Abstract
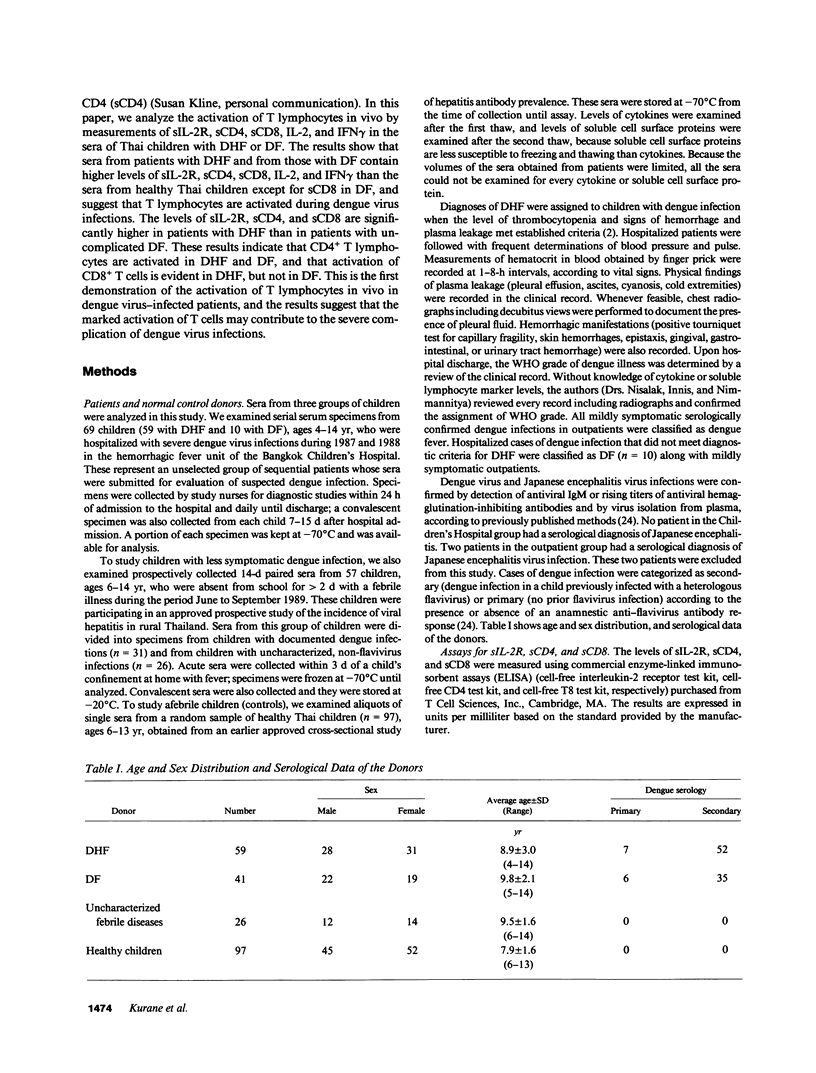
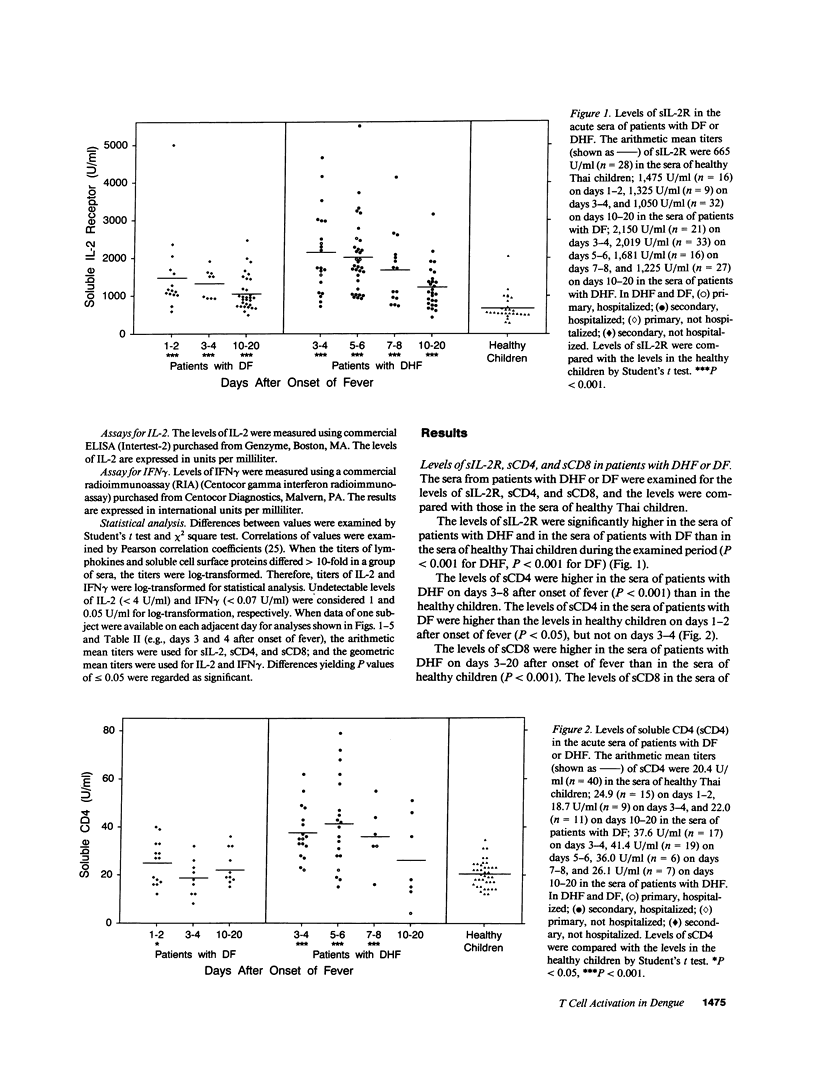
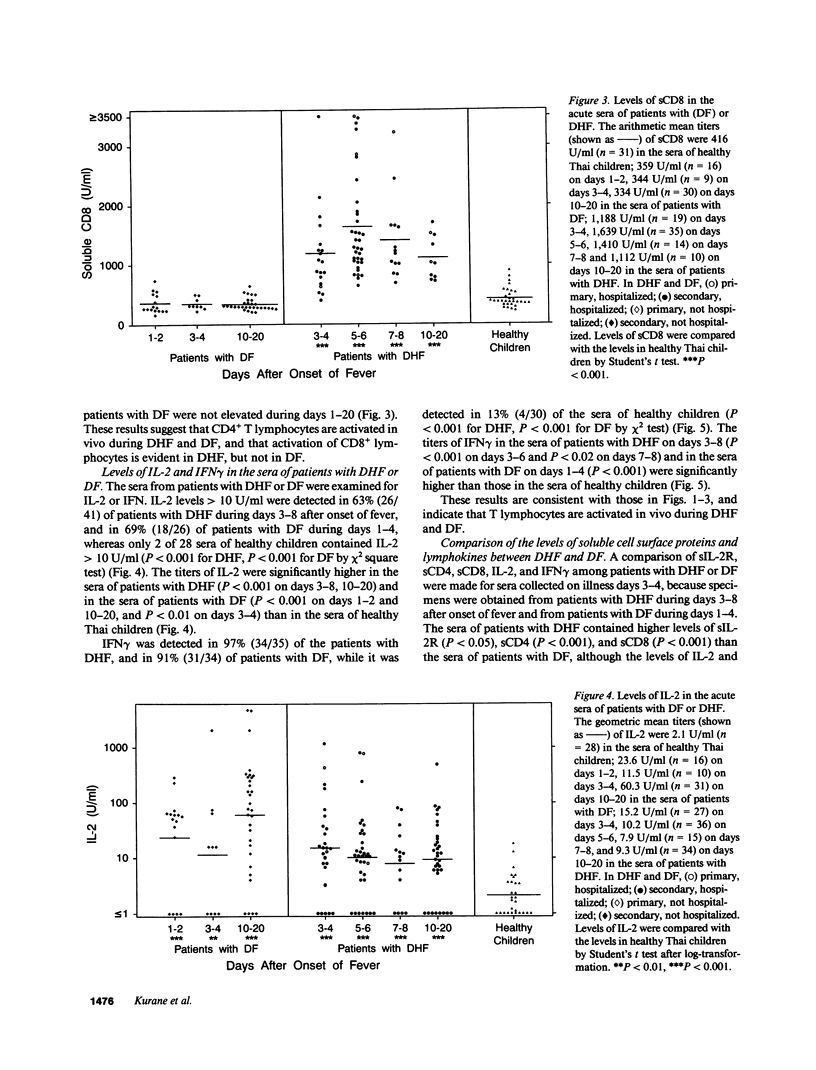
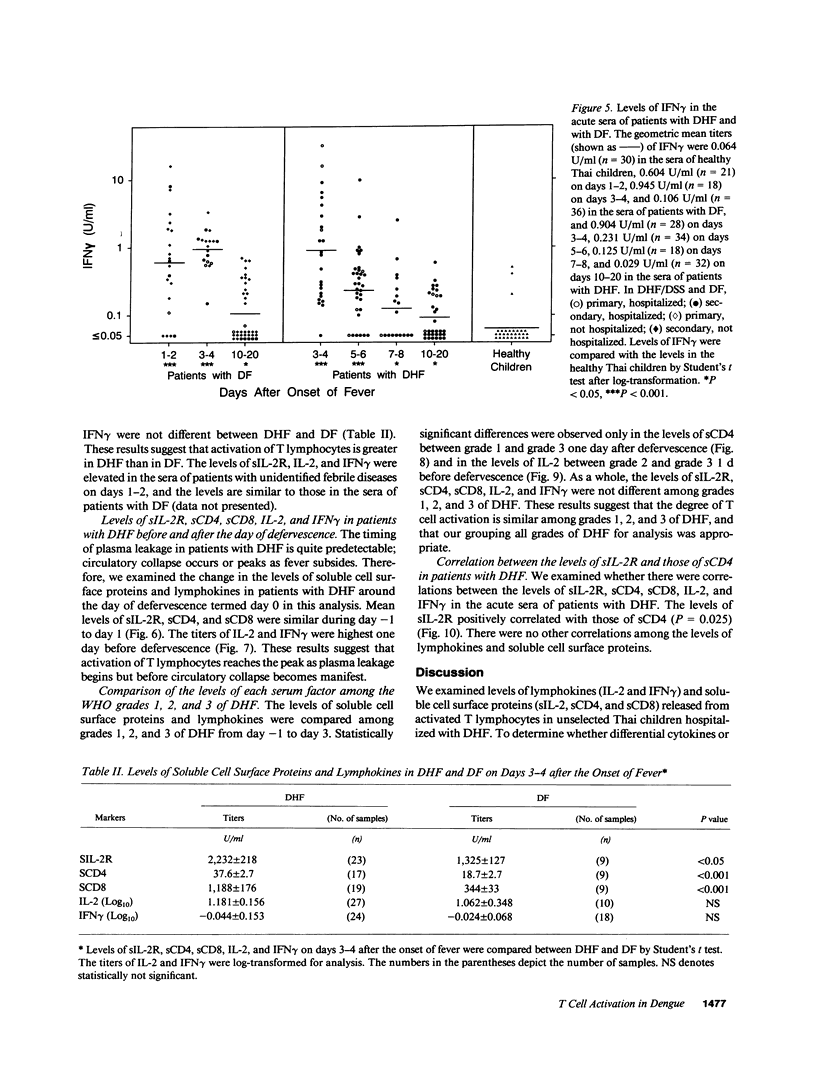
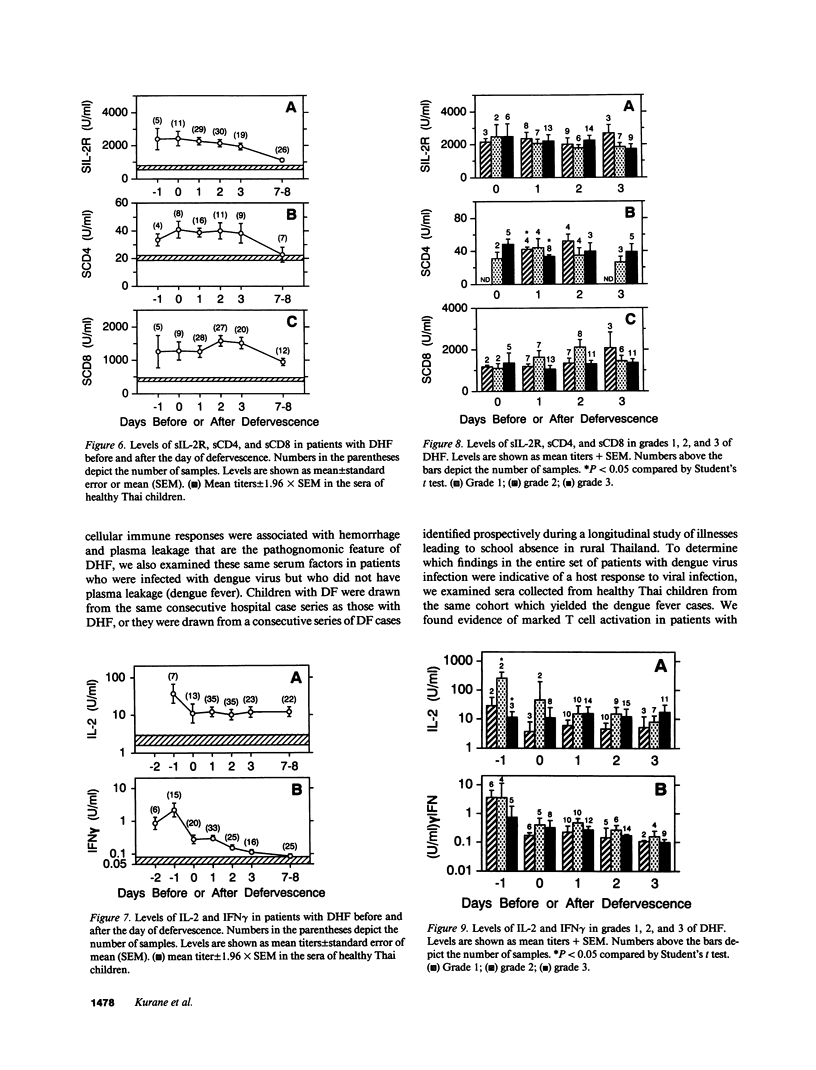
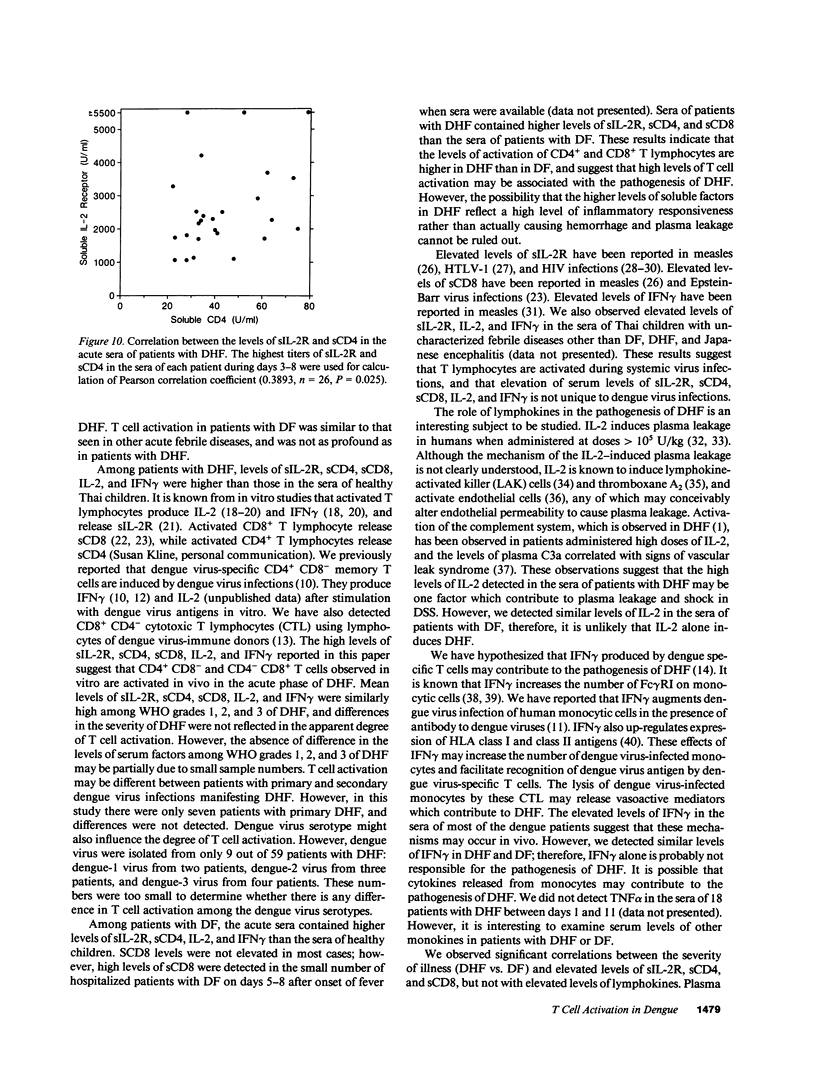
It has been reported that the severe complication of dengue virus infection, dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) is much more commonly observed during secondary dengue virus infections than primary infections. In order to elucidate the role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of DHF, we attempted to determine whether T lymphocytes are activated in vivo during dengue virus infections, by examining the levels of soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R), soluble CD4 (sCD4), soluble CD8 (sCD8), interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN gamma) in the sera of 59 patients with DHF and 41 patients with dengue fever (DF). The levels of sIL-2R, sCD4, sCD8, IL-2, and IFN gamma were significantly higher in the acute sera of patients with DHF than in the sera of healthy children (P less than 0.001 for all markers). The acute sera of patients with DF contained higher levels of sIL-2R, sCD4, IL-2, and IFN gamma than the sera of healthy children (P less than 0.001 for sIL-2R, IL-2, and IFN gamma; P less than 0.05 for sCD4), but did not have elevated levels of sCD8. The levels of sIL-2R (P less than 0.05), sCD4 (P less than 0.001), and sCD8 (P less than 0.001) were higher in DHF than in DF on days 3-4 after the onset of fever. The levels of IL-2 and IFN gamma in patients with DHF were highest 1 d before defervescence. There were no significant