Abstract
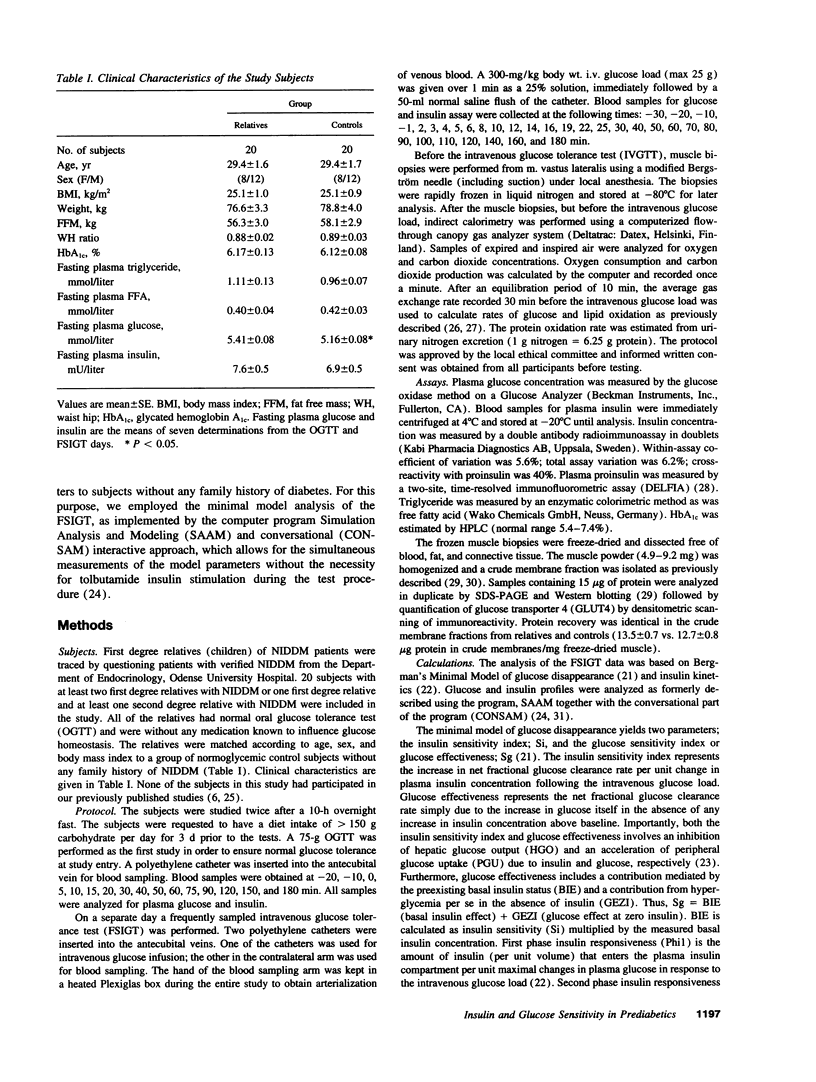
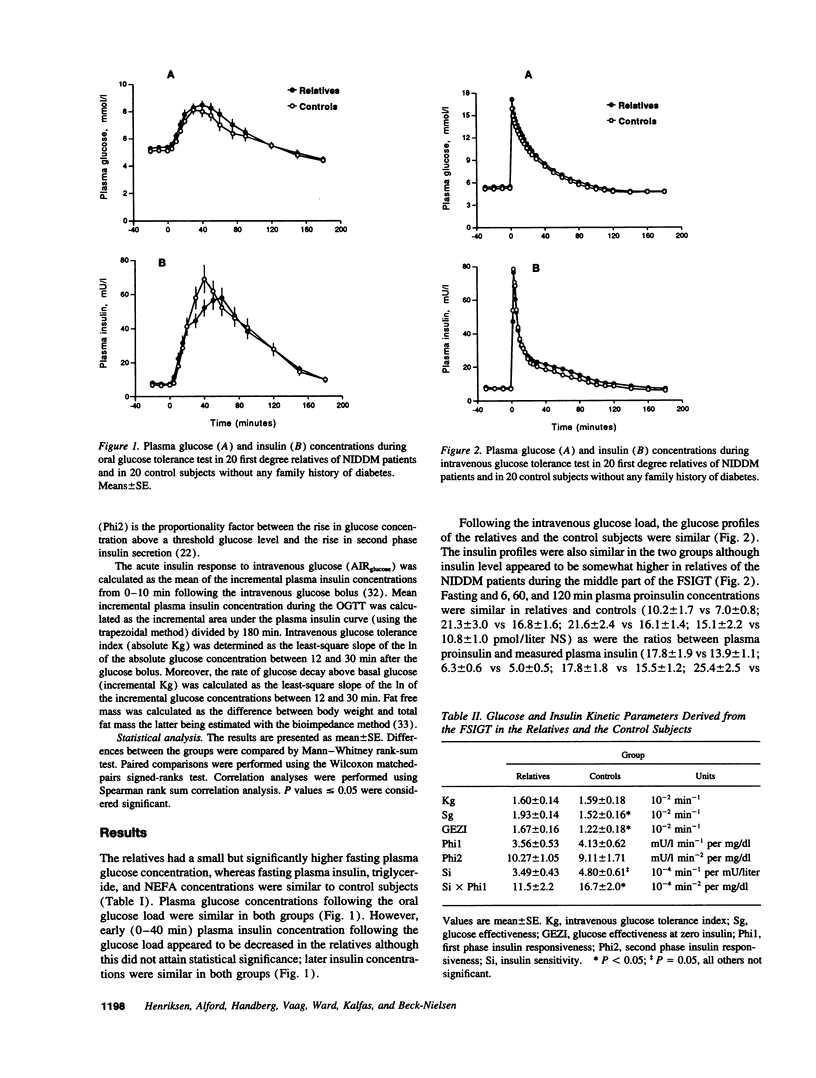
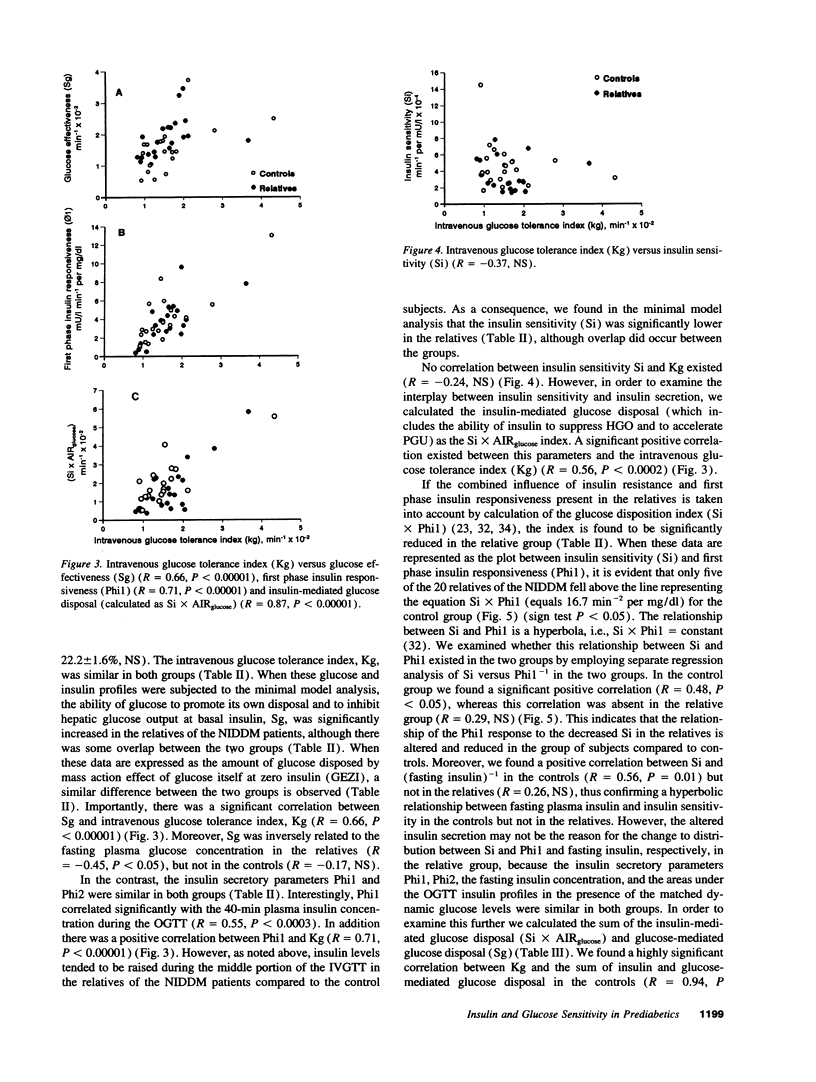
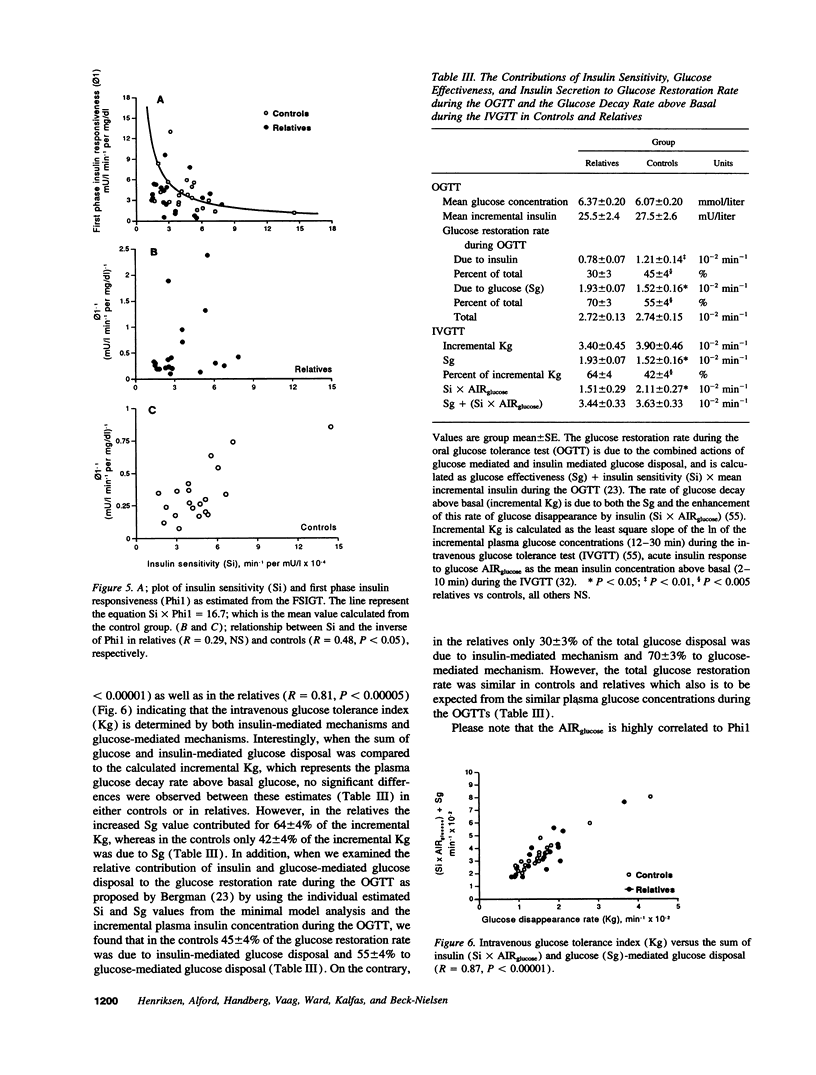
20 normoglycemic first degree relatives of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients were compared with 20 matched subjects without any family history of diabetes using the intravenous glucose tolerance test with minimal model analysis of glucose disappearance and insulin kinetics. Intravenous glucose tolerance index (Kg) was similar in both groups (1.60 +/- 0.14 vs 1.59 +/- 0.18, x 10(-2) min-1, NS). However, insulin sensitivity (Si) was reduced (3.49 +/- 0.43 vs 4.80 +/- 0.61, x 10(-4) min-1 per mU/liter, P = 0.05), whereas glucose effectiveness (Sg) was increased (1.93 +/- 0.14 vs 1.52 +/- 0.16, x 10(-2) min-1, P < 0.05) in the relatives. Despite insulin resistance neither fasting plasma insulin concentration (7.63 +/- 0.48 vs 6.88 +/- 0.45, mU/liter, NS) nor first phase insulin responsiveness (Phi1) (3.56 +/- 0.53 vs 4.13 +/- 0.62, mU/liter min-1 per mg/dl, NS) were increased in the relatives. Phi1 was reduced for the degree of insulin resistance in the relatives so that the Phi1 x Si index was lower in the relatives (11.5 +/- 2.2 vs 16.7 +/- 2.0, x 10(-4) min-2 per mg/dl, P < 0.05). Importantly, glucose effectiveness correlated with Kg and with basal glucose oxidation but not with total glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) content in a basal muscle biopsy. In conclusion we confirm the presence of insulin resistance in first degree relatives of NIDDM patients. However, insulin secretion was altered and reduced for the degree of insulin resistance in the relatives, whereas glucose effectiveness was increased. We hypothesize that increased glucose effectiveness maintains glucose tolerance within normal limits in these "normoinsulinemic" relatives of NIDDM patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ader M., Pacini G., Yang Y. J., Bergman R. N. Importance of glucose per se to intravenous glucose tolerance. Comparison of the minimal-model prediction with direct measurements. Diabetes. 1985 Nov;34(11):1092–1103. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.11.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A. D., Brechtel G., Wallace P., Edelman S. V. Rates and tissue sites of non-insulin- and insulin-mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E769–E774. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A. D., Kolterman O. G., Bell J., Mandarino L. J., Olefsky J. M. Rates of noninsulin-mediated glucose uptake are elevated in type II diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1782–1788. doi: 10.1172/JCI112169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard J. C., Bergman R. N., Ward W. K., Porte D., Jr The insulin sensitivity index in nondiabetic man. Correlation between clamp-derived and IVGTT-derived values. Diabetes. 1986 Mar;35(3):362–369. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Nielsen H., Vaag A., Damsbo P., Handberg A., Nielsen O. H., Henriksen J. E., Thye-Rønn P. Insulin resistance in skeletal muscles in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):418–429. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Ider Y. Z., Bowden C. R., Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E667–E677. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N. Lilly lecture 1989. Toward physiological understanding of glucose tolerance. Minimal-model approach. Diabetes. 1989 Dec;38(12):1512–1527. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.12.1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Prager R., Volund A., Olefsky J. M. Equivalence of the insulin sensitivity index in man derived by the minimal model method and the euglycemic glucose clamp. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):790–800. doi: 10.1172/JCI112886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boston R. C., Greif P. C., Berman M. Conversational SAAM--an interactive program for kinetic analysis of biological systems. Comput Programs Biomed. 1981 Mar-Jun;13(1-2):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Porte D., Jr The effect of rate and dose of glucose infusion on the acute insulin response in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jun;42(6):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-6-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Pacini G., Toffolo G., Saccà L. Estimation of insulin sensitivity and glucose clearance from minimal model: new insights from labeled IVGTT. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):E591–E598. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.5.E591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein S. C., Maxwell T. M., Schumacher M. C. Insulin and glucose levels and prevalence of glucose intolerance in pedigrees with multiple diabetic siblings. Diabetes. 1991 Aug;40(8):1024–1032. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.8.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J., Franssila-Kallunki A., Ekstrand A., Saloranta C., Widén E., Schalin C., Groop L. Early metabolic defects in persons at increased risk for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 10;321(6):337–343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908103210601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J., Koranyi L., Bourey R., Schalin-Jäntti C., Widén E., Mueckler M., Permutt A. M., Groop L. C. Insulin resistance in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients and their relatives is not associated with a defect in the expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter (GLUT-4) gene in human skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 1992 Feb;35(2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00402546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E. The theoretical bases of indirect calorimetry: a review. Metabolism. 1988 Mar;37(3):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari P., Alleman Y., Shaw S., Riesen W., Weidmann P. Reproducibility of insulin sensitivity measured by the minimal model method. Diabetologia. 1991 Jul;34(7):527–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00403291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Pacini G., Bergman R. N. The insulin sensitivity index. Correlation in dogs between values determined from the intravenous glucose tolerance test and the euglycemic glucose clamp. Diabetes. 1984 Apr;33(4):362–368. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.4.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N. Calculation of substrate oxidation rates in vivo from gaseous exchange. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):628–634. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T. Glucose transport and NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):396–417. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groop L. C., Kankuri M., Schalin-Jäntti C., Ekstrand A., Nikula-Ijäs P., Widén E., Kuismanen E., Eriksson J., Franssila-Kallunki A., Saloranta C. Association between polymorphism of the glycogen synthase gene and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 7;328(1):10–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301073280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulli G., Ferrannini E., Stern M., Haffner S., DeFronzo R. A. The metabolic profile of NIDDM is fully established in glucose-tolerant offspring of two Mexican-American NIDDM parents. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1575–1586. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner S. M., Stern M. P., Hazuda H. P., Mitchell B. D., Patterson J. K. Increased insulin concentrations in nondiabetic offspring of diabetic parents. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 17;319(20):1297–1301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811173192001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handberg A., Kayser L., Høyer P. E., Micheelsen J., Vinten J. Elevated GLUT 1 level in crude muscle membranes from diabetic Zucker rats despite a normal GLUT 1 level in perineurial sheaths. Diabetologia. 1994 May;37(5):443–448. doi: 10.1007/s001250050130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handberg A., Vaag A., Damsbo P., Beck-Nielsen H., Vinten J. Expression of insulin regulatable glucose transporters in skeletal muscle from type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1990 Oct;33(10):625–627. doi: 10.1007/BF00400207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handberg A., Vaag A., Vinten J., Beck-Nielsen H. Decreased tyrosine kinase activity in partially purified insulin receptors from muscle of young, non-obese first degree relatives of patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1993 Jul;36(7):668–674. doi: 10.1007/BF00404079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä I., Dakubu S., Mukkala V. M., Siitari H., Lövgren T. Europium as a label in time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. R., Gumbiner B., Flynn T., Thorburn A. W. Metabolic effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on fate of intracellular glucose in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):149–156. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman M. F., Goodyear L. J., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Identification of an intracellular pool of glucose transporters from basal and insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck C. B., Chen N., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Relationship between the plasma insulin response to oral glucose and insulin-stimulated glucose utilization in normal subjects. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):460–463. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck C., Reaven G. M. Variations in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in healthy individuals with normal glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1169–1173. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C., Ward W. K., Beard J. C., McKnight B., Porte D., Jr Islet function and insulin sensitivity in the non-diabetic offspring of conjugal type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 1990 Feb;7(2):119–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. E., Prigeon R. L., McCulloch D. K., Boyko E. J., Bergman R. N., Schwartz M. W., Neifing J. L., Ward W. K., Beard J. C., Palmer J. P. Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in human subjects. Evidence for a hyperbolic function. Diabetes. 1993 Nov;42(11):1663–1672. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.11.1663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. E., Prigeon R. L., McCulloch D. K., Boyko E. J., Bergman R. N., Schwartz M. W., Neifing J. L., Ward W. K., Beard J. C., Palmer J. P. The contribution of insulin-dependent and insulin-independent glucose uptake to intravenous glucose tolerance in healthy human subjects. Diabetes. 1994 Apr;43(4):587–592. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauser R., Prager R., Schernthaner G., Olefsky J. M. Contribution of postprandial insulin and glucose to glucose disposal in normal and insulin-resistant obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Oct;73(4):758–764. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-4-758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws A., Stefanick M. L., Reaven G. M. Insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia in nondiabetic relatives of patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Aug;69(2):343–347. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Ader M., Bray G. A., Bergman R. N. Diurnal variation in glucose tolerance. Cyclic suppression of insulin action and insulin secretion in normal-weight, but not obese, subjects. Diabetes. 1992 Jun;41(6):750–759. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.6.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. D., Volkmann H. P., Poncher M., Hanning I., Orskov H., Alberti K. G. Metabolic abnormalities in children of non-insulin dependent diabetics. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Oct 4;293(6551):840–842. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6551.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Mott D. M., Spraul M., Ferraro R., Foley J. E., Ravussin E., Knowler W. C., Bennett P. H., Bogardus C. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1988–1992. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukaski H. C., Johnson P. E., Bolonchuk W. W., Lykken G. I. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Apr;41(4):810–817. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.4.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Consoli A., Kelley D. E., Reilly J. J., Nurjhan N. Fasting hyperglycemia normalizes oxidative and nonoxidative pathways of insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Dec;71(6):1544–1551. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-6-1544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangou A. G., Weber K. M., Boston R. C., Aitken P. M., Heggie J. C., Kirsner R. L., Best J. D., Alford F. P. Metabolic consequences of prolonged hyperinsulinemia in humans. Evidence for induction of insulin insensitivity. Diabetes. 1986 Dec;35(12):1383–1389. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.12.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. C., Warram J. H., Krolewski A. S., Bergman R. N., Soeldner J. S., Kahn C. R. Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet. 1992 Oct 17;340(8825):925–929. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92814-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. C., Warram J. H., Rosner B., Rich S. S., Soeldner J. S., Krolewski A. S. Familial clustering of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 1992 Jul;41(7):850–854. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.7.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I. K., Weber K. M., Boston R. C., Alford F. P., Best J. D. Effects of epinephrine infusion on determinants of intravenous glucose tolerance in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):E668–E673. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.5.E668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I. K., Weber K. M., Ward G. M., Best J. D., Boston R. C. Application of the SAAM modeling program to minimal model analysis of intravenous glucose tolerance test data. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1990 Dec;33(4):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S. P., Nugent Z., Rudenski A. S., Hosker J. P., Burnett M. A., Darling P., Turner R. C. Beta-cell dysfunction, rather than insulin insensitivity, is the primary defect in familial type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 1986 Aug 16;2(8503):360–364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S., Turner R. C., Matthews D. R. Impaired pulsatile secretion of insulin in relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 12;318(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805123181902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osei K., Cottrell D. A., Orabella M. M. Insulin sensitivity, glucose effectiveness, and body fat distribution pattern in nondiabetic offspring of patients with NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1991 Oct;14(10):890–896. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.10.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Banting lecture 1990. Beta-cells in type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1991 Feb;40(2):166–180. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran A., Snehalatha C., Mohan V., Bhattacharyya P. K., Viswanathan M. Decreased insulin sensitivity in offspring whose parents both have type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990 May;7(4):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayman G., Clark P., Schneider A. E., Hales C. N. The first phase insulin response to intravenous glucose is highly reproducible. Diabetologia. 1990 Oct;33(10):631–634. doi: 10.1007/BF00400209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Røder M. E., Eriksson J., Hartling S. G., Groop L., Binder C. Proportional proinsulin responses in first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 1993;30(3):132–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00572856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalin-Jäntti C., Härkonen M., Groop L. C. Impaired activation of glycogen synthase in people at increased risk for developing NIDDM. Diabetes. 1992 May;41(5):598–604. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M. C., Maxwell T. M., Wu L. L., Hunt S. C., Williams R. R., Elbein S. C. Dyslipidemias among normoglycemic members of familial NIDDM pedigrees. Diabetes Care. 1992 Oct;15(10):1285–1289. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.10.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi A., Nakai Y., Fukushima M., Kawamura H., Imura H., Nagata I., Tokuyama K. Pathogenic factors responsible for glucose intolerance in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1540–1546. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffolo G., Bergman R. N., Finegood D. T., Bowden C. R., Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of beta cell sensitivity to glucose in the intact organism: a minimal model of insulin kinetics in the dog. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):979–990. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaag A., Damsbo P., Hother-Nielsen O., Beck-Nielsen H. Hyperglycaemia compensates for the defects in insulin-mediated glucose metabolism and in the activation of glycogen synthase in the skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1992 Jan;35(1):80–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00400856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaag A., Henriksen J. E., Beck-Nielsen H. Decreased insulin activation of glycogen synthase in skeletal muscles in young nonobese Caucasian first-degree relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):782–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI115656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. M., Ward G. M., Kalfas A., Best J. D., Alford F. P. The effect of epinephrine on glucose-mediated and insulin-mediated glucose disposal in insulin-dependent diabetes. Metabolism. 1992 Jun;41(6):671–677. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90062-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. M., Walters J. M., Aitken P. M., Best J. D., Alford F. P. Effects of prolonged pulsatile hyperinsulinemia in humans. Enhancement of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):501–507. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. M., Weber K. M., Walters I. M., Aitken P. M., Lee B., Best J. D., Boston R. C., Alford F. P. A modified minimal model analysis of insulin sensitivity and glucose-mediated glucose disposal in insulin-dependent diabetes. Metabolism. 1991 Jan;40(1):4–9. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(91)90183-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warram J. H., Martin B. C., Krolewski A. S., Soeldner J. S., Kahn C. R. Slow glucose removal rate and hyperinsulinemia precede the development of type II diabetes in the offspring of diabetic parents. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Dec 15;113(12):909–915. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-12-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch S., Gebhart S. S., Bergman R. N., Phillips L. S. Minimal model analysis of intravenous glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity in diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Dec;71(6):1508–1518. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-6-1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. M., Sutcliffe I. C., Johnson A. B., Taylor R. Abnormal activation of glycogen synthesis in fibroblasts from NIDDM subjects. Evidence for an abnormality specific to glucose metabolism. Diabetes. 1993 Apr;42(4):583–589. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


