Abstract
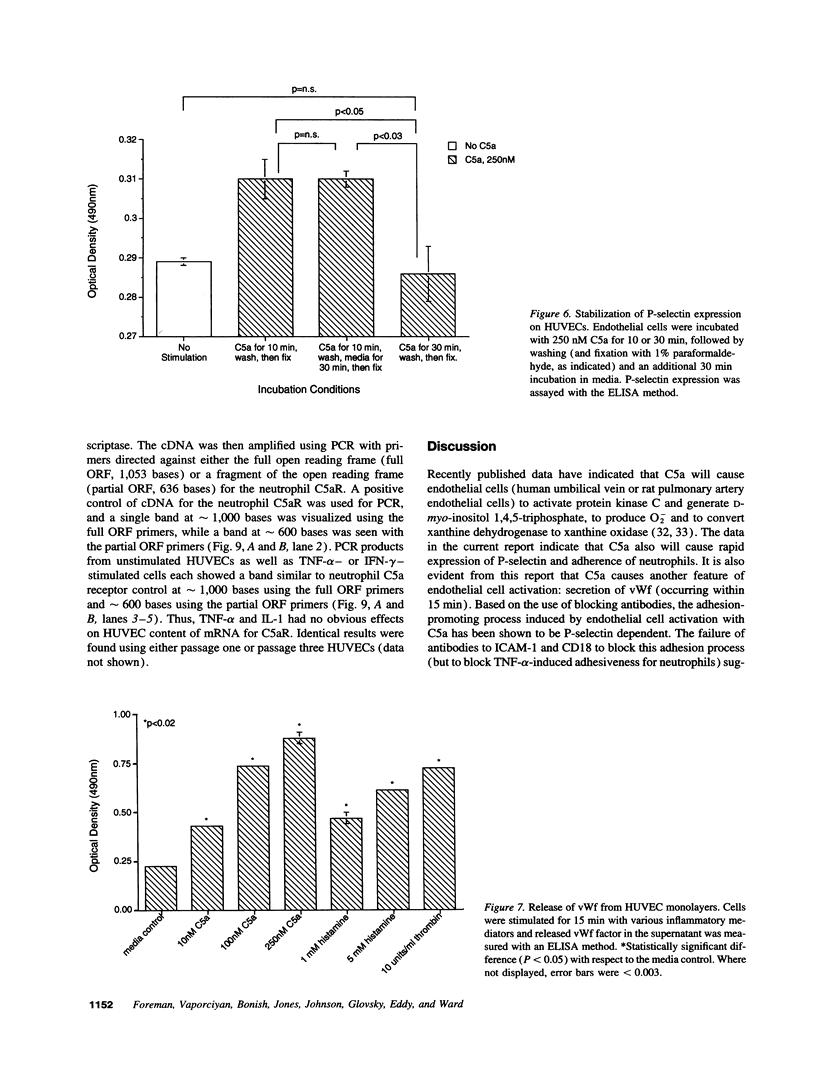
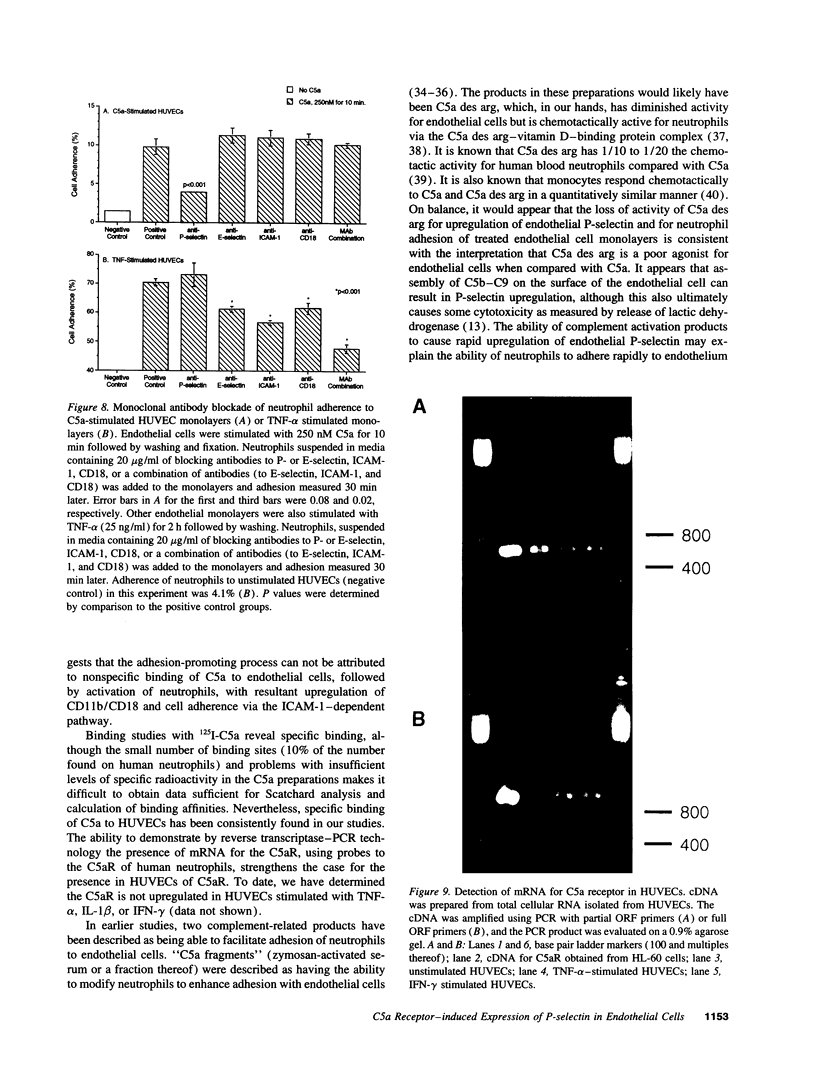
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells have recently been shown to respond to C5a with increases in intracellular Ca2+, production of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and superoxide anion generation. In the current studies, C5a had been found to cause in a time- and dose-dependent manner rapid expression of endothelial P-selectin, secretion of von Willebrand factor, and adhesiveness for human neutrophils. The effects of C5a in P-selectin expression and adhesiveness of neutrophils were similar to the effects of histamine and thrombin on endothelial cells. The adhesiveness of C5a-stimulated endothelium for neutrophils was blocked by anti-P-selectin, but not by antibodies to intercellular adhesion molecule 1, E-selectin, or CD18. A cell-based ELISA technique has confirmed upregulation of P-selectin in endothelial cells exposed to C5a. Binding of C5a to endothelial cells has been demonstrated, with molecules bound being approximately 10% of those binding to neutrophils. By a reverse transcriptase-PCR technique, endothelial cells have been shown to contain mRNA for the C5a receptor. These data suggest that C5a may be an important inflammatory mediator for the early adhesive interactions between neutrophils and endothelial cells in the acute inflammatory response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonfanti R., Furie B. C., Furie B., Wagner D. D. PADGEM (GMP140) is a component of Weibel-Palade bodies of human endothelial cells. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1109–1112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion as an active, multi-step process: a combinatorial mechanism for specificity and diversity in leukocyte targeting. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;323:181–194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3396-2_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Kenney J. S., Jones M. L., Warren J. S., Remick D. G. Biphasic production of IL-8 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human whole blood. Separation of LPS- and cytokine-stimulated components using anti-tumor necrosis factor and anti-IL-1 antibodies. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl H. P., Till G. O., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Mediator-induced activation of xanthine oxidase in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2512–2518. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2806779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng J. G., Heavner G. A., McEver R. P. Lectin domain peptides from selectins interact with both cell surface ligands and Ca2+ ions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19846–19853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng J. G., Moore K. L., Johnson A. E., McEver R. P. Neutrophil recognition requires a Ca(2+)-induced conformational change in the lectin domain of GMP-140. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22313–22318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Response of human neutrophils to C5a: a role for the oligosaccharide moiety of human C5ades Arg-74 but not of C5a in biologic activity. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1978–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Hugli T. E. Identification of classical anaphylatoxin as the des-Arg form of the C5a molecule: evidence of a modulator role for the oligosaccharide unit in human des-Arg74-C5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Hodges M. K., Drazen J. M., Weller P. F., Gerard C. Characterization of a receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1760–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., Fugate R. D., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Stimulated secretion of endothelial von Willebrand factor is accompanied by rapid redistribution to the cell surface of the intracellular granule membrane protein GMP-140. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7768–7771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori R., Hamilton K. K., McEver R. P., Sims P. J. Complement proteins C5b-9 induce secretion of high molecular weight multimers of endothelial von Willebrand factor and translocation of granule membrane protein GMP-140 to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9053–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Folger R., Haering W. A., Ware B. R., Karnovsky M. J. Adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium: roles of divalent cations, surface charge, chemotactic agents and substrate. J Cell Sci. 1980 Oct;45:73–86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.45.