Abstract
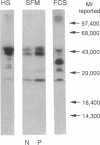
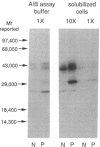
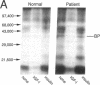
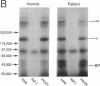
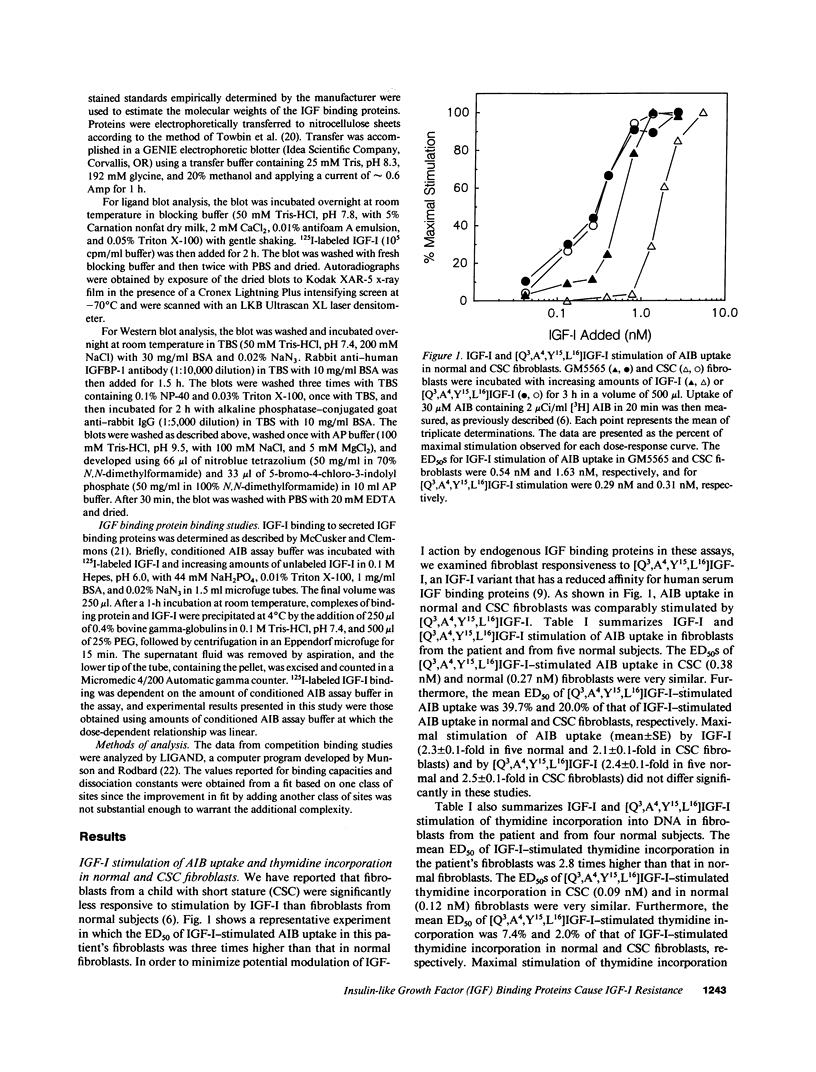
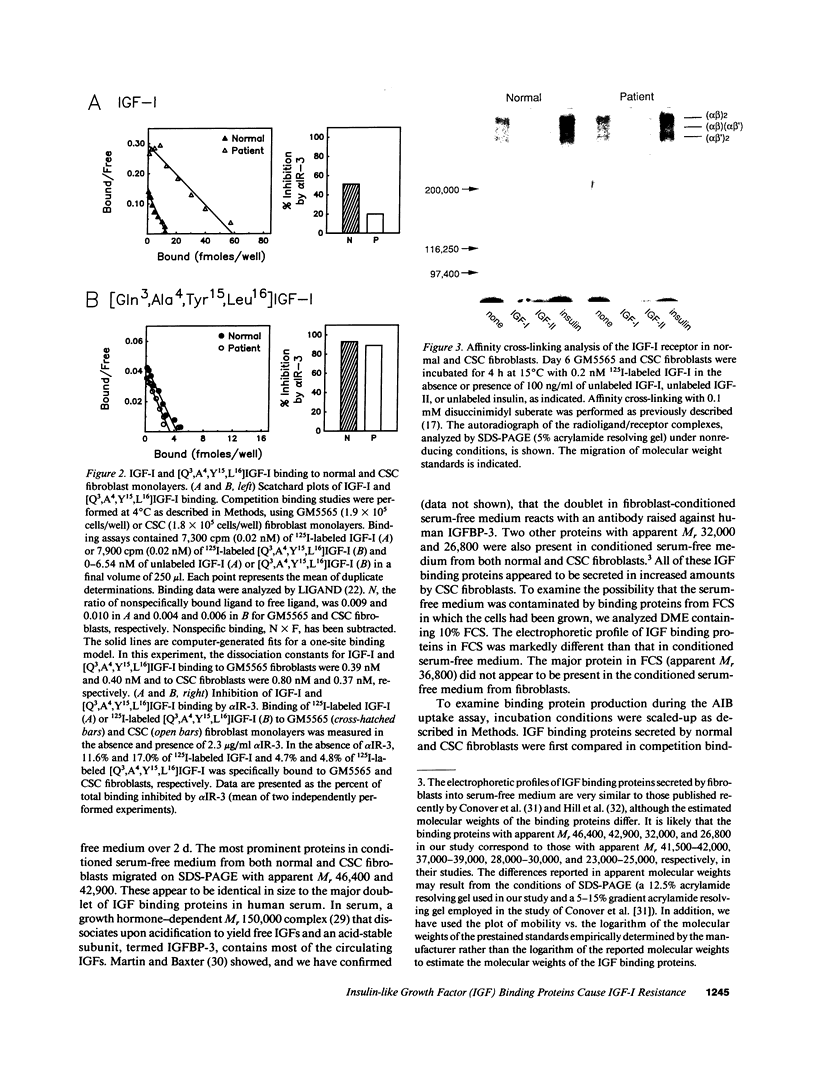
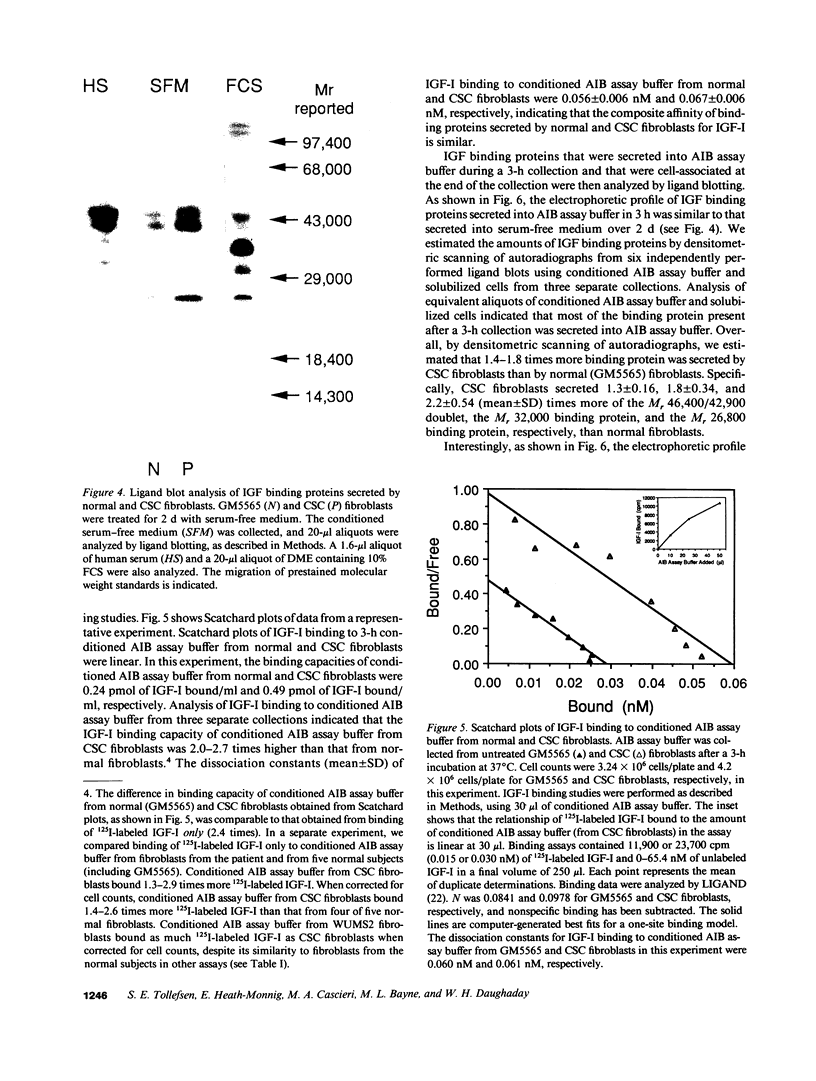
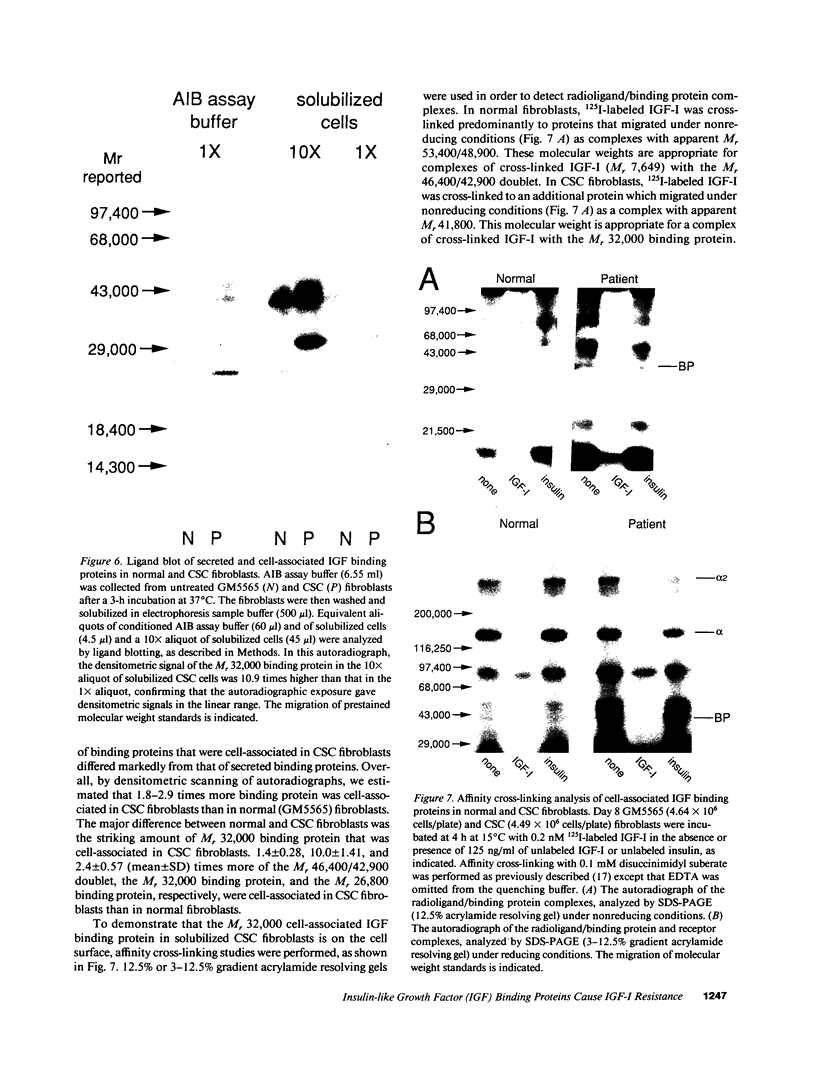
The ED50 of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I-stimulated alpha-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) uptake (mean +/- SD) in cultured fibroblasts from a child with short stature that we have reported (1.40 +/- 0.24 nM), is significantly higher than the ED50 of IGF-I-stimulated AIB uptake in fibroblasts from 11 normal subjects (0.42 +/- 0.12 nM) and from 127 short children (0.35 +/- 0.11 nM). Similarly, the ED50 of IGF-I-stimulated thymidine incorporation in fibroblasts from this child is 2.8 times higher than that in fibroblasts from four normal subjects. To minimize potential modulation of IGF-I action by endogenous IGF binding proteins in these assays, fibroblast responsiveness to [Q3,A4,Y15,L16]IGF-I, an IGF-I variant that has a 600-fold reduced affinity for serum IGF binding proteins, has been examined. The biological activity of this variant is comparable in the patient's and normal fibroblasts, suggesting that the resistance to IGF-I action cannot be attributed to a defective IGF-I receptor. To investigate directly the possibility that IGF-I sensitivity in the patient's fibroblasts is reduced by endogenous IGF binding proteins (IGFBP), binding proteins that are secreted into AIB assay buffer during a 3-h collection and that are cell-associated at the end of the collection have been analyzed. Ligand blot analysis of conditioned AIB assay buffer demonstrates that fibroblasts from the patient secrete 1.3-2.2 times more of Mr 46,400/42,900, 32,000, and 26,800 binding proteins than normal fibroblasts. The major difference between fibroblasts from the patient and from normal subjects is a striking 10-fold increase in the amount of a cell surface Mr 32,000 binding protein in the patient's fibroblasts. The Mr 32,000 binding protein is similar in size to IGFB-1 and different from IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-3, but it does not cross-react with an antibody against IGFBP-1. We conclude that the resistance to IGF-I action in the patient's fibroblasts is caused by an abnormal production and/or cell association of IGF binding proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors: structure, regulation and function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Applebaum