Abstract
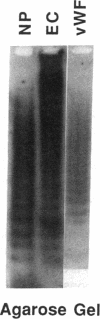
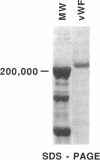
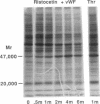
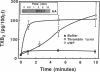
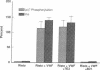
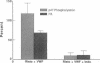
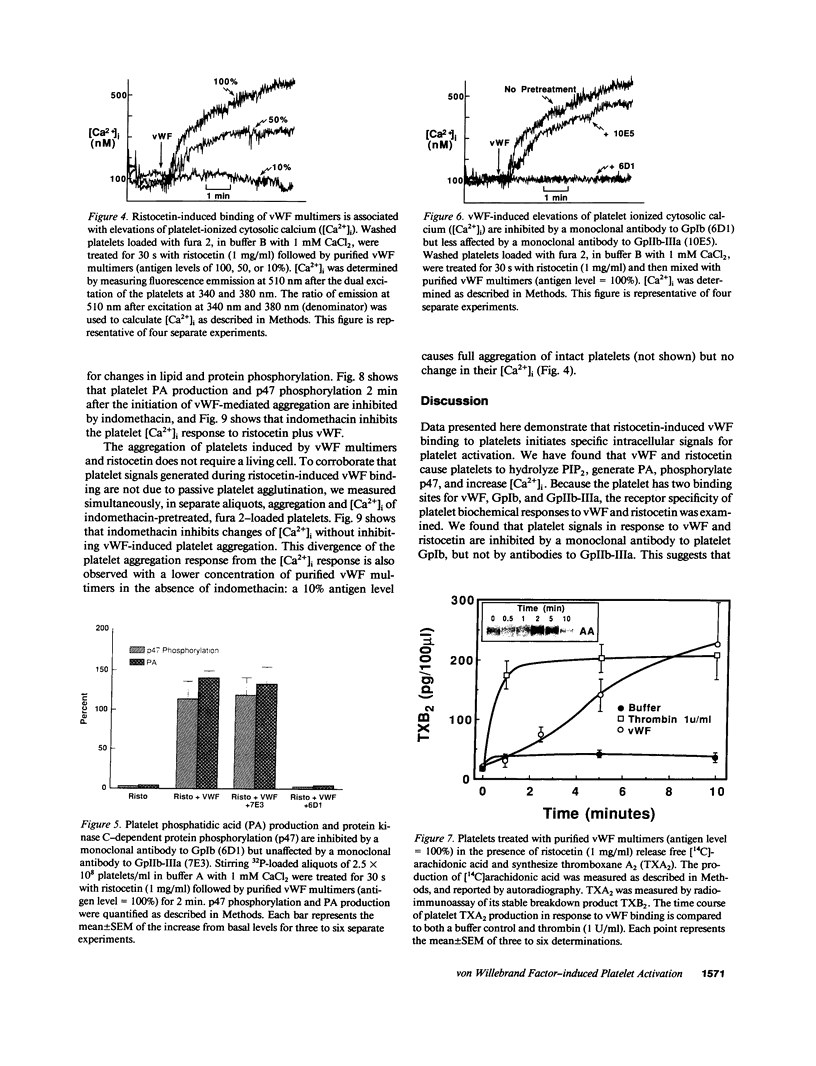
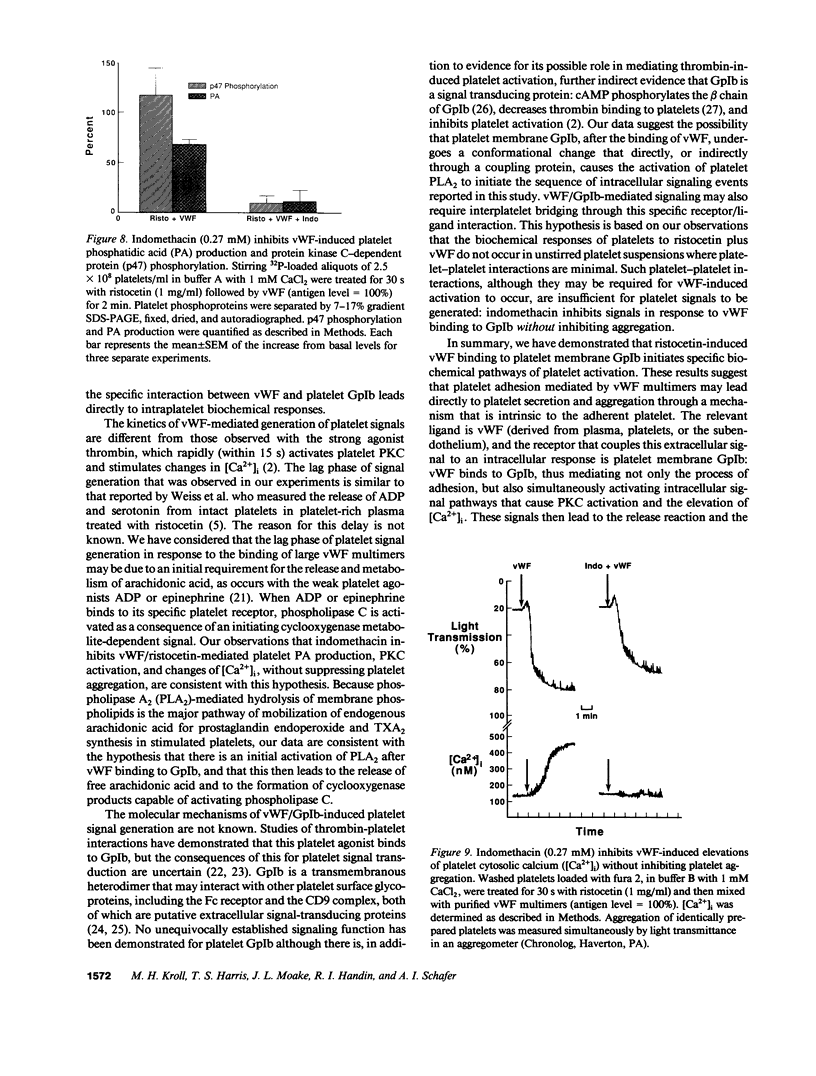
The hypothesis that von Willebrand factor (vWF) binding to platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib (GpIb) initiates intracellular pathways of platelet activation was studied. We measured the biochemical responses of intact human platelets treated with ristocetin plus vWF multimers purified from human cryoprecipitate. vWF plus ristocetin causes the breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, the production of phosphatidic acid (PA), the activation of protein kinase C (PKC), increase of ionized cytoplasmic calcium ([Ca2+]i), and the synthesis of thromboxane A2. PA production, PKC activation, and the rise of [Ca2+]i stimulated by the ristocetin-induced binding of vWF multimers to platelets are inhibited by an anti-GpIb monoclonal antibody, but are unaffected by anti-GpIIb-IIIa monoclonal antibodies. Indomethacin also inhibits these responses without impairing platelet aggregation induced by vWF plus ristocetin. These results indicate that vWF binding to platelets initiates specific intraplatelet signaling pathways. The mechanism by which this occurs involves an arachidonic acid metabolite-dependent activation of phospholipase C after vWF binding to platelet membrane GpIb. This signal then causes PKC activation and increases of [Ca2+]i, which promote platelet secretion and potentiate aggregation.
