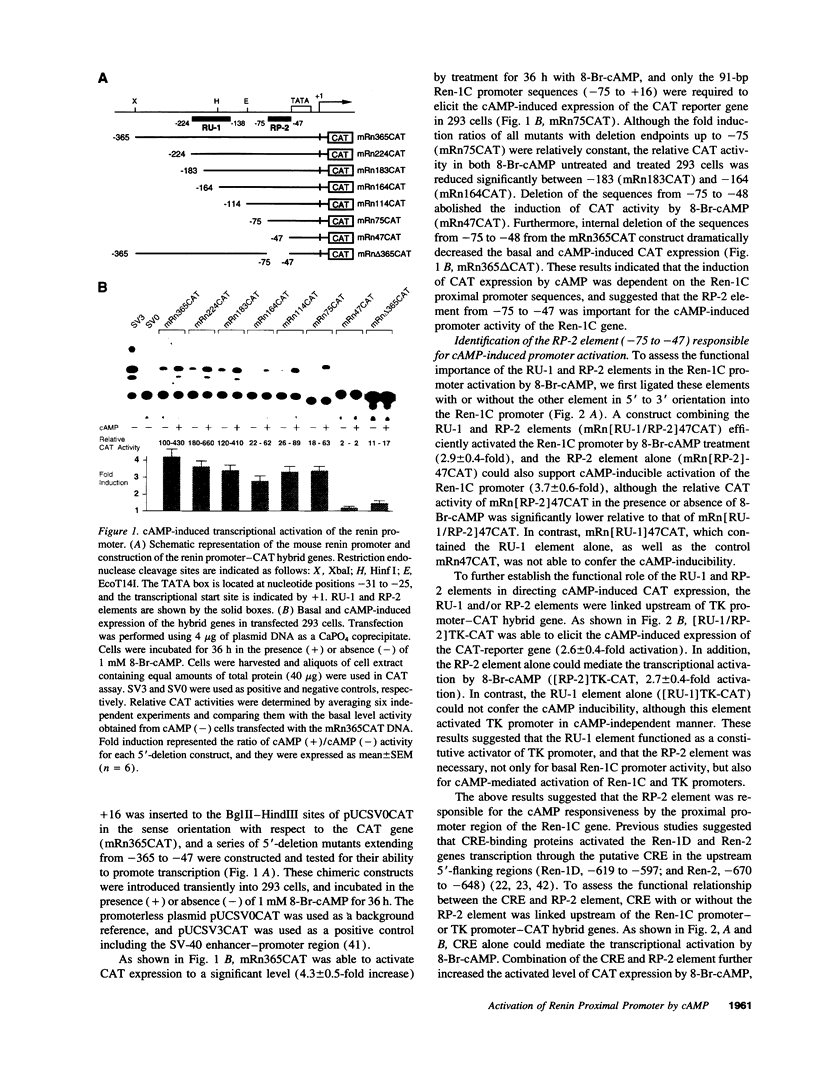
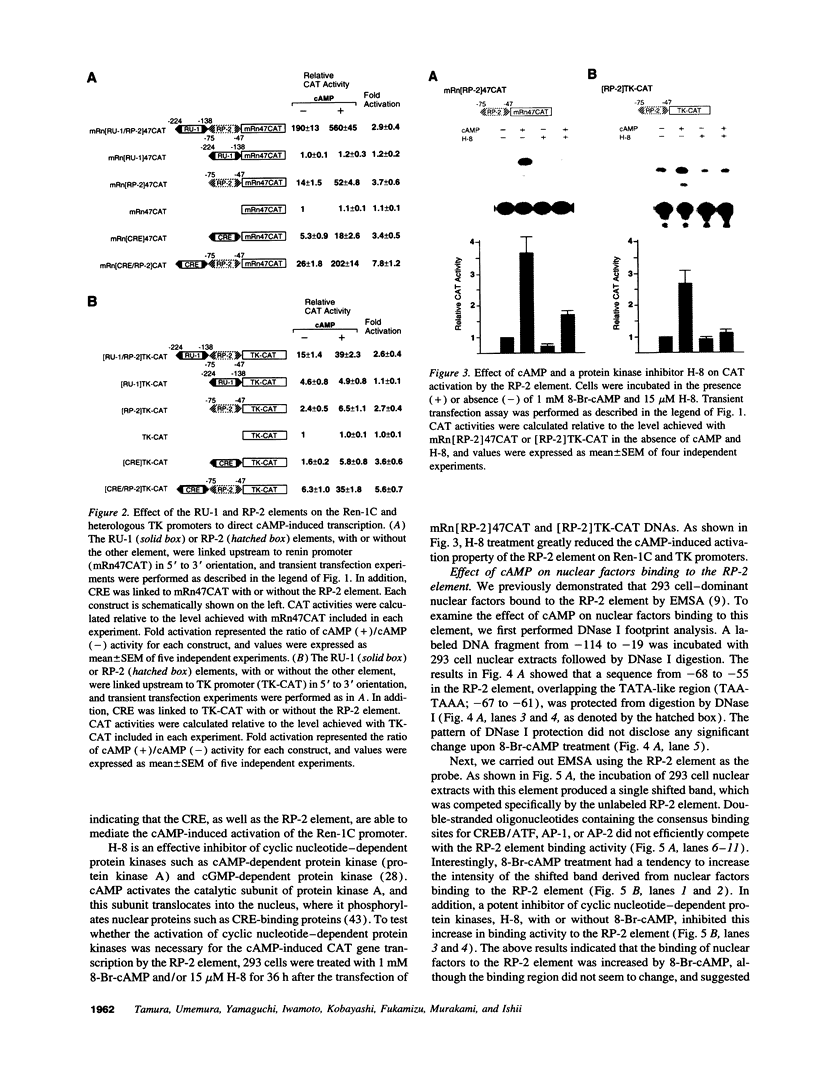
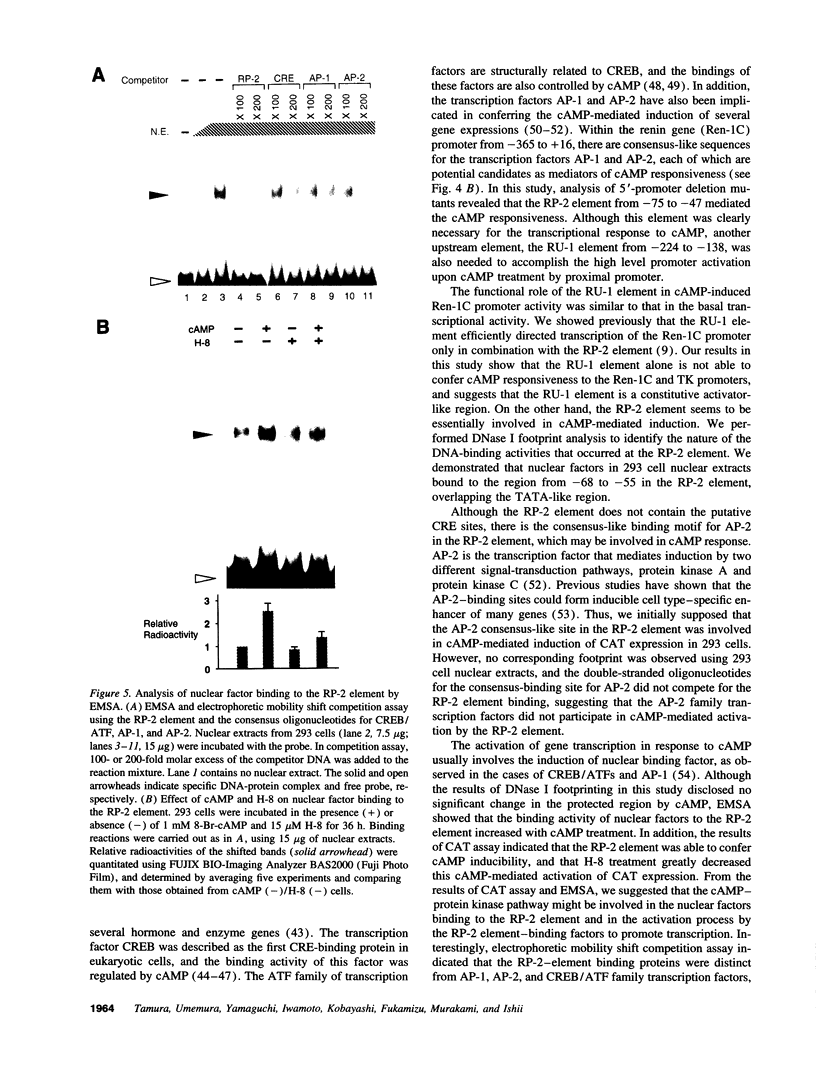
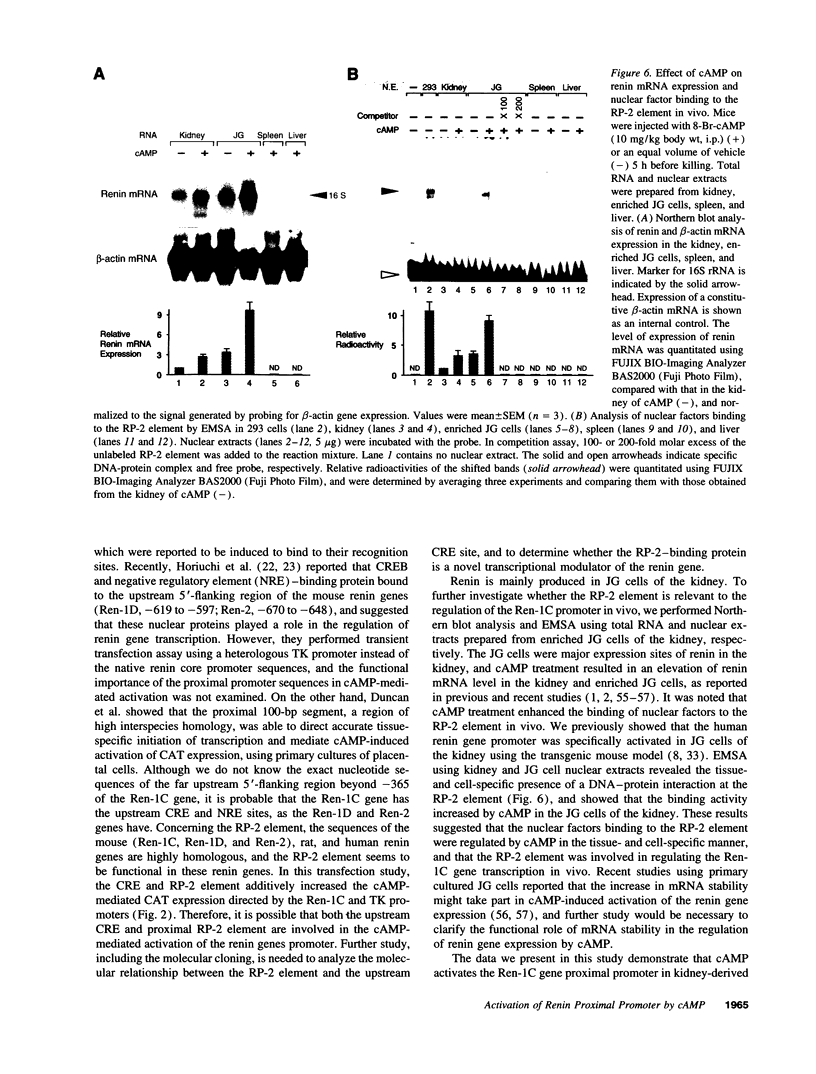
Renin is produced mainly by the kidney, and cAMP is a main positive regulator of its synthesis. This study was undertaken to analyze the molecular mechanism of cAMP-mediated regulation of Ren-1C gene transcription by the proximal promoter. We first showed that the promoter region from -365 to +16 of the mouse renin gene (Ren-1C) mediated the cAMP-induced chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression in embryonic kidney-derived 293 cells. Deletion analysis and heterologous promoter assay disclosed that the proximal promoter region from -75 to +16 was able to activate chloramphenicol acetyltransferase expression by cAMP, and indicated that the proximal promoter element from -75 to -47 (RP-2 element) overlapping the TATA-like region was able to confer cAMP responsiveness. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and DNase I footprinting analysis demonstrated that novel nuclear factors in 293 cells interacted with the RP-2 element, and that cAMP increased the binding activity of these nuclear factors to the RP-2 element. Furthermore, we demonstrated that cAMP enhanced the binding of nuclear factors derived from juxtaglomerular cells, the main production site of renin in the kidney, to the RP-2 element in vivo. These results suggest that the RP-2 element plays an important role in the cAMP-mediated regulation of Ren-1C gene transcription through the proximal promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt D. W., Nakamura N., Kelley P., Dzau V. J. Identification of negative and positive regulatory elements in the human renin gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7357–7362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Schnermann J., Smart A. M., Brosius F. C., Killen P. D., Briggs J. P. Cyclic AMP selectively increases renin mRNA stability in cultured juxtaglomerular granular cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24138–24144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bruna R., Kurtz A., Corvol P., Pinet F. Renin mRNA quantification using polymerase chain reaction in cultured juxtaglomerular cells. Short-term effects of cAMP on renin mRNA and secretion. Circ Res. 1993 Oct;73(4):639–648. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP responsiveness of human gonadotropin-alpha gene transcription is directed by a repeated 18-base pair enhancer. Alpha-promoter receptivity to the enhancer confers cell-preferential expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12169–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan K. G., Haidar M. A., Baxter J. D., Reudelhuber T. L. Regulation of human renin expression in chorion cell primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7588–7592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Burt D. W., Pratt R. E. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F563–F573. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett A. D., Carey R. M., Chevalier R. L., Peach M. J., Gomez R. A. Renin release and gene expression in intact rat kidney microvessels and single cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):169–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI114680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Hatae T., Kon Y., Sugimura M., Hasegawa T., Yokoyama M., Nomura T., Katsuki M., Murakami K. Human renin in transgenic mouse kidney is localized to juxtaglomerular cells. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):601–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2780601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Seo M. S., Hatae T., Yokoyama M., Nomura T., Katsuki M., Murakami K. Tissue-specific expression of the human renin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):826–832. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Takahashi S., Seo M. S., Tada M., Tanimoto K., Uehara S., Murakami K. Structure and expression of the human angiotensinogen gene. Identification of a unique and highly active promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7576–7582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Tanimoto K., Uehara S., Seo M. S., Handa S., Sagara M., Takahashi S., Imai T., Murakami K. Regulation of human renin and angiotensinogen genes. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):659–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamizu A., Uehara S., Sugimura K., Kon Y., Sugimura M., Hasegawa T., Yokoyama M., Nomura T., Katsuki M., Murakami K. Cell type-specific expression of the human renin gene. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1991 Jul-Sep;5(3):112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Wagner J., Zeh K., Bader M., Michel J. B., Paul M., Zimmermann F., Ruf P., Hilgenfeldt U., Ganten U. Species specificity of renin kinetics in transgenic rats harboring the human renin and angiotensinogen genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Murphy T. J., Alexander R. W. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation. 