Abstract
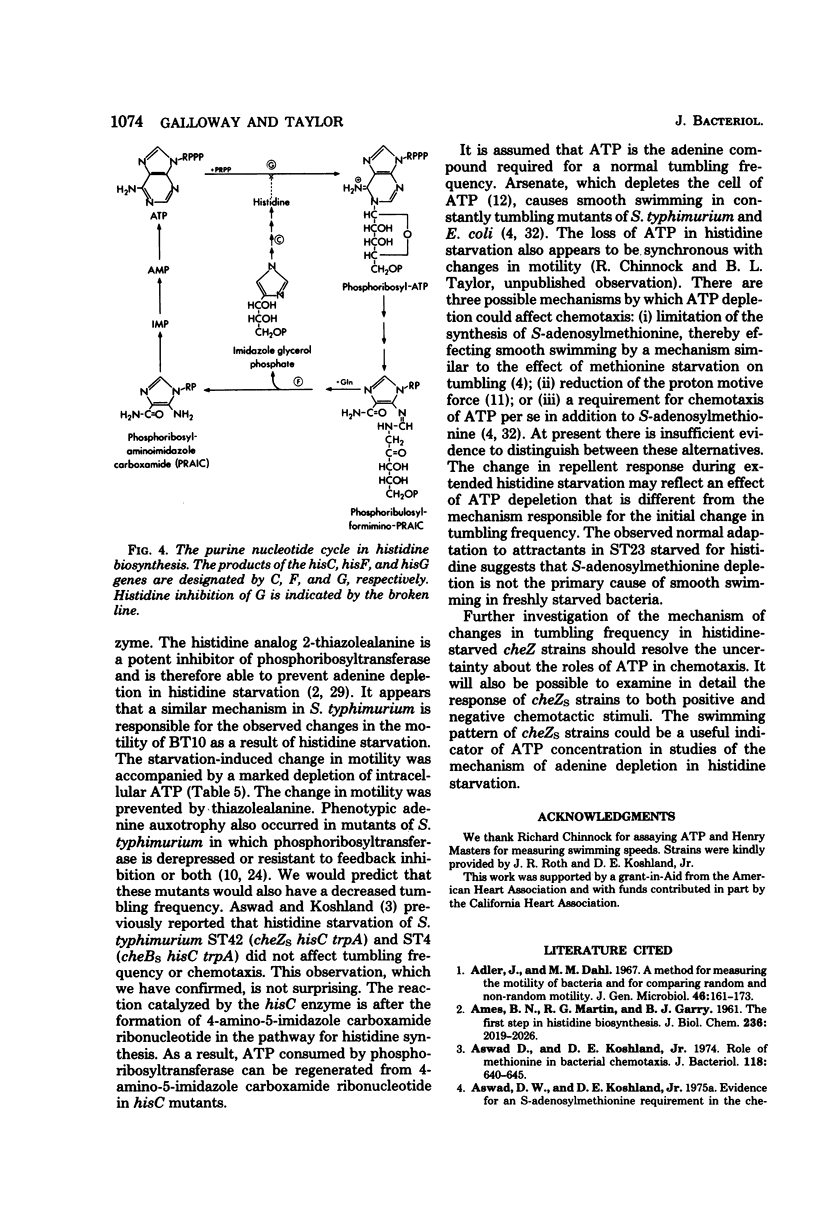
Starvation for histidine prevented tumbling in Salmonella typhimurium hisF auxotrophs, including constantly tumbling strains with an additional mutation in cheB or cheZ. However, histidine-starved cheZs hisF strains were not defective in flagellar function or the tumbling mechanism since freshly starved auxotrophs tumbled in response to a variety of repellents. Tumbling in histidine-starved S. typhimurium could be restored in 13 s by addition of adenine or in 4 min by addition of histidine. Chloramphenicol did not prevent restoration of tumbling by these substances. Assays of adenosine 5'-triphosphate were performed based upon previous demonstration of adenine depletion in hisF auxotrophs starved for histidine. The adenosine 5'-triphosphate concentration dropped rapidly during the course of starvation, falling to less than 5% of the initial level as the cells ceased tumbling entirely. The change to smooth motility was prevented by 2-thiazolealanine, which inhibits phosphoribosyltransferase, thereby preventing adenine depletion during histidine starvation. These results suggest that an adenosine 5'-triphosphate deficiency was responsible for the change in tumbling frequency.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., MARTIN R. G., GARRY B. J. The first step of histidine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:2019–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Dahl M. M. A method for measuring the motility of bacteria and for comparing random and non-random motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):161–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Isolation, characterization and complementation of Salmonella typhimurium chemotaxis mutants. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.640-645.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Parkinson J. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Functional homology of chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.107-114.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: role of a protein methylation reaction in sensory adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. The steady-state counterclockwise/clockwise ratio of bacterial flagellar motors is regulated by protonmotive force. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):563–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L., Boyer P. D. Energization of active transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr A response regulator model in a simple sensory system. Science. 1977 Jun 3;196(4294):1055–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.870969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardini J. B., Coulter A. W., Talalay P. Analogues of methionine as substrates and inhibitors of the methionine adenosyltransferase reaction. Deductions concerning the conformation of methionine. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;6(5):481–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin A., Thore A. Analytical information obtainable by evaluation of the time course of firefly bioluminescence in the assay of ATP. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin A., Thore A. Comparison of methods for extraction of bacterial adenine nucleotides determined by firefly assay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):713–721. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.713-721.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: the molecular biology of a behavioral system. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(4):291–341. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: light-induced tumbling response and visualization of individual flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. L., Hartman P. E. Overproduction of hisH and hisF gene products leads to inhibition of cell cell division in Salmonella. Can J Microbiol. 1972 May;18(5):671–681. doi: 10.1139/m72-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K., Koch A. L. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli. II. Strain differences in the degradation of protein and nucleic acid resulting from starvation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6956–6967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Regulation of intracellular proteolysis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):107–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.107-116.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEDLOVSKY A. E., MAGASANIK B. A defect in histidine biosynthesis causing an adenine deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3725–3730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEDLOVSKY A. E., MAGASANIK B. The enzymatic basis of an adenine-histidine relationship in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3731–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: a requirement for methionine in sensory adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):183–187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Quantitation of the sensory response in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):710–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Intrinsic and extrinsic light responses of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.557-569.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Miller J. B., Warrick H. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Electron acceptor taxis and blue light effect on bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.567-573.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary P. S., Stocker B. A. Nonsense motility mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1973 Feb;73(2):229–245. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Chemotactic mechanism of Salmonella typhimurium: preliminary mapping and characterization of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):223–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.223-231.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]