Full text
PDF
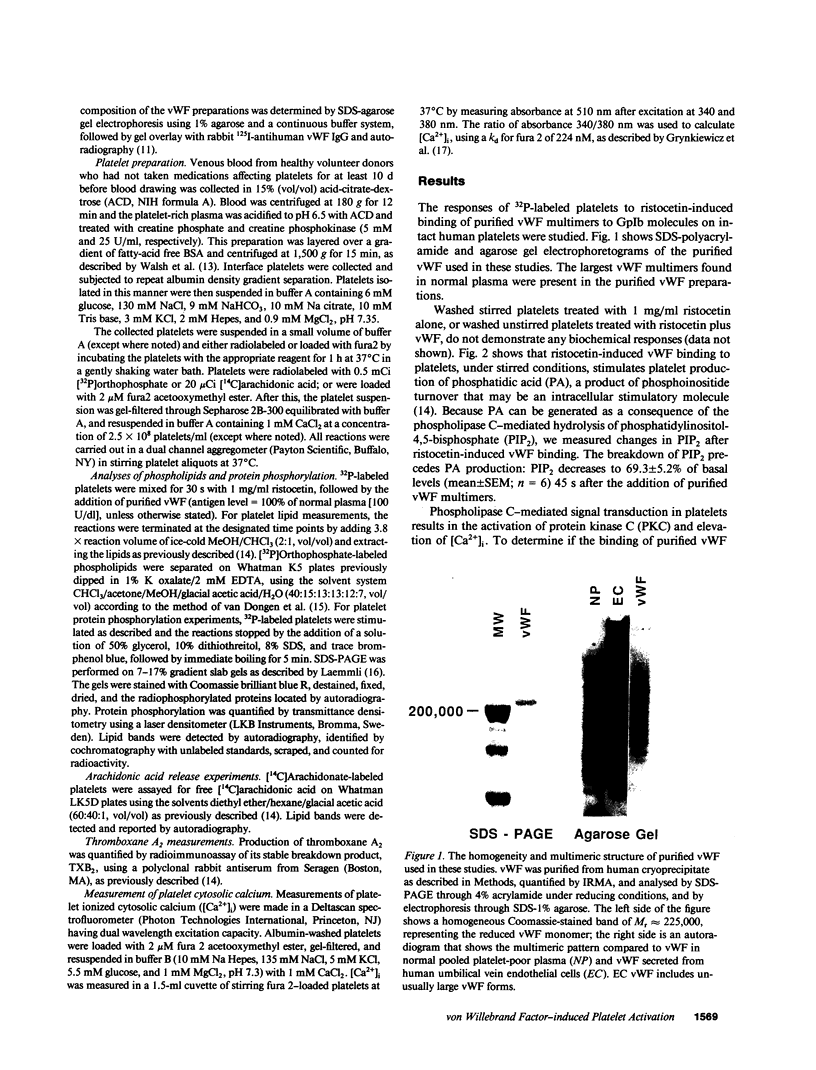
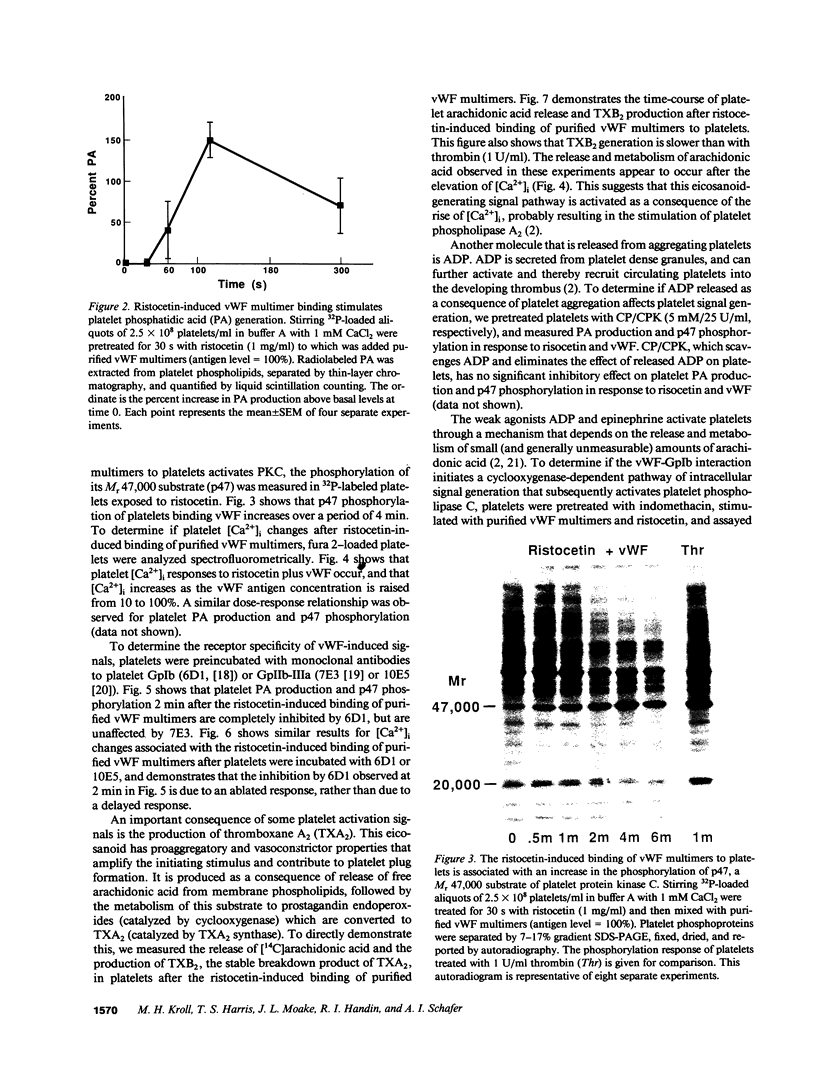

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkhamis T. M., Beissinger R. L., Chediak J. R. Artificial surface effect on red blood cells and platelets in laminar shear flow. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1568–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo M., Mustard J. F., Canciani M. T., Richardson M., Federici A. B., Mannucci P. M. Conditions influencing the interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with human platelets--the effects of external ionized calcium concentration and the role of arachidonate pathway. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):280–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. Studies with a murine monoclonal antibody that abolishes ristocetin-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets: additional evidence in support of GPIb as a platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Russell S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and mediates platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1172/JCI111816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Reynolds C. C., Johnson M. M. Identification of glycoprotein Ib beta as one of the major proteins phosphorylated during exposure of intact platelets to agents that activate cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12627–12631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Asialo von Willebrand factor interactions with platelets. Interdependence of glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa for binding and aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):19–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI111673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Fox C. F., Kouns W. C., McKay C. P., Ballou L. R., Schultz H. E. The activation of human platelets mediated by anti-human platelet p24/CD9 monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Zavoico G. B., Schafer A. I. Second messenger function of phosphatidic acid in platelet activation. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):558–564. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea K. M., Glomset J. A., Krebs E. G. Agents that elevate cAMP levels in platelets decrease thrombin binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Rudy C. K., Troll J. H., Weinstein M. J., Colannino N. M., Azocar J., Seder R. H., Hong S. L., Deykin D. Unusually large plasma factor VIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 2;307(23):1432–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212023072306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L. H., Hellums J. D. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI112736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L., Hellums J. D. Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released from platelets, as well as by exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1366–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M. Hemostatic properties of normal and perturbed vascular cells. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):116–123. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.2.3277885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Blair I. A., Cragoe E. J., Limbird L. E. Inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchange block epinephrine- and ADP-induced stimulation of human platelet phospholipase C by blockade of arachidonic acid release at a prior step. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8660–8666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Mills D. C., White J. G. Metabolism and function of human platelets washed by albumin density gradient separation. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):287–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Rogers J., Brand H. Defective ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in von Willebrand's disease and its correction by factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2697–2707. doi: 10.1172/JCI107464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. B., McKeown L. P., Gralnick H. R. Asialo von Willebrand factor binding to and aggregation of platelets: effects of inhibitors of platelet metabolism and function. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 May;109(5):560–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington R. E., Carroll R. C., Boucheix C. Platelet activation by CD9 monoclonal antibodies is mediated by the Fc gamma II receptor. Br J Haematol. 1990 Feb;74(2):216–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Greco N. J., Barnard M. R., Tanoue K., Yamazaki H., Jamieson G. A., Michelson A. D. Glycoprotein Ib (GPIb)-dependent and GPIb-independent pathways of thrombin-induced platelet activation. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1740–1748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen C. J., Zwiers H., Gispen W. H. Microdetermination of phosphoinositides in a single extract. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]