J., Chicchi G. G., Hayes N. S., Green B. G., Cascieri M. A. Structural analogs of human insulin-like growth factor I with reduced affinity for serum binding proteins and the type 2 insulin-like growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6233–6239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierich J. R., Moeller H., Ranke M. B., Rosenfeld R. G. Pseudopituitary dwarfism due to resistance to somatomedin: a new syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Aug;142(3):186–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00442446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binkert C., Landwehr J., Mary J. L., Schwander J., Heinrich G. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding a novel insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-2). EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2497–2502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C., Kortleve D. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Drop S. L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IBP-1). EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2417–2423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Chiariotti L., Orlowski C. C., Mehlman T., Burgess W. H., Ackerman E. J., Bruni C. B., Rechler M. M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA clone encoding a fetal rat binding protein for insulin-like growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5148–5154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Jr, Klapper D. G., Clemmons D. R. Purification of a 31,000-dalton insulin-like growth factor binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Isolation of two forms with different biologic actions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14203–14210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Elgin R. G., Han V. K., Casella S. J., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Cultured fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that alters the cellular binding of somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1548–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI112470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Liu F., Powell D., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins from cultured human fibroblasts. Characterization and hormonal regulation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):852–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI113968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mellow J. S., Baxter R. C. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein both inhibits and potentiates IGF-I-stimulated DNA synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):199–204. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80824-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vroede M. A., Tseng L. Y., Katsoyannis P. G., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Modulation of insulinlike growth factor I binding to human fibroblast monolayer cultures by insulinlike growth factor carrier proteins released to the incubation media. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI112343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Moses A. C. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the IGF-I receptor that inhibit IGF-I binding to human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):929–936. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Usher P., Moses A. C. Monoclonal antibody to the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) receptor blocks IGF-I receptor-mediated DNA synthesis: clarification of the mitogenic mechanisms of IGF-I and insulin in human skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath-Monnig E., Daughaday W. H. Sensitization of human fibroblasts to insulin-like growth factor I by serum deprivation and dexamethasone pretreatment. Endocr Res. 1989;15(3):303–322. doi: 10.3109/07435808909042743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath-Monnig E., Wohltmann H. J., Mills-Dunlap B., Daughaday W. H. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) responsiveness of fibroblasts of children with short stature: identification of a patient with IGF-I resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):501–507. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Camacho-Hubner C., Rashid P., Strain A. J., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein release by human fetal fibroblasts: dependency on cell density and IGF peptides. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):87–98. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz P. B. Glucocorticoids enhance somatomedin-C binding and stimulation of amino acid uptake in human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):563–571. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Antibody against acid-stable insulin-like growth factor binding protein detects 150,000 mol wt growth hormone-dependent complex in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):799–801. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGF-BPs) produced by human skin fibroblasts: immunological relationship to other human IGF-BPs. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1907–1915. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Production of an insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-inducible IGF-binding protein by human skin fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):781–788. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Willetts K. E., Baxter R. C. Purification and properties of a novel insulin-like growth factor-II binding protein from transformed human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4124–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein secretion by muscle cells: effect of cellular differentiation and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):505–512. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Usher P., Ikari N., King P. P., Tramontano D., Flier J. S. Multiple factors influence insulin-like growth factor-I binding to human skin fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):867–875. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Ranta T., Jalkanen J., Suikkari A. M., Voutilainen R., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human decidua inhibits the binding and biological action of IGF-I in cultured choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2150–2157. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaoka T., Kobayashi M., Takata Y., Ishibashi O., Iwasaki M., Shigeta Y., Goji K., Hisatomi A. Clarification of signaling pathways mediated by insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors in fibroblasts from patients with specific defect in insulin receptor. Diabetes. 1988 Nov;37(11):1515–1523. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.11.1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Lajara R., McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in muscle development. Expression of IGF-I, the IGF-I receptor, and an IGF binding protein during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13810–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Sadow J. L., Rotwein P. Coordinate expression of insulin-like growth factor II and its receptor during muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1543–1547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K., Petersen D. J. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16461–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Nissley S. P., Humbel R. E. Receptors for insulinlike growth factor I are defective in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]