Abstract
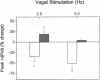
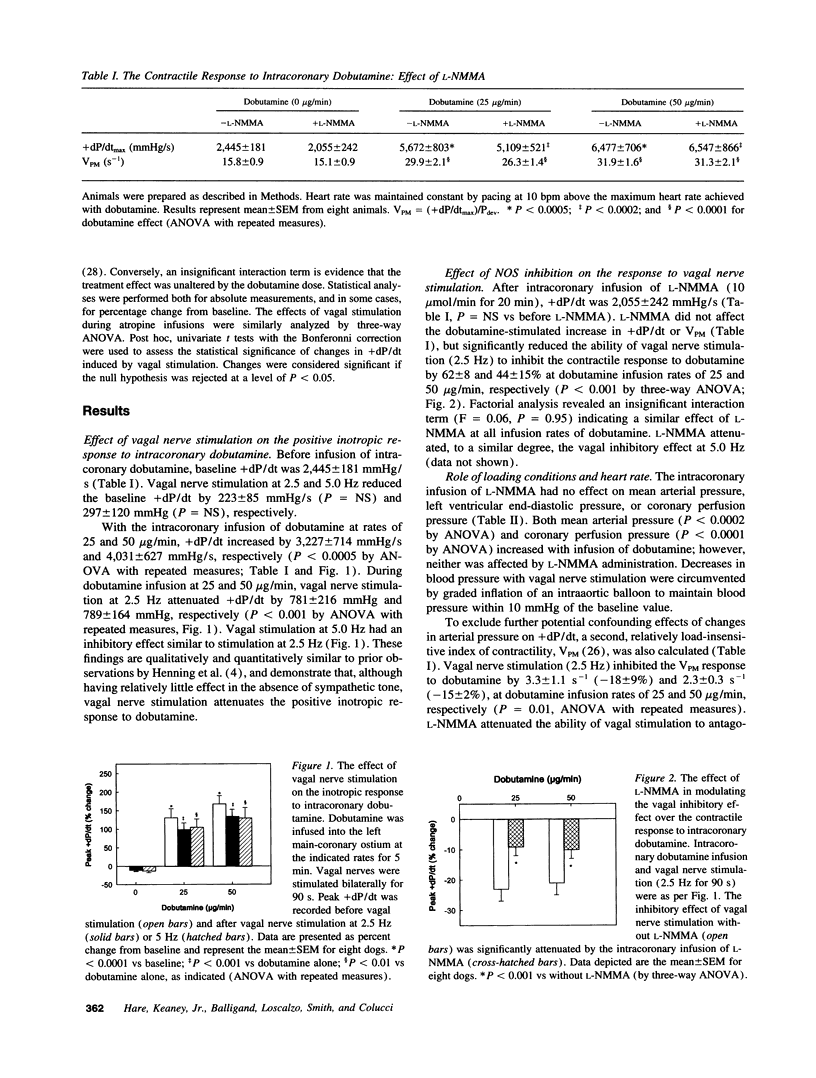
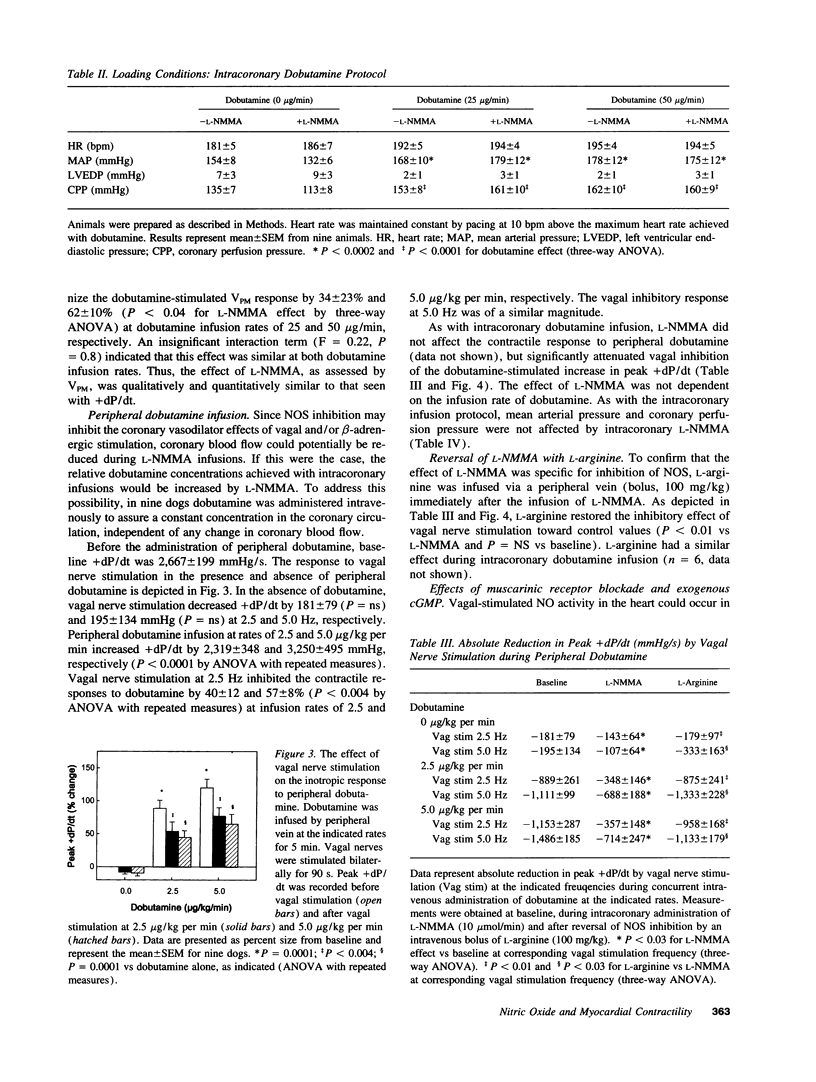
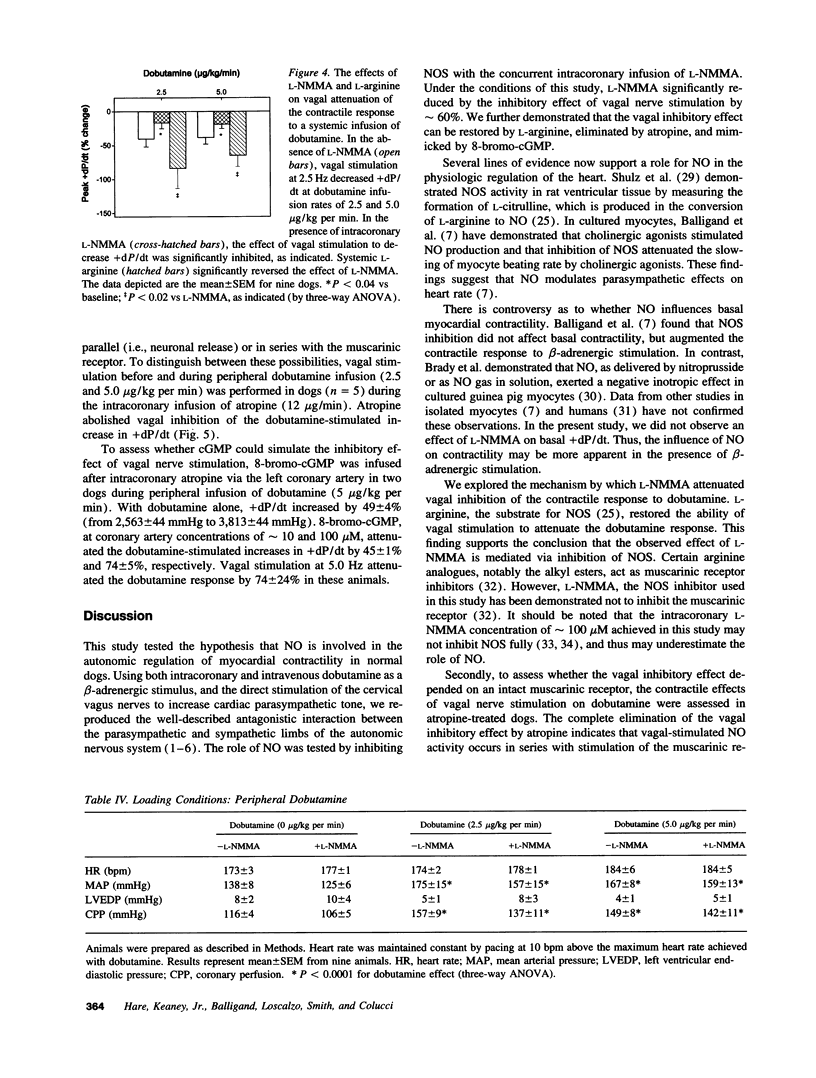
In vitro studies indicate that muscarinic cholinergic inhibition of beta-adrenergic cardiac responses may be modulated in part by nitric oxide (NO). To evaluate the role of NO in parasympathetic inhibition of the beta-adrenergic contractile response in vivo, we assessed the inotropic response to dobutamine before and during bilateral vagus nerve stimulation in closed-chest dogs. Dobutamine administration and vagal stimulation were repeated during intracoronary infusion of the NO synthase inhibitor NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA, 10 mumol/min) and again following infusion of L-arginine (100 mg/kg). In eight dogs, intracoronary dobutamine infusion at rates of 25 and 50 micrograms/min increased peak +dP/dt by 131 +/- 24 and 168 +/- 22%, respectively (P < 0.0001). Vagal stimulation (2.5 Hz) attenuated the responses to dobutamine (25 and 50 micrograms/min) by 23 +/- 4 and 21 +/- 4%, respectively (P < 0.001). L-NMMA reduced (by 44-62%; P < 0.001) and L-arginine restored vagal inhibition of the dobutamine-stimulated inotropic response. In a second group of nine dogs, dobutamine was administered systemically to assure a constant concentration in the coronary circulation. Vagal stimulation (2.5 Hz) attenuated the dobutamine-stimulated inotropic response (2.5 and 5.0 micrograms/kg per min) by 40 +/- 12% and 57 +/- 8%, respectively (P < 0.004). As with intracoronary dobutamine, L-NMMA diminished and L-arginine restored vagal inhibition of the inotropic response to dobutamine. Intracoronary infusion of atropine (12 micrograms/min) abolished the vagal inhibitory effect, and intracoronary infusion of 8-bromo-cyclic GMP (1 and 10 mM) caused a dose-dependent attenuation of the dobutamine-stimulated increase in +dP/dt. These data suggest that NO mediates, at least in part, vagal inhibition of the inotropic response to beta-adrenergic stimulation by dobutamine, and thus may play a role in normal physiologic regulation of myocardial autonomic responses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balligand J. L., Kelly R. A., Marsden P. A., Smith T. W., Michel T. Control of cardiac muscle cell function by an endogenous nitric oxide signaling system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):347–351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand J. L., Ungureanu-Longrois D., Simmons W. W., Pimental D., Malinski T. A., Kapturczak M., Taha Z., Lowenstein C. J., Davidoff A. J., Kelly R. A. Cytokine-inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in cardiac myocytes. Characterization and regulation of iNOS expression and detection of iNOS activity in single cardiac myocytes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27580–27588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand J. L., Ungureanu D., Kelly R. A., Kobzik L., Pimental D., Michel T., Smith T. W. Abnormal contractile function due to induction of nitric oxide synthesis in rat cardiac myocytes follows exposure to activated macrophage-conditioned medium. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2314–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI116461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady A. J., Poole-Wilson P. A., Harding S. E., Warren J. B. Nitric oxide production within cardiac myocytes reduces their contractility in endotoxemia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 2):H1963–H1966. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.6.H1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady A. J., Warren J. B., Poole-Wilson P. A., Williams T. J., Harding S. E. Nitric oxide attenuates cardiac myocyte contraction. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 2):H176–H182. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.1.H176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broten T. P., Miyashiro J. K., Moncada S., Feigl E. O. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in parasympathetic coronary vasodilation. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):H1579–H1584. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.5.H1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush P. A., Gonzalez N. E., Griscavage J. M., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum catalyzes the formation of equimolar quantities of nitric oxide and citrulline from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):960–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91720-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton I. L., Cheek D. J., Eckman D., Westfall D. P., Sanders K. M., Keef K. D. NG-nitro L-arginine methyl ester and other alkyl esters of arginine are muscarinic receptor antagonists. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):387–395. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci W. S., Denniss A. R., Leatherman G. F., Quigg R. J., Ludmer P. L., Marsh J. D., Gauthier D. F. Intracoronary infusion of dobutamine to patients with and without severe congestive heart failure. Dose-response relationships, correlation with circulating catecholamines, and effect of phosphodiesterase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1103–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI113423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii A. M., Vatner S. F. Autonomic mechanisms regulating myocardial contractility in conscious animals. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;29(2):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. J., Wilkerson R. D., Kadowitz P. J. Influence of acetylcholine on contractile force and cyclic nucleotide levels in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jan;184(1):228–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Mirzazadeh S., Hobbs A. J., Moore P. K. L-NG-monomethyl arginine and L-NG-nitro arginine inhibit non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxation of the mouse anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):602–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han X., Shimoni Y., Giles W. R. An obligatory role for nitric oxide in autonomic control of mammalian heart rate. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 15;476(2):309–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fischmeister R. Opposite effects of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP on Ca2+ current in single heart cells. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):273–275. doi: 10.1038/323273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R. J., Khalil I. R., Levy M. N. Vagal stimulation attenuates sympathetic enhancement of left ventricular function. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):H1470–H1475. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Burke T. M., Wood K. S., Wolin M. S., Kadowitz P. J. Association between cyclic GMP accumulation and acetylcholine-elicited relaxation of bovine intrapulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):682–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimaschewski L., Kummer W., Mayer B., Couraud J. Y., Preissler U., Philippin B., Heym C. Nitric oxide synthase in cardiac nerve fibers and neurons of rat and guinea pig heart. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1533–1537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause E. G., Halle W., Wollenberger A. Effect of dibutyryl cyclic GMP on cultured beating rat heart cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubes P., Granger D. N. Nitric oxide modulates microvascular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):H611–H615. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.2.H611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landzberg J. S., Parker J. D., Gauthier D. F., Colucci W. S. Effects of intracoronary acetylcholine and atropine on basal and dobutamine-stimulated left ventricular contractility. Circulation. 1994 Jan;89(1):164–168. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94162-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K., Pappano A. J. The parasympathetic neuroeffector junction of the heart. Pharmacol Rev. 1985 Mar;37(1):1–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURAD F., CHI Y. M., RALL T. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenyl cyclase. III. The effect of catecholamines and choline esters on the formation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate by preparations from cardiac muscle and liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1233–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKirdy H. C., McKirdy M. L., Lewis M. J., Marshall R. W. Evidence for involvement of nitric oxide in the non-adrenergic non-cholinergic (NANC) relaxation of human lower oesophageal sphincter muscle strips. Exp Physiol. 1992 May;77(3):509–511. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon T. J., Kadowitz P. J. Methylene blue inhibits neurogenic cholinergic vasodilator responses in the pulmonary vascular bed of the cat. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):L575–L584. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.5.L575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méry P. F., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Fischmeister R. Ca2+ current is regulated by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cardiac myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1197–1201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méry P. F., Pavoine C., Belhassen L., Pecker F., Fischmeister R. Nitric oxide regulates cardiac Ca2+ current. Involvement of cGMP-inhibited and cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterases through guanylyl cyclase activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26286–26295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent R., al-Obaidi M., Lavallée M. Nitric oxide formation contributes to beta-adrenergic dilation of resistance coronary vessels in conscious dogs. Circ Res. 1993 Aug;73(2):241–251. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus W. J., Vantrimpont P. J., Shah A. M. Acute effects of nitric oxide on left ventricular relaxation and diastolic distensibility in humans. Assessment by bicoronary sodium nitroprusside infusion. Circulation. 1994 May;89(5):2070–2078. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.5.2070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. The role of nitric oxide and cGMP in platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1482–1489. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajfer J., Aronson W. J., Bush P. A., Dorey F. J., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 9;326(2):90–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201093260203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. Effects of intracoronary infusions of acetylcholine and nicotine on the dog heart in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;48(4):612–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmied R., Korth M. Muscarinic receptor stimulation and cyclic AMP-dependent effects in guinea-pig ventricular myocardium. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Nava E., Moncada S. Induction and potential biological relevance of a Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthase in the myocardium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):575–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah A. M., Lewis M. J., Henderson A. H. Effects of 8-bromo-cyclic GMP on contraction and on inotropic response of ferret cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Jan;23(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90038-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah A. M., Spurgeon H. A., Sollott S. J., Talo A., Lakatta E. G. 8-bromo-cGMP reduces the myofilament response to Ca2+ in intact cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1994 May;74(5):970–978. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.5.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner S. F., Rutherford J. D., Ochs H. R. Baroreflex and vagal mechanisms modulating left ventricular contractile responses to sympathomimetic amines in conscious dogs. Circ Res. 1979 Feb;44(2):195–207. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe A. M., Besch H. R., Jr Interaction between cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic gunaosine monophosphate in guinea pig ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):309–317. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]