Abstract
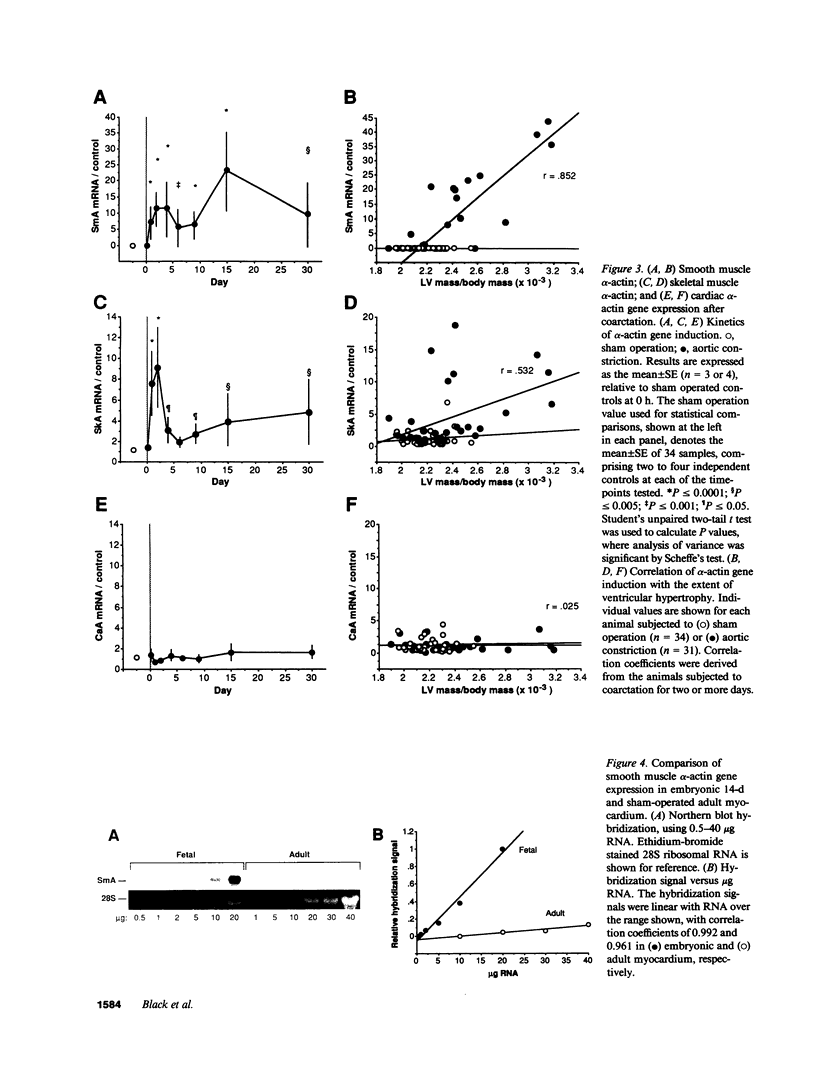
Cardiac hypertrophy triggered by mechanical load possesses features in common with growth factor signal transduction. A hemodynamic load provokes rapid expression of the growth factor-inducible nuclear oncogene, c-fos, and certain peptide growth factors specifically stimulate the "fetal" cardiac genes associated with hypertrophy, even in the absence of load. These include the gene encoding vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin, the earliest alpha-actin expressed during cardiac myogenesis; however, it is not known whether reactivation of the smooth muscle alpha-actin gene occurs in ventricular hypertrophy. We therefore investigated myocardial expression of the smooth muscle alpha-actin gene after hemodynamic overload. Smooth muscle alpha-actin mRNA was discernible 24 h after coarctation and was persistently expressed for up to 30 d. In hypertrophied hearts, the prevalence of smooth muscle alpha-actin gene induction was 0.909, versus 0.545 for skeletal muscle alpha-actin (P less than 0.05). Ventricular mass after 2 d or more of aortic constriction was more highly correlated with smooth muscle alpha-actin gene activation (r = 0.852; P = 0.0001) than with skeletal muscle alpha-actin (r = 0.532; P = 0.009); P less than 0.0005 for the difference in the correlation coefficients. Thus, smooth muscle alpha-actin is a molecular marker of the presence and extent of pressure-overload hypertrophy, whose correlation with cardiac growth at least equals that of skeletal alpha-actin. Induction of smooth muscle alpha-actin was delayed and sustained after aortic constriction, whereas the nuclear oncogenes c-jun and junB were expressed rapidly and transiently, providing potential dimerization partners for transcriptional control by c-fos.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauters C., Moalic J. M., Bercovici J., Mouas C., Emanoil-Ravier R., Schiaffino S., Swynghedauw B. Coronary flow as a determinant of c-myc and c-fos proto-oncogene expression in an isolated adult rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Feb;20(2):97–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(88)80023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishopric N. H., Kedes L. Adrenergic regulation of the skeletal alpha-actin gene promoter during myocardial cell hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishopric N. H., Simpson P. C., Ordahl C. P. Induction of the skeletal alpha-actin gene in alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated hypertrophy of rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1194–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI113179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boheler K. R., Carrier L., de la Bastie D., Allen P. D., Komajda M., Mercadier J. J., Schwartz K. Skeletal actin mRNA increases in the human heart during ontogenic development and is the major isoform of control and failing adult hearts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):323–330. doi: 10.1172/JCI115295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. L., Bergsma D. J., Schwartz R. J. A 29-nucleotide DNA segment containing an evolutionarily conserved motif is required in cis for cell-type-restricted repression of the chicken alpha-smooth muscle actin gene core promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):241–250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. L., Schwartz R. J. A combination of closely associated positive and negative cis-acting promoter elements regulates transcription of the skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):528–538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Peckham M., Sparrow J. C., White D. C. Alteration in crossbridge kinetics caused by mutations in actin. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):440–442. doi: 10.1038/348440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppenberger-Eberhardt M., Flamme I., Kurer V., Eppenberger H. M. Reexpression of alpha-smooth muscle actin isoform in cultured adult rat cardiomyocytes. Dev Biol. 1990 Jun;139(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90296-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner I., Sassoon D., Vandekerckhove J., Alonso S., Buckingham M. E. A developmental study of the abnormal expression of alpha-cardiac and alpha-skeletal actins in the striated muscle of a mutant mouse. Dev Biol. 1989 Jul;134(1):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Wieben E., Markert C. L. Molecular signals for initiating protein synthesis in organ hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2455–2459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki K., Sukhatme V. P., Shubeita H. E., Chien K. R. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation induces distinct patterns of immediate early gene expression in neonatal rat myocardial cells. fos/jun expression is associated with sarcomere assembly; Egr-1 induction is primarily an alpha 1-mediated response. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13809–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Lompré A. M., Matsuoka R., Koren G., Schwartz K., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Myosin heavy chain messenger RNA and protein isoform transitions during cardiac hypertrophy. Interaction between hemodynamic and thyroid hormone-induced signals. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):970–977. doi: 10.1172/JCI112908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Burgan S., Pietra G. G., Conne B., Gabbiani G. Modulation of actin isoform expression in alveolar myofibroblasts (contractile interstitial cells) during pulmonary hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):881–889. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Kaida T., Shibazaki Y., Kurabayashi M., Katoh Y., Hoh E., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Stretching cardiac myocytes stimulates protooncogene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3595–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Katoh Y., Kaida T., Shibazaki Y., Kurabayashi M., Hoh E., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Mechanical loading stimulates cell hypertrophy and specific gene expression in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Possible role of protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1265–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Kurabayashi M., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Expression of cellular oncogenes in the myocardium during the developmental stage and pressure-overloaded hypertrophy of the rat heart. Circ Res. 1988 Jun;62(6):1075–1079. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Different members of the jun proto-oncogene family exhibit distinct patterns of expression in response to type beta transforming growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1556–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Schwartz K., d'Albis A., Lacombe G., Van Thiem N., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzyme redistribution in chronic heart overload. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):105–107. doi: 10.1038/282105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Lowag C., Neuberg M., Müller R. trans-repression of the mouse c-fos promoter: a novel mechanism of Fos-mediated trans-regulation. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor P. F., Abate C., Curran T. Direct cloning of leucine zipper proteins: Jun binds cooperatively to the CRE with CRE-BP1. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Yamamoto J., Hirata Y., Mori Y., Oikawa S., Inada M. Changes of atrial natriuretic peptide and its messenger RNA with development and regression of cardiac hypertrophy in renovascular hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1990 Jan;66(1):176–184. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvagh S. L., Michael L. H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. A hemodynamic load in vivo induces cardiac expression of the cellular oncogene, c-myc. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90977-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. A common factor regulates skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin gene transcription in muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4120–4133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Molecular basis of cardiac performance. Plasticity of the myocardium generated through protein isoform switches. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1693–1700. doi: 10.1172/JCI114351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. A naturally occurring truncated form of FosB that inhibits Fos/Jun transcriptional activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90504-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker T. G., Chow K. L., Schwartz R. J., Schneider M. D. Differential regulation of skeletal alpha-actin transcription in cardiac muscle by two fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7066–7070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker T. G., Packer S. E., Schneider M. D. Peptide growth factors can provoke "fetal" contractile protein gene expression in rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):507–514. doi: 10.1172/JCI114466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker T. G., Schneider M. D. Growth factors, proto-oncogenes, and plasticity of the cardiac phenotype. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:179–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S., Ozgur K., Lu M., Chang W., Mohan S. R., Kumar C. C., Ruley H. E. Structure of the human smooth muscle alpha-actin gene. Analysis of a cDNA and 5' upstream region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1683–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The inner core of the serum response element mediates both the rapid induction and subsequent repression of c-fos transcription following serum stimulation. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):255–268. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovner A. S., McNally E. M., Leinwand L. A. Complete cDNA sequence of rat atrial myosin light chain 1: patterns of expression during development and with hypertension. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1581–1586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka D. L., Schwartz R. J. Sequential activation of alpha-actin genes during avian cardiogenesis: vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin gene transcripts mark the onset of cardiomyocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2575–2586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawtell N. M., Lessard J. L. Cellular distribution of smooth muscle actins during mammalian embryogenesis: expression of the alpha-vascular but not the gamma-enteric isoform in differentiating striated myocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2929–2937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Samuel J. L., Sassoon D., Lompré A. M., Garner I., Marotte F., Buckingham M., Rappaport L., Schwartz K. Nonsynchronous accumulation of alpha-skeletal actin and beta-myosin heavy chain mRNAs during early stages of pressure-overload--induced cardiac hypertrophy demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Circ Res. 1989 May;64(5):937–948. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. D., Parker T. G. Cardiac myocytes as targets for the action of peptide growth factors. Circulation. 1990 May;81(5):1443–1456. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.5.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman S. P., Weiss J. L., Becker L. C., Gottlieb S. O., Woodruff K. M., Weisfeldt M. L., Gerstenblith G. The effects of antihypertensive therapy on left ventricular mass in elderly patients. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 10;322(19):1350–1356. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005103221904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., de la Bastie D., Bouveret P., Oliviéro P., Alonso S., Buckingham M. Alpha-skeletal muscle actin mRNA's accumulate in hypertrophied adult rat hearts. Circ Res. 1986 Nov;59(5):551–555. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Viallet J., Nau M., Segal S., Fedorko J., Minna J. jun-B inhibits and c-fos stimulates the transforming and trans-activating activities of c-jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shubeita H. E., McDonough P. M., Harris A. N., Knowlton K. U., Glembotski C. C., Brown J. H., Chien K. R. Endothelin induction of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, sarcomere assembly, and cardiac gene expression in ventricular myocytes. A paracrine mechanism for myocardial cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20555–20562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starksen N. F., Simpson P. C., Bishopric N., Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Cardiac myocyte hypertrophy is associated with c-myc protooncogene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8348–8350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. Differentiation of cardiac myocytes after mitogen withdrawal exhibits three sequential states of the ventricular growth response. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1911–1918. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. Cross-binding of factors to functionally different promoter elements in c-fos and skeletal actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2191–2201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad S., Wisnewsky C., Schwartz K. Effect of thyroid hormone on the accumulation of mRNA for skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin in hearts from normal and hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2456–2460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock-Mitchell J., Mitchell J. J., Low R. B., Kieny M., Sengel P., Rubbia L., Skalli O., Jackson B., Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed in embryonic rat cardiac and skeletal muscles. Differentiation. 1988 Dec;39(3):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]