1993 Jun;87(6):1816–1828. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.6.1816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Nakamura N., Tang S. S., Barrett G., Dzau V. J. Molecular mechanism of tissue-specific regulation of mouse renin gene expression by cAMP. Identification of an inhibitory protein that binds nuclear transcriptional factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16247–16254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Pratt R. E., Nakamura N., Dzau V. J. Distinct nuclear proteins competing for an overlapping sequence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and negative regulatory elements regulate tissue-specific mouse renin gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1805–1811. doi: 10.1172/JCI116770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. A., Sigmund C. D., McGowan R. A., Kane-Haas C. M., Gross K. W. Expression of murine renin genes during fetal development. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):375–383. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Della Bruna R., Pfeilschifter J., Taugner R., Bauer C. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits renin release from juxtaglomerular cells by a cGMP-mediated process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4769–4773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H. Lewis K. Dahl Memorial Lecture. The renin system and four lines fo hypertension research. Nephron heterogeneity, the calcium connection, the prorenin vasodilator limb, and plasma renin and heart attack. Hypertension. 1992 Sep;20(3):267–279. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J. Molecular biology of renin. II: Gene control by messenger RNA, transfection and transgenic studies. J Hypertens. 1992 Apr;10(4):337–342. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199204000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Peters J., Ganten D. Fulminant hypertension in transgenic rats harbouring the mouse Ren-2 gene. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):541–544. doi: 10.1038/344541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardy K., Adan R. A., Carter D. A., Seah V., Burbach J. P., Murphy D. The identification of a cis-acting element involved in cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate regulation of bovine vasopressin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21746–21752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul M., Burt D. W., Krieger J. E., Nakamura N., Dzau V. J. Tissue specificity of renin promoter activity and regulation in mice. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E644–E650. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. G. Distinct activation domains within cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) mediate basal and cAMP-stimulated transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16999–17009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayson B. M. Juxtaglomerular cells cultured on a reconstituted basement membrane. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C563–C568. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfuss R. P., Walton K. M., Loriaux M. M., Goodman R. H. The cAMP-regulated enhancer-binding protein ATF-1 activates transcription in response to cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18431–18434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Cross-talk in signal transduction: TPA-inducible factor jun/AP-1 activates cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):427–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Gross K. W. Structure, expression, and regulation of the murine renin genes. Hypertension. 1991 Oct;18(4):446–457. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.4.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Jones C. A., Fabian J. R., Mullins J. J., Gross K. W. Tissue and cell specific expression of a renin promoter-reporter gene construct in transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Oddoux C., Lazarus A., Gilbert M. T., Catanzaro D. F. Promoter activity of human renin 5'-flanking DNA sequences is activated by the pituitary-specific transcription factor Pit-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1505–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Tanimoto K., Ishii M., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. Proximal and core DNA elements are required for efficient angiotensinogen promoter activation during adipogenic differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15024–15032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Tanimoto K., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. A combination of upstream and proximal elements is required for efficient expression of the mouse renin promoter in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3617–3623. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Tanimoto K., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. Activation of mouse renin promoter by cAMP and c-Jun in a kidney-derived cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 20;1172(3):306–310. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Tanimoto K., Takahashi S., Sagara M., Fukamizu A., Murakami K. Structure and expression of the mouse angiotensinogen gene. Jpn Heart J. 1992 Jan;33(1):113–124. doi: 10.1536/ihj.33.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Umemura S., Ishii M., Tanimoto K., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. Molecular mechanism of transcriptional activation of angiotensinogen gene by proximal promoter. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1370–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI117113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Umemura S., Iwamoto T., Yamaguchi S., Kobayashi S., Takeda K., Tokita Y., Takagi N., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. Molecular mechanism of adipogenic activation of the angiotensinogen gene. Hypertension. 1994 Mar;23(3):364–368. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.3.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. Possible roles of the 3'-flanking sequences of the human activin beta A subunit gene in its expression. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 May;302(2):409–416. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Taniguchi H., Yoda K., Shimizu M., Sakiyama S. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for mouse cytoskeletal beta-actin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2829–2829. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita N., Higaki J., Kaneda Y., Yu H., Morishita R., Mikami H., Ogihara T. Hypertensive rats produced by in vivo introduction of the human renin gene. Circ Res. 1993 Nov;73(5):898–905. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.5.898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toya Y., Umemura S., Iwamoto T., Hirawa N., Kihara M., Takagi N., Ishii M. Identification and characterization of adenosine A1 receptor-cAMP system in human glomeruli. Kidney Int. 1993 Apr;43(4):928–932. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemura S., Smyth D. D., Pettinger W. A. Regulation of renal cellular cAMP levels by prostaglandins and alpha 2-adrenoceptors: microdissection studies. Kidney Int. 1986 Mar;29(3):703–707. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemura S., Toya Y., Hirawa N., Ishikawa Y., Minamizawa K., Yasuda G., Hayashi S., Ishii M. Inhibitory effect of human atrial natriuretic peptide on cyclic AMP levels in microdissected human glomeruli. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 6):S36–S38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]