Abstract
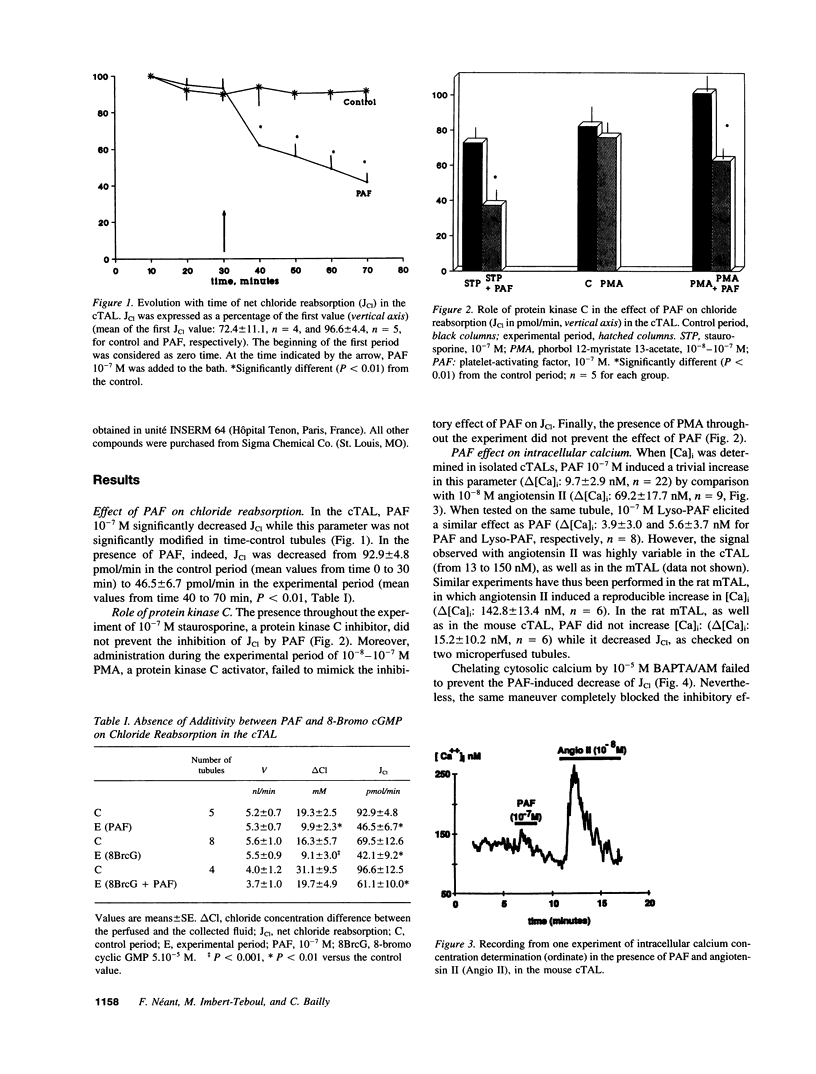
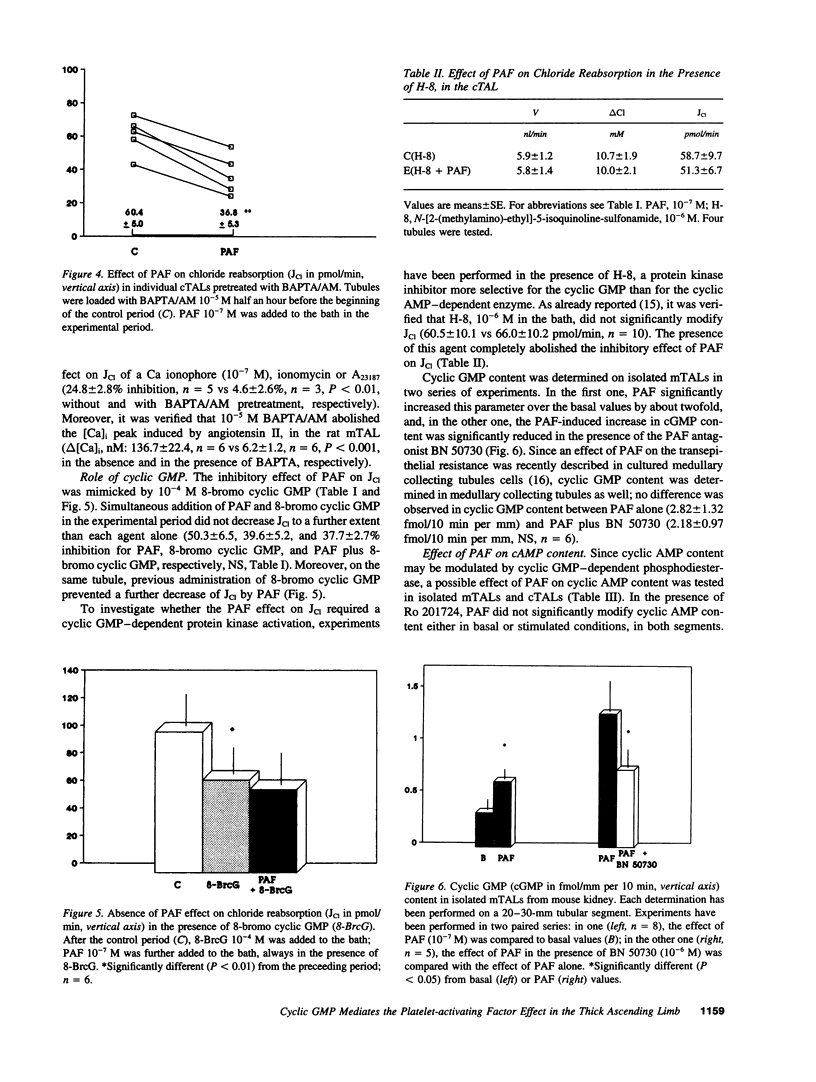
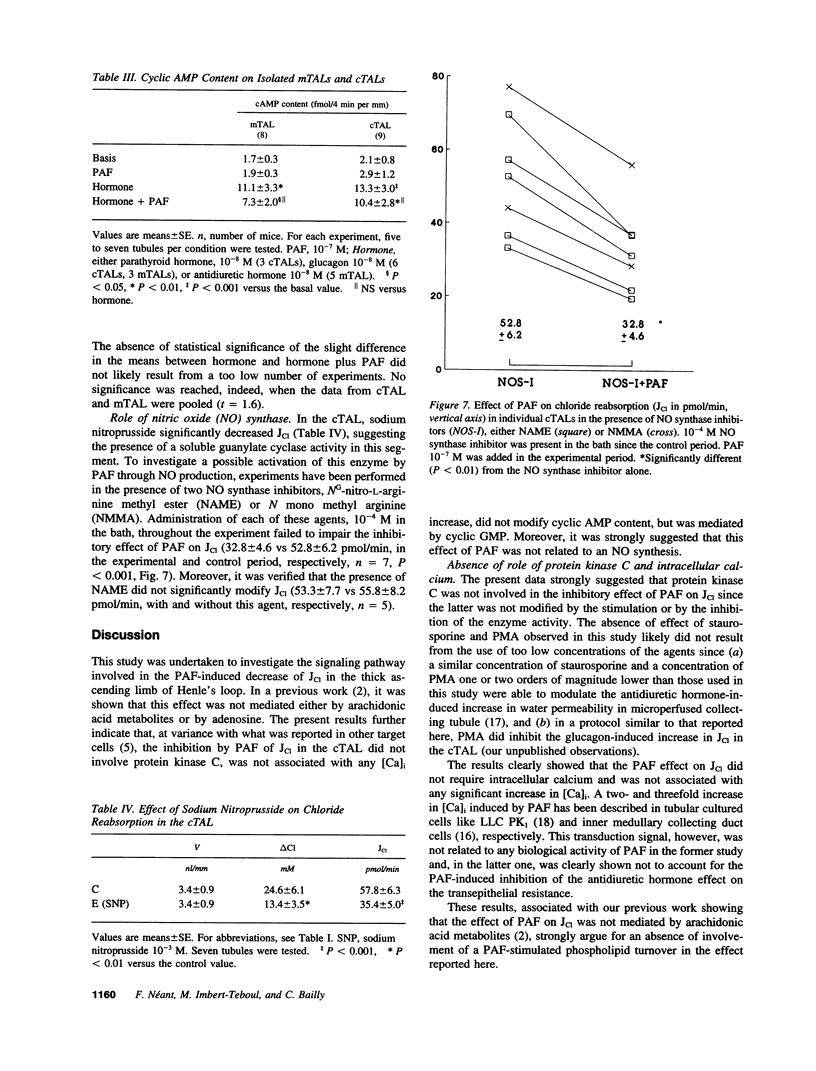
Since we have previously shown a direct inhibitory effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) on Cl reabsorption in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop (TAL), the aim of this study was to extend this effect to the whole TAL and to further investigate the signaling pathway involved. In microperfused cortical TALs, PAF significantly decreased Cl reabsorption by 50.3 +/- 6.5%. On the one hand, this effect was not modified in the presence of staurosporine and was not mimicked by phorbol ester; chelating cytosolic Ca by BAPTA/AM failed to suppress the inhibitory effect of PAF on Cl reabsorption; moreover, no significant increase in intracellular Ca concentration could be observed in the presence of PAF on isolated tubules. On the other hand, 8-bromo cyclic GMP mimicked the PAF effect on Cl reabsorption and prevented a further effect of this agent; the PAF effect was significantly reduced by H-8, a cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor; in medullary TALs, PAF significantly increased by twofold cyclic GMP content, an effect inhibited by the PAF antagonist BN 50730, whereas PAF did not significantly modify cAMP content in basal or stimulated conditions. Finally, inhibition of nitric oxide production by NAME or NMMA failed to prevent the effect of PAF on Cl reabsorption. It is concluded that the PAF-induced inhibition of Cl reabsorption in the TAL was mediated by cyclic GMP, likely independent of a nitric oxide synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando Y., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Phorbol ester and A23187 have additive but mechanistically separate effects on vasopressin action in rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1578–1584. doi: 10.1172/JCI113491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly C., Barlet-Bas C., Amiel C. Platelet activating factor inhibits Cl and K transport in the medullary thick ascending limb. Kidney Int. 1992 Feb;41(2):269–274. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezis M., Rosen S., Silva P., Epstein F. H. Renal ischemia: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1984 Oct;26(4):375–383. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Montégut M., Mistaoui M., Butlen D., Morel F. Atrial natriuretic peptide effects on cGMP and cAMP contents in microdissected glomeruli and segments of the rat and rabbit nephrons. