Abstract
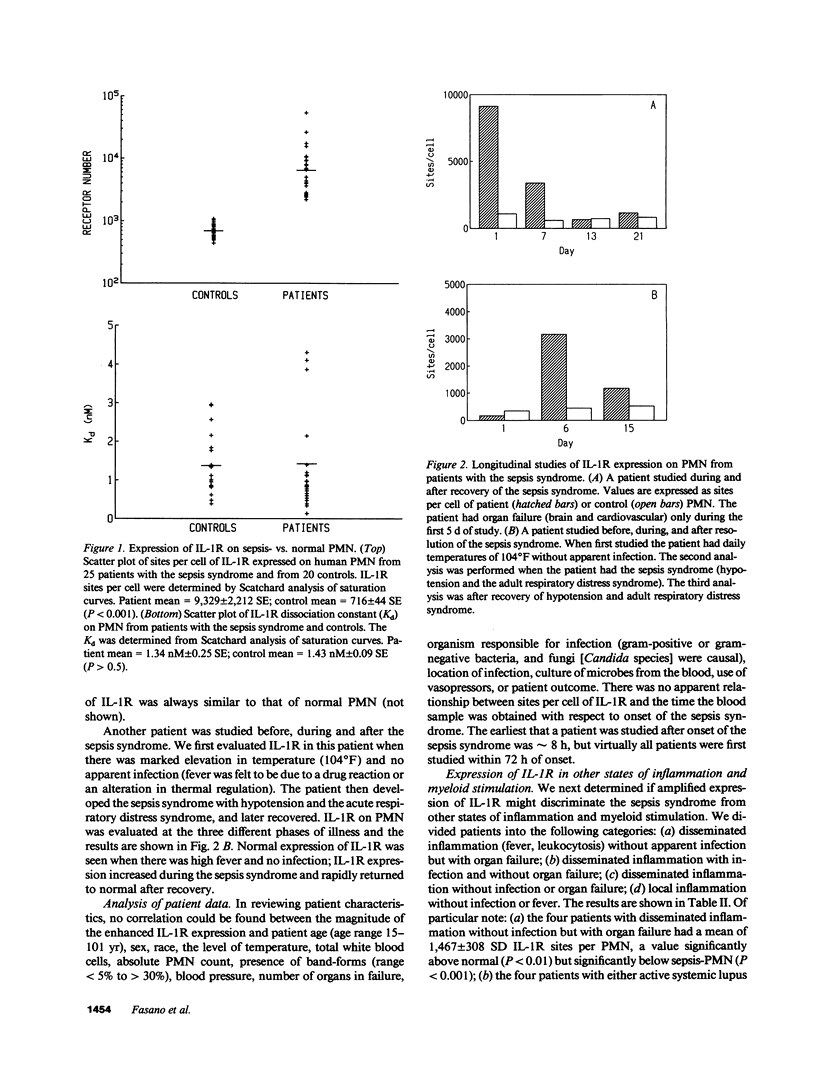
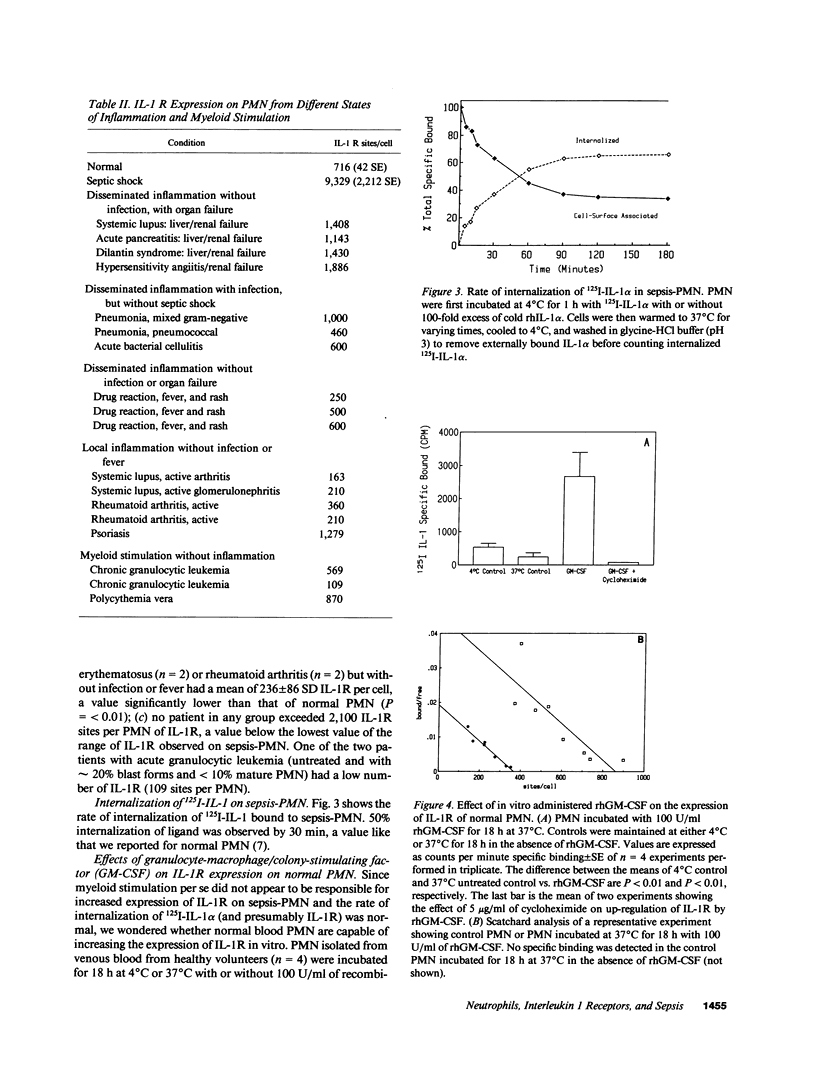
Because of the potential importance of interleukin 1 (IL-1) in modulating inflammation and the observations that human blood neutrophils (PMN) express IL-1 receptors (IL-1R) and synthesize IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, we studied the IL-1R on blood PMN from a group of patients with the sepsis syndrome. We report a marked enhancement in the sites per cell of IL-1R expressed on sepsis-PMN of 25 consecutively studied patients compared to 20 controls (patient mean = 9,329 +/- 2,212 SE; control mean = 716 +/- 42 SE, respectively). There was no demonstrable difference in the Kd of IL-1R on sepsis-PMN (approximately 1 nM) as determined by saturation curves of 125I-IL-1 alpha binding and the IL-1R on sepsis-PMN had an apparent Mr approximately 68,000, a value like that of normal PMN. Cytofluorographic analysis indicated that the sepsis-PMN phenotype is a single homogeneous population with respect to IL-1R expression. In contrast, expression of the membrane complement receptor CR3 is not increased on sepsis-PMN. Similar increases in expression of IL-1R were not observed in various other inflammatory processes, including acute disseminated inflammation and organ failure not caused by infection, acute infection without organ failure, and immunopathologies such as active systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Enhanced expression of IL-1R was not related simply to the state of myeloid stimulation. Increased expression of IL-1R on normal PMN was induced in vitro by incubating cells with recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage/colony-stimulating factor for 18 h and this response was inhibited by cycloheximide, suggesting the possibility that de novo synthesis of IL-1R might occur in PMN during the sepsis syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., O'Shea J., Cross A. S., Folks T. M., Chused T. M., Brown E. J., Frank M. M. Human neutrophils increase expression of C3bi as well as C3b receptors upon activation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1566–1571. doi: 10.1172/JCI111572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Sorensen R. U., Tosi M. F., Dearborn D. G., Döring G. Complement receptor expression on neutrophils at an inflammatory site, the Pseudomonas-infected lung in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1302–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI114298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Sims J. E., Stanton T. H., Slack J., McMahan C. J., Valentine M. A., Dower S. K. Evidence for different interleukin 1 receptors in murine B- and T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8034–8038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyon J. P., Shadick N., Berkman R., Hopkins P., Dalton J., Weissmann G., Winchester R., Abramson S. B. Surface expression of Gp 165/95, the complement