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huey R., Hugli T. E. Characterization of a C5a receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2063–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew R. R., Webster R. O. Gc-globulin (vitamin D-binding protein) enhances the neutrophil chemotactic activity of C5a and C5a des Arg. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):364–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI113596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence M. B., Springer T. A. Leukocytes roll on a selectin at physiologic flow rates: distinction from and prerequisite for adhesion through integrins. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):859–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90393-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorant D. E., Patel K. D., McIntyre T. M., McEver R. P., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Coexpression of GMP-140 and PAF by endothelium stimulated by histamine or thrombin: a juxtacrine system for adhesion and activation of neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):223–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorant D. E., Topham M. K., Whatley R. E., McEver R. P., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Inflammatory roles of P-selectin. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):559–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI116623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg C., Marceau F., Huey R., Hugli T. E. Anaphylatoxin C5a fails to promote prostacyclin release in cultured endothelial cells from human umbilical veins. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Oct;12(2):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder S. R., Chenoweth D. E., Goldstein I. M., Perez H. D. Chemotactic responses of human peripheral blood monocytes to the complement-derived peptides C5a and C5a des Arg. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3325–3331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks R. M., Todd R. F., 3rd, Ward P. A. Rapid induction of neutrophil-endothelial adhesion by endothelial complement fixation. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):314–317. doi: 10.1038/339314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Beckstead J. H., Moore K. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Bainton D. F. GMP-140, a platelet alpha-granule membrane protein, is also synthesized by vascular endothelial cells and is localized in Weibel-Palade bodies. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):92–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI114175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Martin M. N. A monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein binds only to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9799–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Stults N. L., Diaz S., Smith D. F., Cummings R. D., Varki A., McEver R. P. Identification of a specific glycoprotein ligand for P-selectin (CD62) on myeloid cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):445–456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. A., Weigl S. A., Deng X., Phillips D. M. PECAM-1 is required for transendothelial migration of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):449–460. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Polley M. J., Bayer R. J., Nunn M. F., Paulson J. C., Ward P. A. Neutrophil-dependent acute lung injury. Requirement for P-selectin (GMP-140). J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1600–1607. doi: 10.1172/JCI116029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Vaporciyan A. A., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha regulates in vivo intrapulmonary expression of ICAM-1. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1739–1749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Varani J., Dame M. K., Lane C. L., Smith C. W., Anderson D. C., Ward P. A. Role of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) in neutrophil-mediated lung injury in rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1396–1406. doi: 10.1172/JCI115446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard K. E., Moore K. L., Diaz S., Stults N. L., Ushiyama S., McEver R. P., Cummings R. D., Varki A. Characterization of a specific ligand for P-selectin on myeloid cells. A minor glycoprotein with sialylated O-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12764–12774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. D., Zimmerman G. A., Prescott S. M., McEver R. P., McIntyre T. M. Oxygen radicals induce human endothelial cells to express GMP-140 and bind neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):749–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Kelly E., Chenoweth D., Elfman F. Identification of the C5a des Arg cochemotaxin. Homology with vitamin