differences in the levels of sIL-2R, sCD4, sCD8, IL-2, and IFN gamma among grades 1, 2, and 3 of DHF. These results indicate (a) T lymphocytes are activated and produce IL-2 and IFN gamma in vivo during DHF and DF, (b) CD4+ T lymphocytes are activated in DHF and DF, and the level of activation is higher in DHF than in DF, and (c) activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes is evident in DHF, but not in DF.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill F. R., Burke F. The cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonpucknavig S., Boonpucknavig V., Bhamarapravati N., Nimmannitya S. Immunofluorescence study of skin rash in patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1979 Aug;103(9):463–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonpucknavig V., Bhamarapravati N., Boonpucknavig S., Futrakul P., Tanpaichitr P. Glomerular changes in dengue hemorrhagic fever. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Apr;100(4):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A., Johnson D. E., Scott R. M. A prospective study of dengue infections in Bangkok. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):172–180. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro T. J., Johnson A., Everitt J., Malik A. B. IL-2 induces pulmonary edema and vasoconstriction independent of circulating lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1916–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Levy S., Levy R. Spontaneous release of the Leu-2 (T8) molecule from human T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):752–766. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Andrus L., Steinman R. M. Lymphokine and nonlymphokine mRNA levels in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):922–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Ward B. J., Jauregui E., Johnson R. T., Vaisberg A. Immune activation during measles: interferon-gamma and neopterin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in complicated and uncomplicated disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):449–453. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Ward B. J., Jauregui E., Johnson R. T., Vaisberg A. Immune activation in measles. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 22;320(25):1667–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906223202506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. Dengue haemorrhagic fever--a public health problem and a field for research. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(1):1–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. In vivo enhancement of dengue virus infection in rhesus monkeys by passively transferred antibody. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):527–533. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., O'Rourke E. J., Allison A. C. Dengue viruses and mononuclear phagocytes. II. Identity of blood and tissue leukocytes supporting in vitro infection. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):218–229. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., O'Rourke E. J. Dengue viruses and mononuclear phagocytes. I. Infection enhancement by non-neutralizing antibody. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):201–217. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. Pathogenesis of dengue: challenges to molecular biology. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):476–481. doi: 10.1126/science.3277268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. The Alexander D. Langmuir Lecture. The pathogenesis of dengue. Molecular epidemiology in infectious disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Nov;114(5):632–648. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Kitamura K., Matsuda K., Yokota Y., Yamamoto N., Mitsuyasu R., Chermann J. C., Tokunaga T. Soluble IL-2 receptor in AIDS. Correlation of its serum level with the classification of HIV-induced diseases and its characterization. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4248–4255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis B. L., Nisalak A., Nimmannitya S., Kusalerdchariya S., Chongswasdi V., Suntayakorn S., Puttisri P., Hoke C. H. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to characterize dengue infections where dengue and Japanese encephalitis co-circulate. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):418–427. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Fiers W., Strom T. B. Cloned human interferon-gamma, but not interferon-beta or -alpha, induces expression of HLA-DR determinants by fetal monocytes and myeloid leukemic cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontny U., Kurane I., Ennis F. A. Gamma interferon augments Fc gamma receptor-mediated dengue virus infection of human monocytic cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3928–3933. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3928-3933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourí G., Guzmán M. G., Bravo J. Hemorrhagic dengue in Cuba: history of an epidemic. Bull Pan Am Health Organ. 1986;20(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurane I., Innis B. L., Nisalak A., Hoke C., Nimmannitya S., Meager A., Ennis F. A. Human T cell responses to dengue virus antigens. Proliferative responses and interferon gamma production. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):506–513. doi: 10.1172/JCI113911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurane I., Meager A., Ennis F. A. Dengue virus-specific human T cell clones. Serotype crossreactive proliferation, interferon gamma production, and cytotoxic activity. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):763–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. M., Coumaros G., Levy S., Falkenrodt A., Steckmeyer M., Partisani M., Aleksijevic A., Lehr L., Koehl C. Elevated serum levels of soluble interleukin 2 receptors in HIV infection: correlation studies with markers of cell activation. Immunol Lett. 1988 Oct;19(2):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Ettinghausen S. E., Rayner A. A., Sharrow S. O., Seipp C. A., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. II. Half life, immunologic effects, and expansion of peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo with recombinant IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2865–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peace D. J., Cheever M. A. Toxicity and therapeutic efficacy of high-dose interleukin 2. In vivo infusion of antibody to NK-1.1 attenuates toxicity without compromising efficacy against murine leukemia. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):161–173. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon induces the receptor for monomeric IgG1 on human monocytic and myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1092–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Kleinman S., Williams A. E. Soluble IL-2 receptor levels in serum from blood donors seropositive for HIV. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1139–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman A. L., Kurane I., Zhang Y. M., Lai C. J., Ennis F. A. Dengue virus-specific murine T-lymphocyte proliferation: serotype specificity and response to recombinant viral proteins. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2486–2491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2486-2491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thijs L. G., Hack C. E., Strack van Schijndel R. J., Nuijens J. H., Wolbink G. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Van der Vall H., Wagstaff J. Activation of the complement system during immunotherapy with recombinant IL-2. Relation to the development of side effects. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2419–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B. E., Brown M. C., Ip S. H., Carrabis S., Sullivan J. L. Soluble CD8 during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2230–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Nishimura Y., Kiyokawa T., Takatsuki K. Elevated serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in HTLV-I--associated myelopathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Oct;114(4):407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


