Abstract
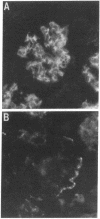
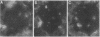
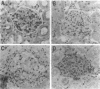
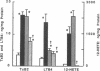
The synthesis, cell origin, and physiologic role of eicosanoids were investigated in a model of mesangial cell immune injury induced by a monoclonal antibody against the rat thymocyte antigen Thy 1.1 also expressed in rat mesangial cells. A single intravenous injection of the antibody resulted in enhanced glomerular synthesis of thromboxane (Tx)B2, leukotriene (LT)B4, and 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE), whereas that of PGE2 and PGF2 alpha was either unaltered or impaired. The enhanced eicosanoid synthesis was associated with decrements in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal blood flow (RBF). Complement activation mediated both the increments in TxB2, LTB4, and 12-HETE and the decrements in GFR and RBF. The decrements in GFR were abolished by the TxA2 receptor antagonist SQ-29,548. Although both neutrophiles and Ia (+) leukocytes infiltrated glomeruli, glomerular LTB4 originated mainly from the latter. Platelets entirely accounted for the enhanced 12-HETE synthesis in isolated glomeruli and to a lesser extent for that of LTB4 and TxB2. Glomerular PGE2 and PGF2 alpha originated from mesangial cells as their impaired synthesis coincided with extensive mesangial cell lysis. The observations indicate that in mesangial cell immune injury vasoactive and proinflammatory eicosanoids originate from recruited or activated Ia (+) leukocytes and platelets and may exert paracrine effects on mesangial cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchus W. M., Hoedemaeker P. J., Rozing J., Bakker W. W. Glomerulonephritis induced by monoclonal anti-Thy 1.1 antibodies. A sequential histological and ultrastructural study in the rat. Lab Invest. 1986 Dec;55(6):680–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchus W. M., Jeunink M. F., Elema J. D. The mesangium in anti-Thy-1 nephritis. Influx of macrophages, mesangial cell hypercellularity, and macromolecular accumulation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):215–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Barton R. W. Thy-1 glycoprotein: structure, distribution, and ontogeny. Lab Invest. 1986 Feb;54(2):122–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Hormonal modulation of glomerular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):F95–104. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.2.F95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldyne M. E., Burrish G. F., Poubelle P., Borgeat P. Arachidonic acid metabolism among human mononuclear leukocytes. Lipoxygenase-related pathways. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8815–8819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. G., Chenoweth D. E., Weigle W. O. Induction of interleukin 1 secretion and enhancement of humoral immunity by binding of human C5a to macrophage surface C5a receptors. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):912–917. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowith J. B., Morrison A. R., Schreiner G. F. Murine glomerular leukotriene B4 synthesis. Manipulation by (n-6) fatty acid deprivation and cellular origin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1655–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI113777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A., Andres G. A., Dunn M. J. Glomerular prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis in rat nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Effects on renal hemodynamics. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1439–1448. doi: 10.1172/JCI111100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A. Eicosanoids and the modulation of glomerular immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):985–992. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A., Noble B. Glomerular leukotriene synthesis in Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 Dec;36(6):998–1002. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A., Rahman M. A., Dunn M. J. Glomerular arachidonate lipoxygenation in rat nephrotoxic serum nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1355–1359. doi: 10.1172/JCI112110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A. Synthesis of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids and leukotrienes in rat nephrotoxic serum glomerulonephritis. Role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody dose, complement, and neutrophiles. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):427–435. doi: 10.1172/JCI113615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Kincade P. W. Phosphatidylinositol is the membrane-anchoring domain of the Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):62–64. doi: 10.1038/318062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclouf J., de Laclos B. F., Borgeat P. Stimulation of leukotriene biosynthesis in human blood leukocytes by platelet-derived 12-hydroperoxy-icosatetraenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6042–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Broekman M. J., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L., Islam N., Sherhan C. N., Rutherford L. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Formation of leukotrienes and other hydroxy acids during platelet-neutrophil interactions in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M., Schwinzer R., Schellekens H., Resch K. Glomerular mesangial cells in local inflammation. Induction of the expression of MHC class II antigens by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1887–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul L. C., Rennke H. G., Milford E. L., Carpenter C. B. Thy-1.1 in glomeruli of rat kidneys. Kidney Int. 1984 May;25(5):771–777. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M. A., Nakazawa M., Emancipator S. N., Dunn M. J. Increased leukotriene B4 synthesis in immune injured rat glomeruli. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1945–1952. doi: 10.1172/JCI113542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt L. A., Dunn M. J. Prostaglandin synthesis by rat glomerular mesangial cells in culture. Effects of angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1756–1764. doi: 10.1172/JCI110931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Origin of the rat mesangial phagocyte and its expression of the leukocyte common antigen. Lab Invest. 1984 Nov;51(5):515–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl R. A., Thaiss F., Kahf S., Schoeppe W., Helmchen U. M. Immune-mediated mesangial cell injury--biosynthesis and function of prostanoids. Kidney Int. 1990 Aug;38(2):273–281. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Johnson K. J., Kunkel R., Ward P. A. Intravascular activation of complement and acute lung injury. Dependency on neutrophils and toxic oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1126–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI110548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]