D-binding protein (group-specific component globulin). J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):360–363. doi: 10.1172/JCI113595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Springer M. S. Identification of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte C5a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7157–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg P. E., McEver R. P., Shuman M. A., Jacques Y. V., Bainton D. F. A platelet alpha-granule membrane protein (GMP-140) is expressed on the plasma membrane after activation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):880–886. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen M. G., Smedly L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions. Modulation of neutrophil adhesiveness induced by complement fragments C5a and C5a des arg and formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1581–1592. doi: 10.1172/JCI111574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaporciyan A. A., DeLisser H. M., Yan H. C., Mendiguren I. I., Thom S. R., Jones M. L., Ward P. A., Albelda S. M. Involvement of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1580–1582. doi: 10.1126/science.8248808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaporciyan A. A., Jones M. L., Ward P. A. Rapid analysis of leukocyte-endothelial adhesion. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Feb 26;159(1-2):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90145-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., Hill H. R. Inflammatory mediators stimulate granulocyte adherence to cultured human endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1984 Jul 15;35(2):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
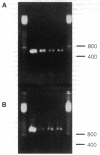
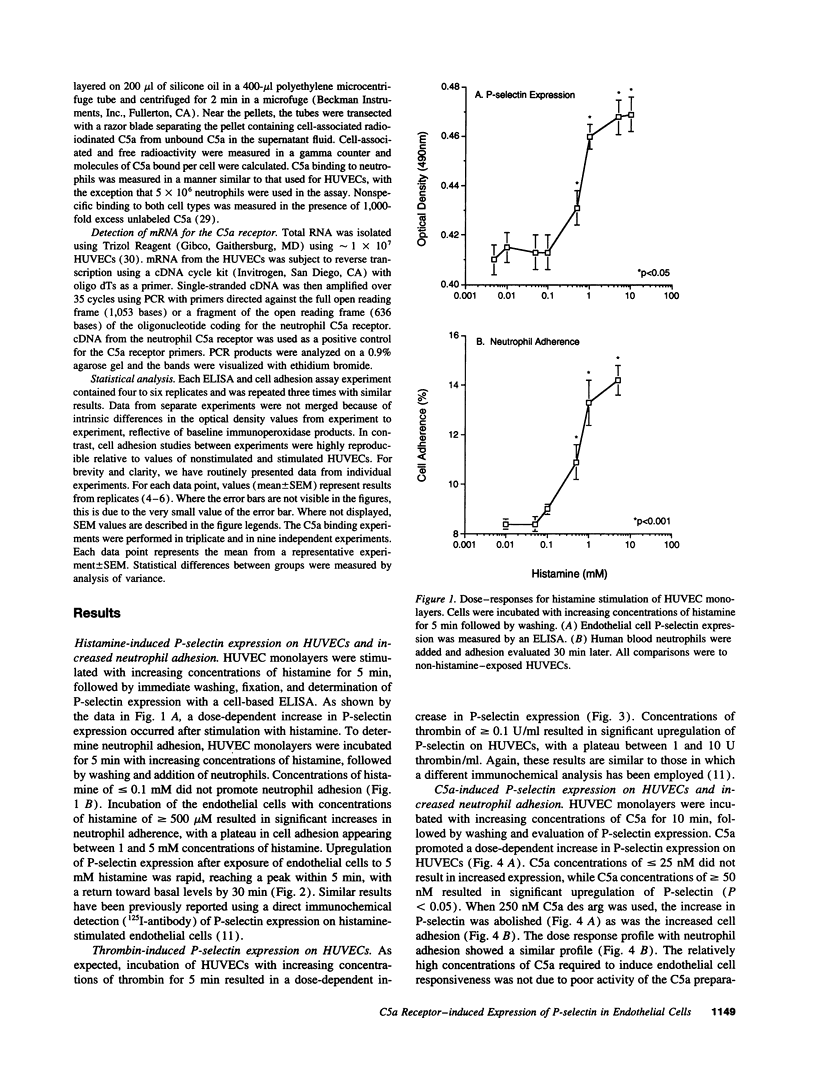
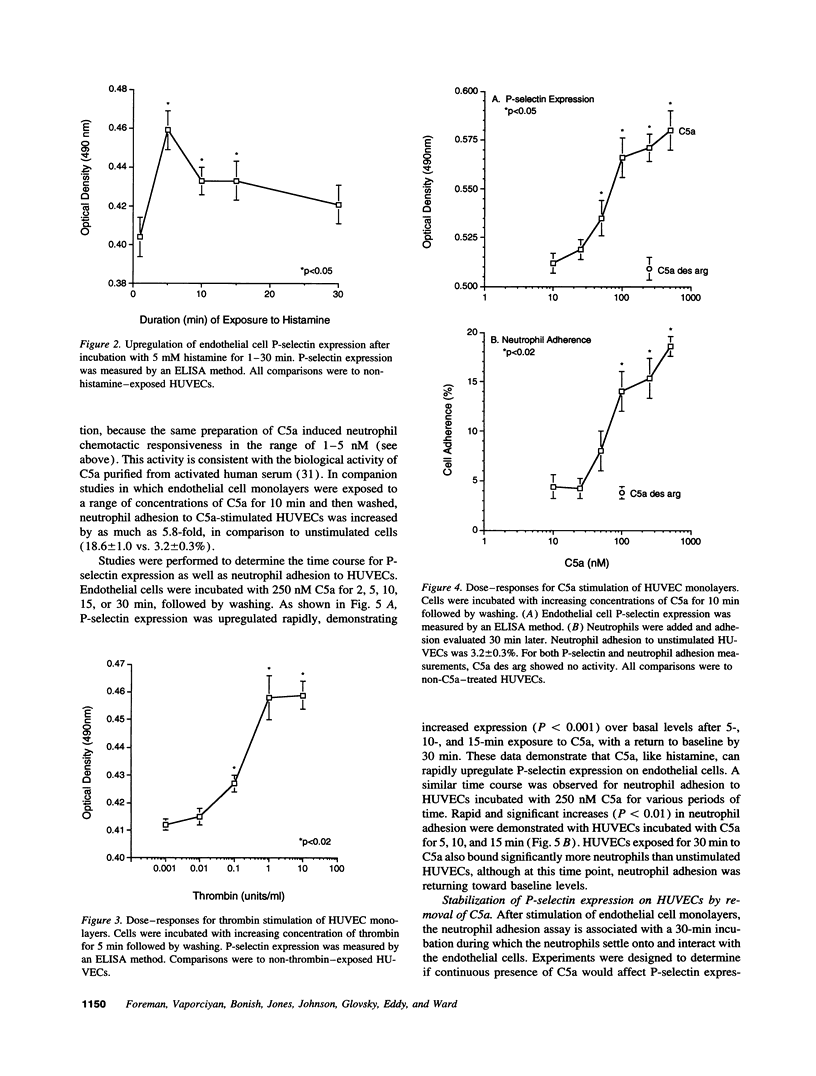
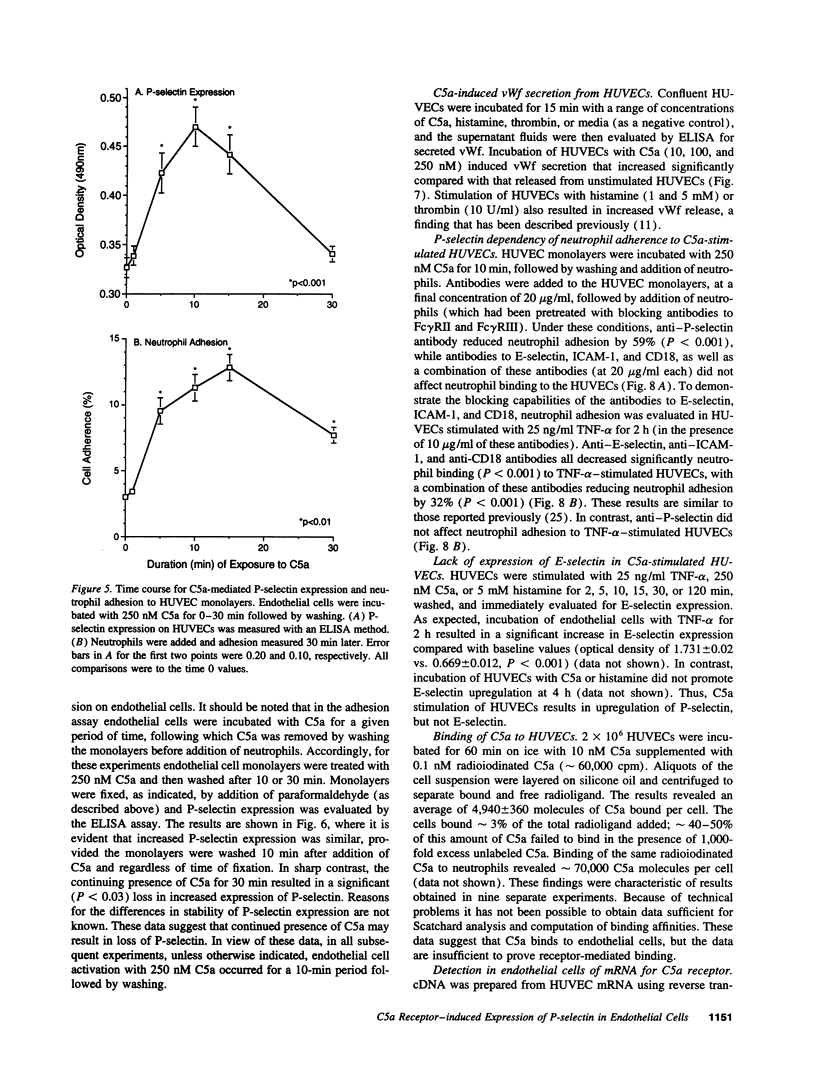
- Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Neutrophil adherence to human endothelium in vitro occurs by CDw18 (Mo1, MAC-1/LFA-1/GP 150,95) glycoprotein-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):531–537. doi: 10.1172/JCI113351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., Prescott S. M., McIntyre T. M. Endothelial cell interactions with granulocytes: tethering and signaling molecules. Immunol Today. 1992 Mar;13(3):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]