Abstract
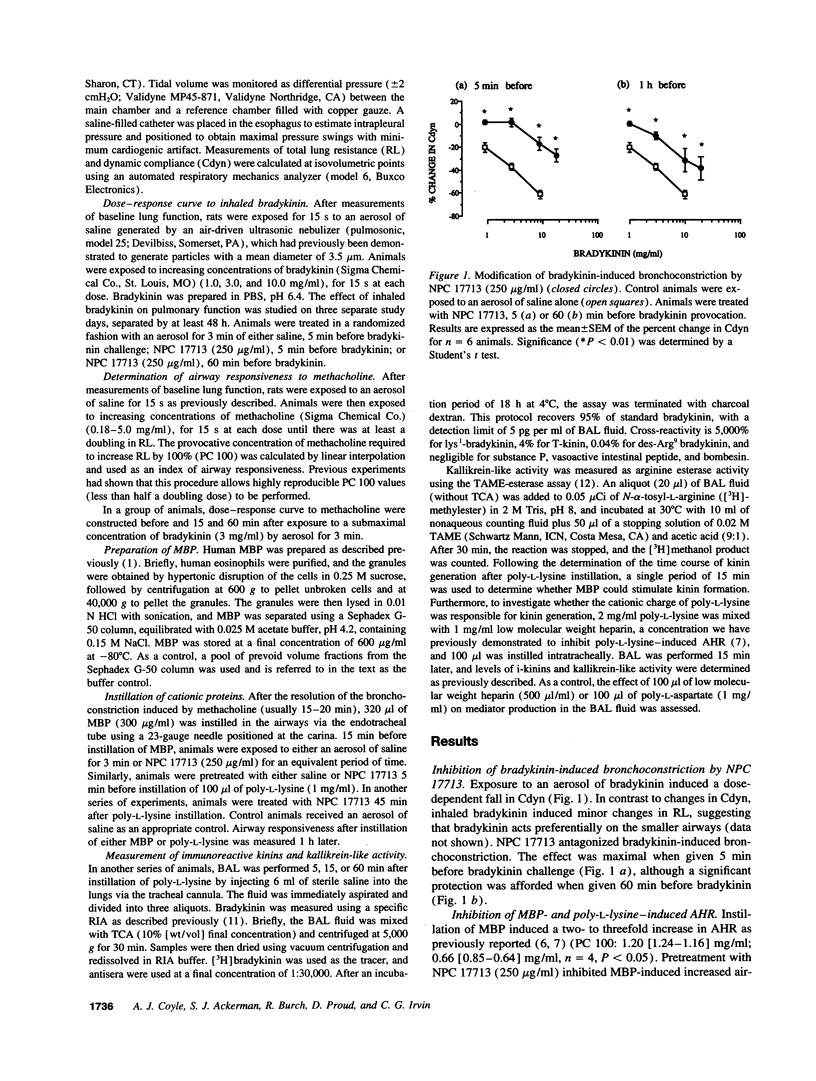
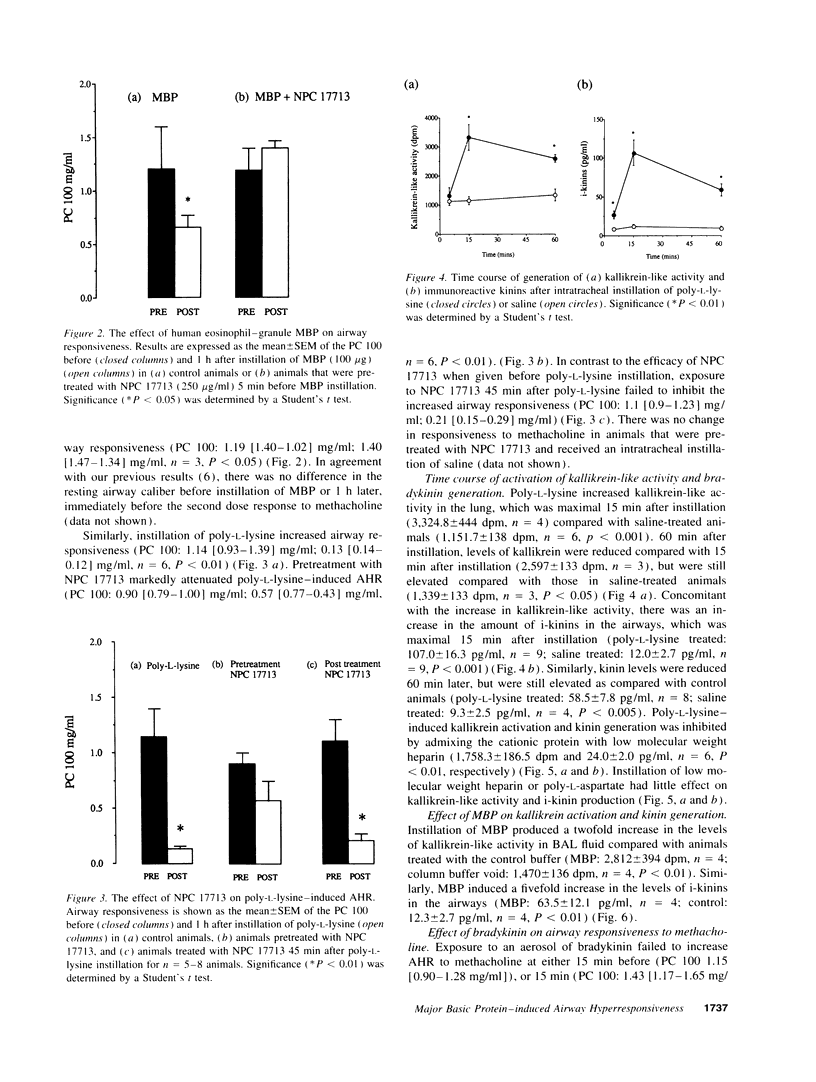
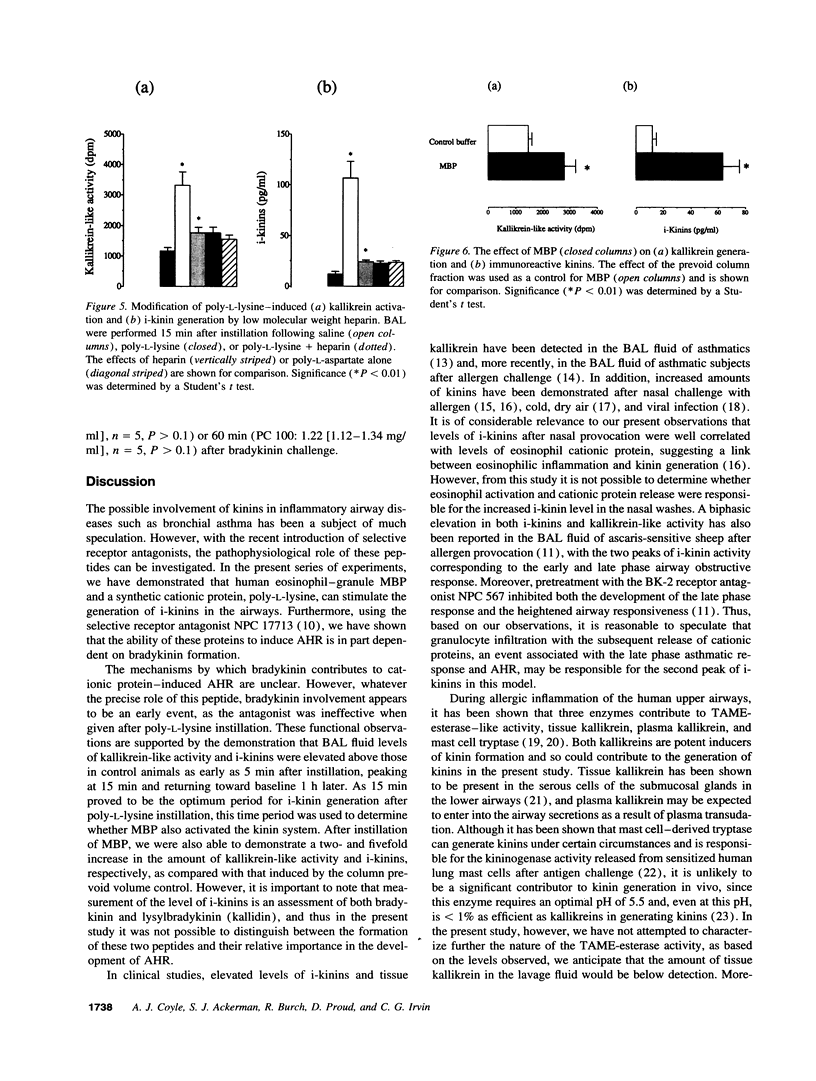
In the current series of experiments we investigated the role of bradykinin in airway hyperresponsiveness induced by human eosinophil-granule major basic protein (MBP). Bronchoalveolar lavage was performed after intratracheal instillation of MBP or poly-L-lysine in anesthetized, intubated rats, and levels of immunoreactive kinins and kallikrein-like activity were determined. Both MBP and poly-L-lysine induced a three- and eightfold increase in levels of kallikrein-like activity and i-kinins, respectively. To determine whether kinin production is required for the development of airway hyperresponsiveness induced by cationic proteins, dose-response curves to methacholine were constructed before and 1 h after intratracheal instillation of either MBP or poly-L-lysine (100 micrograms). MBP and poly-L-lysine induced an increase in airway responsiveness, which was inhibited by pretreatment with a selective BK-2 receptor antagonist, NPC 17713 (250 micrograms/ml). Our results demonstrate that MBP and poly-L-lysine activate kallikrein and stimulate the generation of i-kinins in vivo, an effect that may be related to the cationic charge of these proteins. Furthermore, the ability of these proteins to increase airway responsiveness appears to be dependent on the generation of i-kinins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham W. M., Burch R. M., Farmer S. G., Sielczak M. W., Ahmed A., Cortes A. A bradykinin antagonist modifies allergen-induced mediator release and late bronchial responses in sheep. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Apr;143(4 Pt 1):787–796. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.4_Pt_1.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Venge P., Olsson I., Harley J. B., Fauci A. S., Gleich G. J. Distinctive cationic proteins of the human eosinophil granule: major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2977–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed T., Garrigo J., Danta I. Preventing bronchoconstriction in exercise-induced asthma with inhaled heparin. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):90–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten C. R., Nichols R. C., Naclerio R. M., Lichtenstein L. M., Norman P. S., Proud D. Plasma kallikrein during experimentally induced allergic rhinitis: role in kinin formation and contribution to TAME-esterase activity in nasal secretions. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):977–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten C. R., Nichols R. C., Naclerio R. M., Proud D. Concentrations of glandular kallikrein in human nasal secretions increase during experimentally induced allergic rhinitis. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand C., Geppetti P., Baker J., Petersson G., Piedimonte G., Nadel J. A. Role of peptidases and NK1 receptors in vascular extravasation induced by bradykinin in rat nasal mucosa. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993 May;74(5):2456–2461. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.74.5.2456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Kyle D. J. Recent developments in the understanding of bradykinin receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(12):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90201-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Mullaney I., McNeill M., Dunn P. M., Rang H. P. Second messengers involved in the mechanism of action of bradykinin in sensory neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):3314–3325. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03314.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Cochrane C. G. Detection of tissue kallikrein in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthmatic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):188–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI112782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Sarnoff R. B., Juergens U., Cochrane C. G., Zuraw B. L. Elevation of tissue kallikrein and kinin in the airways of asthmatic subjects after endobronchial allergen challenge. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):900–905. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle A. J., Ackerman S. J., Irvin C. G. Cationic proteins induce airway hyperresponsiveness dependent on charge interactions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):896–900. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle A. J., Mitzner W., Irvin C. G. Cationic proteins alter smooth muscle function by an epithelium-dependent mechanism. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993 Apr;74(4):1761–1768. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.74.4.1761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Solley G. O., Farrow G. M., Gleich G. J. Elevated levels of the eosinophil granule major basic protein in the sputum of patients with bronchial asthma. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jun;56(6):345–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounni A. S., Lamkhioued B., Ochiai K., Tanaka Y., Delaporte E., Capron A., Kinet J. P., Capron M. High-affinity IgE receptor on eosinophils is involved in defence against parasites. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):183–186. doi: 10.1038/367183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundel R. H., Letts L. G., Gleich G. J. Human eosinophil major basic protein induces airway constriction and airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1470–1473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassoun P. M., Thompson B. T., Steigman D., Hales C. A. Effect of heparin and warfarin on chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodeling in the guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):763–768. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced airway microvascular leakage and bronchoconstriction are mediated via a bradykinin B2 receptor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1104–1107. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pig in vivo: role of neural mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Moss J., Manganiello V. C. Effect of bradykinin on prostaglandin production by human skin fibroblasts in culture. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:480–503. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman M. P., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C., Baker D. G. Bradykinin stimulates afferent vagal C-fibers in intrapulmonary airways of dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Mar;48(3):511–517. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T. M., Zimmerman G. A., Satoh K., Prescott S. M. Cultured endothelial cells synthesize both platelet-activating factor and prostacyclin in response to histamine, bradykinin, and adenosine triphosphate. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):271–280. doi: 10.1172/JCI111957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Effect of bradykinin on airway neural responses in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Oct;73(4):1537–1541. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.4.1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motojima S., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):801–805. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. W., Gruenhaupt D. Protamine increases the permeability of cultured epithelial monolayers. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Jan;68(1):220–227. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.1.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Kaplan A. P. Kinin formation: mechanisms and role in inflammatory disorders. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:49–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Newball H. H., Schulman E. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Immunoglobulin E-mediated release of a kininogenase from purified human lung mast cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):405–408. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Siekierski E. S., Bailey G. S. Identification of human lung mast cell kininogenase as tryptase and relevance of tryptase kininogenase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 15;37(8):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Togias A., Naclerio R. M., Crush S. A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Kinins are generated in vivo following nasal airway challenge of allergic individuals with allergen. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1678–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI111127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Vio C. P. Localization of immunoreactive tissue kallikrein in human trachea. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;8(1):16–19. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto T., Elwood W., Barnes P. J., Chung K. F. Effect of Hoe 140, a new bradykinin receptor antagonist, on bradykinin- and platelet-activating factor-induced bronchoconstriction and airway microvascular leakage in guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 31;213(3):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90625-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Martling C. R., Yan Z., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Gamse R., Lundberg J. M. Release of multiple tachykinins from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the lung by bradykinin, histamine, dimethylphenyl piperazinium, and vagal nerve stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solèr M., Sielczak M., Abraham W. M. A bradykinin-antagonist blocks antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in sheep. Pulm Pharmacol. 1990;3(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(90)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Andersson M., Persson C. G., Venge P., Alkner U., Pipkorn U. Albumin, bradykinins, and eosinophil cationic protein on the nasal mucosal surface in patients with hay fever during natural allergen exposure. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 May;85(5):828–833. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90064-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togias A. G., Naclerio R. M., Proud D., Fish J. E., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Kagey-Sobotka A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Nasal challenge with cold, dry air results in release of inflammatory mediators. Possible mast cell involvement. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1375–1381. doi: 10.1172/JCI112113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida D. A., Ackerman S. J., Coyle A. J., Larsen G. L., Weller P. F., Freed J., Irvin C. G. The effect of human eosinophil granule major basic protein on airway responsiveness in the rat in vivo. A comparison with polycations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):982–988. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venge P., Dahl R., Hällgren R. Enhancement of factor XII dependent reactions by eosinophil cationic protein. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


