Abstract
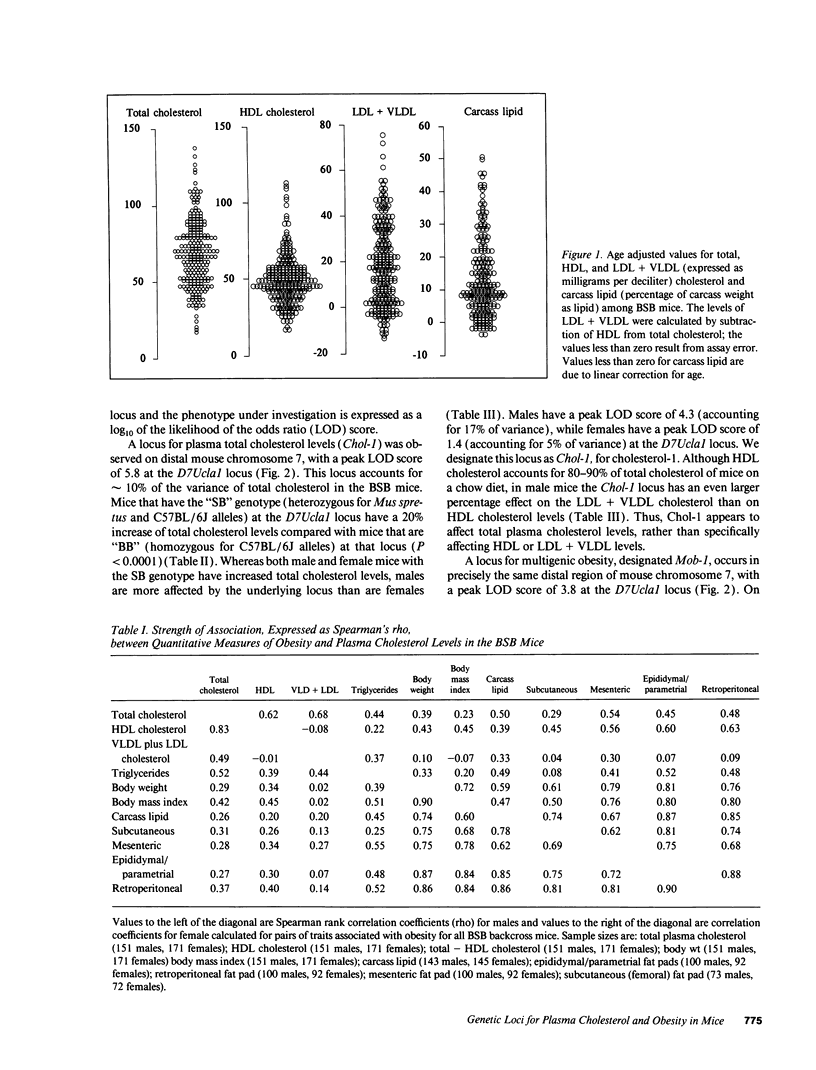
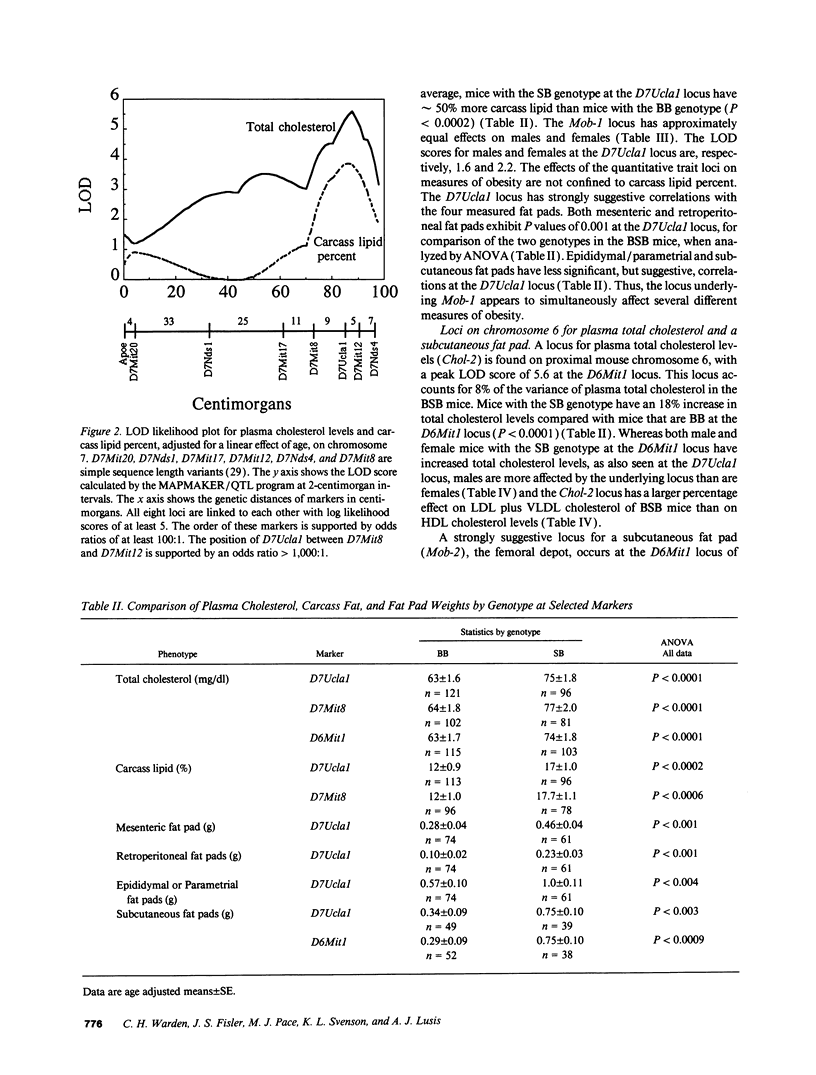
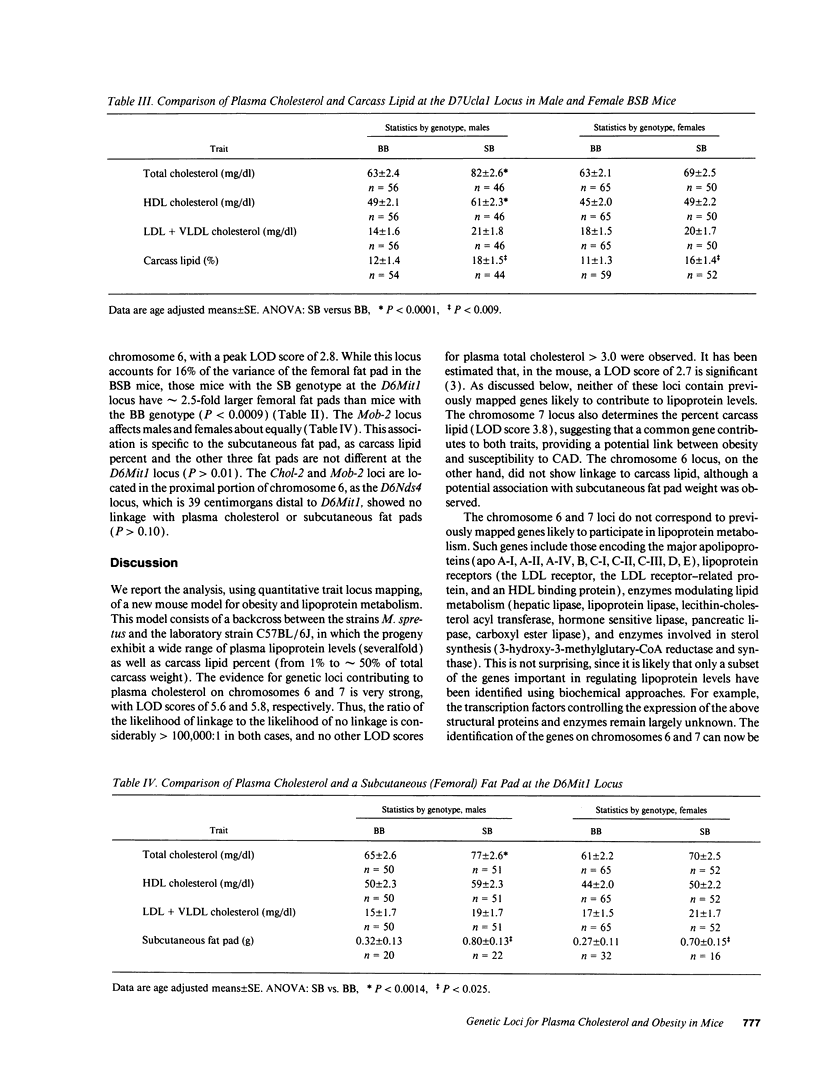
We have examined backcross progeny derived from a cross of Mus spretus with C57BL/6J, that range from 1 to 50% carcass lipid (n = 215), and from 22 to 130 mg/dl plasma total cholesterol (n = 238). Statistical analysis revealed that distal mouse chromosome 7 exhibits significant linkage both to plasma total cholesterol (likelihood of the odds [LOD] 5.8) and to carcass lipid (LOD 3.8). A locus on chromosome 6 also shows significant linkage to plasma total cholesterol (LOD 5.6), but no linkage to carcass lipid. Neither chromosomal region contains any previously mapped genes likely to influence lipoprotein metabolism, indicating that novel genetic factors contributing to plasma lipoprotein levels have been identified.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin M. A. Plasma triglyceride and coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):2–14. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P. Visceral fat accumulation: the missing link between psychosocial factors and cardiovascular disease? J Intern Med. 1991 Sep;230(3):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1991.tb00431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., Davidson M. B., Drenick E. J. Obesity: a serious symptom. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Nov;77(5):779–795. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. The genetic basis of lipoprotein disorders. Introduction and overview. J Intern Med. 1992 Jun;231(6):627–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1992.tb01251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N., Rolland Y. Possible connections between stress, diabetes, obesity, hypertension and altered lipoprotein metabolism that may result in atherosclerosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Nov;77(5):453–461. doi: 10.1042/cs0770453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bultman S. J., Michaud E. J., Woychik R. P. Molecular characterization of the mouse agouti locus. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Jones E. E., Lauris V., Steinke J., Soeldner J. S. Studies on experimental diabetes in the Wellesley hybrid mouse. II. Serum insulin levels and response of peripheral tissues. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):171–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01222194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus M. C., Aubert R., Bourgeois F., Herzog J., Alexiu A., Lemonnier D. Serum lipoprotein and apolipoprotein profiles of the genetically obese ob/ob mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 1;961(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Eicher E. M. Fat (fat) and tubby (tub): two autosomal recessive mutations causing obesity syndromes in the mouse. J Hered. 1990 Nov-Dec;81(6):424–427. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornall R. J., Aitman T. J., Hearne C. M., Todd J. A. The generation of a library of PCR-analyzed microsatellite variants for genetic mapping of the mouse genome. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):874–881. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90175-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Després J. P., Tremblay A., Pérusse L., Leblanc C., Bouchard C. Abdominal adipose tissue and serum HDL-cholesterol: association independent from obesity and serum triglyceride concentration. Int J Obes. 1988;12(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W., Katz H., Lincoln S. E., Shin H. S., Friedman J., Dracopoli N. C., Lander E. S. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics. 1992 Jun;131(2):423–447. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisler J. S., Warden C. H., Pace M. J., Lusis A. J. BSB: a new mouse model of multigenic obesity. Obes Res. 1993 Jul;1(4):271–280. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1993.tb00621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Balasse E. O., Segel N., Basso L. V. Splanchnic metabolism of free fatty acids and production of triglycerides of very low density lipoproteins in normotriglyceridemic and hypertriglyceridemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2017–2035. doi: 10.1172/JCI106422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C., Kirchgessner T., Kwiterovich P. O., Ladias J. A., Derby C., Antonarakis S. E., Lusis A. J. DNA polymorphism haplotypes of the human lipoprotein lipase gene: possible association with high density lipoprotein levels. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):578–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00201544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert P., Lindpaintner K., Beckmann J. S., Serikawa T., Soubrier F., Dubay C., Cartwright P., De Gouyon B., Julier C., Takahasi S. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):521–529. doi: 10.1038/353521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himes J. H., Bouchard C., Pheley A. M. Lack of correspondence among measures identifying the obese. Am J Prev Med. 1991 Mar-Apr;7(2):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Freedman D. S., Peiris A. N. Health risks of obesity. Med Clin North Am. 1989 Jan;73(1):111–138. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30695-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson B., Bengtsson C., Björntorp P., Lapidus L., Sjöström L., Svärdsudd K., Tibblin G., Wedel H., Welin L., Wilhelmsen L. Is abdominal body fat distribution a major explanation for the sex difference in the incidence of myocardial infarction? The study of men born in 1913 and the study of women, Göteborg, Sweden. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Feb 1;135(3):266–273. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson B., Björntorp P., Tibblin G. The health consequences of moderate obesity. Int J Obes. 1981;5(2):97–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. M., Knight A. M., McAleer M. A., Todd J. A. Towards construction of a high resolution map of the mouse genome using PCR-analysed microsatellites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4123–4130. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Taylor B. A., Quon D., Zollman S., LeBoeuf R. C. Genetic factors controlling structure and expression of apolipoproteins B and E in mice. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7594–7604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan M. W., Artiss J. D., Strandbergh D. R., Zak B. A peroxidase-coupled method for the colorimetric determination of serum triglycerides. Clin Chem. 1983 Mar;29(3):538–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Qiao J. H., Hyman R., Ruddle D., Laughton C., Lusis A. J. Influence of the apoA-II gene locus on HDL levels and fatty streak development in mice. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Jan;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. E. Associations of high-density lipoprotein subclasses and apolipoproteins with ischemic heart disease and coronary atherosclerosis. Am Heart J. 1987 Feb;113(2 Pt 2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Mitchell D., Reue K., Morrow A., Lusis A. J., LeBoeuf R. C. Ath-1, a gene determining atherosclerosis susceptibility and high density lipoprotein levels in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. H., Lander E. S., Hewitt J. D., Peterson S., Lincoln S. E., Tanksley S. D. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):721–726. doi: 10.1038/335721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouliot M. C., Després J. P., Nadeau A., Moorjani S., Prud'Homme D., Lupien P. J., Tremblay A., Bouchard C. Visceral obesity in men. Associations with glucose tolerance, plasma insulin, and lipoprotein levels. Diabetes. 1992 Jul;41(7):826–834. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.7.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Mondon C. E. Effect of in vivo plasma insulin levels on the relationship between perfusate free fatty acid concentration and triglyceride secretion by perfused rat livers. Horm Metab Res. 1984 May;16(5):230–232. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer-Polokoff R., Margetin C., Abdollahi A., Tulp O. Effects of phenotype, sex, and diet on plasma lipids in LA/N-cp rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Sep;191(4):326–331. doi: 10.3181/00379727-191-42927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bain S. C. A practical approach to identification of susceptibility genes for IDDM. Diabetes. 1992 Sep;41(9):1029–1034. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.9.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett G. E., Bahary N., Friedman J. M., Leibel R. L. Rat obesity gene fatty (fa) maps to chromosome 5: evidence for homology with the mouse gene diabetes (db). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7806–7809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. E., MacSwiney F. M. An inherited mild middle-aged adiposity in wild mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Apr;82(2):309–317. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. B., Boozer C. N., Moody D. L., Atkinson R. L. Dietary obesity in nine inbred mouse strains. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):R1025–R1032. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.262.6.R1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


