Abstract
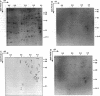
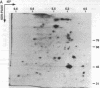
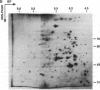
We investigated potential targets for the activity of protein synthesis inhibitors against the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Although nanomolar concentrations of azithromycin and clindamycin prevent replication of T. gondii in both cell culture and in vivo assays, no inhibition of protein labeling was observed in either extracellular or intracellular parasites treated with up to 100 microM drug for up to 24 h. Quantitative analysis of > 300 individual spots on two-dimensional gels revealed no proteins selectively depleted by 100 microM azithromycin. In contrast, cycloheximide inhibited protein synthesis in a dose-dependent manner. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the peptidyl transferase region from genes encoding the large subunit of the parasite's ribosomal RNA predict that the cytoplasmic ribosomes of T. gondii, like other eukaryotic ribosomes, should be resistant to macrolide antibiotics. Combining cycloheximide treatment with two-dimensional gel analysis revealed a small subset of parasite proteins likely to be synthesized on mitochondrial ribosomes. Synthesis of these proteins was inhibited by 100 microM tetracycline, but not by 100 microM azithromycin or clindamycin. Ribosomal DNA sequences believed to be derived from the T. gondii mitochondrial genome predict macrolide/lincosamide resistance. PCR amplification of total T. gondii DNA identified an additional class of prokaryotic-type ribosomal genes, similar to the plastid-like ribosomal genes of the Plasmodium falciparum. Ribosomes encoded by these genes are predicted to be sensitive to the lincosamide/macrolide class of antibiotics, and may serve as the functional target for azithromycin, clindamycin, and other protein synthesis inhibitors in Toxoplasma and related parasites.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blais J., Garneau V., Chamberland S. Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii protein synthesis by azithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Aug;37(8):1701–1703. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.8.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. J., Yayon A., Friedman S., Ginsburg H. Effects of mitochondrial protein synthesis inhibitors on the incorporation of isoleucine into Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. J Protozool. 1984 Aug;31(3):475–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Overdulve J. P., Weijers P. J., Fase-Fowler F., Van den Berg M. DNA circles with cruciforms from Isospora (Toxoplasma) gondii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 24;781(1-2):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. R., Comte R., Pechère J. C. In vitro and in vivo effects of doxycycline on Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I., Mikkelsen R. B. Plasmodium falciparum: ATP/ADP transport across the parasitophorous vacuolar and plasma membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Nov;71(4):452–462. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90071-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E. Resistance to macrolides and lincosamides in Streptomyces lividans and to aminoglycosides in Micromonospora purpurea. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90543-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempster R. P. Toxoplasma gondii: purification of zoites from peritoneal exudates by eight methods. Exp Parasitol. 1984 Apr;57(2):195–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(84)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divo A. A., Geary T. G., Jensen J. B. Oxygen- and time-dependent effects of antibiotics and selected mitochondrial inhibitors on Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S., Aagaard C. Erythromycin binding is reduced in ribosomes with conformational alterations in the 23 S rRNA peptidyl transferase loop. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):725–731. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Tokuda H., Yagita K., Koyama T. Effects of extracellular potassium on acid release and motility initiation in Toxoplasma gondii. J Protozool. 1987 Aug;34(3):291–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Yagita K. Effect of extracellular ions on motility and cell entry in Toxoplasma gondii. J Protozool. 1990 Mar-Apr;37(2):133–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb05883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtado G. C., Cao Y., Joiner K. A. Laminin on Toxoplasma gondii mediates parasite binding to the beta 1 integrin receptor alpha 6 beta 1 on human foreskin fibroblasts and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4925–4931. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4925-4931.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon S., Levesque R. C., Sogin M. L., Gajadhar A. A. Molecular cloning, complete sequence of the small subunit ribosomal RNA coding region and phylogeny of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jul;60(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Moore D. J., Rangachari K., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. Sequence and organization of large subunit rRNA genes from the extrachromosomal 35 kb circular DNA of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1067–1071. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Moore D. J., Spencer D. F., Gray M. W., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. Organisation and expression of small subunit ribosomal RNA genes encoded by a 35-kilobase circular DNA in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Sep;48(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. J., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. A circular DNA in malaria parasites encodes an RNA polymerase like that of prokaryotes and chloroplasts. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Jan;44(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90227-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Capobianco J. O. Role of an energy-dependent efflux pump in plasmid pNE24-mediated resistance to 14- and 15-membered macrolides in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1973–1980. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay J. M., Huot A., Gagnon S., Tremblay A., Levesque R. C. Physical and genetic mapping of cloned ribosomal DNA from Toxoplasma gondii: primary and secondary structure of the 5S gene. Gene. 1992 May 15;114(2):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90570-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurnett A. M., Dulski P. M., Rattray S., Carrington M., Schmatz D. M. Selective labelling of proteins synthesized by intracellular parasites using ricin and host cells lacking mitochondrial DNA. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994 Feb;27(2):489–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Gray M. W., Schnare M. N. A compilation of large subunit (23S and 23S-like) ribosomal RNA structures: 1993. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3055–3074. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. H., Burkhart B. D., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Antibiotic resistance mutations in the chloroplast 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: correlation of genetic and physical maps of the chloroplast genome. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Fuhrman S. A., Miettinen H. M., Kasper L. H., Mellman I. Toxoplasma gondii: fusion competence of parasitophorous vacuoles in Fc receptor-transfected fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2200126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiatfuengfoo R., Suthiphongchai T., Prapunwattana P., Yuthavong Y. Mitochondria as the site of action of tetracycline on Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 May 1;34(2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Olsen G. J., Maidak B. L., McCaughey M. J., Overbeek R., Macke T. J., Marsh T. L., Woese C. R. The ribosomal database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3021–3023. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaers G., Maroteaux L., Michot B., Herzog M. Dinoflagellates in evolution. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of large subunit ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jul;29(1):40–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02106180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;15(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossorio P. N., Sibley L. D., Boothroyd J. C. Mitochondrial-like DNA sequences flanked by direct and inverted repeats in the nuclear genome of Toxoplasma gondii. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90494-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Borotz S. E. Comparison of mutants of Toxoplasma gondii selected for resistance to azithromycin, spiramycin, or clindamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jan;38(1):31–37. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Eckel M. E., McAdams E. Toxoplasma gondii: the biochemical basis of resistance to emimycin. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Nothnagel R. F., Borotz S. E. Parasiticidal effect of clindamycin on Toxoplasma gondii grown in cultured cells and selection of a drug-resistant mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1091–1096. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prapunwattana P., O'Sullivan W. J., Yuthavong Y. Depression of Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase activity in in vitro culture by tetracycline. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. C., Beckers C. J., Joiner K. A. The parasitophorous vacuole membrane surrounding intracellular Toxoplasma gondii functions as a molecular sieve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):509–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. C., Cao Y., Slowik M. R., Joiner K. A. Localization of azithromycin in Toxoplasma gondii-infected cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jul;38(7):1620–1627. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.7.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Gutell R. R., Cummings D. J. Paramecium mitochondrial genes. II. Large subunit rRNA gene sequence and microevolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5173–5181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Boothroyd J. C. Construction of a molecular karyotype for Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Apr;51(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90079-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4653–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Fujiwara T., Akao S. Na+, K+-dependent ATPase activity and effect of K+ on in vitro protein synthesis and NAD pyrophosphorylase in Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1980 Aug;66(4):591–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Akella R., Suplick K. Sequences similar to genes for two mitochondrial proteins and portions of ribosomal RNA in tandemly arrayed 6-kilobase-pair DNA of a malarial parasite. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Lashgari M. S., Pologe L. G., Morrisey J. Structural features of Plasmodium cytochrome b that may underlie susceptibility to 8-aminoquinolines and hydroxynaphthoquinones. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Mar;58(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90088-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. Plastids better red than dead. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):638–638. doi: 10.1038/366638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Williamson D. H. Have malaria parasites three genomes? Parasitol Today. 1991 Jun;7(6):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90276-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G., Stöffler G., Apirion D., Rosen L., Tanaka K., Tamaki M., Takata R., Dekio S., Otaka E. Biochemical and genetic studies on two different types of erythromycin resistant mutants of Escherichia coli with altered ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):175–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00333665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]