Abstract
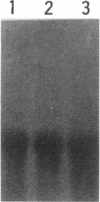
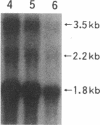
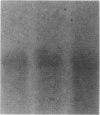
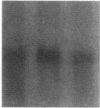
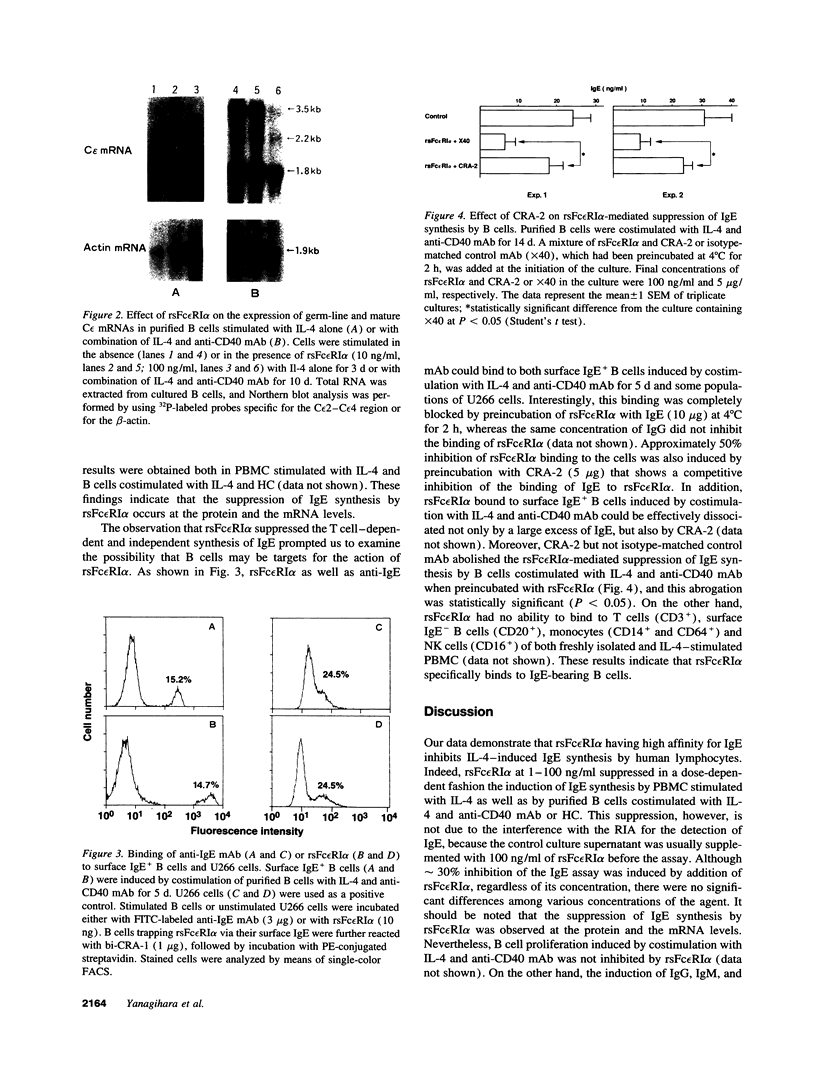
A recombinant soluble form of the alpha subunit of the human high-affinity receptor for IgE (rsFc epsilon RI alpha), one of the potent IgE-binding molecules, was tested for its ability to regulate IL-4-induced IgE synthesis by human lymphocytes. Addition of rsFc epsilon RI alpha to cultures induced a dose-dependent inhibition of the T cell-dependent and independent synthesis of IgE. The suppression of IgE synthesis was observed at the protein and the mRNA levels, and it was IgE class specific. By flow cytometry, specific binding of rsFc epsilon RI alpha was detected on surface IgE-bearing B cells as well as on U266 cells, and it was completely blocked by preincubation with IgE. rsFc epsilon RI alpha bound to the cell surface IgE could be effectively dissociated not only by a large excess of IgE, but also by an anti-rsFc epsilon RI alpha mAb that competes with IgE for the binding to rsFc epsilon RI alpha. This mAb abolished the rsFc epsilon RI alpha-mediated suppression of IgE synthesis. These data suggest that rsFc epsilon RI alpha may have a function in selectively suppressing IgE synthesis through its interaction with the membrane-bound form of IgE.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang T. W., Davis F. M., Sun N. C., Sun C. R., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Hamilton R. G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for human IgE-producing B cells: a potential therapeutic for IgE-mediated allergic diseases. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Feb;8(2):122–126. doi: 10.1038/nbt0290-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Wu C. Y., Fournier S., Letellier M. The low-affinity receptor for IgE. Immunol Rev. 1992 Feb;125:77–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascan H., Gauchat J. F., Roncarolo M. G., Yssel H., Spits H., de Vries J. E. Human B cell clones can be induced to proliferate and to switch to IgE and IgG4 synthesis by interleukin 4 and a signal provided by activated CD4+ T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):747–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauchat J. F., Aversa G., Gascan H., de Vries J. E. Modulation of IL-4 induced germline epsilon RNA synthesis in human B cells by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies or transforming growth factor-beta correlates with levels of IgE production. Int Immunol. 1992 Mar;4(3):397–406. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm B., Marsh P., Vercelli D., Padlan E., Gould H., Geha R. The mast cell binding site on human immunoglobulin E. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):180–183. doi: 10.1038/331180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. IgE-binding factors and regulation of the IgE antibody response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:513–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of immunoglobin E biosynthesis. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:1–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Suemura M., Owaki H., Nakamura H., Sato R., Yamasaki K., Barsumian E. L., Hardy R. R., Kishimoto T. Fc epsilon receptor, a specific differentiation marker transiently expressed on mature B cells before isotype switching. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1455–1469. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata H., Yoshida A., Ishioka C., Lindley I., Mikawa H. Interleukin 8 (IL-8) selectively inhibits immunoglobulin E production induced by IL-4 in human B cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiniwa M., Gately M., Gubler U., Chizzonite R., Fargeas C., Delespesse G. Recombinant interleukin-12 suppresses the synthesis of immunoglobulin E by interleukin-4 stimulated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):262–266. doi: 10.1172/JCI115846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Abo T., Sekizawa T., Sasaki M. Studies of surface immunoglobulins on human B lymphocytes. I. Dissociation of cell-bound immunoglobulins with acid pH or at 37 degrees C. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):982–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira H., Ishizaka K. Reaginic antibody formation in the mouse. XI. Participation of long-lived antibody-forming cells in persistent antibody formation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Feb;58(1):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C., Davis F. M., Sun L. K., Liou R. S., Kim Y. W., Chang T. W. A new isoform of human membrane-bound IgE. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ra C., Kuromitsu S., Hirose T., Yasuda S., Furuichi K., Okumura K. Soluble human high-affinity receptor for IgE abrogates the IgE-mediated allergic reaction. Int Immunol. 1993 Jan;5(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Jabara H. H., Thienes C. P., Ahern D. J., Vercelli D., Gould H. J., Geha R. S. Deletional switch recombination occurs in interleukin-4-induced isotype switching to IgE expression by human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7528–7532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara Y., Kajiwara K., Kiniwa M., Yui Y., Shida T., Delespesse G. Enhancement of IgE synthesis and histamine release by T cell factors derived from atopic patients with bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Mar;79(3):448–456. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(87)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara Y., Kiniwa M., Kajiwara K., Shida T. Establishment of a sensitive radioimmunoassay for the detection of human IgE-binding factor (soluble CD23). Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;98(3):189–199. doi: 10.1159/000236184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Production of IgE-potentiating factor in man by T cell lines bearing Fc receptors for IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):871–878. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]