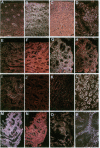
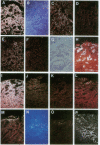
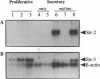
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases are a highly regulated family of enzymes, that together can degrade most components of the extracellular matrix. These proteins are active in normal and pathological processes involving tissue remodeling; however, their sites of synthesis and specific roles are poorly understood. Using in situ hybridization, we determined cellular distributions of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, an inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases, in endometrium during the reproductive cycle. The mRNAs for all the metalloproteinases were detected in menstrual endometrium, but with different tissue distributions. The mRNA for matrilysin was localized to epithelium, while the others were detected in stromal cells. Only the transcripts for the 72-kD gelatinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 were detected throughout the cycle. Transcripts for stromelysin-2 and the 92-kD gelatinase were only detected in late secretory and menstrual endometrium, while those for matrilysin, the 72-kD gelatinase, and stromelysin-3 were also consistently detected in proliferative endometrium. These data indicate that matrix metalloproteinases are expressed in cell-type, tissue, and reproductive cycle-specific patterns, consistent with regulation by steroid hormones, and with specific roles in the complex tissue growth and remodeling processes occurring in the endometrium during the reproductive cycle.
Full text
PDF

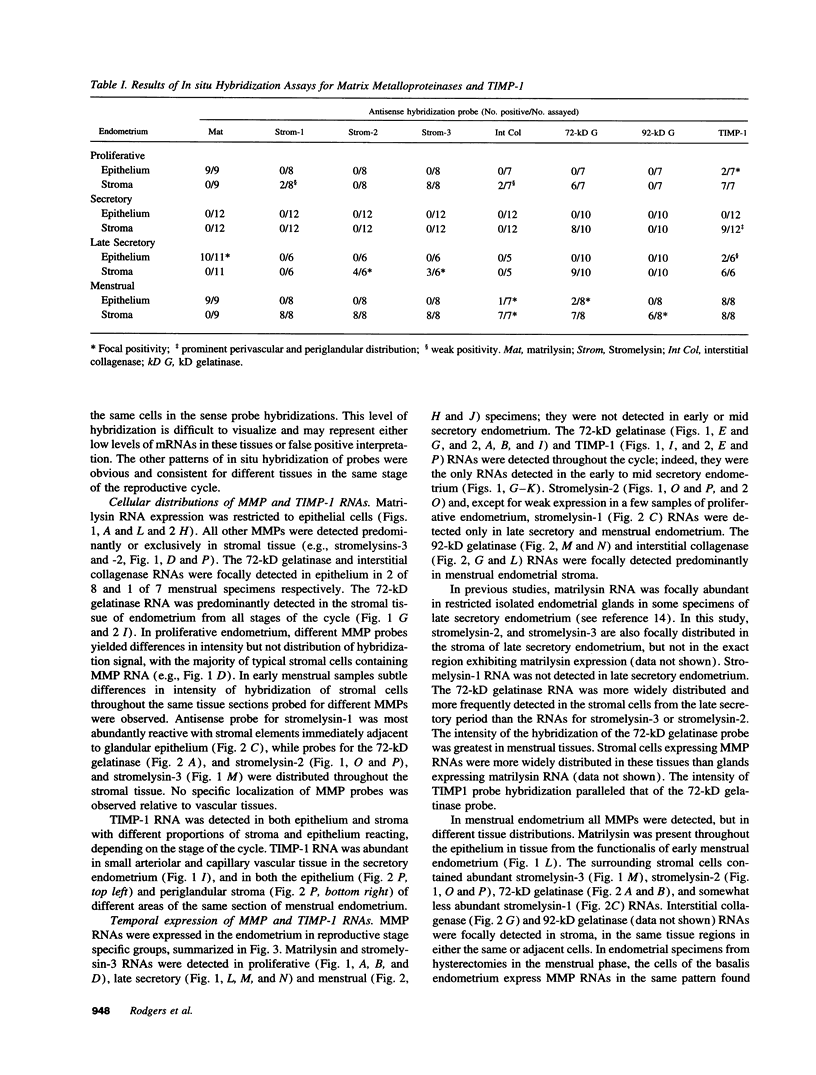


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset P., Bellocq J. P., Wolf C., Stoll I., Hutin P., Limacher J. M., Podhajcer O. L., Chenard M. P., Rio M. C., Chambon P. A novel metalloproteinase gene specifically expressed in stromal cells of breast carcinomas. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):699–704. doi: 10.1038/348699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Moore W. G., Bodden M. K., Windsor L. J., Birkedal-Hansen B., DeCarlo A., Engler J. A. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4(2):197–250. doi: 10.1177/10454411930040020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier I. E., Wilhelm S. M., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Seltzer J. L., Kronberger A., He C. S., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry T. E., Jr, Mann J. S., Huang M. H., Keeble S. C. Gelatinase and proteoglycanase activity during the periovulatory period in the rat. Biol Reprod. 1992 Feb;46(2):256–264. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod46.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Ruley H. E. Transcription from the stromelysin promoter is induced by interleukin-1 and repressed by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16300–16304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaire M., Magbanua Z., McDonnell S., McNeil L., Lovett D. H., Matrisian L. M. Structure and expression of the human gene for the matrix metalloproteinase matrilysin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2032–2040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy D. L., Hodgen G. D. The endocrinology of human endometrium. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1983 Aug;38(8):509–530. doi: 10.1097/00006254-198308000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre O., Wolf C., Limacher J. M., Hutin P., Wendling C., LeMeur M., Basset P., Rio M. C. The breast cancer-associated stromelysin-3 gene is expressed during mouse mammary gland apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):997–1002. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Librach C. L., Werb Z., Fitzgerald M. L., Chiu K., Corwin N. M., Esteves R. A., Grobelny D., Galardy R., Damsky C. H., Fisher S. J. 92-kD type IV collagenase mediates invasion of human cytotrophoblasts. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):437–449. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Metalloproteinases and cancer invasion. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix E., Donnez J., Courtoy P. J., Eeckhout Y. Progesterone regulates the activity of collagenase and related gelatinases A and B in human endometrial explants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11789–11793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martelli M., Campana A., Bischof P. Secretion of matrix metalloproteinases by human endometrial cells in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 1993 May;98(1):67–76. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0980067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. The matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):455–463. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell S., Navre M., Coffey R. J., Jr, Matrisian L. M. Expression and localization of the matrix metalloproteinase pump-1 (MMP-7) in human gastric and colon carcinomas. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(6):527–533. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Quantin B., Gesnel M. C., Millon-Collard R., Abecassis J., Breathnach R. The collagenase gene family in humans consists of at least four members. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2530187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Mader S., Nagpal S., Leid M., Rochette-Egly C., Chambon P. Negative regulation of the rat stromelysin gene promoter by retinoic acid is mediated by an AP1 binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4443–4454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavloff N., Staskus P. W., Kishnani N. S., Hawkes S. P. A new inhibitor of metalloproteinases from chicken: ChIMP-3. A third member of the TIMP family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17321–17326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop M., Knapp B., Winter H., Schweizer J. Aminoalkylsilane-treated glass slides as support for in situ hybridization of keratin cDNAs to frozen tissue sections under varying fixation and pretreatment conditions. Histochem J. 1986 May;18(5):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01676237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17374–17378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Li L., Jancic V., Wenczak B. A., Nanney L. B. Localization of mRNAs representing collagenase and TIMP in sections of healing human burn wounds. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1657–1666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Welgus H. G. Human skin fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Purification and biochemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12252–12258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr, Taplin C. J. Purification and properties of a small latent matrix metalloproteinase of the rat uterus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16918–16925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C., Rouyer N., Lutz Y., Adida C., Loriot M., Bellocq J. P., Chambon P., Basset P. Stromelysin 3 belongs to a subgroup of proteinases expressed in breast carcinoma fibroblastic cells and possibly implicated in tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]