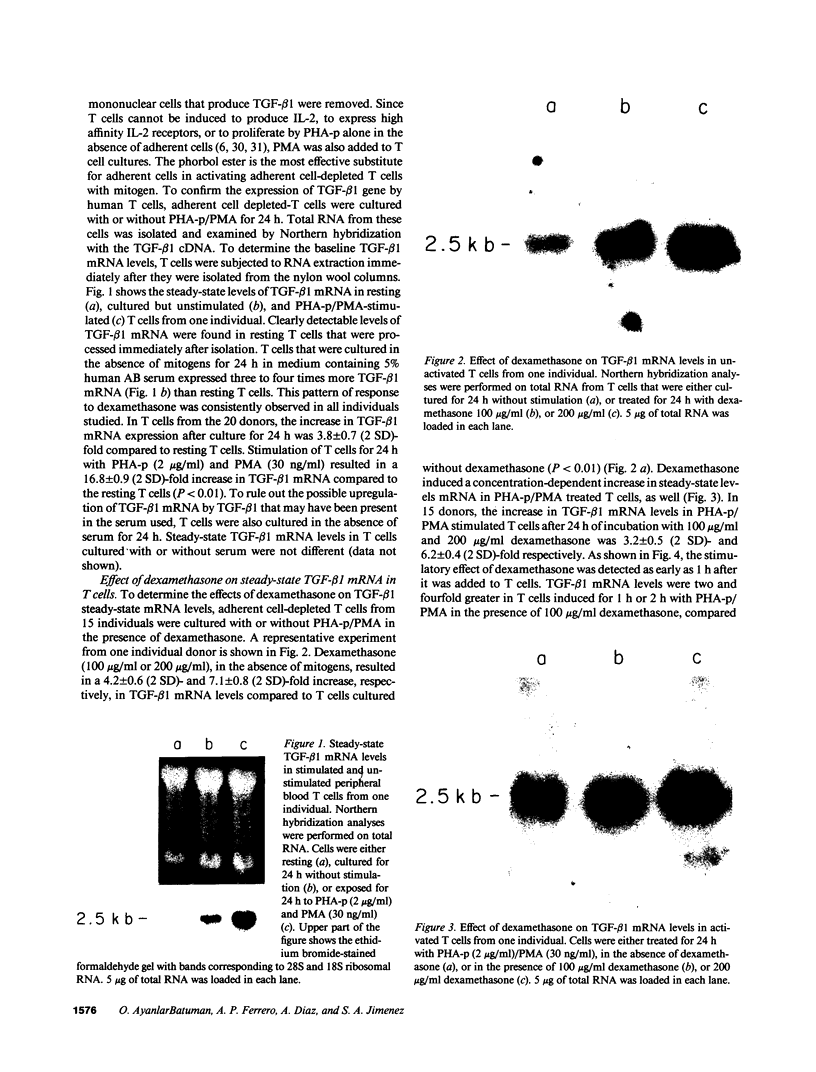
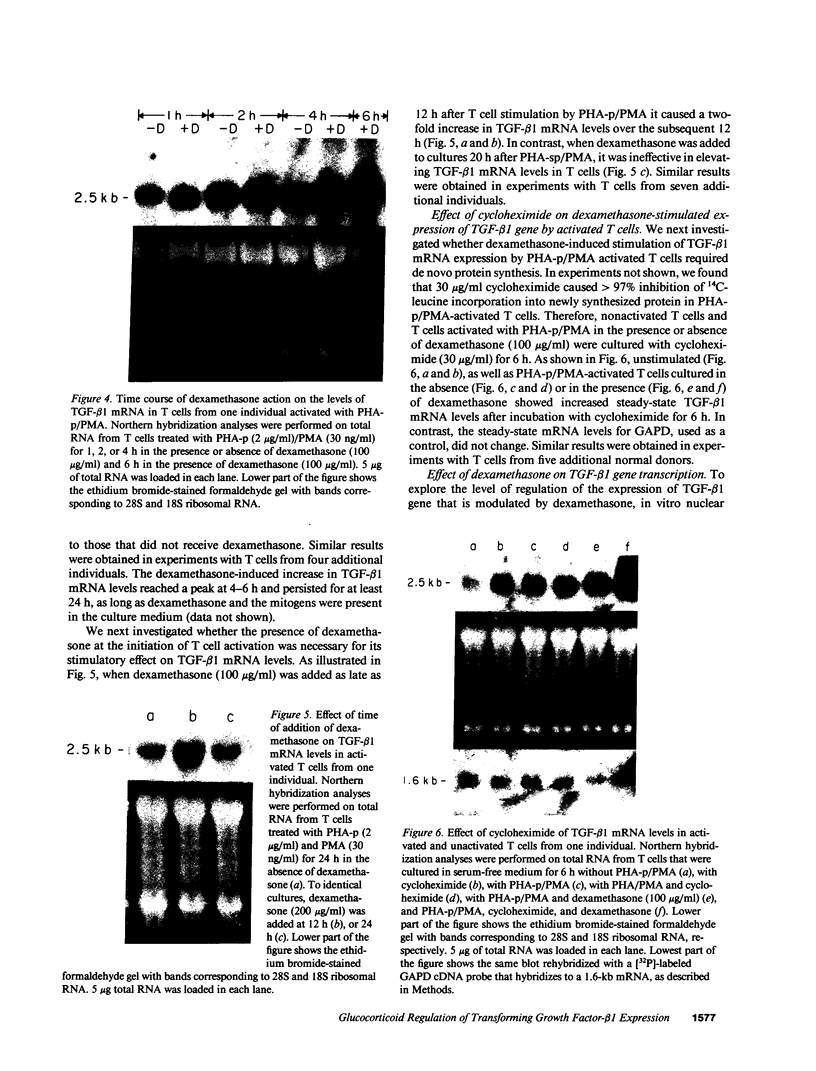
Abstract
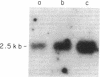
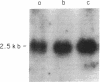
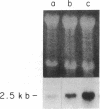
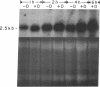
Glucocorticoids (GC) modulate immune function in a number of ways, including suppression of T cell proliferation and other IL-2-mediated T cell functions. These inhibitory effects are similar to those induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1), a cytokine with potent T cell inhibiting activities. We examined the hypothesis that GC effects may be at least partially achieved through modulation of the expression of the TGF-beta 1 gene in activated T cells. Normal T cells were cultured with or without purified phytohemagglutinin (PHA-p) and 4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) in the presence or absence of the synthetic GC, dexamethasone (100-200 micrograms/ml). The production of latent and active forms of TGF beta by these cells were analyzed by immunoblotting and bioassays. The steady-state levels of TGF-beta 1 mRNA were analyzed in total RNA from these cells by Northern hybridizations using a human TGF-beta 1 cDNA. The results showed that dexamethasone caused an increase in TGF beta production and a dose-dependent two to fourfold increase in TGF-beta 1 mRNA in activated as well as in unstimulated T cells, 1 h after exposure of the cultures to the steroid. The increase in TGF-beta 1 mRNA levels by dexamethasone was further potentiated two to threefold by cycloheximide, suggesting that the steroid effect may be due to inhibition of the synthesis of proteins that decrease TGF-beta 1 gene transcription or the stability of its transcripts. Finally, in vitro nuclear transcription studies indicated the dexamethasone effects on TGF-beta 1 gene expression to be largely transcriptional.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of human T cell growth factor and gamma-interferon messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayanlar-Batuman O., Ebert E., Hauptman S. P. Defective interleukin-2 production and responsiveness by T cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia of B cell variety. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batuman O. A., Sajewski D., Ottenweller J. E., Pitman D. L., Natelson B. H. Effects of repeated stress on T cell numbers and function in rats. Brain Behav Immun. 1990 Jun;4(2):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(90)90013-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer S., Strommer K., Frei K., Siepl C., de Tribolet N., Heid I., Fontana A. Immunosuppression and transforming growth factor-beta in glioblastoma. Preferential production of transforming growth factor-beta 2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3222–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol L. A., Ruscetti F. W., Brody D. T., Durum S. K. IL-1 alpha induces expression of active transforming growth factor-beta in nonproliferating T cells via a post-transcriptional mechanism. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4108–4114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha reciprocally regulate the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Comparison between natural porcine platelet-derived TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2, and recombinant human TGF-beta 1. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2312–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Frei K., Bodmer S., Hofer E., Schreier M. H., Palladino M. A., Jr, Zinkernagel R. M. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits the generation of cytotoxic T cells in virus-infected mice. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3230–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Dart L. L., Meyers C. A., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Purification and initial characterization of a type beta transforming growth factor from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3676–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Crabtree G. R., Smith K. A. Glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of T cell growth factor production. I. The effect on mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1624–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson J., Dooley N. J., Koski I. R., Blaese R. M. Immunoglobulin production induced in vitro by glucocorticoid hormones: T cell-dependent stimulation of immunoglobulin production without B cell proliferation in cultures of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1539–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI110408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C. The human interleukin-2 receptor: a molecular and biochemical analysis of structure and function. Clin Res. 1987 Sep;35(5):439–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Jakowlew S., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Transforming growth factor beta is an important immunomodulatory protein for human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3855–3860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Glick A., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Characterization of the promoter region of the human transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):402–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi K., Moller D. R., Saltini C., Kirby M., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous expression of the interleukin 2 receptor gene and presence of functional interleukin 2 receptors on T lymphocytes in the blood of individuals with active pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):775–781. doi: 10.1172/JCI113678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C., Bald L. N., Fendly B. M., Mora-Worms M., Figari I. S., Patzer E. J., Palladino M. A. The autocrine production of transforming growth factor-beta 1 during lymphocyte activation. A study with a monoclonal antibody-based ELISA. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Guyre P. M., Holbrook N. J. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984 Winter;5(1):25–44. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Vogel R. Fibroblast growth factor enhances type beta 1 transforming growth factor gene expression in osteoblast-like cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2529–2535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action on immune processes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1979;19:179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.19.040179.