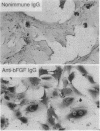
Abstract
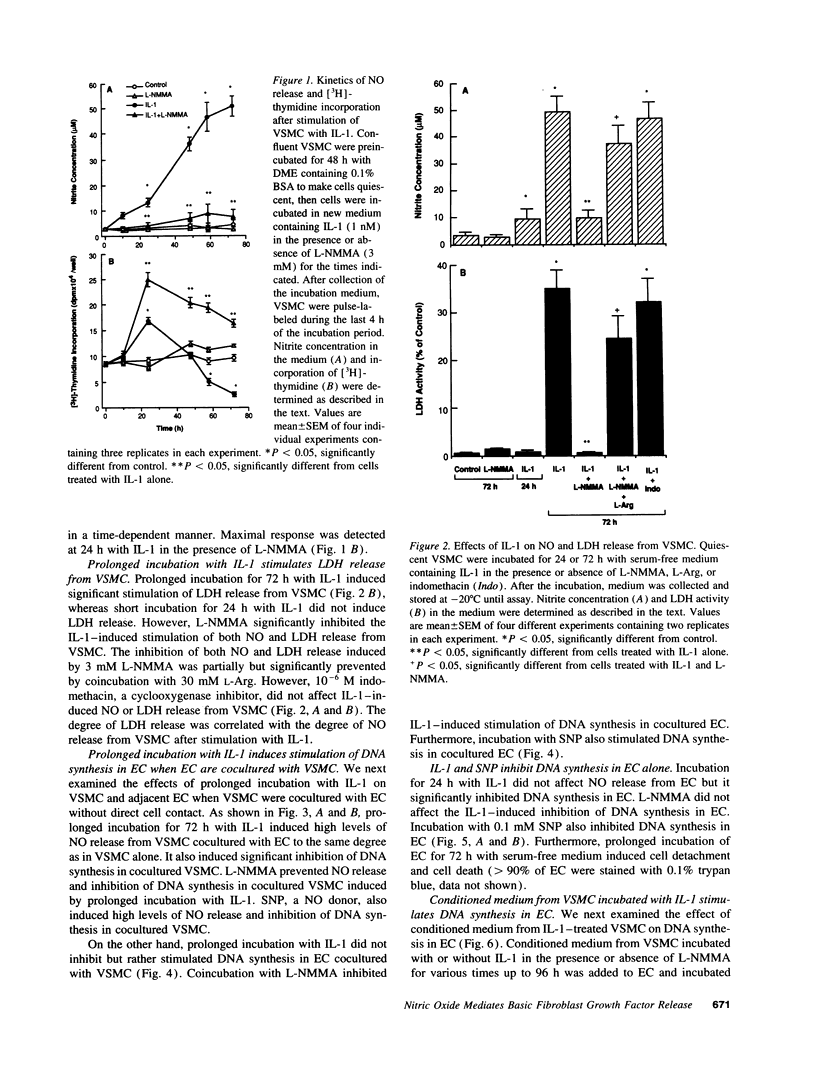
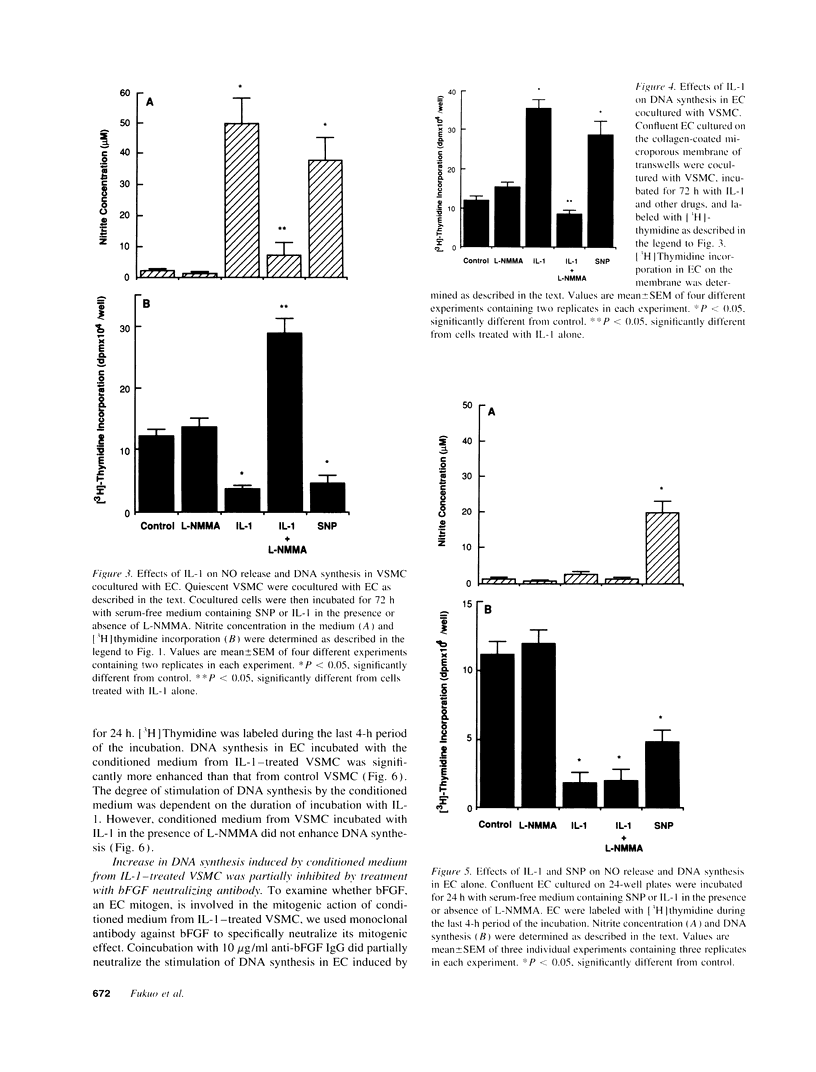
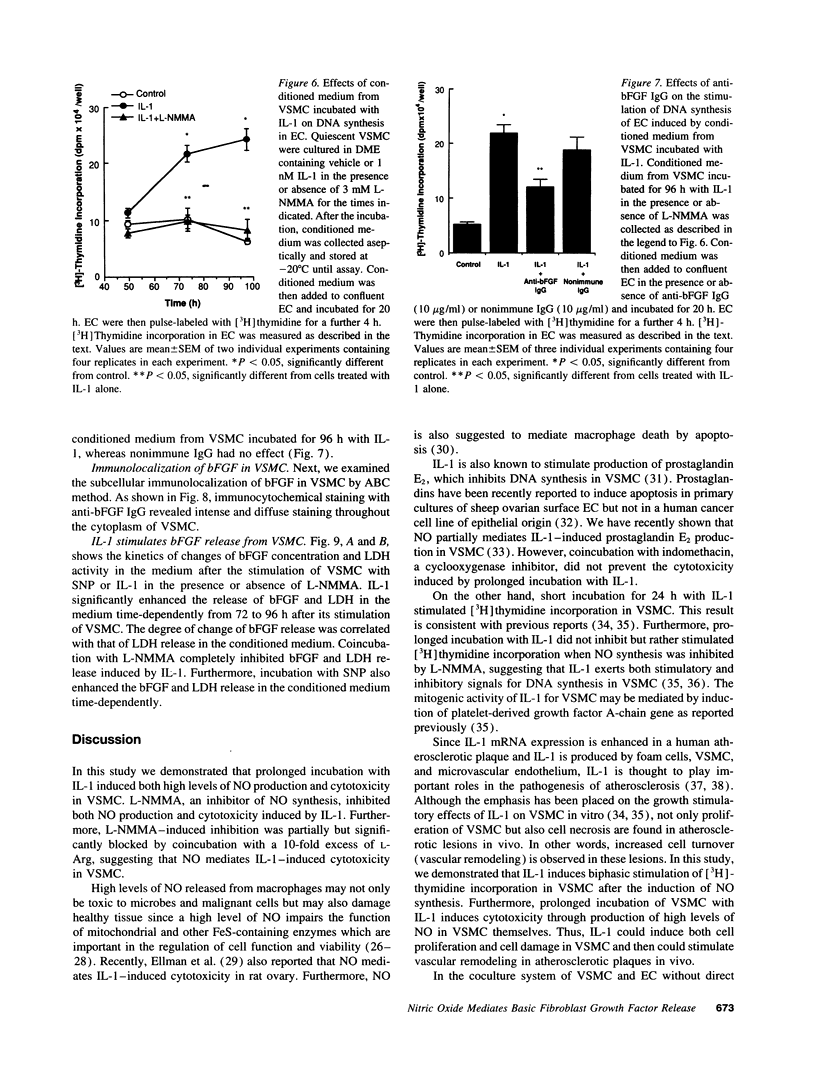
To define the pathophysiological role of nitric oxide (NO) released from vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), we examined whether NO released from VSMC induces cytotoxicity in VSMC themselves and adjacent endothelial cells (EC) using a coculture system. Prolonged incubation with interleukin-1 (IL-1) induced large amounts of NO release and cytotoxicity in VSMC. NG-Monomethyl-L-arginine, an inhibitor of NO synthesis, inhibited both NO release and cytotoxicity induced by IL-1. In contrast, DNA synthesis in cocultured EC was not inhibited but rather stimulated by prolonged incubation with IL-1 or sodium nitroprusside (SNP), a NO donor. However, IL-1 and SNP did not stimulate but inhibited DNA synthesis in EC alone. On the other hand, conditioned medium from VSMC incubated for a long period with IL-1 or SNP stimulated DNA synthesis in EC alone. Furthermore, the concentration of basic fibroblast growth factor in the conditioned medium was increased and correlated with the degree of cytotoxicity in VSMC. These results indicate that NO released from VSMC induces VSMC death, which results in release of basic fibroblast growth factor, which then stimulates adjacent EC proliferation. Thus, NO released from VSMC may participate in the mechanism of neovascularization in atherosclerotic plaques.
Full text
PDF


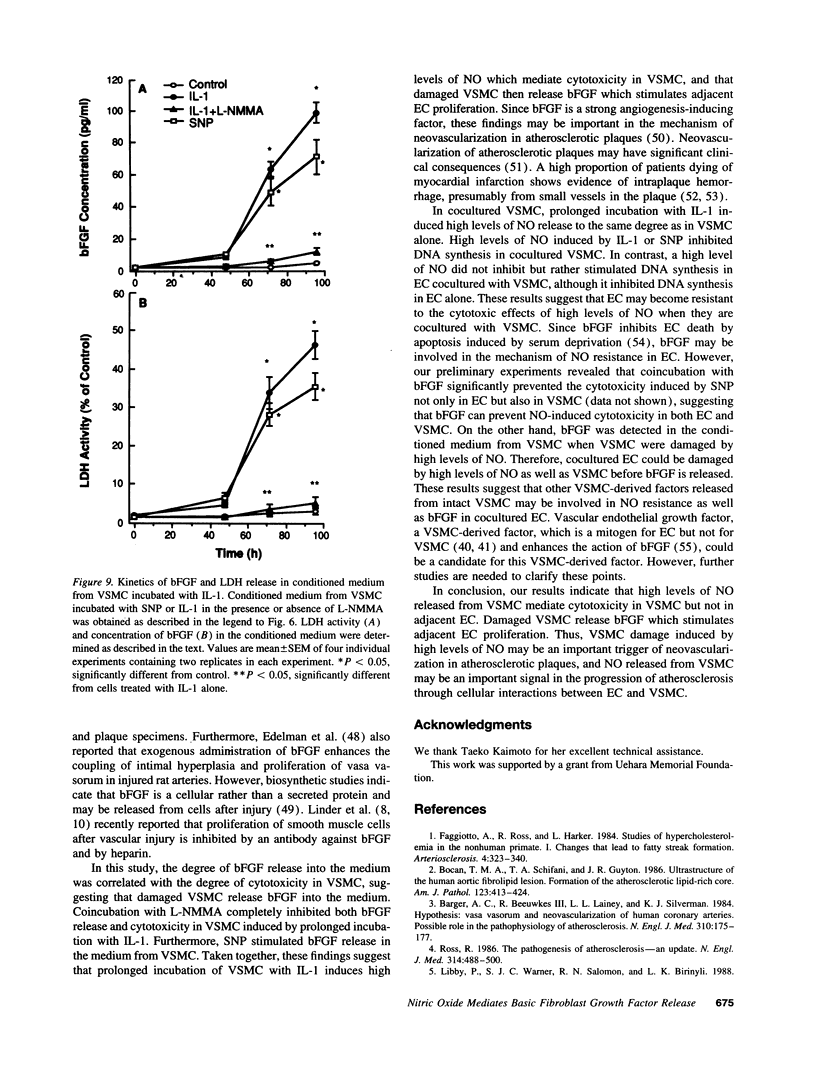

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman R. C., Murdoch W. J. Prostaglandin-induced apoptosis of ovarian surface epithelial cells. Prostaglandins. 1993 May;45(5):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(93)90123-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albina J. E., Caldwell M. D., Henry W. L., Jr, Mills C. D. Regulation of macrophage functions by L-arginine. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1021–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki S., Simada Y., Kaji K., Hayashi H. Role of protein kinase C in the inhibition by fibroblast growth factor of apoptosis in serum-depleted endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1081–1085. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91557-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Mormède P., Böhlen P. Immunoreactive fibroblast growth factor in cells of peritoneal exudate suggests its identity with macrophage-derived growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90614-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger A. C., Beeuwkes R., 3rd, Lainey L. L., Silverman K. J. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of human coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):175–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger A. C., Beeuwkes R., 3rd, Lainey L. L., Silverman K. J. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of human coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):175–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley D., Schwartz J. H., Brenner B. M. Interleukin 1 induces prolonged L-arginine-dependent cyclic guanosine monophosphate and nitrite production in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):602–608. doi: 10.1172/JCI115036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt J., Tschudi M. R., Dohi Y., Gut I., Urwyler B., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Release of nitric oxide from human vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):907–912. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocan T. M., Schifani T. A., Guyton J. R. Ultrastructure of the human aortic fibrolipid lesion. Formation of the atherosclerotic lipid-rich core. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jun;123(3):413–424. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogi E., Winkles J. A., Underwood R., Clinton S. K., Alberts G. F., Libby P. Distinct patterns of expression of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in human atheroma and nonatherosclerotic arteries. Association of acidic FGF with plaque microvessels and macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2408–2418. doi: 10.1172/JCI116847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casscells W., Lappi D. A., Olwin B. B., Wai C., Siegman M., Speir E. H., Sasse J., Baird A. Elimination of smooth muscle cells in experimental restenosis: targeting of fibroblast growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman J. L., Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide regulation. Potential relevance to cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1993 Aug;73(2):217–222. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Differentiation of murine macrophages to express nonspecific cytotoxicity for tumor cells results in L-arginine-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial iron-sulfur enzymes in the macrophage effector cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2829–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman E. R., Nugent M. A., Smith L. T., Karnovsky M. J. Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances the coupling of intimal hyperplasia and proliferation of vasa vasorum in injured rat arteries. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):465–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R. Angiogenesis in arteries: review. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;49(1-2):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90019-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman C., Corbett J. A., Misko T. P., McDaniel M., Beckerman K. P. Nitric oxide mediates interleukin-1-induced cellular cytotoxicity in the rat ovary. A potential role for nitric oxide in the ovulatory process. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):3053–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI116930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Houck K., Jakeman L., Leung D. W. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Winer J., Burton T. Aortic smooth muscle cells express and secrete vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors. 1991;5(2):141–148. doi: 10.3109/08977199109000278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuo K., Morimoto S., Koh E., Yukawa S., Tsuchiya H., Imanaka S., Yamamoto H., Onishi T., Kumahara Y. Effects of prostaglandins on the cytosolic free calcium concentration in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90901-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek C. M., Carbon S. Injury-induced release of basic fibroblast growth factor from bovine aortic endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):570–579. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Reidy M. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Cell proliferation in human coronary arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4600–4604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Esch F., Bohlen P. Corpus luteum angiogenic factor is related to fibroblast growth factor. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2383–2391. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori A., Sasada R., Matsutani E., Naito K., Sakura Y., Fujita T., Kozai Y. Suppression of solid tumor growth by immunoneutralizing monoclonal antibody against human basic fibroblast growth factor. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 15;51(22):6180–6184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Fukuto J. M., Griscavage J. M., Rogers N. E., Byrns R. E. Oxidation of nitric oxide in aqueous solution to nitrite but not nitrate: comparison with enzymatically formed nitric oxide from L-arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8103–8107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imparato A. M., Riles T. S., Mintzer R., Baumann F. G. The importance of hemorrhage in the relationship between gross morphologic characteristics and cerebral symptoms in 376 carotid artery plaques. Ann Surg. 1983 Feb;197(2):195–203. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198302000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Fukuo K., Morimoto S., Koh E., Ogihara T. Nitric oxide mediates interleukin-1-induced prostaglandin E2 production by vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 15;194(1):420–424. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly G. A., Schini V. B., Vanhoutte P. M. Balloon injury and interleukin-1 beta induce nitric oxide synthase activity in rat carotid arteries. Circ Res. 1992 Aug;71(2):331–338. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Edelman E. R. Biological and biochemical properties of fibroblast growth factors. Implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H., Kolb-Bachofen V. Nitric oxide: a pathogenetic factor in autoimmunity. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90118-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Warner S. J., Friedman G. B. Interleukin 1: a mitogen for human vascular smooth muscle cells that induces the release of growth-inhibitory prostanoids. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):487–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI113346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Warner S. J., Salomon R. N., Birinyi L. K. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like mitogen by smooth-muscle cells from human atheroma. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1493–1498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Olson N. E., Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A. Inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation in injured rat arteries. Interaction of heparin with basic fibroblast growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2044–2049. doi: 10.1172/JCI116085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer C. F., Sajuthi D., Tulli H., Williams J. K. Synthesis of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta by arterial cells in atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):951–960. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., Olsson A. G. Prostaglandin E1 inhibits DNA synthesis in arterial smooth muscle cells stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. Atherosclerosis. 1984 Oct;53(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunokawa Y., Ishida N., Tanaka S. Cloning of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 26;191(1):89–94. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Ferrara N., Orci L., Montesano R. Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):824–831. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Dower S. K., Ross R. Interleukin-1 mitogenic activity for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells is due to PDGF-AA. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.2783498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangnekar V. V., Waheed S., Davies T. J., Toback F. G., Rangnekar V. M. Antimitogenic and mitogenic actions of interleukin-1 in diverse cell types are associated with induction of gro gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2415–2422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Wight T. N., Strandness E., Thiele B. Human atherosclerosis. I. Cell constitution and characteristics of advanced lesions of the superficial femoral artery. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):79–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarih M., Souvannavong V., Adam A. Nitric oxide synthase induces macrophage death by apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):503–508. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Neufeld G., Friedman J., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C., Gospodarowicz D. Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):257–259. doi: 10.1038/325257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno M., Iwane M., Sasada R., Moriya N., Kurokawa T., Igarashi K. Monoclonal antibodies against human basic fibroblast growth factor. Hybridoma. 1989 Apr;8(2):209–221. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitters. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.1353273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J. Biochemistry of nitric oxide and its redox-activated forms. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1898–1902. doi: 10.1126/science.1281928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkles J. A., Friesel R., Burgess W. H., Howk R., Mehlman T., Weinstein R., Maciag T. Human vascular smooth muscle cells both express and respond to heparin-binding growth factor I (endothelial cell growth factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziche M., Morbidelli L., Masini E., Granger H., Geppetti P., Ledda F. Nitric oxide promotes DNA synthesis and cyclic GMP formation in endothelial cells from postcapillary venules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 14;192(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler R. E., Bandyk D. F., Thiele B. L., Strandness D. E., Jr Carotid artery stenosis following endarterectomy. Arch Surg. 1982 Nov;117(11):1408–1415. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380350016003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]