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):366–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00581130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigneulle A., Siga E., Vassent G., Imbert-Teboul M. V2-like vasopressin receptor mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in rat medullary collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 2):F35–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culpepper R. M., Andreoli T. E. Interactions among prostaglandin E2, antidiuretic hormone, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in modulating Cl- absorption in single mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1588–1601. doi: 10.1172/JCI110915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Stefano A., Roinel N., de Rouffignac C., Wittner M. Transepithelial Ca2+ and Mg2+ transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of the mouse is a voltage-dependent process. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1993 Jul-Aug;16(4):157–166. doi: 10.1159/000173762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Vanderwel M. Inhibition of platelet adenylate cyclase by 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine (platelet-activating factor). J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6879–6885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert S. C., Friedman P. A., Andreoli T. E. Effects of antidiuretic hormone on cellular conductive pathways in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle: I. ADH increases transcellular conductance pathways. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(3):201–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01868439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juncos L. A., Ren Y. L., Arima S., Ito S. Vasodilator and constrictor actions of platelet-activating factor in the isolated microperfused afferent arteriole of the rabbit kidney. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase products. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1374–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI116339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester M., Thomas C. P., Wang J., Dunn M. J. Platelet-activating factor stimulates multiple signaling pathways in cultured rat mesangial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Nov;153(2):244–255. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041530204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike J., Nonoguchi H., Terada Y., Tomita K., Marumo F. Effect of urodilatin on cGMP accumulation in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993 Apr;3(10):1705–1709. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V3101705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M., Hosford D., Guinot P., Esanu A., Braquet P. PAF. A review of its effects, antagonists and possible future clinical implications (Part II). Drugs. 1991 Aug;42(2):174–204. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199142020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. A., Mishler D. R., Aboolian A., Nagami G. T. Platelet-activating factor attenuates the arginine vasopressin-induced fall of transepithelial resistance across inner medullary collecting duct monolayers. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1992;18(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., McCracken R., Kaneto H., Vehaskari M., Montani D., Klahr S. Location of an inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the normal kidney. Kidney Int. 1994 Apr;45(4):998–1005. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neant F., Bailly C. Luminal and intracellular cGMP inhibit the mTAL reabsorptive capacity through different pathways. Kidney Int. 1993 Oct;44(4):741–746. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Knepper M. A., Manganiello V. C. Effects of atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic guanosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation in microdissected nephron segments from rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):500–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI112840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Tomita K., Marumo F. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide and vasopressin on chloride transport in long- and short-looped medullary thick ascending limbs. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI115869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D. Platelet-activating factor receptor and signal transduction mechanisms. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2296–2301. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1312046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordano C., Cristino E., Bussolino F., Wurster B., Bozzaro S. Platelet activating factor modulates signal transduction in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jan;104(Pt 1):197–202. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Honda Z., Watanabe T., Uchida S., Shimizu T., Kurokawa K. Demonstration of platelet activating factor receptor in guinea pig kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91947-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Polymerase chain reaction localization of constitutive nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase messenger RNAs in microdissected rat nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):659–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI115908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torikai S., Kurokawa K. Effect of PGE2 on vasopressin-dependent cell cAMP in isolated single nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F58–F66. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda N., Mayeux P. R., Walker P. D., Shah S. V. Receptor-mediated increase in cytosolic calcium in LLC-PK1 cells by platelet activating factor and thromboxane A2. Kidney Int. 1991 Dec;40(6):1075–1081. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Prossnitz E. R., Zou A. H., Cochrane C. G. Characterization of a human cDNA that encodes a functional receptor for platelet activating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]