Abstract
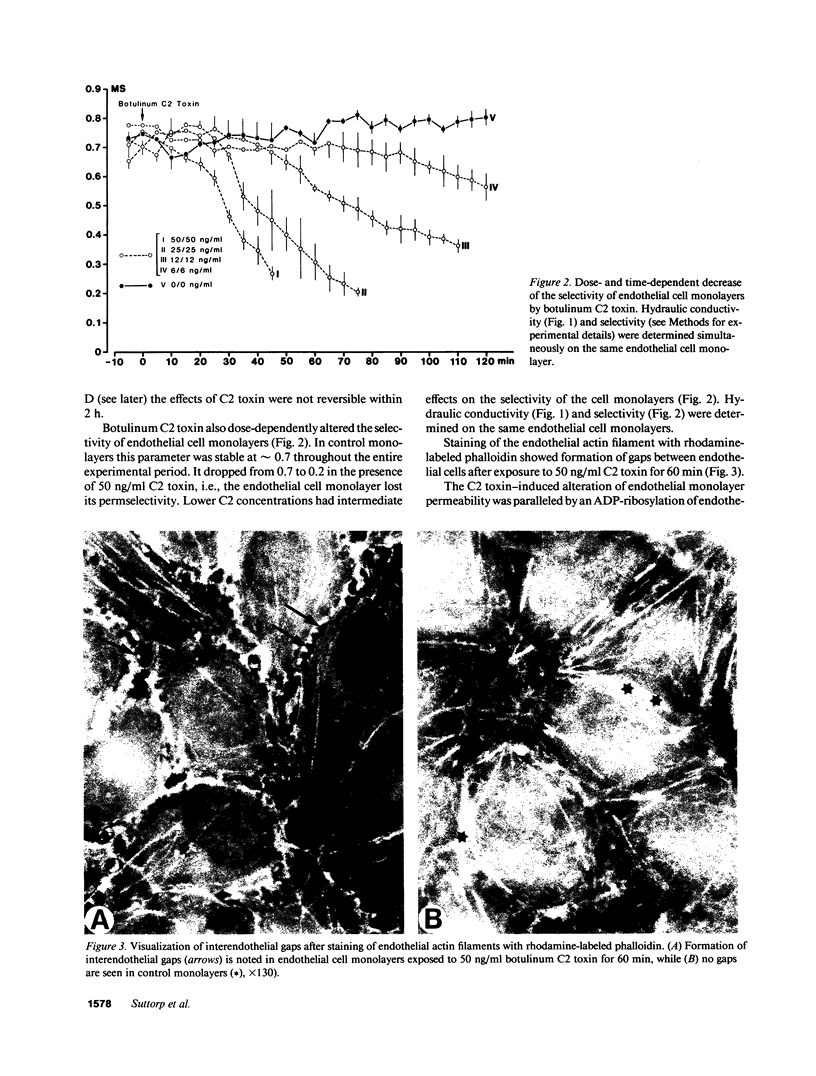
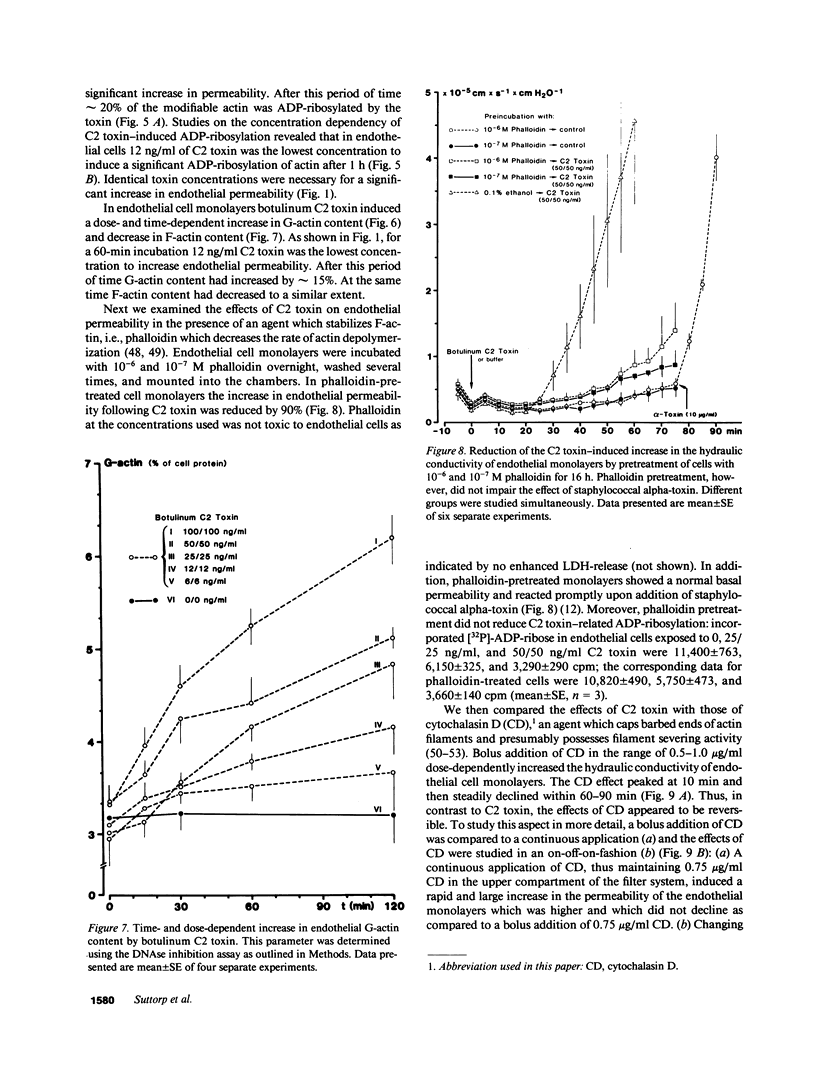
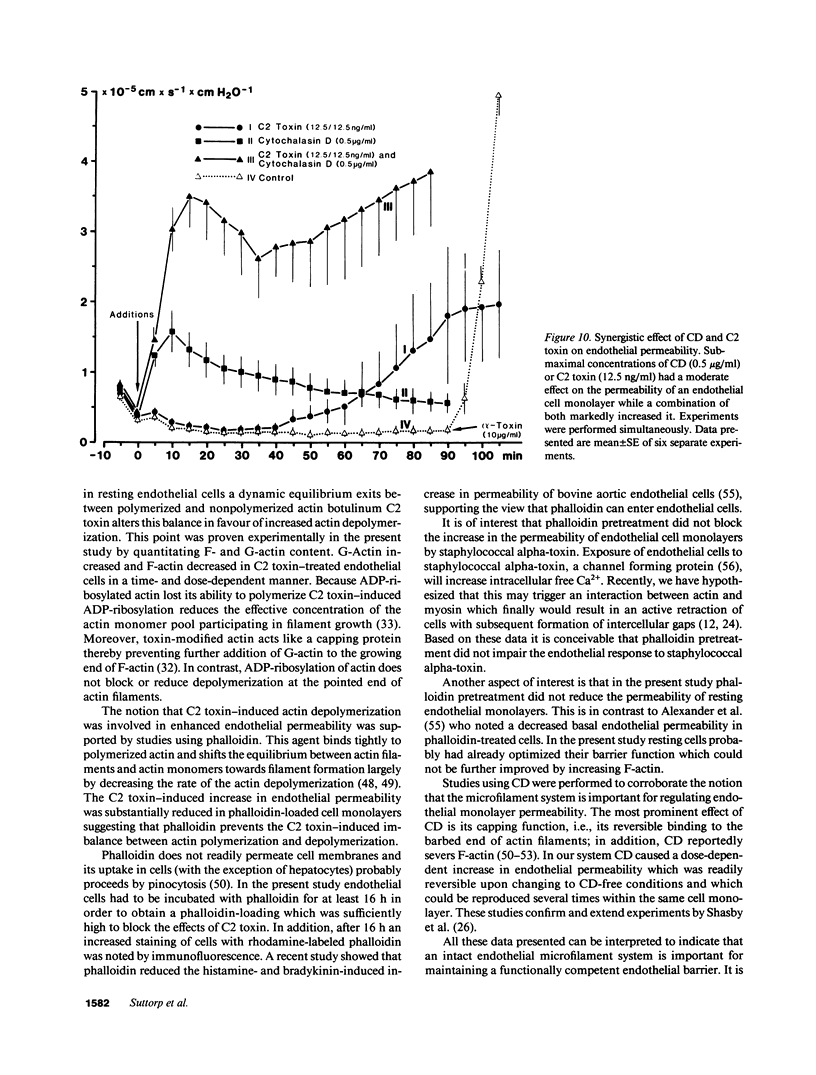
The endothelial cytoskeleton is believed to play an important role in the regulation of endothelial permeability. We used botulinum C2 toxin to perturb cellular actin and determined its effect on the permeability of endothelial cell monolayers derived from porcine pulmonary arteries. The substrate for botulinum C2 toxin is nonmuscle monomeric actin which becomes ADP-ribosylated. This modified actin cannot participate in actin polymerization and, in addition, acts as a capping protein. Exposure of endothelial cell monolayers to botulinum C2 toxin resulted in a dose- (3-100 ng/ml) and time-dependent (30-120 min) increase in the hydraulic conductivity and decrease in the selectivity of the cell monolayers. The effects of C2 toxin were accompanied by a time- and dose-dependent increase in ADP-ribosylatin of G-actin. G-Actin content increased and F-actin content decreased time- and dose-dependently in C2 toxin-treated endothelial cells. Phalloidin which stabilizes filamentous actin prevented the effects of botulinum C2 toxin on endothelial permeability. Botulinum C2 toxin induced interendothelial gaps. The effects occurred in the absence of overt cell damage and were not reversible within 2 h. The data suggest that the endothelial microfilament system is important for the regulation of endothelial permeability.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Ankenbauer T., Schering B., Jakobs K. H. ADP-ribosylation of platelet actin by botulinum C2 toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Bärmann M., Ohishi I., Tsuyama S., Jakobs K. H., Habermann E. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):390–392. doi: 10.1038/322390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Reuner K. H., Presek P., Bärmann M. Botulinum C2 toxin treatment increases the G-actin pool in intact chicken cells: a model for the cytopathic action of actin-ADP-ribosylating toxins. Toxicon. 1989;27(9):989–993. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Wegner A. ADP-ribosylation of actin by clostridial toxins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1385–1387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. S., Hechtman H. B., Shepro D. Phalloidin enhances endothelial barrier function and reduces inflammatory permeability in vitro. Microvasc Res. 1988 May;35(3):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(88)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Markey F., Carlsson L., Persson T., Lindberg U. Selective assay of monomeric and filamentous actin in cell extracts, using inhibition of deoxyribonuclease I. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. The effects of cytochalasins on actin polymerization and actin ATPase provide insights into the mechanism of polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):841–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Aglietta M., Braquet P., Bosia A., Pescarmona G., Sanavio F., D'Urso N., Marchisio P. C. Human endothelial cells are target for platelet-activating factor. I. Platelet-activating factor induces changes in cytoskeleton structures. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2439–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CABAUD P. G., WROBLEWSKI F. Colorimetric measurement of lactic dehydrogenase activity of body fluids. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;30(3):234–236. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/30.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella J. F., Flanagan M. D., Lin S. Cytochalasin D inhibits actin polymerization and induces depolymerization of actin filaments formed during platelet shape change. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):302–305. doi: 10.1038/293302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coluccio L. M., Tilney L. G. Phalloidin enhances actin assembly by preventing monomer dissociation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):529–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Wagner J. Stress fibers in the splenic sinus endothelium in situ: molecular structure, relationship to the extracellular matrix, and contractility. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1738–1747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes J. E., Selden L. A., Gershman L. C. Mechanism of action of phalloidin on the polymerization of muscle actin. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):708–712. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. P., Gräfe M., Schnittler H., Seiffge D., Mittermayer C., Drenckhahn D. Induction of human vascular endothelial stress fibres by fluid shear stress. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):648–649. doi: 10.1038/307648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M., Ryan U. S., Davenport W. C., Chaney E. L., Strickland D. L., Kwock L. Reversible alterations in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cell monolayer morphology and albumin permeability induced by ionizing radiation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Nov;129(2):237–249. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Bizios R., Del Vecchio P. J., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Malik A. B. Thrombin-induced increase in albumin permeability across the endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jul;128(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heltianu C., Bogdan I., Constantinescu E., Simionescu M. Endothelial cells express a spectrin-like cytoskeletal protein. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):605–610. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw D. B., Armstrong B. C., Burger J. M., Beals T. F., Hyslop P. A. ATP and microfilaments in cellular oxidant injury. Am J Pathol. 1988 Sep;132(3):479–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Majno G., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A. The mechanism of vascular leakage induced by leukotriene E4. Endothelial contraction. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):19–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey J. J., Johnston M. G., Movat H. Z. Increased permeability of microcarrier-cultured endothelial monolayers in response to histamine and thrombin. A model for the in vitro study of increased vasopermeability. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):50–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Moore R., Carlson S. Alteration of intestinal tight junction structure and permeability by cytoskeletal contraction. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C854–C861. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Shea S. M., Leventhal M. Endothelial contraction induced by histamine-type mediators: an electron microscopic study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):647–672. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. B., Selig W. M., Burhop K. E. Cellular and humoral mediators of pulmonary edema. Lung. 1985;163(4):193–219. doi: 10.1007/BF02713821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O., Ryan U. S., Brigham K. L. Direct effects of E coli endotoxin on structure and permeability of pulmonary endothelial monolayers and the endothelial layer of intimal explants. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):140–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Burger M. M. Interaction of the cytoskeleton with the plasma membrane. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):97–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02209144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgauer J., Kownatzki E., Seifert R., Aktories K. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin and enhances O2- production and secretion but inhibits migration of activated human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1376–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI113741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi I., Iwasaki M., Sakaguchi G. Purification and characterization of two components of botulinum C2 toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):668–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.668-673.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. G., Tsan M. F. Hyperoxia causes increased albumin permeability of cultured endothelial monolayers. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Mar;64(3):1196–1202. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.3.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt B. M., Harris A. S., Morrow J. S., Madri J. A. Mechanisms of cytoskeletal regulation. Modulation of aortic endothelial cell spectrin by the extracellular matrix. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):349–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuner K. H., Presek P., Boschek C. B., Aktories K. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin and disorganizes the microfilament network in intact cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;43(1):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I. Histamine type I receptor occupancy increases endothelial cytosolic calcium, reduces F-actin, and promotes albumin diffusion across cultured endothelial monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2379–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittler H. J., Wilke A., Gress T., Suttorp N., Drenckhahn D. Role of actin and myosin in the control of paracellular permeability in pig, rat and human vascular endothelium. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:379–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Lind S. E., Shasby S. S., Goldsmith J. C., Hunninghake G. W. Reversible oxidant-induced increases in albumin transfer across cultured endothelium: alterations in cell shape and calcium homeostasis. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Peach M. J. Granulocytes and phorbol myristate acetate increase permeability to albumin of cultured endothelial monolayers and isolated perfused lungs. Role of oxygen radicals and granulocyte adherence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):72–76. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Fuchs T., Seeger W., Wilke A., Drenckhahn D. Role of Ca2+ and Mg2+ for endothelial permeability of water and albumin in vitro. Lab Invest. 1989 Aug;61(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Galanos C., Neuhof H. Endotoxin alters arachidonate metabolism in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C384–C390. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Hessz T., Seeger W., Wilke A., Koob R., Lutz F., Drenckhahn D. Bacterial exotoxins and endothelial permeability for water and albumin in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C368–C376. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Uhl J., Lutz F., Roka L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin stimulates prostacyclin production in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells: membrane attack and calcium influx. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zinsky S., Bhakdi S. Complement complex C5b-8 induces PGI2 formation in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C13–C21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Simon L. M. Lung cell oxidant injury. Enhancement of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in lung cells exposed to sustained in vitro hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):342–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI110623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Toepfer W., Roka L. Antioxidant defense mechanisms of endothelial cells: glutathione redox cycle versus catalase. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):C671–C680. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.5.C671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Schering B., Bärmann M., Aktories K. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates cytoplasmic beta/gamma-actin in arginine 177. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):696–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volberg T., Geiger B., Kartenbeck J., Franke W. W. Changes in membrane-microfilament interaction in intercellular adherens junctions upon removal of extracellular Ca2+ ions. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1832–1842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner A., Aktories K. ADP-ribosylated actin caps the barbed ends of actin filaments. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13739–13742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A. J., Pollard T. D., Herman I. M. Actin filament stress fibers in vascular endothelial cells in vivo. Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.6681677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. K., Gotlieb A. I. Endothelial cell monolayer integrity. I. Characterization of dense peripheral band of microfilaments. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):212–219. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R. B., Lagunoff D. Inhibition of endothelial cell retraction by ATP depletion. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):28–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R. B., Lagunoff D. Involvement of myosin light-chain kinase in endothelial cell retraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R., Lagunoff D. The effect of ethchlorvynol on cultured endothelial cells. A model for the study of the mechanism of increased vascular permeability. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):505–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]