Abstract
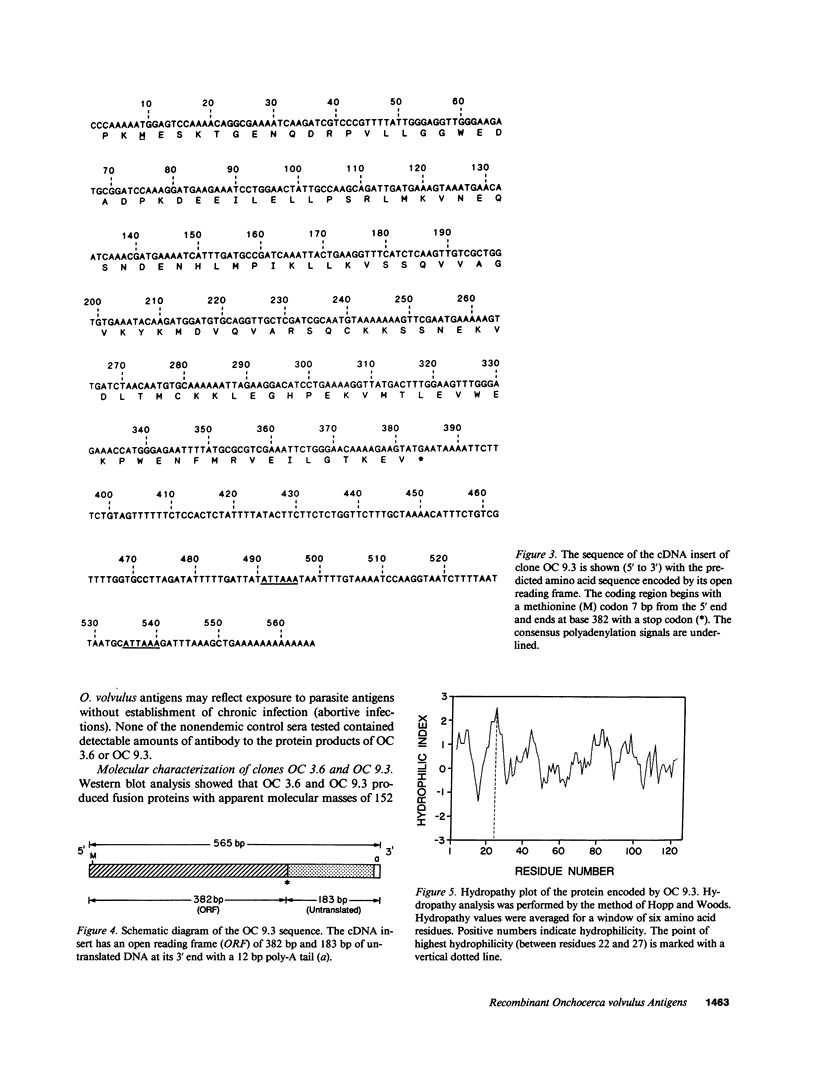
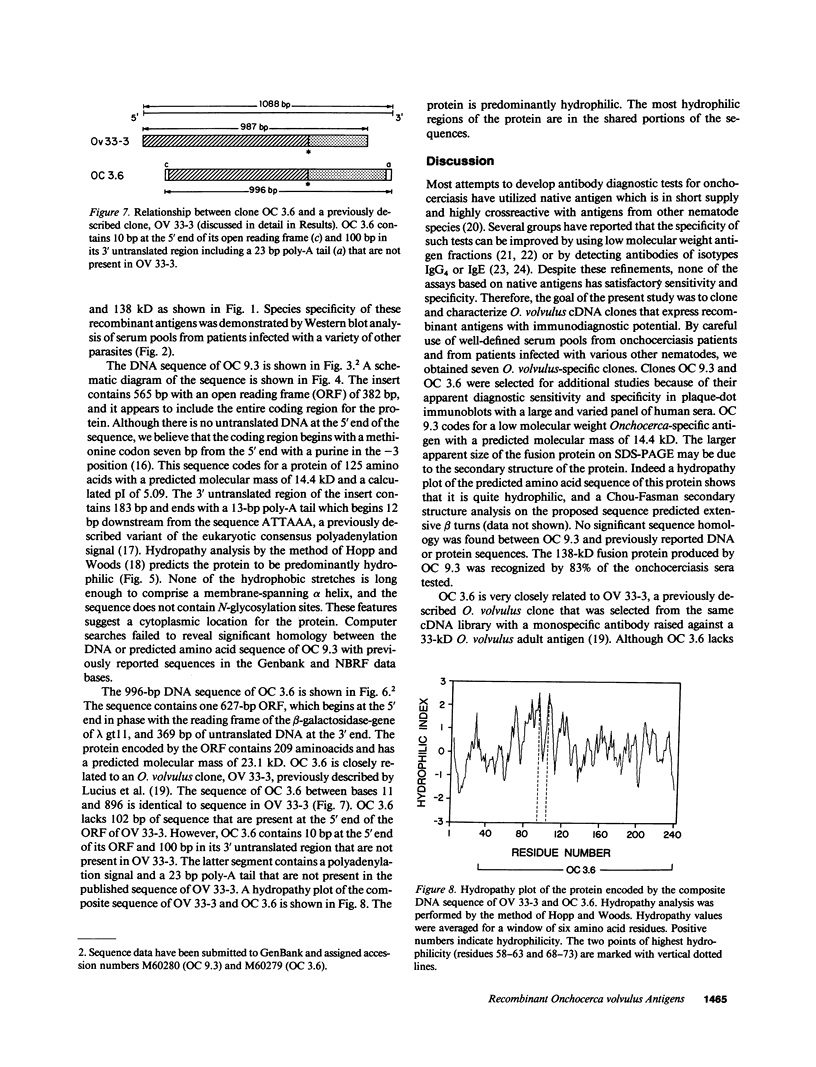
Immunological cross-reactivity among nematodes has hampered the development of specific serodiagnostic assays for onchocerciasis. In the present study, an Onchocerca volvulus adult worm complementary DNA expression library was differentially screened with human sera from patients infected with O. volvulus and with an omnibus anti-nematode serum pool comprised of sera from patients infected with Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Wuchereria bancrofti, Mansonella perstans, Strongyloides stercoralis, Ancylostoma duodenale, Ascaris lumbricoides, and Dracunculus medinensis. Seven Onchocerca-specific clones were identified and screened with individual onchocerciasis patient sera. Additional studies were performed to characterize the most immunoreactive clones, OC 3.6 and OC 9.3. OC 3.6 produced a 152-kD beta-galactosidase fusion protein that was recognized in dot-immunoblots by 54 of 55 sera from onchocerciasis patients (98%). The OC 3.6 DNA insert is 996 bp long with an open reading frame of 627 bp and a 369-bp untranslated 3' end. OC 3.6 is closely related to a previously reported clone (OV 33-3), but it differs from that clone at both the 5' and 3' ends. OC 9.3 contained a novel 565-bp insert and produced a 138-kD fusion protein that was recognized by 46 of 55 sera from onchocerciasis patients (83%). Additional studies are in progress to develop and evaluate immunodiagnostic tests for onchocerciasis based on measurement of antibodies to these promising recombinant antigens.
