Abstract
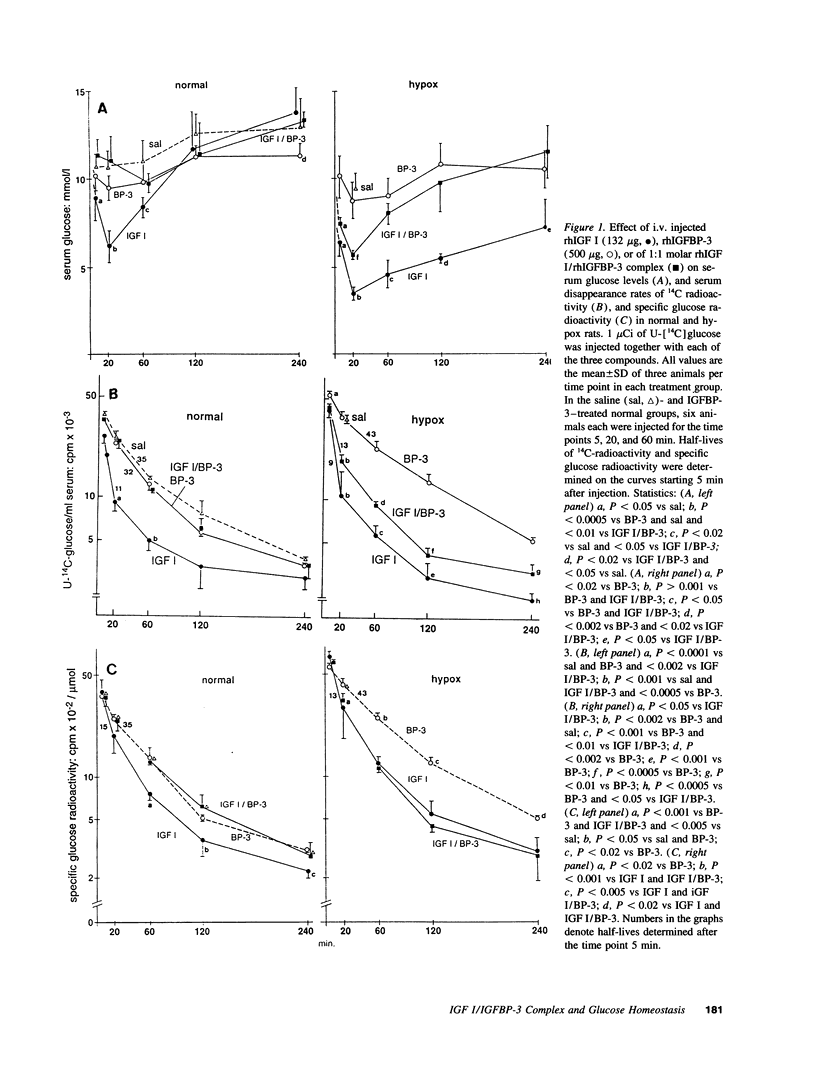
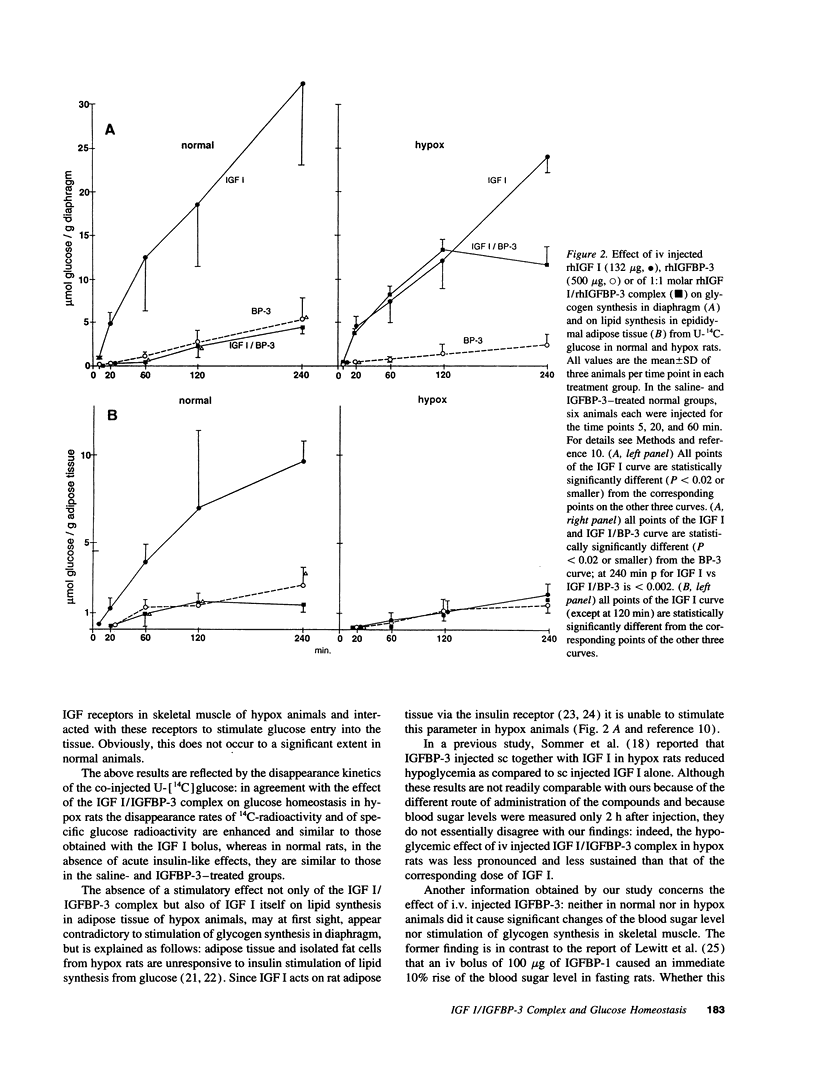
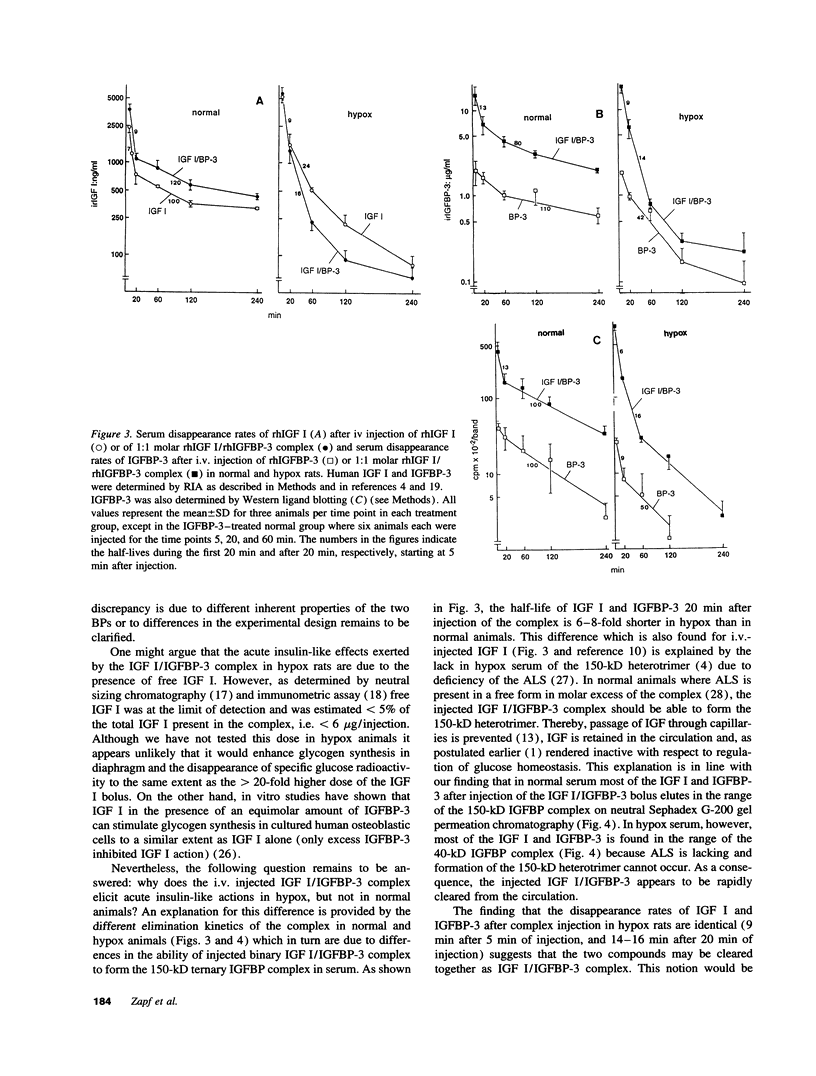
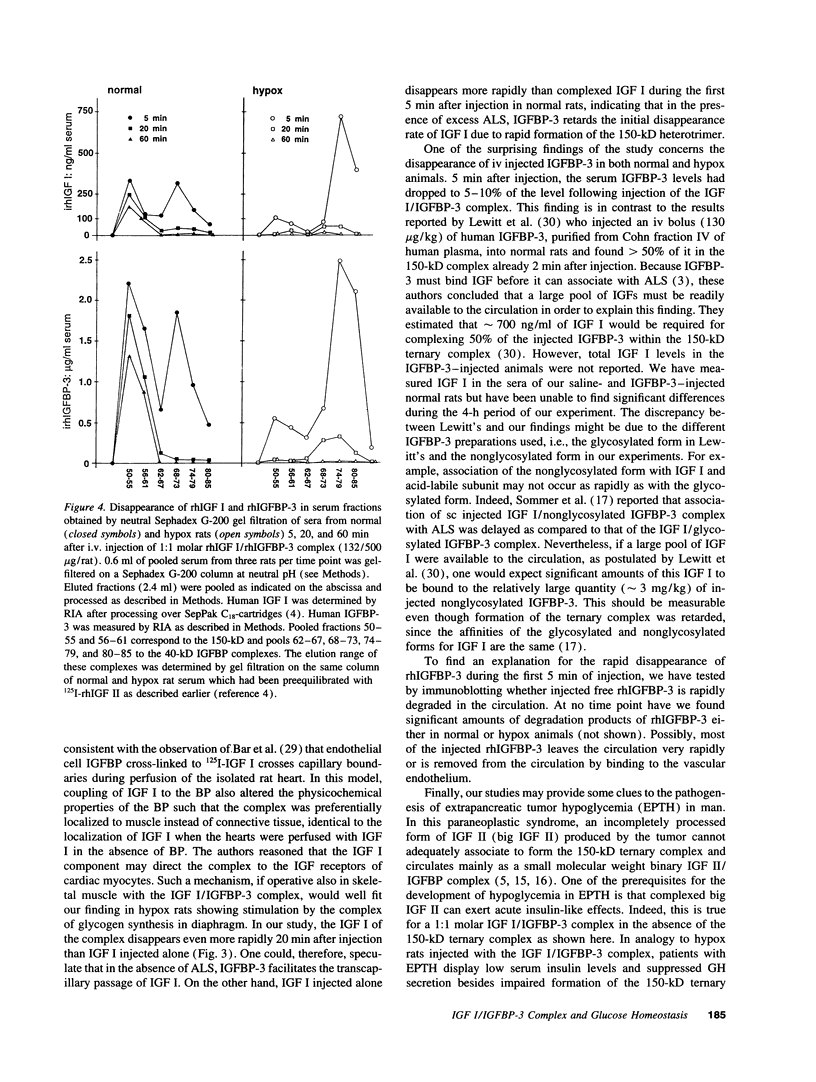
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) circulates in blood in two large molecular mass forms of 150 and 40 kD. Under normal conditions, most of the IGF is bound to the 150-kD complex by which it is retained in the circulation and therefore unable to exert acute insulin-like actions. The aim of this study was to answer the question whether or not IGF in the 40-kD complex is bioavailable to insulin target tissues and thus can cause acute insulin-like effects in vivo. Intravenously injected 1:1 molar recombinant human (rh) IGF I/rhIGF binding protein (BP)-3 complex lowered blood glucose and stimulated glycogen synthesis in diaphragm of hypophysectomized, but not of normal rats. The serum half-lives of the two components of the complex were similar to each other, but considerably shorter in hypox than in normal rats. On neutral gel filtration of serum both components of the injected complex appeared predominantly in the 150-kD region in normal rats. In hypox rats which lack the 150-kD complex they were found in the 40-kD region and disappeared rapidly from the circulation. We conclude that in the absence of the 150-kD complex, IGF associated with the 40-kD complex can rapidly leave the vascular compartment, reach insulin or type 1 IGF receptors and exert acute insulin-like effects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Dake B. L., Sandra A., Bayne M., Cascieri M., Booth B. A. Tissue localization of perfused endothelial cell IGF binding protein is markedly altered by association with IGF-I. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):3243–3245. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-3243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):265–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Daughaday W. H. Impaired formation of the ternary insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex in patients with hypoglycemia due to nonislet cell tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Oct;73(4):696–702. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-4-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Structure of the Mr 140,000 growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex: determination by reconstitution and affinity-labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6898–6902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binoux M., Hossenlopp P. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding proteins: comparison of human serum and lymph. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Sep;67(3):509–514. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen K. L., Nissley S. P. Comparison of somatomedin activity in rat serum and lymph. Endocrinology. 1975 Sep;97(3):654–658. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-3-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Kapadia M. Significance of abnormal serum binding of insulin-like growth factor II in the development of hypoglycemia in patients with non-islet-cell tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6778–6782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B., Baxter R. C. Serum "big insulin-like growth factor II" from patients with tumor hypoglycemia lacks normal E-domain O-linked glycosylation, a possible determinant of normal propeptide processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5823–5827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Scheiwiller E., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth and has distinct effects on organ size in hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Dec;121(6):753–758. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Barrett E., Plewe G., Fagin K. D., Sherwin R. S. Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1717–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI114072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Masiarz F. R., Bauer D. M., Zapf J. Identification and molecular cloning of two new 30-kDa insulin-like growth factor binding proteins isolated from adult human serum. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9043–9049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewitt M. S., Denyer G. S., Cooney G. J., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 modulates blood glucose levels. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2254–2256. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewitt M. S., Saunders H., Baxter R. C. Bioavailability of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in rats determined by the molecular distribution of human IGF-binding protein-3. Endocrinology. 1993 Oct;133(4):1797–1802. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.4.7691582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Passamani J., White R. M. Further characterization of growth hormone-dependent somatomedin-binding proteins in rat serum and demonstration of somatomedin-binding proteins produced by rat liver cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):536–546. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Rutishauser J., Schläpfer I., Froesch E. R., Zapf J. Intact but not truncated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) blocks IGF I-induced stimulation of osteoblasts: control of IGF signalling to bone cells by IGFBP-3-specific proteolysis? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91410-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin on glucose metabolism and glucose transport in fat cells of hormone-treated hypophysectomized rats: evidence that growth hormone restricts glucose transport. Endocrinology. 1979 Nov;105(5):1237–1242. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-5-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Baxter R. C. Synthesis of the acid-labile subunit of the growth-hormone-dependent insulin-like-growth-factor-binding protein complex by rat hepatocytes in culture. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):441–446. doi: 10.1042/bj2750441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Spratt S. K., Tatsuno G. P., Tressel T., Lee R., Maack C. A. Properties of glycosylated and non-glycosylated human recombinant IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3). Growth Regul. 1993 Mar;3(1):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Futo E., Peter M., Froesch E. R. Can "big" insulin-like growth factor II in serum of tumor patients account for the development of extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia? J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2574–2584. doi: 10.1172/JCI116152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1768–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI112500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Futo E., Häsler H., Binz K., Guler H. P., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I induces its own specific carrier protein in hypophysectomized and diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3813–3817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Kiefer M., Merryweather J., Musiarz F., Bauer D., Born W., Fischer J. A., Froesch E. R. Isolation from adult human serum of four insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins and molecular cloning of one of them that is increased by IGF I administration and in extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14892–14898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Biological and immunological properties of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):3–30. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Guler H. P., Waldvogel M., Hauri C., Futo E., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M., Froesch E. R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):952–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Waldvogel M., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Effect of trypsin treatment of rat adipocytes on biological effects and binding of insulin and insulin-like growth factors: further evidence for the action of insulin-like growth factors through the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Effect of insulin on glucose transport and metabolism in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of hypophysectomized rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80976-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


