Abstract
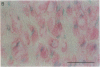
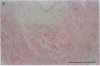
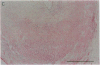
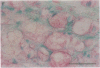
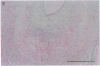
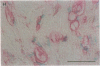
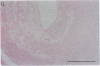
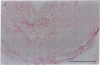
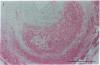
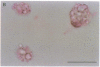
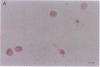
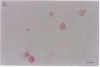
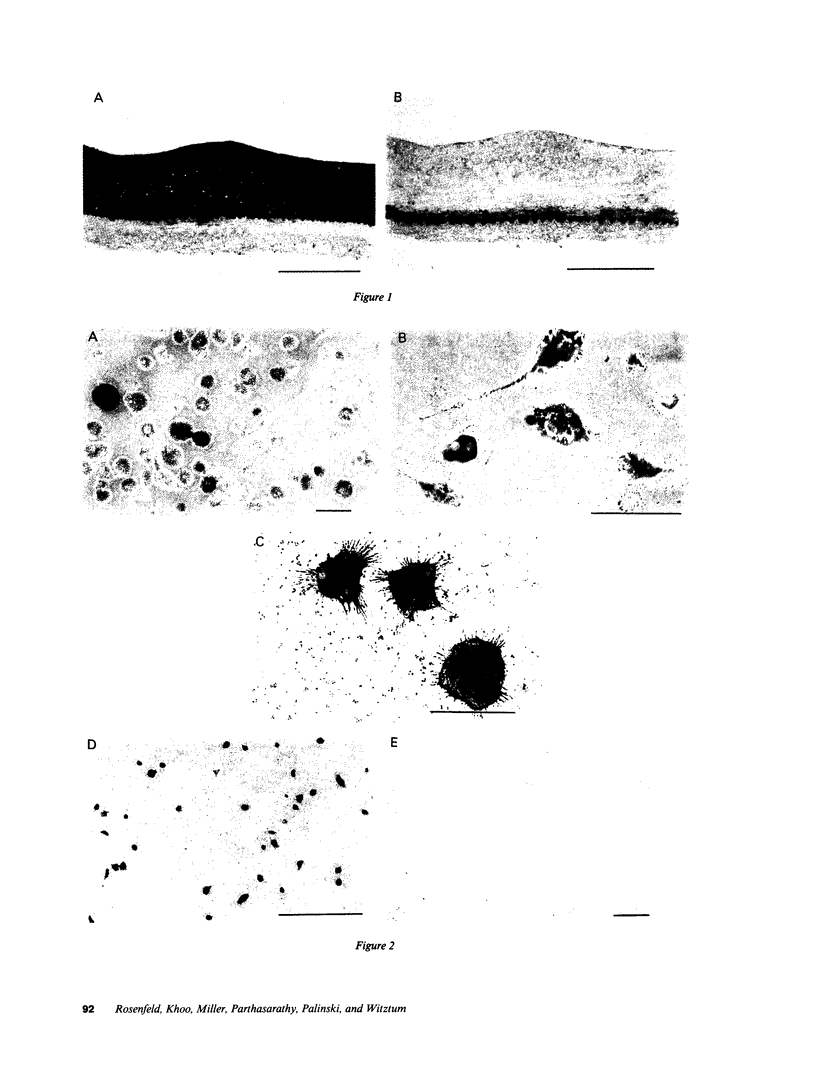
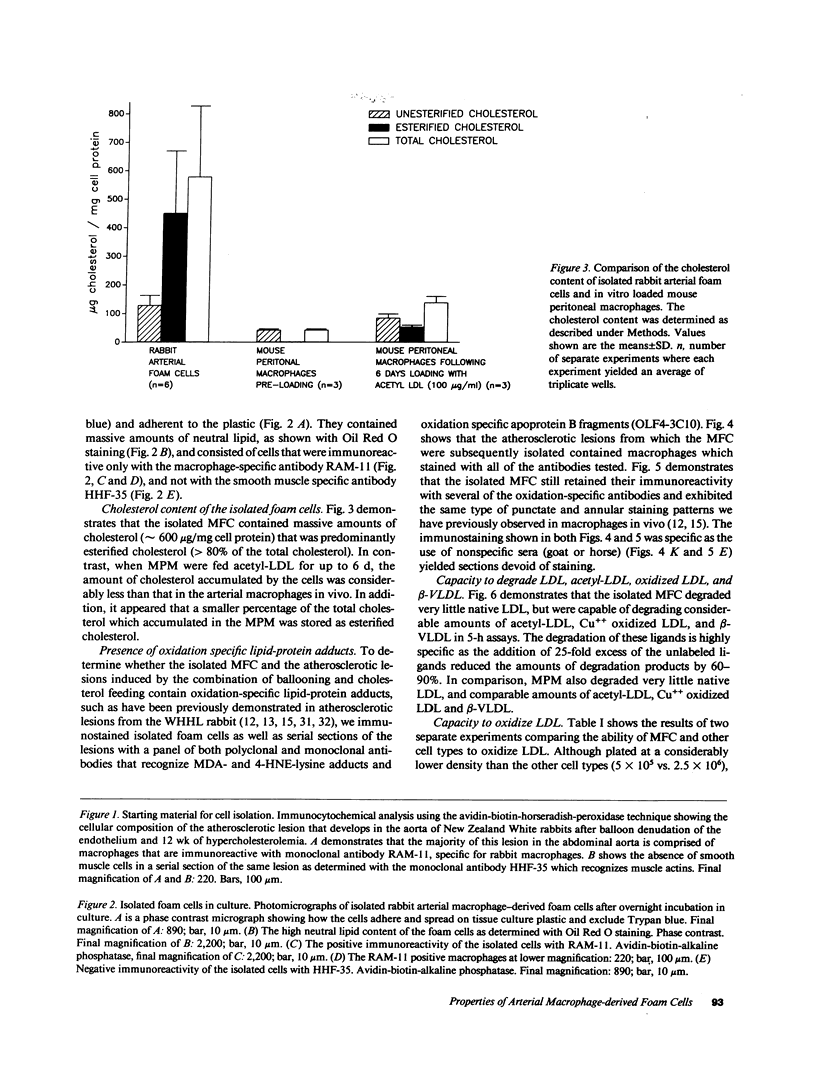
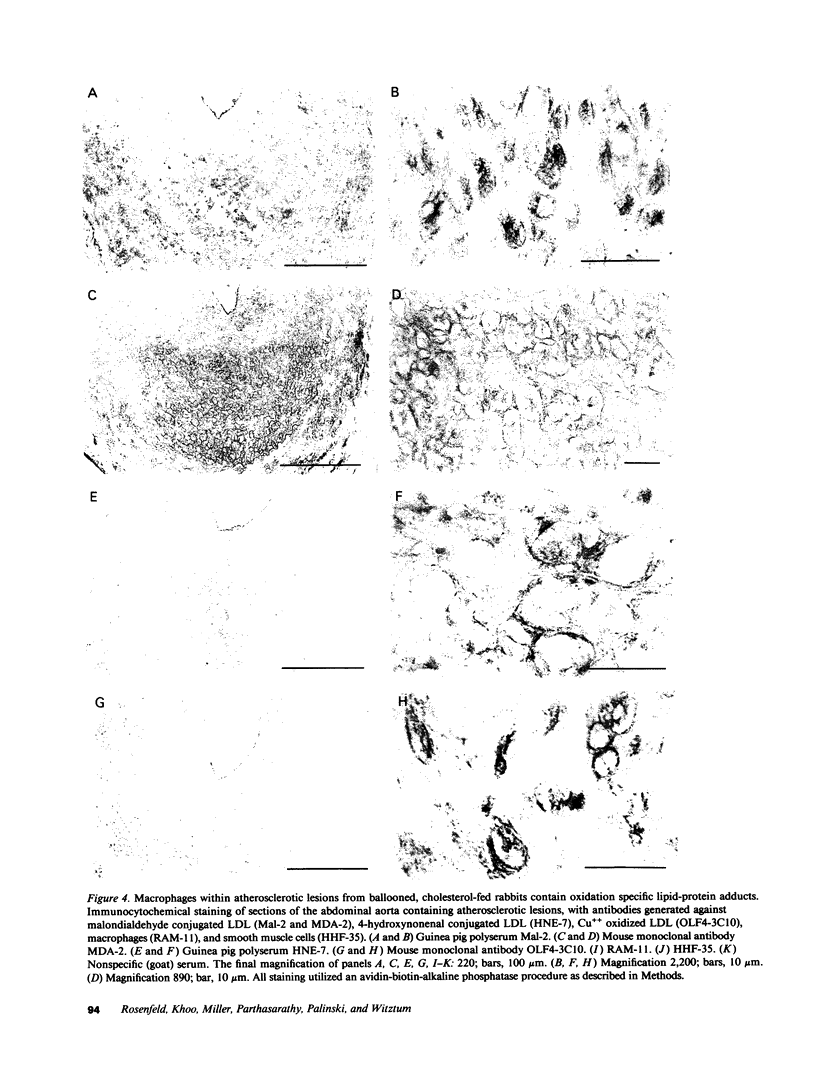
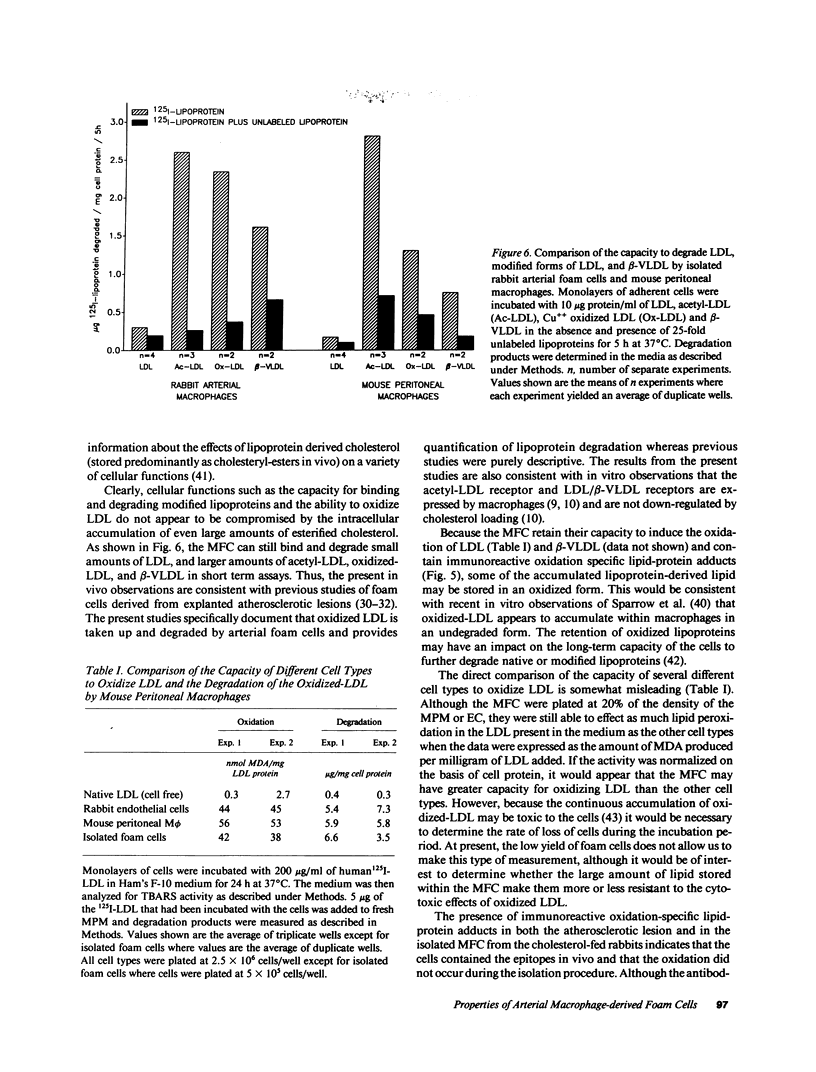
Pure macrophage-derived foam cells (MFC) were isolated from the aortas of rabbits made atherosclerotic by balloon deendothelialization followed by diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. The MFC were isolated under sterile conditions using an enzymatic digestion procedure and discontinuous density gradient centrifugation. The purity of the MFC preparations was verified immunocytochemically with the macrophage specific monoclonal antibody RAM-11. MFC plated in medium containing 0.5% FCS for 24 h contained approximately 600 micrograms cholesterol per mg cell protein, 80% of which was esterified cholesterol. The MFC specifically degraded low density lipoprotein (LDL), acetyl-LDL, copper oxidized LDL, and beta-very low density lipoprotein (beta-VLDL) at rates comparable to mouse peritoneal macrophages (MPM) in 5-h assays. MFC within sections of the atherosclerotic lesions from the ballooned rabbits as well as the MFC isolated from the same lesions in the presence of antioxidants, exhibited positive immunoreactivity with polyclonal guinea pig antisera and mouse monoclonal antibodies directed against malondialdehyde-LDL, and 4-hydroxynonal-LDL. The MFC also exhibited the capacity to induce the oxidation of LDL at rates comparable to those exhibited by MPM and rabbit aortic endothelial cells. These data provide direct evidence that arterial wall macrophages express modified LDL receptors in vivo, contain epitopes found in oxidized-LDL and are capable of oxidizing LDL even when maximally loaded with cholesterol.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson G. W., Brown M. S. Degradation of cationized low density lipoprotein and regulation of cholesterol metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberian P. A., Jenison M. W., Roddick V. Arterial prostaglandins and lysosomal function during atherogenesis. II. Isolated cells of diet-induced atherosclerotic aortas of rabbit. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Aug;43(1):36–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd H. C., Gown A. M., Wolfbauer G., Chait A. Direct evidence for a protein recognized by a monoclonal antibody against oxidatively modified LDL in atherosclerotic lesions from a Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1989 Nov;135(5):815–825. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart M. K., Morel D. W., Chisolm G. M., 3rd Monocytes and neutrophils oxidize low density lipoprotein making it cytotoxic. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Aug;38(2):341–350. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Seager J., Hokom M., Edwards P. A. Factors regulating the activities of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the scavenger receptor on human monocyte-macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1981 Sep;22(7):1131–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S., Berberian P. A., Shio H., Goldfischer S., Wolinsky H. Characterization of cell populations isolated from aortas of rhesus monkeys with experimental atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 1980 Apr;46(4):520–530. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S., Shio H., Haley N. J. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. IV. Investigation of macrophage-like properties of aortic cell populations. Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;41(4):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble W., Vaughan M., Kruth H. S., Avigan J. Procedure for determination of free and total cholesterol in micro- or nanogram amounts suitable for studies with cultured cells. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1068–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Fong D., Cheng L. Malondialdehyde-altered protein occurs in atheroma of Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.2455346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley N. J., Shio H., Fowler S. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. I. Resolution of aortic cell populations by metrizamide density gradient centrifugation. Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(3):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola O., Kallioniemi O. P., Nikkari T. Lipoprotein uptake in primary cell cultures of rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. A fluorescence microscopic and flow cytometric study. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Feb;69(2-3):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola O., Ylä-Herttuala S., Särkioja T., Nikkari T. Macrophage foam cells from human aortic fatty streaks take up beta-VLDL and acetylated LDL in primary culture. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Oct;79(2-3):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Zand T., Nunnari J. J., Krolikowski F. J., Majno G. Studies on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. I. Adhesion and emigration of mononuclear cells in the aorta of hypercholesterolemic rats. Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):341–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Miller E., McLoughlin P., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage uptake of low density lipoprotein after self-aggregation. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):348–358. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.4.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Innerarity T. L. Uptake of canine beta-very low density lipoproteins by mouse peritoneal macrophages is mediated by a low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11194–11201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Gump H., Diller P., Getz G. S. Macrophage free cholesterol content regulates apolipoprotein E synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11657–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., van der Walt J. D., Munro C. S., Chalmers J. A., Cox E. L. An immunohistochemical analysis of human aortic fatty streaks. Hum Pathol. 1987 Apr;18(4):375–380. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito M., Kuzuya M., Funaki C., Nakayama Y., Asai K., Kuzuya F. Separation and characterization of macrophages and smooth muscle cells in rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Artery. 1987;14(5):266–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Ylä-Herttuala S., Gurtner G. C., Socher S. S., Butler S. W., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Low density lipoprotein undergoes oxidative modification in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1372–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Rosenfeld M. E., Butler S. W., Socher S. A., Parthasarathy S., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Antisera and monoclonal antibodies specific for epitopes generated during oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):325–335. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Quinn M. T., Schwenke D. C., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Oxidative modification of beta-very low density lipoprotein. Potential role in monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):398–404. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Foam cells in explants of atherosclerotic rabbit aortas have receptors for beta-very low density lipoproteins and modified low density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):2–12. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Butler S., Witztum J. L. Distribution of oxidation specific lipid-protein adducts and apolipoprotein B in atherosclerotic lesions of varying severity from WHHL rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):336–349. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Tsukada T., Gown A. M., Ross R. Fatty streak initiation in Watanabe Heritable Hyperlipemic and comparably hypercholesterolemic fat-fed rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):9–23. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Taylor K., Bartucci E. J., Fischer-Dzoga K., Beeson J. H., Glagov S., Wissler R. W. Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. F., Kim D. N., Schmee J., Thomas W. A. Atherosclerotic lesions in coronary arteries of hyperlipidemic swine. Part 2. Endothelial cell kinetics and leukocyte adherence associated with early lesions. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Oct;62(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shio H., Haley N. J., Fowler S. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. III. Intracellular localization of cholesterol and cholesteryl ester. Lab Invest. 1979 Aug;41(2):160–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. A macrophage receptor that recognizes oxidized low density lipoprotein but not acetylated low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Parthasarathy S., Leake D. S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suits A. G., Chait A., Aviram M., Heinecke J. W. Phagocytosis of aggregated lipoprotein by macrophages: low density lipoprotein receptor-dependent foam-cell formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Rosenfeld M., Ross R., Gown A. M. Immunocytochemical analysis of cellular components in atherosclerotic lesions. Use of monoclonal antibodies with the Watanabe and fat-fed rabbit. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):601–613. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Tippens D., Gordon D., Ross R., Gown A. M. HHF35, a muscle-actin-specific monoclonal antibody. I. Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten B. J., Fogelman A. M., Hokom M. M., Benson L., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A. Regulation of the uptake and degradation of beta-very low density lipoprotein in human monocyte macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5151–5157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Butler S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Evidence for the presence of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbit and man. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI114271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]