Full text
PDF
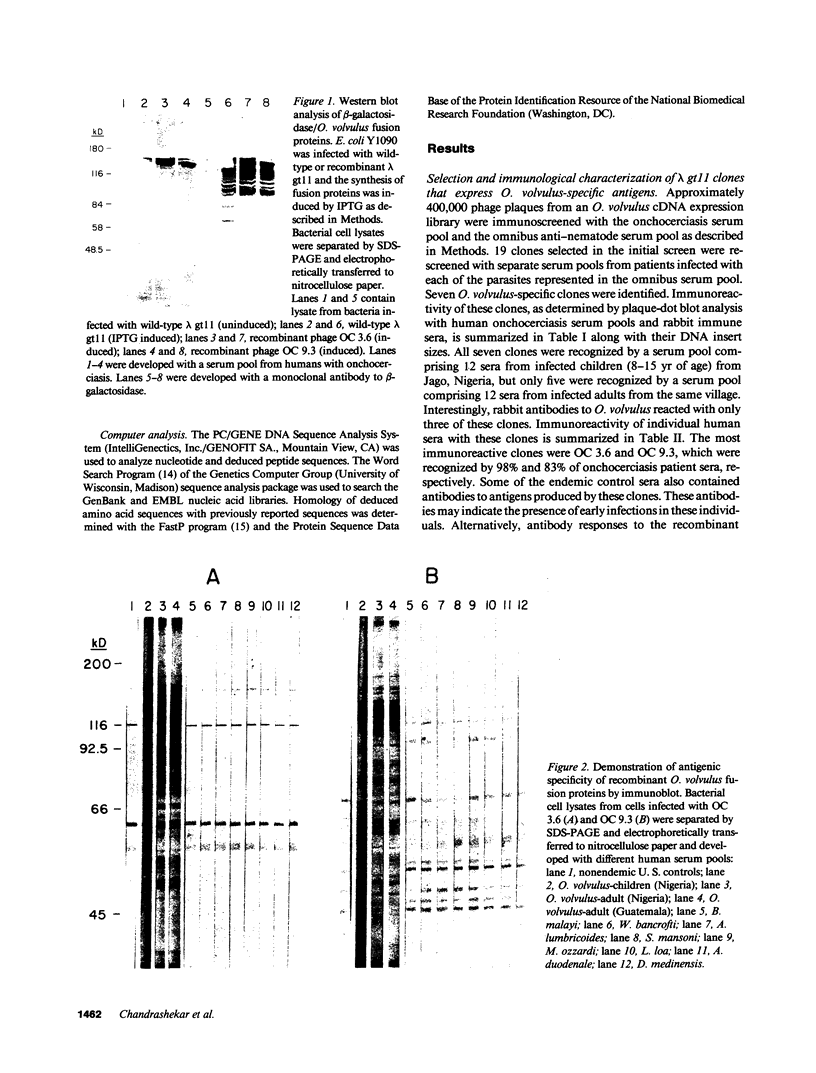


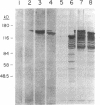
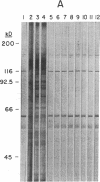
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabrera Z., Parkhouse R. M. Isolation of an antigenic fraction for diagnosis of onchocerciasis. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Jan;9(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrashekar R., Ogunrinade A. F., Alvarez R. M., Kale O. O., Weil G. J. Circulating immune complex-associated parasite antigens in human onchocerciasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1159–1164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelson J. E., Duke B. O., Moser D., Zeng W. L., Erondu N. E., Lucius R., Renz A., Karam M., Flores G. Z. Construction of Onchocerca volvulus cDNA libraries and partial characterization of the cDNA for a major antigen. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Dec;31(3):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke B. O. Onchocerciasis (river blindness)- can it be eradicated? Parasitol Today. 1990 Mar;6(3):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90217-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garate T., Conraths F. J., Harnett W., Büttner D. W., Parkhouse R. M. Cloning of specific diagnostic antigens of Onchocerca volvulus. Trop Med Parasitol. 1990 Sep;41(3):245–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobos E., Weiss N., Karam M., Taylor H. R., Ottesen E. A., Nutman T. B. An immunogenic Onchocerca volvulus antigen: a specific and early marker of infection. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1603–1605. doi: 10.1126/science.2011741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucius R., Erondu N., Kern A., Donelson J. E. Molecular cloning of an immunodominant antigen of Onchocerca volvulus. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1199–1204. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost A. Latence parasitaire dans l'onchocercose. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(6):923–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Amara S. G., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing: determining neuronal phenotype. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1315–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.6089345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. R., Munoz B., Keyvan-Larijani E., Greene B. M. Reliability of detection of microfilariae in skin snips in the diagnosis of onchocerciasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Oct;41(4):467–471. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. R., Pacqué M., Muñoz B., Greene B. M. Impact of mass treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin on the transmission of infection. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):116–118. doi: 10.1126/science.2218502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil G. J., Ogunrinade A. F., Chandrashekar R., Kale O. O. IgG4 subclass antibody serology for onchocerciasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):549–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss N., Hussain R., Ottesen E. A. IgE antibodies are more species-specific than IgG antibodies in human onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):129–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss N., Karam M. Evaluation of a specific enzyme immunoassay for onchocerciasis using a low molecular weight antigen fraction of Onchocerca volvulus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Mar;40(3):261–267. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]