Abstract
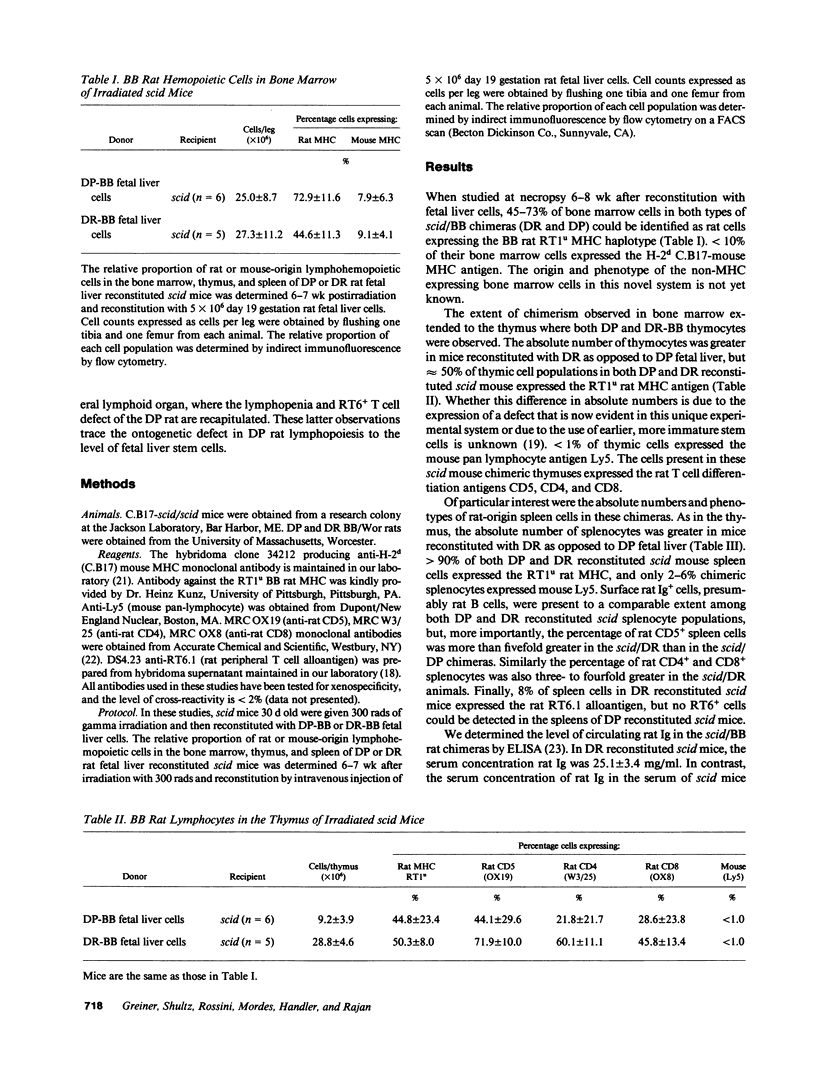
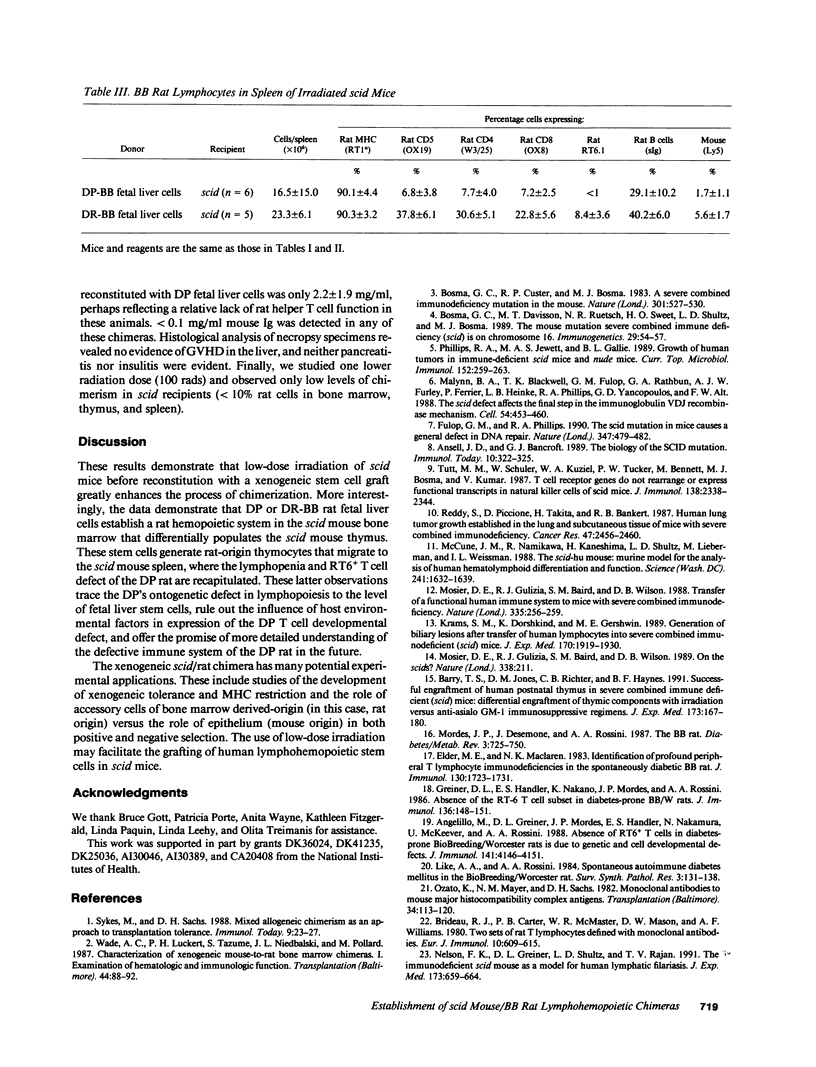
Mice homozygous for the mutation "severe combined immune deficiency" (C.B17-scid/scid) lack functional T and B lymphocytes and readily accept tumor xenografts. Partial lymphohemopoietic scid/human and mouse/rat chimeras have been described, but complete chimerization with thymic engraftment and generation of donor-origin thymocytes has not been achieved. We now report that low-dose irradiation permits the engraftment of BB rat fetal liver stem cells in scid recipients. We observed that BB rat fetal liver cells injected into irradiated scid mice establish a rat hemopoietic system in the scid mouse bone marrow and populate the scid mouse thymus. These stem cells generated rat-origin thymocytes that migrated to the scid mouse spleen, a peripheral lymphoid organ. Finally, we found that xenogeneic chimeras created using fetal liver cells from the abnormal (lymphopenic, diabetes prone) subline of BB rats recapitulated both the quantitative and phenotypic abnormalities of the donor rat. Xenogeneic lymphohemopoietic chimeras established in scid mice may provide a powerful new tool in the study of immune system development and autoimmunity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelillo M., Greiner D. L., Mordes J. P., Handler E. S., Nakamura N., McKeever U., Rossini A. Absence of RT6+ T cells in diabetes-prone biobreeding/Worcester rats is due to genetic and cell developmental defects. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4146–4151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell J. D., Bancroft G. J. The biology of the SCID mutation. Immunol Today. 1989 Oct;10(10):322–325. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry T. S., Jones D. M., Richter C. B., Haynes B. F. Successful engraftment of human postnatal thymus in severe combined immune deficient (SCID) mice: differential engraftment of thymic components with irradiation versus anti-asialo GM-1 immunosuppressive regimens. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):167–180. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Davisson M. T., Ruetsch N. R., Sweet H. O., Shultz L. D., Bosma M. J. The mouse mutation severe combined immune deficiency (scid) is on chromosome 16. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02341614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder M. E., Maclaren N. K. Identification of profound peripheral T lymphocyte immunodeficiencies in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1723–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A. The scid mutation in mice causes a general defect in DNA repair. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):479–482. doi: 10.1038/347479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Handler E. S., Nakano K., Mordes J. P., Rossini A. A. Absence of the RT-6 T cell subset in diabetes-prone BB/W rats. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):148–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krams S. M., Dorshkind K., Gershwin M. E. Generation of biliary lesions after transfer of human lymphocytes into severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1919–1930. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A. Spontaneous autoimmune diabetes mellitus in the BioBreeding/Worcester rat. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1984;3(2):131–138. doi: 10.1159/000156921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Blackwell T. K., Fulop G. M., Rathbun G. A., Furley A. J., Ferrier P., Heinke L. B., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The scid defect affects the final step of the immunoglobulin VDJ recombinase mechanism. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Kaneshima H., Shultz L. D., Lieberman M., Weissman I. L. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1632–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordes J. P., Desemone J., Rossini A. A. The BB rat. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jul;3(3):725–750. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson F. K., Greiner D. L., Shultz L. D., Rajan T. V. The immunodeficient scid mouse as a model for human lymphatic filariasis. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):659–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Jewett M. A., Gallie B. L. Growth of human tumors in immune-deficient scid mice and nude mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;152:259–263. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74974-2_31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S., Piccione D., Takita H., Bankert R. B. Human lung tumor growth established in the lung and subcutaneous tissue of mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Cancer Res. 1987 May 1;47(9):2456–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Sachs D. H. Mixed allogeneic chimerism as an approach to transplantation tolerance. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutt M. M., Schuler W., Kuziel W. A., Tucker P. W., Bennett M., Bosma M. J., Kumar V. T cell receptor genes do not rearrange or express functional transcripts in natural killer cells of scid mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2338–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade A. C., Luckert P. H., Tazume S., Niedbalski J. L., Pollard M. Characterization of xenogeneic mouse-to-rat bone marrow chimeras. I. Examination of hematologic and immunologic function. Transplantation. 1987 Jul;44(1):88–92. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198707000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