receptor CR3, as a marker of disease activity in systemic Lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jan;46(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Cameron P. M., Rupp E., Schmidt J. A. Identification of a high-affinity receptor for native human interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 alpha on normal human lung fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):70–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R., Truitt T., Kilian P. L., Stern A. S., Nunes P., Parker K. P., Kaffka K. L., Chua A. O., Lugg D. K., Gubler U. Two high-affinity interleukin 1 receptors represent separate gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clark B. D., Puren A. J., Savage N., Rosoff P. M. The interleukin 1 receptor. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Call S. M., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Similarity between the interleukin 1 receptors on a murine T-lymphoma cell line and on a murine fibroblast cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Kronheim S. R., March C. J., Conlon P. J., Hopp T. P., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Detection and characterization of high affinity plasma membrane receptors for human interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):501–515. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis K., Schaefer C., Dinarello C. A., Klempner M. S. Human recombinant interleukin 1 beta has no effect on intracellular calcium or on functional responses of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3403–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Huang J. J., Covington M., Newton R. C. A biochemical and kinetic analysis of the interleukin-1 receptor. Evidence for differences in molecular properties of IL-1 receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16275–16278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord P. C., Wilmoth L. M., Mizel S. B., McCall C. E. Expression of interleukin-1 alpha and beta genes by human blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1312–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI115134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marucha P. T., Zeff R. A., Kreutzer D. L. Cytokine regulation of IL-1 beta gene expression in the human polymorphonuclear leukocyte. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2932–2937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Akahoshi T., Yamada M., Furutani Y., Oppenheim J. J. Properties of a specific interleukin 1 (IL 1) receptor on human Epstein Barr virus-transformed B lymphocytes: identity of the receptor for IL 1-alpha and IL 1-beta. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4496–4502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by chemoattractants and other soluble stimuli. Evidence that the same oxidase is activated by different transductional mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):192–200. doi: 10.1172/JCI110957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. D., Jr, Davis C., Rodrick M., Mannick J. A., Fearon D. T. Neutrophil activation in thermal injury as assessed by increased expression of complement receptors. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):948–953. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Hasslen S. R., Ahrenholz D. H., Haus E., Solem L. D. Influence of minor thermal injury on expression of complement receptor CR3 on human neutrophils. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):563–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. P., Benjamin W. R., Kaffka K. L., Kilian P. L. Presence of IL-1 receptors on human and murine neutrophils. Relevance to IL-1-mediated effects in inflammation. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):537–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Parker M. M., Natanson C., Suffredini A. F., Danner R. L., Cunnion R. E., Ognibene F. P. Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Aug 1;113(3):227–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyne J. A., Mizel S. B., Taylor R. G., Chedid M., McCall C. E. Characterization of the human interleukin 1 receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Sep;48(3):354–361. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Tanaka Y., Ota T., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Expression of interleukin 1 receptors on human peripheral T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4243–4248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Lioubin P. J., Slack J., Dower S. K., Jonas U., Cosman D., Sims J. E., Bauer J. Induction of an interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) on monocytic cells. Evidence that the receptor is not encoded by a T cell-type IL-1R mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22499–22505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Albert J. D., Fong Y., Hesse D., Beutler B., Manogue K. R., Calvano S., Wei H. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces lethal shock and stress hormone responses in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987 May;164(5):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Bender J. G., Simpson S. J., Chenoweth D. E. Relationship of chemotactic receptors for formyl peptide and C5a to CR1, CR3, and Fc receptors on human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jun;47(6):519–527. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.6.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Seligmann B., Gallin J. I. Exudation primes human and guinea pig neutrophils for subsequent responsiveness to the chemotactic peptide N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine and increases complement component C3bi receptor expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):925–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI112391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]