Abstract
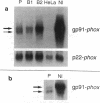
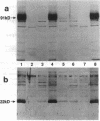
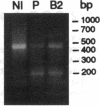
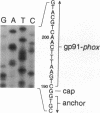
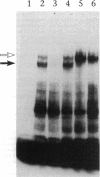
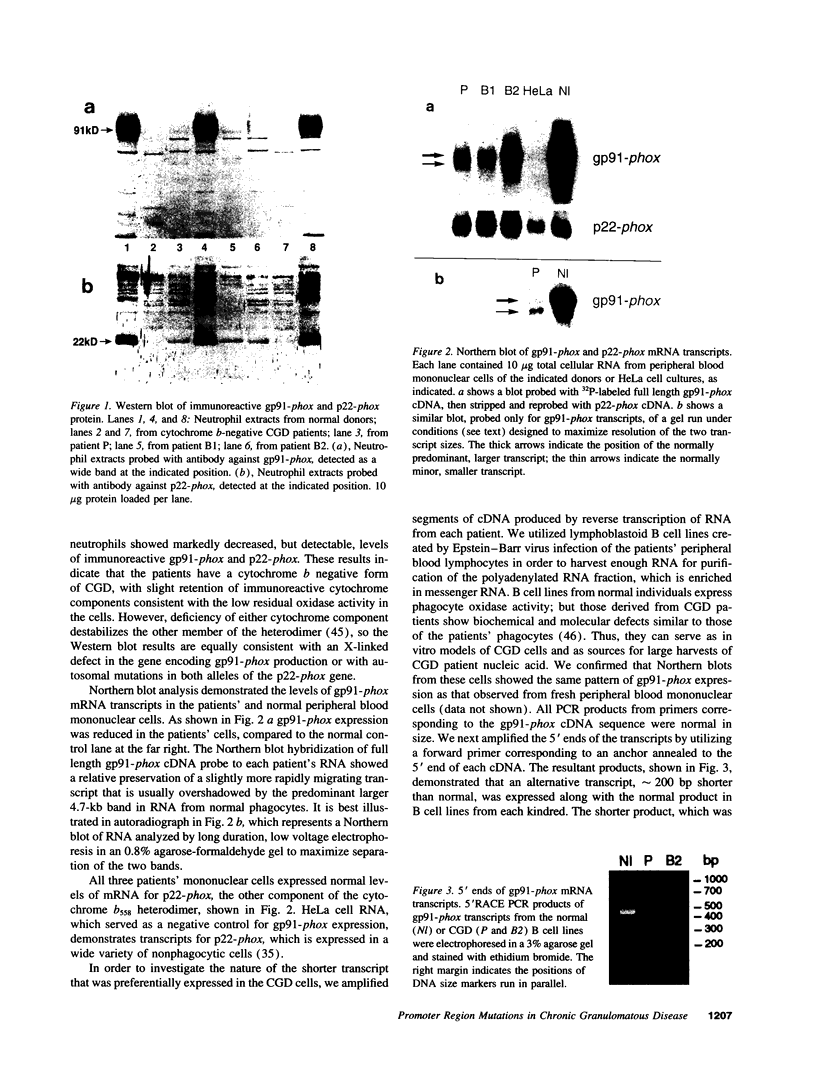
We examined the molecular defect in two kindreds with "variant" X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Western blots of neutrophil extracts showed decreased immunoreactive cytochrome b558 components gp91-phox and p22-phox. Analysis of mRNA demonstrated reduced gp91-phox transcripts, with relative preservation of an alternative mRNA species created by transcription initiation in the third exon of the gene. Single strand conformation polymorphism analysis of the 5' flanking region of the patients' gp91-phox genes revealed an electrophoretic abnormality not detected in 40 other gp91-phox genes. Genomic sequencing demonstrated a single base change associated with CGD in each kindred: in one, adenine to cytosine at base pair-57 and in the other, thymidine to cytosine at -55. These mutations are located between the "CCAAT" and "TATA" box consensus sequences involved in eukaryotic gene transcription. Gel shift assays revealed two specific DNA-protein complexes formed between phagocyte nuclear extracts and an oligonucleotide probe representing bases -31 to -68 of the gp91-phox promoter region; the faster-migrating complex could not be formed with oligonucleotides containing either of the promoter mutations. Thus, these promoter region mutations appear to be causally related to the loss of association of a DNA-binding protein and lead to diminished gp91-phox expression, abnormal transcription initiation, and the development of CGD.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERENDES H., BRIDGES R. A., GOOD R. A. A fatal granulomatosus of childhood: the clinical study of a new syndrome. Minn Med. 1957 May;40(5):309–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyavsky A., Vinogradova T., Rajewsky K. PCR-based cDNA library construction: general cDNA libraries at the level of a few cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2919–2932. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolscher B. G., de Boer M., de Klein A., Weening R. S., Roos D. Point mutations in the beta-subunit of cytochrome b558 leading to X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2482–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Cross A. R., Herlin T., Jones O. T., Segal A. W., Valerius N. H. A variant form of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease with normal nitroblue tetrazolium slide test and cytochrome b. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;13(3):243–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Chronic granulomatous disease: the solving of a clinical riddle at the molecular level. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jun;67(3 Pt 2):S2–15. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Scott P. J. Activation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system. Partial purification of components and characterization of the activation process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5563–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Whitten D. M., Babior B. M. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):593–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Curnutte J. T., Rosen H., Orkin S. H. A missense mutation in the neutrophil cytochrome b heavy chain in cytochrome-positive X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2012–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI114393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Pierce E. A., Erickson R. W., Muhlebach T. J., Messner H., Orkin S. H., Seger R. A., Curnutte J. T. Point mutation in the cytoplasmic domain of the neutrophil p22-phox cytochrome b subunit is associated with a nonfunctional NADPH oxidase and chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11231–11235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. B., Delort J., Mallet J. Oligodeoxyribonucleotide ligation to single-stranded cDNAs: a new tool for cloning 5' ends of mRNAs and for constructing cDNA libraries by in vitro amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5227–5232. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A., Hadzić N., Morgan G., Strobel S., Levinsky R. J. Prognosis of chronic granulomatous disease. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Sep;65(9):942–945. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.9.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest C. B., Forehand J. R., Axtell R. A., Roberts R. L., Johnston R. B., Jr Clinical features and current management of chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):253–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey D., Mächler M., Seger R., Schmid W., Orkin S. H. Gene deletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease and McLeod syndrome: fine mapping of the Xk gene locus. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):252–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Bonthron D. T., Donlon T. A., Bruns G. A., Latt S. A., Orkin S. H. Human von Willebrand factor (vWF): isolation of complementary DNA (cDNA) clones and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3874428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirzmann J., Luo D., Hahnen J., Hobom G. Determination of messenger RNA 5'-ends by reverse transcription of the cap structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3597–3598. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Page A. R., Good R. A. Studies of the metabolic activity of leukocytes from patients with a genetic abnormality of phagocytic function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1422–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI105634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Erlanger B. F., Guntaka R. V. Evidence for extensive methylation of ribosomal RNA genes in a rat XC cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;739(3):258–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Southwick F. S., Stossel T. P., Whitin J. C., Simons E., Cohen H. J. A variant of chronic granulomatous disease: deficient oxidative metabolism due to a low-affinity NADPH oxidase. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 26;305(22):1329–1333. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111263052207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouy R., Fischer A., Vilmer E., Seger R., Griscelli C. Incidence, severity, and prevention of infections in chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1989 Apr;114(4 Pt 1):555–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Luscinskas F. W., Ryan T., Beard C. J., Wright J., Platt O. S., Simons E. R., Tauber A. I. Variant chronic granulomatous disease: modulation of the neutrophil defect by severe infection. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Iwahana H., Kanazawa H., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Molecular genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Allen R. A., Cochrane C. G., Jesaitis A. J. Purified cytochrome b from human granulocyte plasma membrane is comprised of two polypeptides with relative molecular weights of 91,000 and 22,000. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):732–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI113128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., de Boer M., Borregard N., Bjerrum O. W., Valerius N. H., Seger R. A., Mühlebach T., Belohradsky B. H., Weening R. S. Chronic granulomatous disease with partial deficiency of cytochrome b558 and incomplete respiratory burst: variants of the X-linked, cytochrome b558-negative form of the disease. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Feb;51(2):164–171. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro B. L., Newburger P. E., Klempner M. S., Dinauer M. C. Chronic granulomatous disease presenting in a 69-year-old man. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 19;325(25):1786–1790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112193252506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. Absence of both cytochrome b-245 subunits from neutrophils in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):88–91. doi: 10.1038/326088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Cross A. R., Garcia R. C., Borregaard N., Valerius N. H., Soothill J. F., Jones O. T. Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. A multicenter European evaluation of its incidence and relevance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):245–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R. A., Tiefenauer L., Matsunaga T., Wildfeuer A., Newburger P. E. Chronic granulomatous disease due to granulocytes with abnormal NADPH oxidase activity and deficient cytochrome-b. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):423–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Strauss E. C., Orkin S. H. CCAAT displacement protein as a repressor of the myelomonocytic-specific gp91-phox gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16736–16744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Curnutte J. T. Molecular basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1991 Feb 15;77(4):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker K. A., Lilly M. B., Heck L., Jr, Rado T. A. Characterization of a new human diploid myeloid leukemia cell line (PLB-985) with granulocytic and monocytic differentiating capacity. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Buescher E. S., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. B cell lines as models for inherited phagocytic diseases: abnormal superoxide generation in chronic granulomatous disease and giant granules in Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3006–3009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer M., Bolscher B. G., Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Smith C. I., Ahlin A., Weening R. S., Roos D. Splice site mutations are a common cause of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1992 Sep 15;80(6):1553–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint-Basile G., Bohler M. C., Fischer A., Cartron J., Dufier J. L., Griscelli C., Orkin S. H. Xp21 DNA microdeletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod phenotype. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00451463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]