Abstract
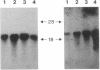
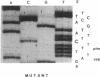
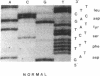
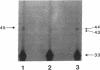
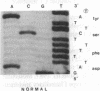
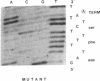
Members of two unrelated families with type I hereditary angioneurotic edema (HANE) were found to have elevated levels of C1 inhibitor (C1INH) mRNA. DNA sequence analysis of PCR-amplified monocyte C1INH mRNA revealed normal and mutant transcripts, as expected in this disorder that occurs in heterozygous individuals. Single base mutations near the 3' end of the coding sequence were identified in affected members of each family. One mutation consisted of insertion of an adenosine at position 1304 which created a premature termination codon (TAA), whereas the second consisted of deletion of the thymidine at position 1298 which created a premature termination codon (TGA) 23 nucleotides downstream. These mutations are approximately 250 nucleotides upstream of the natural termination codon. Nuclear run-off experiments in one kindred revealed no difference in transcription rates of the C1INH gene between the patients and normals. C1INH mRNA half-life experiments were not technically feasible because of the prolonged half-life of the normal transcript. Dideoxynucleotide primer extension experiments allowed the differentiation of the normal and mutant transcripts. These studies showed that the mutant transcript was not decreased relative to the normal, and this therefore was at least partially responsible for the C1INH mRNA elevation. This elevation may be due to the decreased catabolism of the mutant transcript.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariga T., Carter P. E., Davis A. E., 3rd Recombinations between Alu repeat sequences that result in partial deletions within the C1 inhibitor gene. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90246-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Brickner H. E., Zhu X. X., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Forget B. G. New amber mutation in a beta-thalassemic gene with nonmeasurable levels of mutant messenger RNA in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):557–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI113632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulak K. S., Pemberton P. A., Rosen F. S., Carrell R. W., Lachmann P. J., Harrison R. A. Dysfunctional C1-inhibitor(At), isolated from a type II hereditary-angio-oedema plasma, contains a P1 'reactive centre' (Arg444----His) mutation. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):615–618. doi: 10.1042/bj2530615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Benz E. J., Jr Nonsense mutations in the human beta-globin gene affect mRNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschini L., Cicardi M., Tucci A., Gardinali M., Frangi D., Valle C., Agostoni A. C1 INH concentrate in the therapy of hereditary angioedema. Allergy. 1983 Feb;38(2):81–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1983.tb01590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Skriver K., Nielsen E., Thøgersen H. C., Wiman B., Donaldson V. H., Eddy R. L., Marrinan J., Radziejewska E., Huber R. Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4292–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Steigerwalt R. W., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A., Grunberger D. DNA base changes and RNA levels in N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene-induced dihydrofolate reductase mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. E., Dunbar B., Fothergill J. E. Genomic and cDNA cloning of the human C1 inhibitor. Intron-exon junctions and comparison with other serpins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):163–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicardi M., Bergamaschini L., Marasini B., Boccassini G., Tucci A., Agostoni A. Hereditary angioedema: an appraisal of 104 cases. Am J Med Sci. 1982 Jul-Aug;284(1):2–9. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicardi M., Igarashi T., Kim M. S., Frangi D., Agostoni A., Davis A. E., 3rd Restriction fragment length polymorphism of the C1 inhibitor gene in hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1640–1643. doi: 10.1172/JCI113252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicardi M., Igarashi T., Rosen F. S., Davis A. E., 3rd Molecular basis for the deficiency of complement 1 inhibitor in type I hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):698–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI112873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd C1 inhibitor and hereditary angioneurotic edema. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:595–628. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Whitehead A. S., Harrison R. A., Dauphinais A., Bruns G. A., Cicardi M., Rosen F. S. Human inhibitor of the first component of complement, C1: characterization of cDNA clones and localization of the gene to chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3161–3165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein L. P., Schneeberger E. E., Colten H. R. Synthesis of the second component of complement by long-term primary cultures of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):114–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Lohse P., Parrott C., Baggio G., Gabelli C., Thomas F., Hoffman J., Brewer H. B., Jr A nonsense mutation in the apolipoprotein C-IIPadova gene in a patient with apolipoprotein C-II deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1215–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI114287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hosea S. W., Gelfand J. A., Frank M. M. Response of variant hereditary angioedema phenotypes to danazol therapy. Genetic implications. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):280–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulatory control of beta-tubulin mRNA stability is linked to translation elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Sherins R. J., Alling D. W., Frank M. M. Treatment of hereditary angioedema with danazol. Reversal of clinical and biochemical abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 23;295(26):1444–1448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612232952602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Beta O-39 thalassemia gene: a premature termination codon causes beta-mRNA deficiency without affecting cytoplasmic beta-mRNA stability. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäck H. M., Berg J., Wabl M. Translation affects immunoglobulin mRNA stability. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):843–847. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., McPhaden A. R., Yap P. L., Carter P. E., Birnie G. D., Fothergill J. E., Whaley K. Monocyte C1-inhibitor synthesis in patients with C1-inhibitor deficiency. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;19(1):45–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S., Davis C. G., Elhammer A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L. The Lebanese allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus. Nonsense mutation produces truncated receptor that is retained in endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J., Ramesh N., Cicardi M., Harrison R. A., Davis A. E., 3rd Type II hereditary angioneurotic edema that may result from a single nucleotide change in the codon for alanine-436 in the C1 inhibitor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):265–268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Coleman M. B., Adams J. G., 3rd, Cash F. E., Steinberg M. H. Molecular basis for nondeletion alpha-thalassemia in American blacks. Alpha 2(116GAG----UAG). J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):154–159. doi: 10.1172/JCI113041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parad R. B., Kramer J., Strunk R. C., Rosen F. S., Davis A. E., 3rd Dysfunctional C1 inhibitor Ta: deletion of Lys-251 results in acquisition of an N-glycosylation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6786–6790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Ross J. Autogenous regulation of histone mRNA decay by histone proteins in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4345–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Alper C. A., Pensky J., Klemperer M. R., Donaldson V. H. Genetically determined heterogeneity of the C1 esterase inhibitor in patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2143–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI106708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver K., Radziejewska E., Silbermann J. A., Donaldson V. H., Bock S. C. CpG mutations in the reactive site of human C1 inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3066–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppa-Lyonnet D., Carter P. E., Meo T., Tosi M. Clusters of intragenic Alu repeats predispose the human C1 inhibitor locus to deleterious rearrangements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1551–1555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppa-Lyonnet D., Tosi M., Laurent J., Sobel A., Lagrue G., Meo T. Altered C1 inhibitor genes in type I hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 2;317(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707023170101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]