Abstract
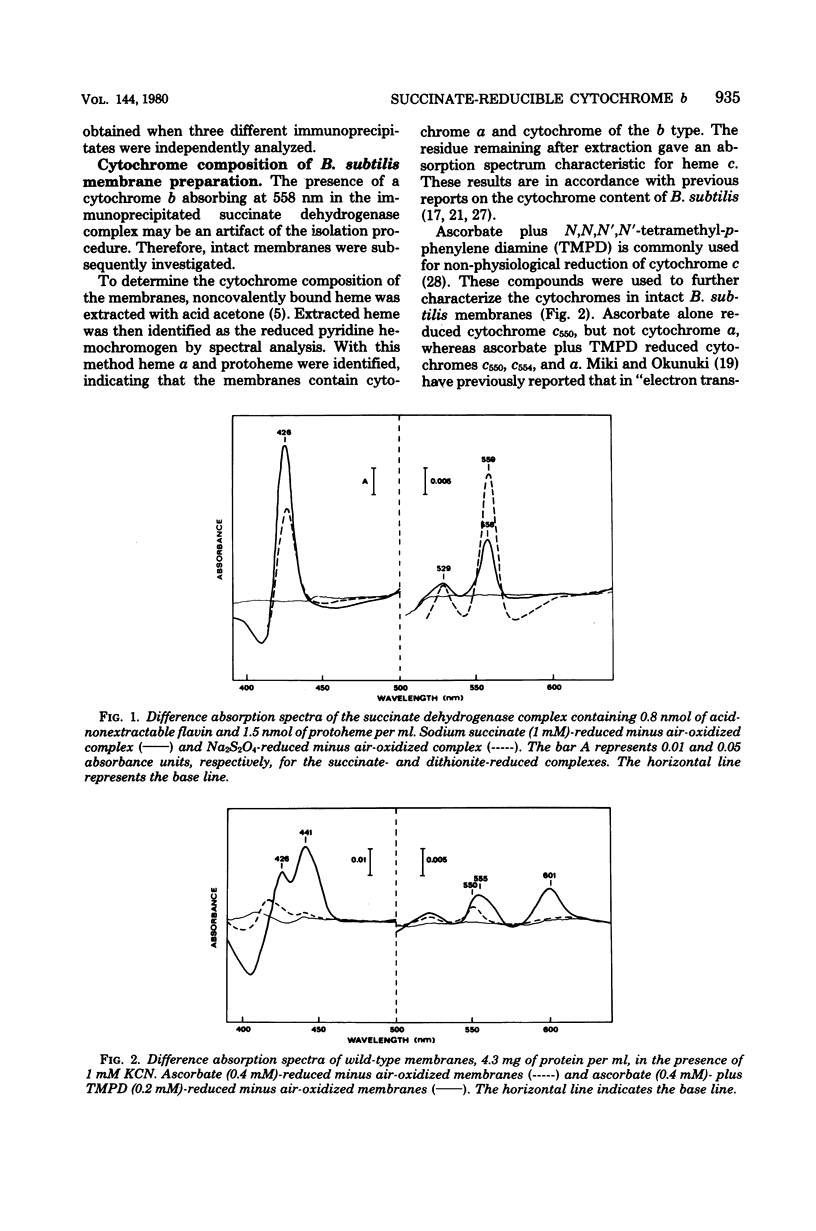
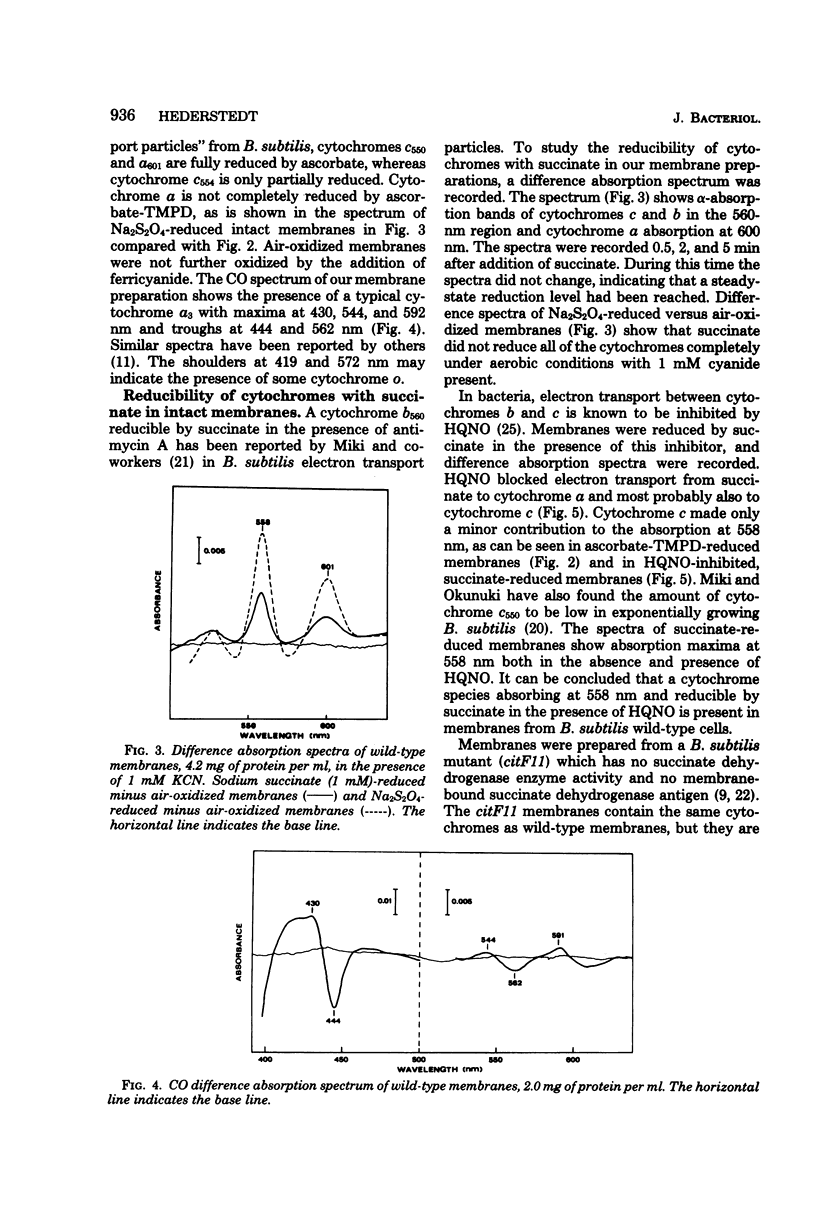
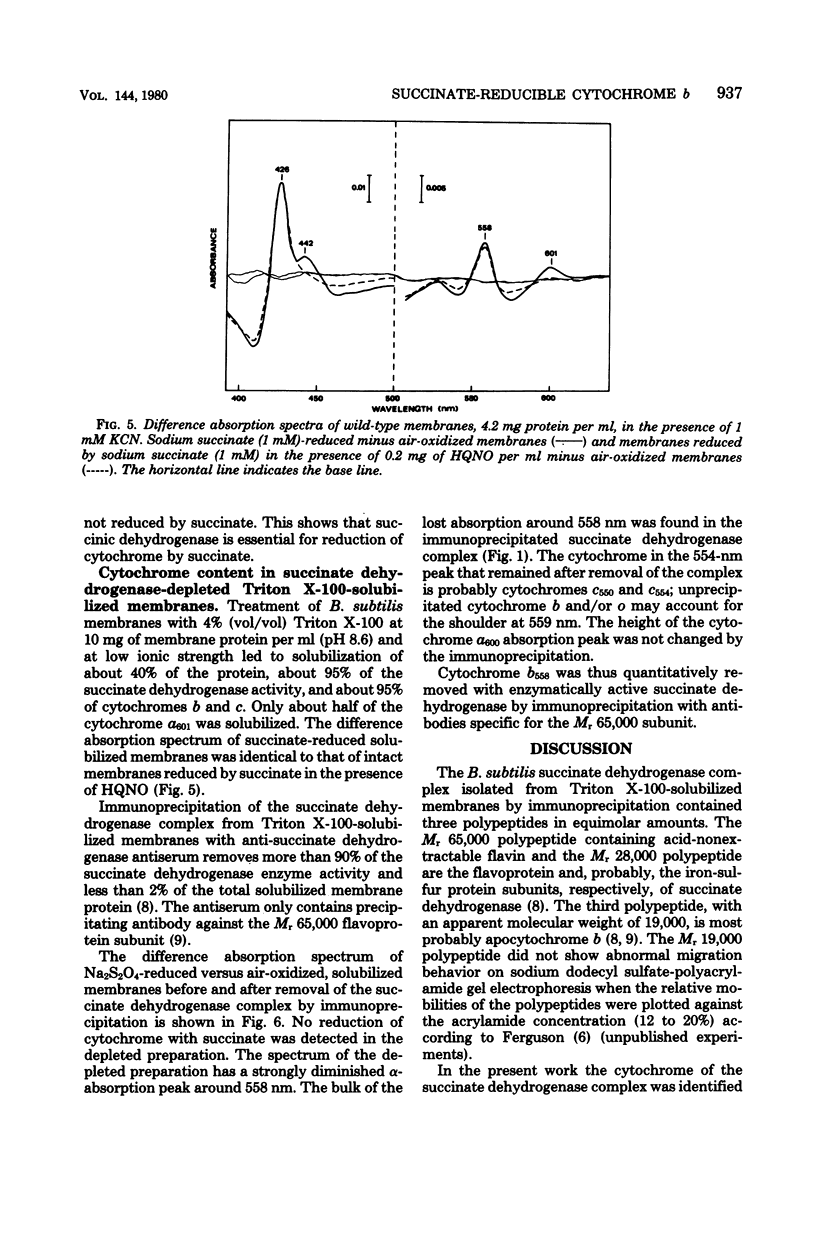
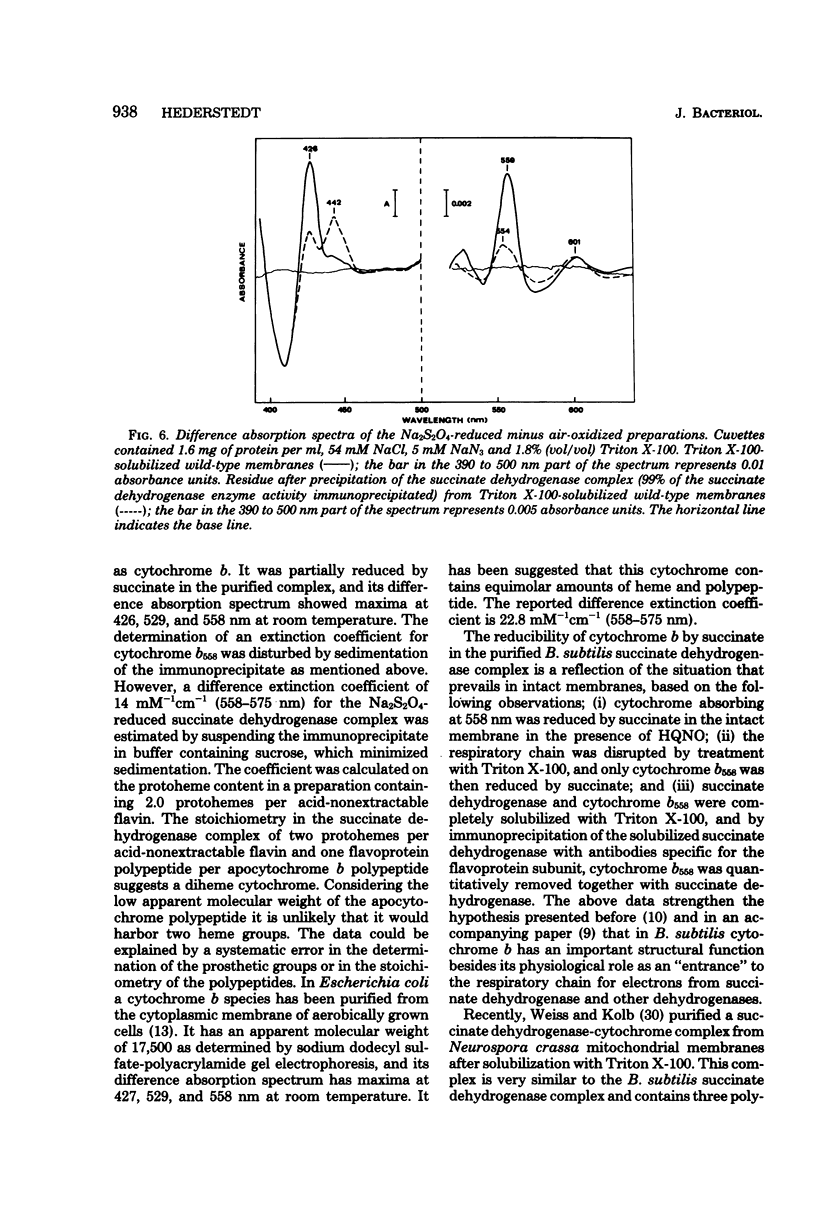
In previous work with membranes of Bacillus subtilis, the succinate dehydrogenase complex was isolated by immunoprecipitation of Triton X-100-solubilized membranes. The complex included a polypeptide with an apparent molecular weight of 19,000, probably attributable to apocytochrome. This paper reports the further characterization of this cytochrome and its relation to the respiratory chain of B. subtilis. The cytochrome was identified as cytochrome b, and its difference absorption spectra showed maxima at 426, 529, and 558 nm at room temperature. The oxidized cytochrome had an absorption maximum at 413 nm. The cytochrome was reduced by succinate in the isolated succinate dehydrogenase complex and in Triton X-100-solubilized membranes. In whole membranes cytochromes b, c, and a were reduced by succinate. In membranes from a mutant containing normal cytochromes but lacking succinate dehydrogenase no reduction of cytochrome was seen with succinate. It was concluded that the isolated succinate dehydrogenase-cytochrome b complex is a functional unit in the intact B. subtilis membrane. An accompanying paper describes cytochrome b as a structural unit involved in the membrane binding of succinate dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAIX P., PETIT J. F. Influence du taux de croissance sur la constitution du spectre hématinique de B. subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):481–486. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90517-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. A., Hatefi Y., Crawford I. P., Baltscheffsky H. Purification, molecular properties, and amino acid composition of the subunits of Rhodospirillum rubrum succinate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 30;180(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. A., Hatefi Y. Succinate dehydrogenase. I. Purification, molecular properties, and substructure. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2509–2516. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie P., Weiner J. H. Purification and characterization of membrane-bound fumarate reductase from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):813–821. doi: 10.1139/o79-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hederstedt L., Holmgren E., Rutberg L. Characterization of a succinate dehydrogenase complex solubilized from the cytoplasmic membrane of Bacillus subtilis with the nonionic detergent Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):370–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.370-376.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hederstedt L., Rutberg L. Biosynthesis and membrane binding of succinate dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):941–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.941-951.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren E., Hederstedt L., Rutberg L. Role of heme in synthesis and membrane binding of succinic dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):377–382. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.377-382.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen M. D., Horio T. Bacterial cytochromes. I. Structural aspects. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:673–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney W. C., Kröger A. The covalently bound flavin of Vibrio succinogenes succinate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 1;73(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80989-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita K., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Purification and properties of cytochrome b556 in the respiratory chain of aerobically grown Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8910–8915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Bisschop A., Veenhuis M., Vermeulen C. A. New procedure for the isolation of membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis and an electron microscopy study of their ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1456–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1456-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger A. Fumarate as terminal acceptor of phosphorylative electron transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 23;505(2):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki K., Okunuki K. Cytochromes of Bacillus subtilis. 3. Physicochemical and enzymatic properties of cytochromes c-550 and c-554. J Biochem. 1969 Dec;66(6):845–854. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki K., Okunuki K. Cytochromes of Bacillus subtilis. II. Purification and spectral properties of cytochromes c-550 and c-554. J Biochem. 1969 Dec;66(6):831–843. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Hederstedt L., Holmgren E., Rutberg L. Characterization of succinic dehydrogenase mutants of Bacillus subtilis by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):304–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.304-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. Bacterial cytochromes and their spectral characterization. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:202–212. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tochikubo K. Changes in terminal respiratory pathways of Bacillus subtilis during germination, outgrowth and vegetative growth. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):652–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.652-661.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON D. F., KING T. E. THE DETERMINATION OF ACID-NONEXTRACTABLE FLAVIN IN MITOCHONDRIAL PREPARATIONS FROM HEART MUSCLE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2683–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J. H., Dickie P. Fumarate reductase of Escherichia coli. Elucidation of the covalent-flavin component. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8590–8593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H., Kolb H. J. Isolation of mitochondrial succinate: ubiquinone reductase, cytochrome c reductase and cytochrome c oxidase from Neurospora crassa using nonionic detergent. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gelder B. F. Optical properties of cytochromes from beef heart mitochondria, submitochondrial vesicles, and derived preparations. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:125–128. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