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Saltini C., Müller-Quernheim J., Crystal R. G. Corticosteroid therapy suppresses spontaneous interleukin 2 release and spontaneous proliferation of lung T lymphocytes of patients with active pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M. Structure-function relationships for the IL 2-receptor system. IV. Analysis of the sequence and ligand-binding properties of soluble Tac protein. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M. Structure-function relationships for the IL 2-receptor system. IV. Analysis of the sequence and ligand-binding properties of soluble Tac protein. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegemer J. J., Ho S. N., Augustine J. A., Schlager J. W., Bell M. P., McKean D. J., Abraham R. T. Regulatory effects of transforming growth factor-beta on IL-2- and IL-4-dependent T cell-cycle progression. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1767–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Stevens R. H., Ramer S. J., Clements P. J., Yu D. T. Glucocorticoids administered in vivo inhibit human suppressor T lymphocyte function and diminish B lymphocyte responsiveness in in vitro immunoglobulin synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):922–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto L., Vaduva P. I., Wager R. E., Assoian R. K. Type beta 1 transforming growth factor gene expression. A corrected mRNA structure reveals a downstream phorbol ester responsive element in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2203–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeck M., Ruegg C., Miescher S., Carrel S., Cox D., Von Fliedner V., Alkan S. Comparison of the immunosuppressive properties of milk growth factor and transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3258–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuchinda M., Newcomb R. W., DeVald B. L. Effect of prednisone treatment on the human immune response to keyhole limpet hemocyanin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(4):533–544. doi: 10.1159/000230634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. F., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L., Holley R. W. Growth inhibitor from BSC-1 cells closely related to platelet type beta transforming growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.6093254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Rosenbloom J., Jimenez S. A. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):597–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2470597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wong H. L., Dougherty S., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Ellingsworth L., Schmidt J. A., Hall G., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent immunosuppressive agent that inhibits IL-1-dependent lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharchuk C. M., Merćep M., Chakraborti P. K., Simons S. S., Jr, Ashwell J. D. Programmed T lymphocyte death. Cell activation- and steroid-induced pathways are mutually antagonistic. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4037–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]